Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 10
Uploaded by
jaga67Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 10
Uploaded by
jaga67Copyright:
Available Formats
RETAINING STRUCTURES
1. Definitions
A retaining wall is defined, for the purposes of this There are two main types of retaining walls:
chapter, as a slim vertical structure used for ground - continuous walls: diaphragm or precast walls, sheet
retention during excavation. Unlike gravity retaining piling, slurry trenches, secant piles, etc.,
walls, the weight of a slim retaining wall has little effect - discontinuous walls: Berlin and Parisian-type walls,
on its capacity to balance the pressures. A slim retaining Lutetian and Moscow-type walls, contiguous piles, etc.
wall acts like a series of juxtaposed vertical beams
holding back the pressures exerted by the soil, water and The vertical structural components which provide the
existing structures. It is supported by struts or ground flexural capacity of the wall are installed before the
anchors and is embedded into the ground below excava- excavation work commences and therefore do not inter-
tion level, in order to: fere with the earthworks.
- mobilise the passive pressure at the toe, The temporary supports (and sometimes permanent
- allow the wall to support vertical loads if necessary, supports), and lagging in the case of discontinuous walls,
- Provide hydraulic stability (for which a continuous are installed during earthworks. This needs to be consi-
wall is required). dered in the construction sequence.
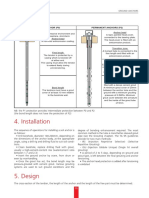
2. The different types of retaining structures
2.1. Discontinuous walls
Discontinuous walls include: The following conditions must be satisfied during exca-
- regularly-spaced deep foundation elements (piles, vation and the lagging phase:
micro piles, barrettes) that form the rigid vertical struc- - there must be no significant flow of water through
ture. These elements are installed before the start of the ground,
earthworks, - the ground must be able to stand vertically until the
- shoring between these elements, hence transferring lagging is installed.
the soil loads to them. The lagging is installed in succes-
sive phases during the excavation process and often
includes a drainage system to prevent the build up of
water pressure.
The table below summarises the various types of discontinuous wall:
Name Vertical elements Shoring
Berlin-type wall Steel sections Wood, shotcrete or cast-in-situ concrete
Lutetian-type wall Bored piles Sprayed or formed concrete
Parisian-type walls Precast piles Sprayed or formed concrete
Moscow-type walls Barrettes (elements of diaphragm walls) Sprayed or formed concrete
15
You might also like
- BQS552 Earth Retaining StructureDocument93 pagesBQS552 Earth Retaining StructureShakir ZufayriNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls: Shivang Kumar BMCT-V A51204018005Document36 pagesRetaining Walls: Shivang Kumar BMCT-V A51204018005Shivang Kumar50% (2)
- Theoryofstructures 140306102151 Phpapp01Document57 pagesTheoryofstructures 140306102151 Phpapp01Uriel Alexander RamirezNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm WallDocument8 pagesDiaphragm Wall08DALVI PRASHANINo ratings yet
- BUILDING MATERIAL (Types of Walls) and Swimming Pool DetailDocument63 pagesBUILDING MATERIAL (Types of Walls) and Swimming Pool DetailTejas Joshi100% (1)
- Gravity CantileverDocument3 pagesGravity Cantileverfaroukm91No ratings yet
- Unit Retaining Walls: StructureDocument32 pagesUnit Retaining Walls: Structurebaduru muralikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Building TechnologyDocument29 pagesBuilding TechnologyJohn Louie100% (1)
- Types Quay WallDocument8 pagesTypes Quay WallSâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument3 pagesRetaining WallKarthick RNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE Magazine - Condition Assessment of Old Stone Retaining Walls PDFDocument8 pagesSTRUCTURE Magazine - Condition Assessment of Old Stone Retaining Walls PDFShabbir LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall (R1)Document68 pagesRetaining Wall (R1)Edmund Chui100% (1)
- Cour 7 AnglaisDocument2 pagesCour 7 Anglaismahedi abedNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentMizel PayaoNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Reader - NotesDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Reader - NotesmurtazaNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Edit 1Document39 pagesRetaining Wall Edit 1Yash ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument26 pages01 IntroductionJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- B III SEM 2. Foundations and BasementsDocument26 pagesB III SEM 2. Foundations and BasementsNishma GuragaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Earth Retaining Structures-13Document23 pagesChapter 8-Earth Retaining Structures-13Alexander AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallsDocument6 pagesRetaining WallsmikiNo ratings yet
- 13.0 Investigation & Evaluation of Claims Involving Retaining WallsDocument14 pages13.0 Investigation & Evaluation of Claims Involving Retaining WallsShabbir LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Exposé Mur de SoutenementDocument22 pagesExposé Mur de SoutenementJunior LNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls - Failure ModesDocument8 pagesRetaining Walls - Failure ModesAbukalam MullaNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls: A.B.C.MDocument23 pagesRetaining Walls: A.B.C.MAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Embedded Walls Finished)Document17 pagesEmbedded Walls Finished)Tun Sheikh HambaleeNo ratings yet
