Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Process Line of Cooking Oil and Vegetable Ghee Vanaspati and Their Analysis During Processing
Uploaded by
Muhammad aliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Process Line of Cooking Oil and Vegetable Ghee Vanaspati and Their Analysis During Processing
Uploaded by
Muhammad aliCopyright:
Available Formats
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
Research & Reviews: Journal of Food and Dairy
Technology
Process Line of Cooking Oil and Vegetable Ghee (Vanaspati) and their
Analysis during Processing
Asim Shabir*
National Institute of Food Science & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad,Pakistan, ZipCode-38000.
Research Article
Received Date: 16/12/2015 ABSTRACT
Accepted Date: 23/03/2016 This study was conducted to evaluate the process line and quality of
Published Date: 29/03/2016 cooking oil and vanaspati ghee manufactured in Madni ghee mills (pvt)
Ltd. in Pakistan. The commercially available brands were investigated for
*For Correspondence free fatty acid, peroxide value, smell, weight, color, rancidity, foreign matter,
appearance and cold point. Analysis showed that free fatty acid, peroxide,
Asim Shabir, National Institute of Food Science smell, weight and rancidity value significantly same as standards set by
& Technology, University of Agriculture, Pakistan standard quality control authority (PSQCA). These results confirm
Faisalabad,Pakistan, ZipCode-38000; the product development under the hygienic conditions and quality limits
Tel:00923246435874. sets by Pakistan standard quality control authority.
E-mail: foodtech555@gmail.com
Keywords: Cooking oil, Quality evaluation,
Pakistan, Ffree fatty acid, Color.
INTRODUCTION
Madni oil industry is situated in 32 Km Sheikpura road. It is reputed and a leading name in vegetable ghee, cooking oil and
soap products. The organization manages the process of vegetable ghee, cooking oil, tin packaging and printing and laundry and
toilet soap within existing premises.
Madni Ghee Mills (Pvt.) Limited having production capacity of vegetable ghee as 24000 Metric Ton, cooking oil 20000
Metric Ton and laundry soap 24000 Metric Ton on per annum. Its products are registered with defense forces, utility stores
corporation and canteen stores department of defense forces. Where its supplies are successfully being supplied and many
contracts of vegetable ghee, cooking oil and laundry soaps have already been successfully completed and few in pipelines.
The unit is registered with Pakistan Vanaspati Ghee Manufacturing Association, Chamber of Commerce and industry, Sales Tax
Department Government of Pakistan, Pakistan Army, Navy and Trade Marks Government of Pakistan [1].
Technical staff of Madni Ghee Mills (Pvt.) limited is highly experienced and well educated in this field. The unit comprised
upon 74 Kanal 04 Marlas and 165 sq. ft of land, which is equipped with unique type of latest machinery and plant installed in
its attractive building. The beautiful roadside Mosque, fruity garden on the front side of the office block creates extra ordinary
beauty [2]. Private energy source, Gas connection and sewerage line linked with disposal drain are in existence within premises
of the mills.
The people who are dealing in vegetable ghee, cooking oil and laundry soap they know well the name of madni ghee mills
renowned products, which are in the market with the name and style of Madni banaspati, Madni cooking oil and Madni laundry
soap.
Considered Brands for Comparision
The industrial brands and products which were considered for this analysis were Pakwan cooking oil,Madni cooking oil and
Madni banaspati.
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 1
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
Considered Factors for Comparision
During this study the following factors were considered for the comparison and analysis.
Set-up of Industry
Industry set-up tremendously has impact on everything an industry is part of. The parameters which were accounted for this
study were Administration block,Oil refinery,Neutralizers,Bleachers,Deodorizers,Autoclaves,Filter press,Coolers,Hydrogenation
plant,Quality assurance lab,Steam boiler unit,Soap preparation plant,Filling unit,Work shop,Tin printing unit,Raw oil storage
tank,Water storage tank,Caustic soda tank and Centrifugal pumps.
Additionally it was noted that, There are two Boilers with a capacity of 250 Pounds each. The Boilers are wet heat energy
source in the form of steam [3,4]. This heat circulates in all the heating coils of processing units. Its input is water treated with
softening chemicals (NaCl, Aqua Prime) and output is heat energy in the form of steam. The maximum temperature is 205OC.
Gas Cracking Plant
The requirement of Hydrogen (H2) Gas is met through the production of gas by the Gas Cracking Plant using Natural Gas as
raw material by cracking Methane (CH4). CO 2 is the bye-product.
Receiving and Storage of Raw Oil
The raw oil is imported from Malaysia, Indonesia, America and Brazil. It is transported to the factory through lorry tankers
and is stored in storage tanks. Usually Cottonseed oil, Canola oil, Sunflower oil, Soybean oil and R.B.D. Palm oil are used for
manufacturing of ghee.
Policies of Madni Ghee Mills (Pvt) Limited
Quality and consumer safety policy: Madni ghee mills take care to ensure that their customers & consumers are provided
with the best quality products that are safe in use. To meet the customers expectation and needs. Madni ghee mills is committed
to develop and ensure consistent supply of affordable, convenient, safe and high quality products. As a service company we take
care to ensure that our customers are provided with the best quality services to fulfill all customers needs [5,6].
