Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8-St Lines and Circles
Uploaded by
Md Rizwan Ahmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pages8-St Lines and Circles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document8-St Lines and Circles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pages8-St Lines and Circles
Uploaded by
Md Rizwan Ahmad8-St Lines and Circles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
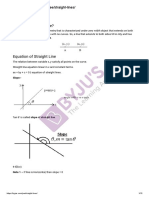
STRAIGHT LINES AND CIRCLES
Different standard form of the equation of a straight b1c 2 b 2 c1 a 2 c1 a 1c 2
line : ,
General form : Ax + By + C = 0 a1 b 2 a 2 b1 a1 b 2 a 2 b1
where A, B, C are any real numbers not all zero. Angle between two lines :
Gradient (Tangent) form : y = mx + c The angle between two lines whose slopes are m1
and m2 is given by
It is the equation of a straight line which cuts off an
intercept c on y-axis and makes an angle with the m1 m 2
tan =
positive direction (anticlockwise) of x-axis such that 1 + m1m 2
tan = m. The number m is called slope or the
If is angle between two lines then is also the
gradient of this line.
angle between them.
Intercept form :
The equation of any straight line parallel to a given
x y line ax + by + c = 0 is ax + by + k = 0.
+ =1
a b The equation of any straight line perpendicular to a
It is the equation of straight line which cuts off given line, ax + by + c = 0 is bx ay + k = 0.
intercepts a and b on the axis of x and y respectively. The equation of any straight line passing through the
Normal form (Perpendicular form) : point of intersection of two given lines l1 a1x + b1y
x cos + y sin = p + c1 = 0 and l2 a2x + b2y + c 2 = 0 is l1 + l 2 = 0
It is the equation of a straight line on which the where is any real number, which can be determined
length of the perpendicular from the origin is p and by given additional condition in the question.
is the angle which , this perpendicular makes with the The length of perpendicular from a given point (x1,
positive direction of x-axis. y1) to a given line ax + by + c = 0 is
One point form : ax 1 + by1 + c
= p (say)
y y1 = m(x x1)
(a 2 + b 2 )
It is the equation of a straight line passing through a
given point (x1, y1) and having slope m. In particular, the length of perpendicular from origin
Parametric equation : c
(0, 0) to the line ax + by + c = 0 is
x x1 y y1 a 2 + b2
= =r
cos sin Equation of Bisectors :
It is the equation of a straight line passes through a The equations of the bisectors of the angles between
given point A(x1, y1) and makes an angle with x- the lines a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a 2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are
axis. a 1 x + b1 y + c1 a 2x + b2 y + c 2
=
Two points form :
a 12 + b12 a 22 + b 22
y y1
y y1 = 2 (x x1) Distance between parallel lines :
x 2 x1
Choose a convenient point on any of the lines (put x
It is the equation of a straight line passing through = 0 and find the value of y or put y = 0 and find the
y y1 value of x). Now the perpendicular distance from this
two given points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), where 2 point on the other line will give the required distance
x 2 x1
between the given parallel lines.
is its slope.
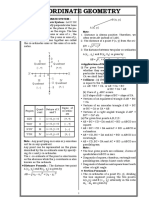
Pair of straight lines :
Point of intersection of two lines a1x + b 1y + c1 = 0
The equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 represents a pair
and a2x + b2y + c 2 = 0 is given by
of straight lines passing through the origin.
