Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8.7.3. Applying Determinants
Uploaded by
chunkymonkey3230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pagecty jhu precalc determinants
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcty jhu precalc determinants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 page8.7.3. Applying Determinants
Uploaded by
chunkymonkey323cty jhu precalc determinants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
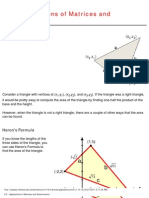
Applying Determinants
Determinants can be used to calculate areas of figures.
The area of a triangle equals one-half the value of a 3x3 determinant.
One application of matrices is finding the area of a triangle.
Compare the general statement for setting up the matrix with
the array for this example. Notice how the coordinates for
each vertex are placed in its own row with 1 being the term
in the third column on every row.
Remember your sign chart as you add your products. Then
use your process for evaluating the determinant of a matrix.
In this example, the arithmetic will be easy to do because
there are so many zeros.
In this case, the area will be:
{0[(1x1) (1x0)] 0[(0x1) (1x3)] + 1[(0x0) (1x3)]} =
(0 0 + 3) = (3).
Area is always positive, so use the absolute value.
The area of the triangle is (3) = 3/2.
This is an easy area to check because the triangle is half of
the rectangle that is 3 units long and 1 unit wide. Therefore,
the area of the triangle will be (3)(1) = 3/2. That matches
what you found using determinants.
Here is another example.
Once again, the coordinates are placed in the matrix.
The area of the triangle equals:
{1[(0x1) (1x1)] 1[(-1x1) (1x2)] + 1[(-1x1)
(0x2)]}. This expression simplifies as shown in the graphic.
It results in an area of 5/2.
www.thinkwell.com Thinkwell Corp. 1
You might also like
- Perturbation MethodDocument27 pagesPerturbation MethodBillyawanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CalculusDocument246 pagesFundamentals of CalculusIbtisam Elahi Jappa67% (3)
- FDM, Fem, FVMDocument32 pagesFDM, Fem, FVMRaj EaswarmoorthiNo ratings yet
- Linear Relations and Functions PracticeDocument1 pageLinear Relations and Functions PracticeCatalinaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- 1.6 Area ComputationDocument37 pages1.6 Area ComputationLiyana AmaniNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegralDocument64 pagesDefinite IntegralCynthania Luntayao50% (4)
- Pre-Algebra: Angela Milano 3 EditionDocument411 pagesPre-Algebra: Angela Milano 3 EditionFaist Name Last NameNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants for Area and CryptographyDocument10 pagesMatrices and Determinants for Area and CryptographyMuhammad Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Determinants Math 130 Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesDeterminants Math 130 Linear AlgebraCody SageNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Application of Integrals (Area)Document12 pagesModule 8 - Application of Integrals (Area)TOP ERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4..1Document19 pagesChapter 4..1Ed CasasNo ratings yet
- Demystified GMAT Quant CapsuleDocument14 pagesDemystified GMAT Quant CapsulePankaj DebnathNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Detection Using StatisticsDocument12 pagesClimate Change Detection Using StatisticsAracely SandovalNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Random Variables Lecture - 4: Descriptors of Random Variables (Contd.) Measure of SkewnessDocument8 pagesModule 3: Random Variables Lecture - 4: Descriptors of Random Variables (Contd.) Measure of SkewnessabimanaNo ratings yet
- The Cross Product and Geometry in The PlaneDocument1 pageThe Cross Product and Geometry in The PlaneSamNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelDocument729 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelHajveri Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Computation of The Risk FunctionDocument29 pagesComputation of The Risk FunctionKim MellNo ratings yet
- Interduction: Trapezoidal RuleDocument5 pagesInterduction: Trapezoidal RuleanandNo ratings yet
- Application of MatricesDocument10 pagesApplication of MatricesSamantha Priyadarshana MallawaNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument21 pagesLinear AlgebraMUSHTAQ AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesExperiment No. 1Hygeia Knoll Cloa BorjaNo ratings yet
- S Ccs AnswersDocument192 pagesS Ccs AnswersnoshinNo ratings yet
- Lagrange and Newton Interpolation Polynomial ApproximationDocument13 pagesLagrange and Newton Interpolation Polynomial ApproximationCoder DNo ratings yet
- Notes Math 9A: Module 1: Part 1Document5 pagesNotes Math 9A: Module 1: Part 1Clarence DeitaNo ratings yet
- Ch09-Areas and VolumesDocument36 pagesCh09-Areas and VolumesRizwan ullahNo ratings yet
- Computing Area Using IntegrationDocument11 pagesComputing Area Using IntegrationniggsNo ratings yet