In order to achieve these goals Madni ghee mills maintains quality and consumer safety objectives along with implementation
plans on annual basis and maintain follow up by reporting process. The organization design, operate and maintain processes and
plants to establish and maintain standards and procedures for the control and monitoring of all operations that prevent potential
product safety hazards [7]. It ensures the compliance with applicable legislation and set standards. The authority introduce
appropriate product quality management system and maintain HACCAP as a management tool at all their operation.
Helping their suppliers to develop their quality process and standard so as to get consistent quality suppliers and develop
supply chain to improve overall quality performance audits is followed under the strict regulation under the organization.
Responsibility to implement this policy lies with general manager & the same is filtered to the functional heads and respective
managers in their areas of responsibility.
Environmental policy: Madni ghee mills is committed to meet the needs of the customers and society in a sound environment
and sustainable manner. The organization is working in co-operation with members of industry, government bodies and public
interest groups, scientists, environmentalists, technical department and customers to promote achievements of high standards
of environmental care through multiple aqpproaches [5,7]. The organization is continuously striving to reduce the wastage,
conserve energy, examine reuse & recycle throughout the operation. They are also ensuring that all the employees are aware of
the company environmental policy and are motivated to apply it in their respective sector. Apart from these, the organization is
considering to ensure the safety of their product manufacture at their side & continuing monitoring and reporting all progress and
notifying the environmental associated issues on regular basis.
REFINING PROCESSING
Refining of vegetable oils in simple terms means Removal of Impurities. Major impurities in the oils may be mentioned
as follows: Dirt and other foreign matters to the seeds, solid matters from the seeds, mucilage, free fatty acids, coloring matters,
substances imparting taste and smell to the oil and moisture.
Refining eliminates all the impurities [3,8]. The process employed in refining is comparatively simple. If the raw material from
which oil is extracted is clean, dry and sound the oil produced is of good quality while oil obtained from inferior, unsound oil seeds
contain more impurities. The processes employed in refining are either mechanical, chemical, or combination of two.
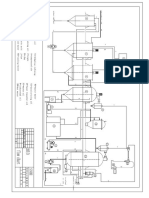
Following steps are involved in manufacturing of cooking oil and vegetable ghee (Figures 1 and 2).
Pre-Neutralization
Pre-neutralization is carried out in a vessel called pre-neutralizer. It is cylindrical in shape and has electric motor for
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 2
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
centrifugation of oil. Motor has steering shaft with baffles for complete mixing of contents. It has steam heating coils and caustic
soda washing coils [8-10]. Temperature gauge is also mounted on it. Generally the process of pre-neutralization is completed in 7-8
hours.
Figure 1. General processing steps of oil preparation.
Figure 2. General processing steps of vegetable ghee.
The objective of pre-neutralization is the removal of free fatty acids. Oils have 2-2.5% free fatty acids. It has to be reduce it
to 1-1.5%. PSI (Pakistan Standard Institute) recommends 0.20 - 0.25% free fatty acids. Due to removal of F.F.A. the color of oil is
improved. Usual method of removing the free fatty acids is to treat the crude oil with Sodium hydroxide solution carefully regulated
in strength and amount, and at carefully regulated temperature. Firstly free fatty acid percentage of crude oil is determined and
then NaOH of required Baume is added. Generally NaOH of 20-22 Baume is used[11,12]. Then crude oil is charged in to the pre-
neutralizer and it is centrifugally moved with the help of electric motor. The temperature of oil is raised up to 70oC with the help
of steam heating coils. When required temperature is achieved NaOH of 20 - 22 Baume having 70oC temperature is added to
crude oil with the help of caustic soda washing coils, it is thoroughly mixed for 10-15 minutes. The soda solution combined with
the free acids turned of soap. After this it is given one-hour rest. During rest soap settles in the bottom and oil becomes on upper
side. The soap is drained through the drain valve mounted at the bottom of vessel. Then the oil is washed with water having 100oC
temperature. Water dissolves soap and free alkali and settle down oil comes on upper side. It is given 1-hour rest and the water
is drained through drain valve.
Oil sample is taken to check free fatty acid percentage up to 0.25% or less. Soapy particles should not be present. If soapy
particles are present then oil, again washed with water and given 1 hour rest. The number of water washing depends upon nature
of oil e.g. cotton seed and soybean require three washer, canola requires two washer. Pre-neutralized oil has 0.25% or less
F.F.A.%. Madni Banaspati has 0.08% F.F.A.
Following tests are applied at pre-neutralization stage: F.F.A % test prior to processing, F.F.A % test after processing, Soap
test. After the tests, the pre-neutralized oil is then passed to pre-bleacher for bleaching. Amount of caustic soda required to
neutralize free fatty acids is 9 Kg of solid NaOH. It is required to neutralize 0.4% F.F.A in a Batch of 16 tons.