XtraEdge for IIT-JEE 51 NOVEMBER 2009
Let the lines represented by ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 be If C 1, C2 are the centres and a1, a2 are the radii of two
y m1x = 0 and y m2x = 0, then circles, then
2h a (i) The circles touch each other externally, if
m1 + m2 = and m1m2 =
b b C1C 2 = a1 + a2
General equation of second degree in x, y is (ii) The circles touch each other internally, if
ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 ...(i) C1C 2 = |a1 a 2|
This equation represents two straight lines, if (iii) The circles intersects at two points, if
= abc + 2fgh af2 bg2 ch2 = 0 |a1 a 2| < C 1C 2 < a1 + a2
a h g (iv) The circles neither intersect nor touch each other, if
or h b f =0 C1C 2 > a1 + a2 or C1C2 < |a1 a2|
g f c Equation of any circle through the point of
and point of intersection of these lines is given by intersection of two given circles S1 = 0 and S 2 = 0 is
given by S 1 + S2 = 0 ( 1) and can be
hf bg hg af
, determined by an additional condition.
ab h 2 ab h 2 Equation of the tangent to the given circle
The angle between the two straight lines represented x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 at any point (x1, y1) on it,
by (i) is given by is xx1 + yy1 + g(x + x1) + f(y + y1) + c = 0
2 h 2 ab The straight line y = mx + c touches the circle x2 + y2
tan =
a +b = a2, if c2 = a2(1 + m2) and the point of contact of the
If ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents a m ma a
pair of parallel straight lines, then the distance tangent y = mx a 1 + m 2 , is ,
2
between them is given by 1+ m 1 + m2
Length of tangent drawn from the point (x1, y1) to the
g 2 ac f 2 bc
2 or 2 circle S = 0 is S1 , where
a (a + b) b (a + b)
2
S1 = x1 + y12 + 2gx1 + 2fy1 + c
Circle:
The equation of pair of tangents drawn from point
Different forms of the equations of a circle : (x1, y1) to the circle
Centre radius form : the equation of a circle whose S = 0 i.e. x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, is SS1 = T2,
centre is the point (h, k) and radius 'a' is where T xx1 + yy1 + g(x + x1) + f(y + y1) + c and S1 as
(x h)2 + (y k)2 = a 2 mentioned above.
General equation of a circle : It is given by Chord with a given Middle point :
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 ...(i) the equation of the chord of the circle S = 0 whose
Equation (i) can also be written as mid-point is (x1, y1) is given by T = S1, where T and
S1 as defined a above.
|x (g)|2 + |y (f)|2 = | g 2 + f 2 c |2
If be the angle at which two circles of radii r1 and r2
which is in centre-radius form, so by comparing, we intersect, then
get the coordinates of centre (g, f) and radius is
r12 + r22 d 2
g2 + f 2 c . cos =
2 r1r2
Parametric Equations of a Circle :
The parametric equations of a circle where d is distance between their centres.
(x h)2 + (y k)2 = a 2 are x = h + a cos and Note Two circles are said to be intersect
orthogonally if the angle between their tangents at
y = k + a sin , where is a parameter.
their point of intersection is a right angle i.e.
Lengths of intercepts on the coordinate axes made by
r12 + r22 = d2 or
2 2
the circle (i) are 2 g c and 2 f c
2g1g2 + 2f1f2 = c1 + c2
Equation of the circle on the line joining the points Radical axis : The equation of the radical axis of the
A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) as diameter is given by two circle is S1 S2 = 0 i.e.