- 06 Retaining WallsDocument58 pages06 Retaining WallsGarima Mehta100% (1)
- Retaining Wall PDFDocument18 pagesRetaining Wall PDFG. M. BayazidNo ratings yet
- Diagonal CracksDocument18 pagesDiagonal CracksNaveen Kumar Nil100% (1)
- Retaining Wall TypeDocument7 pagesRetaining Wall Typeian100% (1)
- Foundation and Footing PDFDocument4 pagesFoundation and Footing PDFHANNAH KIMBERLY AREJOLANo ratings yet
- DPT1Document70 pagesDPT1jayawiadnyanaNo ratings yet
- Twana Akram Omar PDFDocument41 pagesTwana Akram Omar PDFDaniel BriñezNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument41 pagesRetaining WallAlnazer100% (1)
- HW Retaining WallDocument76 pagesHW Retaining Wallrutuja100% (1)
- Geotechnical Consultants For DA Approvals - Geotechnical Site Investigation, Geotechnical Design and Footing Inspections!Document1 pageGeotechnical Consultants For DA Approvals - Geotechnical Site Investigation, Geotechnical Design and Footing Inspections!kaung sanNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Types NewDocument33 pagesRetaining Wall Types NewIsbel100% (1)
- CFDocument11 pagesCFchristopherNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Retaining WallsDocument8 pagesUnit 7 Retaining WallsFaher Gaosel WatamamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Analysis and Design of Retaining WallsDocument21 pagesChapter 5-Analysis and Design of Retaining WallsBerhanu Zemecha Habte100% (1)
- Earthquake-Resistant Confined Masonry ConstructionDocument8 pagesEarthquake-Resistant Confined Masonry ConstructionVaish NaviNo ratings yet
- BCM-V U2 Part-B 19-07-2021Document55 pagesBCM-V U2 Part-B 19-07-2021hyperloop707 designNo ratings yet
- PG Tech Update Piled WallsDocument6 pagesPG Tech Update Piled Wallsparamarthasom1974No ratings yet
- Design of Retaining Wall: A Mini Project Report ONDocument40 pagesDesign of Retaining Wall: A Mini Project Report ONMohnika SamineniNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall: For Most Readers To Understand. Please HelpDocument7 pagesRetaining Wall: For Most Readers To Understand. Please HelpbaktinusantaraNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls: A.B.C.MDocument23 pagesRetaining Walls: A.B.C.MnilminaNo ratings yet
- PDF Basement Water Proofing by Ar Pranoti Lad - Compress PDFDocument35 pagesPDF Basement Water Proofing by Ar Pranoti Lad - Compress PDFDhritiNo ratings yet
- "Calzaduras": Universidad Privada Antenor Orrego Facultad de Ingeniería Escuela Profesional de Ingeniería CivilDocument14 pages"Calzaduras": Universidad Privada Antenor Orrego Facultad de Ingeniería Escuela Profesional de Ingeniería CivilJuan Manuel Silva LévanoNo ratings yet
- Retaing WallsDocument13 pagesRetaing Walls24x7civilconsultantNo ratings yet
- Describe The Importance of Raft and Mat FoundationDocument4 pagesDescribe The Importance of Raft and Mat FoundationIZni AZemiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Earth - Rentaining - StructuresDocument38 pagesChapter 8 - Earth - Rentaining - StructuresAlexander AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallsDocument12 pagesRetaining WallsSIZA THE POETNo ratings yet
- Structural Presentation2Document45 pagesStructural Presentation2Jherome ManuelNo ratings yet
- Lec 26Document18 pagesLec 26SagarNo ratings yet
- Desisignof Earth Retaining StructuresDocument3 pagesDesisignof Earth Retaining StructuresThotho KennedyNo ratings yet
- Deep ExcavationDocument34 pagesDeep ExcavationsafrasacmNo ratings yet
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Byzantine Fortifications: Protecting the Roman Empire in the EastFrom EverandByzantine Fortifications: Protecting the Roman Empire in the EastNo ratings yet
- The Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcFrom EverandThe Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 60Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 60jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 50Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 50JoeNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 56Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 56jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 55Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 55jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 51 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 51 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 49Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 49jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 52Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 52jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 52 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 52 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 41 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 41 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 42 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 42 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 45Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 45jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 48 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 