Pre-Bleaching
Pre-bleaching is carried out in a vessel called pre-bleacher. It is cylindrical in shape and vertical in direction. It has an electric
motor having steering shaft with baffles for centrifugation of pre-neutralized oil [12-14]. It has temperature gauge, vacuum gauge ,
pressure gauge and steam heating coils for raising temperature of input oil. Generally the process of pre-bleaching is completed
in 3-4 hours.The objective of pre-bleaching is to get rid of unwanted pigments and coloring matters from input oil. Bleaching is
done by means of bleaching earth (Clay+silica dioxide, mixed in certain proportion and ground to particle size of 250 micron and
acidified with HCl). It contains 3-4% moisture known as Fullers earth. First pre-neutralized oil is charged in to the bleaching vessel
and stirring is started. Then it is warmed and dehydrated under vacuum at 120 oC to remove water and free air. It takes 1-2 hours
for complete dehydration. After this, the oil is cooled to lower down its temperature up to 110 oC. Later on, the bleaching earth is
considered at recommended rate depending upon the intensity of color of oil as below is carried out.
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 3
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
Palm and palmoline = 2 Kg/ton of oil.
Soybean and canola = 5 Kg/ton of oil.
Cotton seed = 8 Kg/ton of oil.
The amount of bleaching earth is doubled in case of cooking oil. 75% of bleaching earth is added in pre-bleacher & rest of
25% is added in post-bleacher.
The process consists of thoroughly stirring the dry absorbent powder into the oil when gently heated under vacuum status.
Activated carbon at the rate of 100 g/ton is also added in case of cottonseed oil, to bleach the darker color of cottonseed oil.
Fuller's earth is mixed slowly so that every particle of the oil combines with every particle of the earth. Stirring continues and that
the whole process takes about an hour. Fullers earth removes all the impurities and color, and makes the oil fine. It also absorbs
any particle of soap that is left behind. Explanation of the matter lies in the fact that the coloring substances, which pass from the
seed into oil, is absorbed and held back by earth. Maintaining the input oil temperature at 100oC 05 oC. Bleached Oil is filtered
the through filter press. It removes the bleaching earth and clear oil is obtained. The color index of bleached oil is measured with
the help of spectrophotometer / tintometer. Following tests are applied at this stage:Color index R,Y,F.F.A%. The pre-bleached oil
is then passed to converter for hydrogenation[14-16].
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation or hardening may be defined as a process whereby part or in some cases nearly all the unsaturated acids in
an oil are caused to combine with hydrogen under the influence of a catalyst. In this way the glycerides of the unsaturated acids
are converted into the saturated acids of another series. Thus in case of olein which is unsaturated, the addition of 6 atoms of
hydrogen produces stearin, which is saturated in accordance with the following formula:
(C17 H 33COO)3C3 H 5 + 3H 2 Ni / Pt .D H
(C17 H 35CO3O)C3 H 5
Olein (unsaturated ) Stearin ( saturated )
Out of the many processes, which has been suggested with the objective of converting liquid oils into solid fats, hydrogenation
is the only one, which has been applied on large commercial scale [17]. When it is considered that only 0.68% of H2 by weight is
necessary to convert olein into stearin and how great is the change brought about in a simple manner by so small addition. By
volume 30 feet3 of hydrogen is required for each percent reduction in iodine value of per ton of oil [11,16].
Hydrogenation is carried out in a vessel called converter or autoclave. It is completely airtight vessel and has heating coils,
steering shaft having baffles, perforated hydrogen coils, compound gauge to measure pressure and vacuum and temperature
gauge to measure temperature[18]. Generally the process of hydrogenation is completed in 6-8 hours.
First the vessel is filled with neutralized and bleached oil. It is dehydrate it up to 170o C temperature under vacuum for 1-
to 2 hours. If water is present then it will poison nickel and which effect its quality. After this hydrogen gas is applied through
perforated hydrogen coils under vacuum and thoroughly mixed by continues stirring. Now food grade Nickle catalyst (G-53,
Germany) is added in recommended quantity as follow: 1100 grams/ton for palm oil(1), 2250 grams/ton for soybean oil, and
2200 grams/ton for sunflower & cottonseed oil.
Hydrogen gas is applied continuously and samples are drawn for the inspection and testing of melting point. Desired/
approved/recommended melting point for Banaspati ghee is 36 2 oC. When approved melting point is achieved then hydrogen
gas is stopped. After this, the converted product is cooled up to 100-110oC. Then product is filtered through filter press. It removes
Ni catalyst and clean, clear oil is obtained. The product may not be cooled below 90oC otherwise it will create problem in filtration.
Again melting point is verified after filtration. Hydrogenation is not carried out in manufacturing of cooking oil[19,20].
The extent to which an oil has been hydrogenated, is measured by the fall in iodine value, which the oil has undergone, since
it is directly proportional to the amount of hydrogen gas, which has been added to the oil. F.F.A% increases during hydrogenation.
As hydrogenation proceeds and the unsaturated bodies become saturated, the fall in iodine value is coincident with a steady fall
in refractive index and rise in melting and solidifying points.
This can be verified as: =140.2
Iodine value of cotton seed oil at charging = 140.2
Iodine value of cotton seed oil before gas passing = 95.8
Iodine value of cotton seed oil after complete hydrogenation = 71.69
Following tests are applied at this stage:Melting point,Color index Red, Yellow,F.F.A percentage and Iodine value. The hard
oil is then passed to post-neutralizer for post-neutralization.