y y1 y y 2 2x(g1 g2) + 2y(f1 f2) + c1 c2 = 0
= 1
x x1 x x 2
XtraEdge for IIT-JEE 52 NOVEMBER 2009
You might also like
- Straight Line Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument6 pagesStraight Line Formula Sheets QuizrrCletus DemarcusNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument5 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformPravar GargNo ratings yet
- Straight Line MathongoDocument4 pagesStraight Line MathongoArya NairNo ratings yet
- Double: Cheat Sheet - Straight LineDocument1 pageDouble: Cheat Sheet - Straight Linearnab dasNo ratings yet
- 11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryDocument20 pages11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryUmakant AvateNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument2 pagesStraight Linesnabhijain9No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Analytical Geometry Marge FileDocument84 pagesChapter 3 Analytical Geometry Marge FileBhuwan GhimireNo ratings yet
- Cartesian CoordinatesDocument3 pagesCartesian CoordinatesmahitumikoiNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Straight LinesDocument15 pagesSheet - 01 - Straight LinesNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Formulae NewDocument2 pagesStraight Line Formulae New卂丂卄山丨几ツNo ratings yet
- (Template) Chy-Straight LinesDocument20 pages(Template) Chy-Straight LinesVoot Kids75No ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument6 pagesStraight LinesSarangNo ratings yet
- 1 Slope (Gradient) of A Line: 2.1 Condition For Parallel LinesDocument4 pages1 Slope (Gradient) of A Line: 2.1 Condition For Parallel LinesSheikh Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Advanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedDocument299 pagesAdvanced Problems in Coordinate Geometry For JEE Main & AdvancedShikhar Gupta90% (31)
- Chapter 10 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Combain File - 2 ST, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola PDFDocument33 pagesCombain File - 2 ST, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola PDFAniruddha Kawade100% (1)
- Straight LineDocument2 pagesStraight LinenitinjoshicscNo ratings yet
- Brahmastra - Straight LineDocument16 pagesBrahmastra - Straight LineVikas Mittal100% (1)
- Conic Section RevisionDocument111 pagesConic Section RevisionBsprogrammer100% (1)
- Formula Sheet of Coordinate GeometryDocument14 pagesFormula Sheet of Coordinate GeometryBhavesh Kumar100% (1)
- Straight Line Theory (1-27) - F24Document27 pagesStraight Line Theory (1-27) - F24neerajNo ratings yet
- 3D SummaryDocument5 pages3D SummaryYug KhotNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument5 pagesStraight LinesNutan MishraNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument12 pagesStraight LinesKshitij BansalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryDocument10 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryAmaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines SynopsisDocument3 pagesStraight Lines SynopsisSameer Kumar Singh0% (1)
- Key Concepts:) y y X X (Document5 pagesKey Concepts:) y y X X (virat gandhiNo ratings yet
- Pair of LinesDocument58 pagesPair of LinesKahaan KakabaliaNo ratings yet
- Lines and CirclesDocument2 pagesLines and CirclesJohnny MurrayNo ratings yet
- Straight LineDocument15 pagesStraight LineAyanNo ratings yet
- Xi-Quarterly Time TableDocument31 pagesXi-Quarterly Time TableInbloodNo ratings yet
- 07 Straight Line BrahmastraDocument16 pages07 Straight Line BrahmastraAnkit Ranjan100% (1)
- StraightLine Sheet3Document79 pagesStraightLine Sheet3Harsh100% (1)
- Math NotesDocument107 pagesMath Notesahmed5030 ahmed5030100% (1)
- Key Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Document21 pagesKey Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Ayah100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11 Assignment For Straight LinesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Assignment For Straight LinesNikhil HegdeNo ratings yet
- Form 2Document1 pageForm 2vvskrNo ratings yet
- Book - 1 - Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument10 pagesBook - 1 - Co-Ordinate GeometrySusmita Mukherjee100% (1)
- Mathematics Formula Booklet: D (X-X) (Y-Y)Document2 pagesMathematics Formula Booklet: D (X-X) (Y-Y)Akshit RajputNo ratings yet
- Percentile: ClassesDocument16 pagesPercentile: ClassesVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Straight Line - 2: Normal FormDocument11 pagesStraight Line - 2: Normal FormakshitaNo ratings yet