48 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 45Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 45jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 46Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 46jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 42Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 42jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 41 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 41 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Construction of Concrete1Document1 pageConstruction of Concrete1jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 42Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 42jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 42 PDFDocument1 pageDiaphragm-Walls-And-Stractures 42 PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Concrete Gravity DamsDocument69 pagesDesign and Construction of Concrete Gravity Damshenybam83% (6)
- Maths PracticeDocument16 pagesMaths Practicesamisoma2011No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 41Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 41jaga67No ratings yet
- Dam Present PDFDocument16 pagesDam Present PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- Math Test One PDFDocument20 pagesMath Test One PDFjaga67No ratings yet
- READMEDocument1 pageREADMEjaga67No ratings yet
- Practice Book Math PDFDocument66 pagesPractice Book Math PDFNoureldinYosriNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths June 2015Document12 pagesIGCSE Maths June 2015annnlowNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument70 pagesReadmejaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 40Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 40jaga67No ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls and Stractures 37Document1 pageDiaphragm Walls and Stractures 37jaga67No ratings yet
- Labor Requirement For Various Construction WorksDocument4 pagesLabor Requirement For Various Construction WorksPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- The Eriophyidae Mites of California - Keifer 1952Document127 pagesThe Eriophyidae Mites of California - Keifer 1952Fátima ZeniNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Forestry Outlook 2020Document58 pagesIndonesian Forestry Outlook 2020Banjar Yulianto LabanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Bamboo and Bamboo BuildingDocument19 pagesIntro To Bamboo and Bamboo BuildingEvan Schoepke92% (13)
- QCS 2010 Section 18 Part 3 Structural TimberDocument5 pagesQCS 2010 Section 18 Part 3 Structural Timberbryanpastor106No ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Roofing Siding & TrimDocument272 pagesThe Complete Guide To Roofing Siding & TrimHao LinKinyao92% (13)
- Bahasa Inggris ArtikelDocument2 pagesBahasa Inggris ArtikelIngridNo ratings yet
- Ramos vs. Director of LANDS-Adverse Possession: IssueDocument1 pageRamos vs. Director of LANDS-Adverse Possession: IssueReyshanne Joy B MarquezNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 4: Información para Padres Plants: Plantas Important VocabularyDocument2 pagesScience Unit 4: Información para Padres Plants: Plantas Important Vocabularynefe_emeNo ratings yet
- EIADocument189 pagesEIARaja GuruNo ratings yet
- Wardha Valley 2016Document41 pagesWardha Valley 2016Pushpendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants in Manipur PDFDocument82 pagesMedicinal Plants in Manipur PDFbharat100% (3)
- Modern Gardens and The Landscape PDFDocument124 pagesModern Gardens and The Landscape PDFJairo Marin BarraganNo ratings yet
- Haunts and Hobbies of An Indian Official (1899) by Mark ThornhillDocument368 pagesHaunts and Hobbies of An Indian Official (1899) by Mark Thornhill30chr100% (1)
- Pub - Landscape Plants That Attract Birds Animals Pets PDFDocument12 pagesPub - Landscape Plants That Attract Birds Animals Pets PDFNiwut Lai100% (1)
- Zoning OrdinanceDocument55 pagesZoning OrdinanceErnan BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Paper TerminologyDocument5 pagesGlossary of Paper Terminologykarzol73No ratings yet
- Book of SeamanshipDocument665 pagesBook of SeamanshipRaresForest100% (4)
- Swedish English+VocabularyDocument18 pagesSwedish English+Vocabularyslazaroy1987No ratings yet
- Scanning and SkimmingDocument4 pagesScanning and SkimmingsteamboycardonaNo ratings yet
- Basic Roof Part 2 - Pages 47 To 80Document34 pagesBasic Roof Part 2 - Pages 47 To 80Eddis Armin PerezNo ratings yet
- Build 139 36 Design Right Free Standing Timber DecksDocument3 pagesBuild 139 36 Design Right Free Standing Timber Deckssuejack2020No ratings yet
- Techniques of BuddingDocument25 pagesTechniques of BuddingManuelNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Accreditation United Kingdom Accreditation ServiceDocument4 pagesSchedule of Accreditation United Kingdom Accreditation ServiceEmha AdamNo ratings yet
- Olive Oil ProductionDocument15 pagesOlive Oil ProductionSilviu GramaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document34 pagesChapter 2rcrisjell40% (5)
- E5 01A ThemeContentsDocument24 pagesE5 01A ThemeContentsmohammadNo ratings yet
- Tanga Tourism in TanzaniaDocument23 pagesTanga Tourism in TanzaniaKrishan KantNo ratings yet
- Rainforest Fact Sheet-MergedDocument3 pagesRainforest Fact Sheet-MergedRobert GloverNo ratings yet
- EnP 201-250Document11 pagesEnP 201-250Cedric Recato DyNo ratings yet