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 4
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
Post-Neutralization
Post-neutralization is carried out to remove the soap and Ni catalyst if it is present due to poor filtration. Firstly hard oil
is charged into post-neutralizer. The temperature of hard oil is maintained at 90 5oC by heating or cooling. Its free fatty acid
percentage is calculated and caustic soda is added accordingly. Generally caustic soda of 8-10 Baume is added without any
agitation, light wash of water is given. After this 2 hour rest is given, due to rest soap settles down at the bottom and oil becomes
on upper surface. The soap is drained through the drain valve present at the bottom of vessel.
Now two washes of boiled water are given. After 1st wash give 1 hour rest, drain soap and water through drain valve. Then
2 wash is given and same process is repeated. Apply soap test, it should be negative. If it is positive then 3rd wash is given.
nd
Generally the process is completed in 5-6 hours. Following tests are applied at this stage:F.F.A percentage prior to neutralization,,
F.F.A percentage after neutralization and Soap test.
Post-Bleaching
Post-bleaching is carried out in a vessel similar to that used for pre-bleaching. First post-neutralized oil is charged into
post-bleacher and its temperature is raised up to 110 oC. It is completely dehydrated under vacuum and stirring is continued
throughout the process. When complete dehydration is achieved then bleaching earth is added in recommended quantity. It is
thoroughly mixed in oil for 45 minutes. At the end post-bleached oil is filtered through filter press to remove the bleaching agent
from oil. Generally the process is completed in 3-4 hours. Following tests are applied at this stage:Color index Red,Yellow, Melting
point and F.F.A percentage. The post-bleached oil is then passed to deodorizer for deodorization.
Deodorization
Deodorization is carried out in cylindrical vessel. It is completely air tight and vertical in direction. It has open steam lines,
steam heating coils and low and high vacuum system. Steam pressure, temperature and vacuum gauges are mounted on it.
Electric motor with steering shaft having baffles is not present. A fat catcher is present to catch volatile matters. Generally the
process is completed in 7-8 hours.
Deodorization is a process of steam distillation whereby relatively volatile odoriferous and flavored substances are stripped
from the relatively nonvolatile oil. The operation is carried out at a high temperature to increase the volatility of the odoriferous
components. The application of reduced pressure during operation protects the hot oil from atmospheric oxidation, prevents
undue hydrolysis of oil by steam and greatly reduces the quantity of steam required. The objective of deodorization is removal of
unwanted odors, odoriferous matters and other volatile fatty materials and to improve smell, odor and taste of finished product.
Some of compounds responsible for tastes and odors of oil are ketones, terpenoids and aldehydes. Flavor and odor removal
generally parallels free fatty acid removal. The concentration of odoriferous substances in oil is generally quite low. In case of
cottonseed, soybean, tallow and peanut oil, it does not appear to be greater than 0.10%. Deodorization also reduces the color
of oil and destroys peroxides in oils. The process of deodorization is influenced by temperature, vacuum, steam and design of
deodorizer. Generally the process is completed in 8 hours in case of ghee and 12 hours in case of cooking oil.
Firstly post-bleached oil is charged into deodorizing vessel. Oil is warmed and dehydrated up to 170oC under low vacuum
status to remove moisture. When the oil is completely dehydrated and required temperature is achieved, then the process is
boosted up to high vacuum status along with increase in temperature to 190 10oC. Now citric acid is added at the rate of
100grams/ton of oil. 50% of citric acid is added before application of live steam and rest of 50% is added before cooling. Citric
acid helps in removal of volatile matters and increase shelf life of final product. The process is assisted with treatment of oil with
live steam for 3-4 hours. Samples are drawn for sensory evaluation and tests are also applied for justification of deodorization.
When the product is free from bad odors the live steam is stopped and product is cooled down up to 140 oC. Now it is shifted to
cooling vessel (cooler) for further lowering down of temperature to 70 oC. Cooling is done under vacuum to avoid oxidation and to
remove water. After this it is filtered through filter press and passed to churns. Following tests are applied at this stage:General
appearance,Odor/smell,Taste,F.F.A. percentage,Rancidity,Moisture,Soap test,Melting point,Peroxide value and Color index.
In case of Cooking Oil Hydrogenation, Post Neutralization & Post Bleaching are not performed.
Blending (Addition of Vitamin A&D3)
Completely deodorized product after filtration is taken into filling churns. Here vitamin A&D3 are added in recommendedquantity/
dose. Vitamins are imported from Germany (Merck). (BASF).Generally 33 ml of vitamins/ ton of the product are added and
thoroughly mixed by continuous stirring. Samples are drawn for vitamin confirmation test, the vitamin test should be +ive. Now it
is ready for filling and packaging [9].