- Maths 11Document4 pagesMaths 11Satyam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formula Booklet - Gyaan Sutra Straight Line: D (X-X) (Y-Y)Document2 pagesMathematics Formula Booklet - Gyaan Sutra Straight Line: D (X-X) (Y-Y)harshanandiniNo ratings yet
- 3 Straight LinesDocument3 pages3 Straight Linespefesed686No ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-24 PDFDocument13 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-24 PDFKamal Kama KamaNo ratings yet
- Lec 08Document55 pagesLec 08xuanzhengxie726No ratings yet
- 07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirDocument44 pages07 Straight Line - Sheet - by MC SirPiyush Agarwal100% (1)
- Coordinate Geometry: Length of SegmentDocument2 pagesCoordinate Geometry: Length of SegmentStrixNo ratings yet
- 3d SynopsisDocument10 pages3d SynopsisUppu EshwarNo ratings yet
- Response CurveDocument11 pagesResponse CurveGrt grtNo ratings yet
- Simple Reciprocal Functions: Created by T. MadasDocument26 pagesSimple Reciprocal Functions: Created by T. MadasAyan Dualeh Year 11No ratings yet
- Straight Lines Conceptsdssd-241Document12 pagesStraight Lines Conceptsdssd-241asdasd100% (1)
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Document11 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Aarti Sharma100% (1)
- Geometry, Matrix and Vector Calculus: Lecture Note Course Code: MAT 102B (For CEP)Document56 pagesGeometry, Matrix and Vector Calculus: Lecture Note Course Code: MAT 102B (For CEP)MUNIA AKTER MOONNo ratings yet
- FMSQ Revision NotesDocument5 pagesFMSQ Revision NotesJay AmbadkarNo ratings yet
- 11 - Straight LineDocument3 pages11 - Straight LineHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- CM2202 Geometric Computing 2DDocument50 pagesCM2202 Geometric Computing 2Dkhalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines ArigantDocument167 pagesStraight Lines ArigantVarun JishnuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable WorksheetMd Rizwan Ahmad75% (8)
- Xii Class - Inverse TrigonometryDocument3 pagesXii Class - Inverse TrigonometryMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 12th Test PaperDocument5 pages12th Test PaperMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020Document12 pagesFiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020Lohit DakshaNo ratings yet
- Part 01 Theory (1-8)Document9 pagesPart 01 Theory (1-8)Meena SharmaNo ratings yet
- Part 02 Question (9-20)Document14 pagesPart 02 Question (9-20)Mahendra Panda0% (1)
- Important QuestionDocument4 pagesImportant QuestionMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Restitution (E) : Very Heavy ObjectDocument5 pagesCoefficient of Restitution (E) : Very Heavy ObjectMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 1Document4 pagesTrigonometry 1Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Moment: Classical Concept Review 27Document2 pagesMagnetic Moment: Classical Concept Review 27Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry-3 Jee Main and AdvancedDocument4 pagesTrigonometry-3 Jee Main and AdvancedMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Matrices Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMatrices Worksheet 1Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Equivalence RelationsDocument5 pages2.2 Equivalence RelationsMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2018 04 23 16 11 57Document29 pages2018 04 23 16 11 57Prabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Math-09Document2 pagesPractice Paper Math-09Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtomDocument1 pageStructure of The AtomMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical Based Questions To Prepare For CBSE Class 10 Science ExamDocument6 pagesPractical Based Questions To Prepare For CBSE Class 10 Science ExamMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus BookDocument53 pagesDifferential Calculus BookMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions OMR SheetDocument1 page100 Questions OMR SheetMd Rizwan Ahmad100% (1)
- 03-AC-Solution-Critical, Graphical, Ass. ResonDocument5 pages03-AC-Solution-Critical, Graphical, Ass. ResonMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1Karthiik88No ratings yet
- Practice Paper Math-09Document5 pagesPractice Paper Math-09Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sample Mathematicia XIIDocument49 pagesSample Mathematicia XIIMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 211Document31 pages211Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- How To Use Microsoft Word 2007Document14 pagesHow To Use Microsoft Word 2007sbikmmNo ratings yet