Filling/Packaging
Product is cooled up to 50 5oC. Now it is manually/mechanically/automatically filled in food grade approved packaging
material. Automatic filling is carried out in case of pouches. The Prepack Click 2 machine is used for automatic filling and it fills
2000pouch of 1.0 Kg size/hour and 2400 pouch of Kg /hour. After filling tins/buckets/pouches are properly sealed. The
products are packed into different pack mix for marketing as detailed below:
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 5
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
Vegetable Ghee
16 Kg. Tin and Bucket
05 Kg. Tin and Bucket
2.5 Kg. Tin and Bucket
01 Kg. Pouch pack
Kg. Pouch pack
Kg. Pouch pack
05 Kg. Pouch Pack
Cooking Oil
16 Letters Tin
10 Letters Plastic Can
05 Letters Pet Bottle
05 Letters Pouch Pack
05 Letters Tin
2.5 Letters Tin
03 Letters Pet bottle
Letter Pouch pack
Chilling: When a fat is allowed to cool slowly without any agitation, then it sets up grain. After packaging ghee is gradually
chilled in chilling rooms, which are made of insulating material to maintain the temperature of chilling room. Ammonia compressed
air conditioning machine is used for this purpose.
The chilling process of vegetable ghee is completed in 18-22 hours in summer& 8-10 hours in winter and temperature of
8-9oC is maintained in chilling room. After chilling ghee is stored in ware houses at room temperature and is ready for consumption.
SOAP SECTION
There are 5 steps in soap manufacturing:-
Soap Grain Mixing Pan
It is cylindrical in shape, fitted with separate lines for induction of caustic soda and water. Soapy matters are transferred in
pan from neutralizer, cutting wastes and fats from the deodorizers. After charging, H2O is added to convert it in liquid form. After
this caustic soda of 50 Baume in recommended quantity is added, it is heated till the required texture is achieved, which almost
depends upon experience[1].
Soap Boiling / Boiling and Mixing Pans
These are large pans and have capacity of 34 tons. In this soap is heated for 78 hrs. Till water is evaporated and soap
grains becomes smaller.
Crutching and Mixing Tank
It is cylindrical in shape and has capacity of 5 tons. Soap is manually filled in it with the help of tins from the boiling pans.
After filling 60 to 75 kg of soap stone mixed in 15 tons of oil is added. Sodium Silicate , 120 to 150 kg is added. Subsequently, 2
tons of Resin are added. All the material is thoroughly mixed for 1 hour. It has baffles for mixing. Steam heating coils are present
for heating. After completion of the process one-hour rest is given to settle.
Convertion in Iron Frames
From crutching tank soap is filled into iron frames to convert it in blocks.
Cutting and Packaging
Soap blocks are stored for 24 hrs. to reduce moisture. Cutting is carried out with the cutters to convert the blocks in cakes
of different sizes which are packed in cartons of 9 kg capacity.
CONCLUSION
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 6
e-ISSN:2321-6204
p-ISSN:2347-2359
At last its concluded that every step of ghee and oil processing from receiving of crude oil till packaging of final product is
carried out under hygienic conditions. All the rules and regulations not only related to food safety but also related to safety of
the employees are followed strictly. From these results it is proved that quality of Vanaspati ghee and cooking oil available in
Pakistan according to the standards set by PSQCA. The values of free fatty acids, nickle content and peroxide are significantly low
as compared to standard values. Healthy and nutritious Vanaspati ghee and cooking oil is available for consumer.
Internship duration of 10 weeks make a lot of contribution in my practical knowledge related to processing of vegetable oil.
REFERENCES
1. Andersek AJ. Refining of Oils and Fats, 1953.
2. AOAC. The Official Methods of Analysis, 2000; 17.
3. http://corn.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/CornOil.pdf
4. http://www.psqca.com.pk/test2/index.html
5. Blaser B, Industrial Oil and Fat Products, Angewandte Chemie. 1953; 65:96.
6. Che Man YB and TCP. Effects of natural and synthetic antioxidants on changes in refined, bleached, and deodorized palm
olein during deep-fat frying of potato chips, Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 1999;76: 331-339.
7. E L. Laboratory Methods for Sensory Evaluation, 1977; 1637.
8. ELLIS C. The Hydrogenation of Oils, 1914.
9. Firestone D. Official and Recommended Methods of the American Oil Chemists Society, Methods. 1989.
10. Albert JD, et al. Fatty acids: structure, occurrence, nomenclature, biosynthesis and properties, Trans Fatty Acids. 2008;
1-24.
11. Harrod M and Moller P. Hydrogenation of a Substrate and Products Manufactured According to the Process. 1996.
12. Rossel JB. Classical analysis of Fats and Oils. In: Hamilton R, Rossel J. 1986 (ed.): Analysis of Fats and Oils, 1-90. New
York,USA
13. Koritala S, et al. Selective Hydrogenation of Soybean Oil. X. Ultra High-Pressure and Low-Pressure, Journal of the American
Oil Chemists Society. 1980;57:15
14. Patterson HBW. Hydrogenation of Fats and Oils, Patterson HBW. 1994: 3940. Hydrogenation of Fats and Oils: Theory and
Practice. AOCS Press, Champaign, Illinois.
15. PSQCA. Specification for cooking oil (Blended): 2003.
16. Smouse TH. Factors affecting oil quality and stability in methods to assess oil quality and stability of oils and fat containing
food. 1994;17-36.
17. Susu AA and Ogunye AF. Nickel-Catalyzed Hydogenation of Soybean Oil. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society,
1981;58:657661.
18. Tacke TS, et al. Hardening of Unsaturated Fatty Acids, Fatty Acids, or Fatty Acid Esters. 1998.
19. Duff JH. Heavy metals a meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report), Pure and Applied Chemistry. 2002;74:793807.
20. Gunstone FD. Vegetable Oils in Food Technology Composition, Properties and Uses, Times by SPi Publisher Services,
Pondicherry, India. 2011.
RRJFPDT | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | June, 2016 7
You might also like
- Bioprocessing Technology for Production of Biopharmaceuticals and BioproductsFrom EverandBioprocessing Technology for Production of Biopharmaceuticals and BioproductsClaire KomivesNo ratings yet
- Egg Processing Guide BookDocument31 pagesEgg Processing Guide BookClaudia Melissa Orlandini MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Safe and Effective Salt FortificationDocument28 pagesEnsuring Safe and Effective Salt FortificationHenok DireNo ratings yet
- Poeb108 RaviDocument8 pagesPoeb108 RaviMuhammad GaneshaNo ratings yet
- Interband Enterprise: Blackstone Impex SDN BHDDocument3 pagesInterband Enterprise: Blackstone Impex SDN BHDFarooq AliNo ratings yet
- Indian Dairy IndustryDocument39 pagesIndian Dairy IndustryAmrish GargNo ratings yet
- Palm Oil in FryingDocument73 pagesPalm Oil in FryingGenesis Custodio100% (1)
- What Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record) ?Document2 pagesWhat Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record) ?YousifNo ratings yet
- Rapeseed and Canola Oil: Production, Processing, Properties and UsesFrom EverandRapeseed and Canola Oil: Production, Processing, Properties and UsesNo ratings yet
- Cold Pressed Oils: Green Technology, Bioactive Compounds, Functionality, and ApplicationsDocument29 pagesCold Pressed Oils: Green Technology, Bioactive Compounds, Functionality, and ApplicationsDijana Dencic NalovskaNo ratings yet
- HACCP Palm OilDocument5 pagesHACCP Palm OilLaura Arango Rojas100% (1)
- Edible Oil GheeDocument25 pagesEdible Oil GheeLTE00233% (3)
- Cleaning and disinfection of food factories: a practical guideFrom EverandCleaning and disinfection of food factories: a practical guideNo ratings yet
- 0707-0712 (1117) Microbiological Best Laboratory PracticesDocument7 pages0707-0712 (1117) Microbiological Best Laboratory PracticesDr usama El ShafeyNo ratings yet
- MOFPIDocument42 pagesMOFPIcardticket0% (2)
- BIS CreamsDocument13 pagesBIS CreamsNAVNEET BAGGA100% (2)
- 1 Production Section 11Document44 pages1 Production Section 11Kunal RanaNo ratings yet
- NanotechnologyApplicationsintheFoodIndustry PDFDocument319 pagesNanotechnologyApplicationsintheFoodIndustry PDFjesus cuevasNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil - WikipediaDocument11 pagesCoconut Oil - WikipediaYusuf Aliyu UNo ratings yet
- Crude Palm OilDocument19 pagesCrude Palm OilmarpadanNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Cottonseed Oil Expeller Method One Ton Per Day PDFDocument2 pagesExtraction of Cottonseed Oil Expeller Method One Ton Per Day PDFHenryNo ratings yet
- Specification for highly pure white sugar commodityDocument2 pagesSpecification for highly pure white sugar commodityaaicoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Final ReportDocument34 pagesIndustrial Training Final ReportCheng KaiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training - Report - Format MU (1) (1) FINAL REPORTDocument36 pagesIndustrial Training - Report - Format MU (1) (1) FINAL REPORTniraj kumarNo ratings yet
- MHL-VLP-XX Fumigation ValidationDocument10 pagesMHL-VLP-XX Fumigation ValidationMedicare Hygiene LimitedNo ratings yet
- Weight Variation of BiscuitsDocument12 pagesWeight Variation of BiscuitsSandeep Haridas MNo ratings yet
- HACCP Oil RefiningDocument20 pagesHACCP Oil RefiningAnand Namdeo100% (1)
- Codex Alimentarius Final Version of CAC32 ReportDocument115 pagesCodex Alimentarius Final Version of CAC32 ReportNzlWolfNo ratings yet
- Dry Fractionation Pilot Plant GuideDocument15 pagesDry Fractionation Pilot Plant GuideSyahrul EzanieNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment 2012-11-6 FDA GuidanceDocument95 pagesRisk Assessment 2012-11-6 FDA GuidancedahearnNo ratings yet
- Palm Oil and Palm Kernel OilDocument26 pagesPalm Oil and Palm Kernel OilRachel Yessica WinartiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Api and IntermediatesDocument34 pagesManufacturing of Api and IntermediatesShaileshNo ratings yet
- Indian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchDocument24 pagesIndian Agrochemicals Industry: Insights and Outlook: February, 2019 I Industry ResearchSurajNo ratings yet
- G. Amphray Laboratories: Paracetamol BPDocument2 pagesG. Amphray Laboratories: Paracetamol BPAlhamzah Rachmat FadjarNo ratings yet
- Final - Print Adh Lam Slit - May 6 2010Document22 pagesFinal - Print Adh Lam Slit - May 6 2010cassilda_carvalho@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Hygisoft For FarmsDocument8 pagesHygisoft For FarmsHariprasad ManavalanNo ratings yet