- 49/HIS/1 A: MathematicsDocument12 pages49/HIS/1 A: MathematicsMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- EEE Question BankDocument19 pagesEEE Question BankMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- E Prospectus 2018 19Document13 pagesE Prospectus 2018 19Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 150 Questions OMR SheetDocument1 page150 Questions OMR SheetMd Rizwan Ahmad50% (6)
- Polynomials Assignment 1Document1 pagePolynomials Assignment 1Md Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Micronet TMRDocument316 pagesMicronet TMRHaithem BrebishNo ratings yet
- Islcollective Present SimpleDocument2 pagesIslcollective Present Simplecrisan mirunaNo ratings yet
- New - BMP3005 - ABF - Assessment Brief - FDocument5 pagesNew - BMP3005 - ABF - Assessment Brief - Fmilka traykovNo ratings yet
- Caldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignDocument6 pagesCaldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignJim LimNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TDocument46 pagesBakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TAlif NakyukoNo ratings yet
- 100 IdeasDocument21 pages100 IdeasNo ID100% (1)
- Final Matatag Epp Tle CG 2023 Grades 4 10Document184 pagesFinal Matatag Epp Tle CG 2023 Grades 4 10DIVINE GRACE CABAHUGNo ratings yet
- Airworthiness Directive: FAA Aviation SafetyDocument2 pagesAirworthiness Directive: FAA Aviation SafetyCarlos VarrentiNo ratings yet
- Retail Visibility Project of AircelDocument89 pagesRetail Visibility Project of Aircelabhishekkraj100% (1)
- Template Remarks For IIDocument18 pagesTemplate Remarks For IIjasleeneceNo ratings yet
- Laporan Keuangan TRIN Per Juni 2023-FinalDocument123 pagesLaporan Keuangan TRIN Per Juni 2023-FinalAdit RamdhaniNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Toko Jeremy LengkapDocument2 pagesDaftar Harga Toko Jeremy LengkapSiswadi PaluNo ratings yet
- Fish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Document32 pagesFish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Bagas IndiantoNo ratings yet
- The Attachment To Woman's Virtue in Abdulrazak Gurnah's Desertion (2005)Document7 pagesThe Attachment To Woman's Virtue in Abdulrazak Gurnah's Desertion (2005)IJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- PC's & Laptop Accessories PDFDocument4 pagesPC's & Laptop Accessories PDFsundar chapagainNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice #2Document6 pagesGrammar Practice #2Constantin OpreaNo ratings yet
- Npad PGP2017-19Document3 pagesNpad PGP2017-19Nikhil BhattNo ratings yet
- Little: PrinceDocument18 pagesLittle: PrinceNara Serrano94% (18)
- B2B Marketing: Chapter-8Document23 pagesB2B Marketing: Chapter-8Saurabh JainNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: ConceptualDocument53 pagesCapital Structure and Leverage: Multiple Choice: ConceptualArya StarkNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Write-UpDocument4 pagesPortfolio Write-UpJonFromingsNo ratings yet
- Tanque: Equipment Data SheetDocument1 pageTanque: Equipment Data SheetAlonso DIAZNo ratings yet
- 762id - Development of Cluster-7 Marginal Field Paper To PetrotechDocument2 pages762id - Development of Cluster-7 Marginal Field Paper To PetrotechSATRIONo ratings yet
- Portfolio AdityaDocument26 pagesPortfolio AdityaAditya DisNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development SCHOOL YEAR 2020-2021Document2 pagesTeacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development SCHOOL YEAR 2020-2021Diether Mercado Padua100% (8)
- Presentation No. 3 - Songs and ChantsDocument44 pagesPresentation No. 3 - Songs and Chantsandie hinchNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Immobilization - Advances in Industry, Agriculture, Medicine, and The Environment-Springer International Publishing (2016)Document141 pagesEnzyme Immobilization - Advances in Industry, Agriculture, Medicine, and The Environment-Springer International Publishing (2016)Komagatae XylinusNo ratings yet
- The Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in WordDocument23 pagesThe Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in Wordlei ann magnayeNo ratings yet
- Regulated and Non Regulated BodiesDocument28 pagesRegulated and Non Regulated Bodiesnivea rajNo ratings yet
- Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis Provides Update As Hurricane Ian Prompts EvDocument1 pageFlorida Gov. Ron DeSantis Provides Update As Hurricane Ian Prompts Evedwinbramosmac.comNo ratings yet