- Canola Oil Physical Chemical Properties 1Document6 pagesCanola Oil Physical Chemical Properties 1elpancaseroNo ratings yet
- THAI COATER Spec PDFDocument4 pagesTHAI COATER Spec PDFConfundo Paa DuroNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 & 3 - PDE Implementation On CleaningDocument101 pagesTopic 2 & 3 - PDE Implementation On Cleaningmelimaulani-1No ratings yet
- Banstag Life Sciences proposed manufacturing plantDocument66 pagesBanstag Life Sciences proposed manufacturing plantemad hayekNo ratings yet
- Edible Oil Fortification Technical HandbookDocument4 pagesEdible Oil Fortification Technical HandbookramcatNo ratings yet
- Type III DMF White Papr (1) .Rev 1 Final - Doc5!8!023Document65 pagesType III DMF White Papr (1) .Rev 1 Final - Doc5!8!023bot38100% (2)
- Cleaning Validation Guideline (GUI 0028) Revision Draft 201201Document16 pagesCleaning Validation Guideline (GUI 0028) Revision Draft 201201Chang Woo JongNo ratings yet
- ASEAN Guideline Process OnDocument7 pagesASEAN Guideline Process OnVipin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Single PotDocument7 pagesSingle Potsky.blueNo ratings yet
- Sorbates Food and Pharma Quality Information PackDocument39 pagesSorbates Food and Pharma Quality Information PackMiguelNo ratings yet
- FAO Herbs and Spice ProductsDocument10 pagesFAO Herbs and Spice ProductsUsman CheemaNo ratings yet
- Oils and Fats Glossary TermsDocument19 pagesOils and Fats Glossary TermsThais Soraluz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Palm Oil Refinery NewDocument2 pagesCase Study Palm Oil Refinery NewFong Leong Chee 馮亮智100% (2)
- Frying OilsDocument10 pagesFrying OilsSuryadi XuNo ratings yet
- Chemical cleaning 1 رائعة PDFDocument16 pagesChemical cleaning 1 رائعة PDFmohamed karem100% (1)
- HEB EspecificacionesDocument7 pagesHEB EspecificacionesAna María SnzNo ratings yet
- Action Plan For Quality System Improvement - 06 - 12Document9 pagesAction Plan For Quality System Improvement - 06 - 12Parveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Effervescent Dosage ManufacturingDocument5 pagesEffervescent Dosage ManufacturingResk CavalierNo ratings yet
- INSWABU - Check List - Sparkling PET - 20190619Document136 pagesINSWABU - Check List - Sparkling PET - 20190619YogiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pakistan's Edible Oil IndustryDocument45 pagesAnalysis of Pakistan's Edible Oil IndustryAbbas Zia80% (10)
- Refining and Degumming Systems for Edible OilsDocument7 pagesRefining and Degumming Systems for Edible Oilsjaymie_llanera100% (1)
- SOPs For IQMS in Food Manufacturing FacilitiesDocument7 pagesSOPs For IQMS in Food Manufacturing FacilitiesmineeNo ratings yet
- FSSC 22000: Foundation For Food Safety CertificationDocument14 pagesFSSC 22000: Foundation For Food Safety CertificationAhmedElSayedNo ratings yet
- Dairy Techniques Verka PlantDocument7 pagesDairy Techniques Verka PlantHarkesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TL-MR3420 V3 DatasheetDocument2 pagesTL-MR3420 V3 DatasheetMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Customs Tariff 2017-18 AnalysisDocument12 pagesCustoms Tariff 2017-18 AnalysisMuhammad ali100% (2)
- Ghee and Oil MillDocument54 pagesGhee and Oil Millshani27100% (4)
- Square Can Making Machine Line-Linda-FSTDocument3 pagesSquare Can Making Machine Line-Linda-FSTMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Keyboard Layout PDFDocument1 pagePhonetic Keyboard Layout PDFziabutt100% (1)
- Wenzhou Bangcheng Grain and Oil Machinery Co.,Ltd: 20T/D Soybean & Sunflower Oil Full Continuous Refinery Plant QuotationDocument3 pagesWenzhou Bangcheng Grain and Oil Machinery Co.,Ltd: 20T/D Soybean & Sunflower Oil Full Continuous Refinery Plant QuotationMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- The Palm Oil Market in Pakistan: Mohd Fairus Mohd Hidzir and Hisamuddin Mohd AsparDocument5 pagesThe Palm Oil Market in Pakistan: Mohd Fairus Mohd Hidzir and Hisamuddin Mohd AsparMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- PAKISTAN CUSTOMS TARIFF 2014-15Document348 pagesPAKISTAN CUSTOMS TARIFF 2014-15AliChana1No ratings yet
- Square Can Making Machine Line-Linda-FSTDocument3 pagesSquare Can Making Machine Line-Linda-FSTMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Suzhou First Packing Co.,Ltd Catolog - LindaDocument12 pagesSuzhou First Packing Co.,Ltd Catolog - LindaMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- 20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListDocument4 pages20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- 20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListDocument4 pages20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Quotation of 20T Crude Oil Refinery Plant and Palm Oil Fractionation PlantDocument11 pagesQuotation of 20T Crude Oil Refinery Plant and Palm Oil Fractionation PlantMuhammad ali33% (3)
- Engineering Proposal and Quotation: 50T/D Continuous Refining Workshop EquipmentDocument26 pagesEngineering Proposal and Quotation: 50T/D Continuous Refining Workshop EquipmentMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- 20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListDocument4 pages20TPD Oil Refining Equipment ListMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- 15TPD Palm Oil, Cottonseed Oil and Canola Oil Refining LineDocument15 pages15TPD Palm Oil, Cottonseed Oil and Canola Oil Refining LineMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart-20T Crude Oil Refinery PlantDocument1 pageFlow Chart-20T Crude Oil Refinery PlantMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Corn OilDocument24 pagesCorn OilAmol RautNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Physical Process Variables For Development of Aloe Veramango Rts BeveragesDocument12 pagesOptimization of Physical Process Variables For Development of Aloe Veramango Rts BeveragesMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Corn OilDocument24 pagesCorn OilAmol RautNo ratings yet
- InsstallDocument1 pageInsstallMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- InsstallDocument1 pageInsstallMuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Galapagos Penguins: Shelter, Niche and NeedsDocument8 pagesGalapagos Penguins: Shelter, Niche and Needsjim munkNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole medication guideDocument3 pagesAripiprazole medication guidemissayayaya100% (1)
- Carte Tehnica Partea IDocument22 pagesCarte Tehnica Partea IadrianNo ratings yet
- PE1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1-ADMDocument12 pagesPE1 q1 Mod6 ProperEtiquetteand-Safetyinthe-UseofFacilitiesEquip v1-ADMelvira.raagas2No ratings yet
- Seizure Acute ManagementDocument29 pagesSeizure Acute ManagementFridayana SekaiNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi v500 VFD IB NA 0600065-F FR-V500-NA Instruction Manual-DetailedDocument221 pagesMitsubishi v500 VFD IB NA 0600065-F FR-V500-NA Instruction Manual-DetailedMROstop.comNo ratings yet
- Weld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceDocument1 pageWeld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceRicardo SoaresNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Solubility - Water As A SolventDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Solubility - Water As A Solventben4657No ratings yet
- FICHA TECNICA Smart-EvoDocument4 pagesFICHA TECNICA Smart-EvoClaudio A.No ratings yet
- Assessments and Rubrics For Unit 2Document13 pagesAssessments and Rubrics For Unit 2api-302258576No ratings yet
- Escala de Violencia e Índice de SeveridadDocument11 pagesEscala de Violencia e Índice de SeveridadpsiserviciosprofesioNo ratings yet
- 2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryDocument5 pages2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryJulio Cesar Velasco CastroNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Aspects of School Health ServicesDocument4 pagesObjectives and Aspects of School Health ServicesRaed AlhnaityNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureRajib DasNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor For Air Pollution ControlDocument6 pagesBioreactor For Air Pollution Controlscarmathor90No ratings yet
- Sem-V Principle of Taxation Law PDFDocument3 pagesSem-V Principle of Taxation Law PDFAnantHimanshuEkkaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells Crossword Puzzle: FreebieDocument5 pagesPlant and Animal Cells Crossword Puzzle: FreebieAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Prosecution and elements of crimes under Philippine lawsDocument14 pagesProsecution and elements of crimes under Philippine lawsNoel Cagigas FelongcoNo ratings yet
- Trinidad and Tobago Budget 2022 focuses on resilience amid pandemicDocument167 pagesTrinidad and Tobago Budget 2022 focuses on resilience amid pandemicAliyah AliNo ratings yet
- ECOSIADocument8 pagesECOSIAaliosk8799No ratings yet
- Prac - 2Document3 pagesPrac - 2nv471646No ratings yet
- Tracking SARDO StudentsDocument2 pagesTracking SARDO StudentsLean ABNo ratings yet
- BSN-2D 1st Semester ScheduleDocument2 pagesBSN-2D 1st Semester ScheduleReyjan ApolonioNo ratings yet
- What is Intermodulation InterferenceDocument3 pagesWhat is Intermodulation InterferencedekcarcNo ratings yet
- State-of-the-Art Reactor Consequence Analyses (SOARCA) ReportDocument200 pagesState-of-the-Art Reactor Consequence Analyses (SOARCA) ReportKingba OlayemiNo ratings yet
- List of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolDocument8 pagesList of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolAspci Assumption Passi100% (1)
- Asbestos exposure bulletinDocument2 pagesAsbestos exposure bulletintimNo ratings yet
- Load Summary for Premise Under 100kVADocument2 pagesLoad Summary for Premise Under 100kVAMuhammad Zulhelmi ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Isolation of Saponins PDFDocument2 pagesExtraction and Isolation of Saponins PDFMikeNo ratings yet
- Nothing But The Truth D2Document89 pagesNothing But The Truth D2Jamie Nicholas100% (1)