- College of Information Engineering Systems Department Integration byDocument21 pagesCollege of Information Engineering Systems Department Integration byReverse OsmosisNo ratings yet
- Mantle Lab HandoutDocument12 pagesMantle Lab Handoutapi-574567198No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IDocument60 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IComical comicNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 KL SMK Desa Mahkota - MATHS QADocument9 pages2014 2 KL SMK Desa Mahkota - MATHS QASK100% (1)
- Chương Dãy Và Chu I. Bài 11Document23 pagesChương Dãy Và Chu I. Bài 11Hiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Fuzzification: by Considering Quantities As Uncertain: Imprecision Ambiguity VaguenessDocument60 pagesFuzzification: by Considering Quantities As Uncertain: Imprecision Ambiguity Vaguenesssun_barathi6149No ratings yet
- Reg. Name Year 6 ( ) No. DUNMAN HIGH SCHOOL, SENIOR HIGH PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2008 Mathematics Paper 1Document6 pagesReg. Name Year 6 ( ) No. DUNMAN HIGH SCHOOL, SENIOR HIGH PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2008 Mathematics Paper 109S43 ASHLEY CHUA YI HENGNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics: Basic Statistical ParametersDocument7 pagesData Analytics: Basic Statistical Parametersحسين رامي كريم A 12No ratings yet
- 9709 s10 QP 33Document4 pages9709 s10 QP 33roukaiya_peerkhanNo ratings yet
- Report About Applications of IntegralDocument9 pagesReport About Applications of IntegralAhmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Understanding Statistics and ProbabilityDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Statistics and ProbabilityFerly TaburadaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 One Dimensional Line Elements: Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 1: Natural CoordinatesDocument8 pages3.1.1 One Dimensional Line Elements: Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 1: Natural CoordinatesJaseel Hassan KNo ratings yet
- Circular Plates (Symmetrical Bending) : XY YZDocument5 pagesCircular Plates (Symmetrical Bending) : XY YZNewtonNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods On Finding The RootsDocument26 pagesNumerical Methods On Finding The RootsRobby Andre ChingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes PDFDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Notes PDFCharles GribbenNo ratings yet
- 9709 s13 QP 32Document4 pages9709 s13 QP 32Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- C1 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesC1 Revision Notesxxtrim100% (1)
- Math PaperDocument8 pagesMath PaperRushil MohabeerNo ratings yet
- Lec Week2 PDFDocument5 pagesLec Week2 PDFNavanNo ratings yet
- Pure Maths 2 9709 - s05 - QP - 2Document4 pagesPure Maths 2 9709 - s05 - QP - 2Nana_Banana_94No ratings yet
- Tensor PDFDocument25 pagesTensor PDFPero PericNo ratings yet
- Letcore MathDocument15 pagesLetcore MathAljon Tupas TevesNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary LevelDilan HarindraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document5 pagesChapter 18Dhynelle MuycoNo ratings yet
- Calculus Fundamentals at University of CordillerasDocument7 pagesCalculus Fundamentals at University of CordillerasGemma AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Sum of An Infinite Geometric Series: Student Activity Name ClassDocument5 pagesSum of An Infinite Geometric Series: Student Activity Name ClassJOSE MIGUEL CERVANTES SERRANONo ratings yet
- Computation of AreaDocument34 pagesComputation of AreaShamoyal KhanNo ratings yet
- Interval Notation Worksheet for TeachersDocument4 pagesInterval Notation Worksheet for TeachersmayjNo ratings yet
- Maximum Area of an Inscribed Rectangle in an EllipseDocument13 pagesMaximum Area of an Inscribed Rectangle in an EllipseRemalyn Villahermosa FajardoNo ratings yet
- Boundness of A Function Definition 1. 2 A Function Defined On Some Set X Is Called Bounded If There Suc H That For All inDocument27 pagesBoundness of A Function Definition 1. 2 A Function Defined On Some Set X Is Called Bounded If There Suc H That For All inUsmanSwiftNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Area & Volume: General Methods of Determining AreasDocument7 pagesCalculation of Area & Volume: General Methods of Determining AreasASIF CUETNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Mathematical Foundations: 1.1-Tensors and Continuum MechanicsDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Mathematical Foundations: 1.1-Tensors and Continuum MechanicsMat MatttNo ratings yet
- Geom SerjDocument3 pagesGeom SerjAyoubKhattabiNo ratings yet
- Non-Abelian Gauge Theories LectureDocument23 pagesNon-Abelian Gauge Theories Lecturecifarha venantNo ratings yet
- Applications of Taylor PolynomialsDocument4 pagesApplications of Taylor PolynomialsBanh Duc DungNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trig Functions ExamplesDocument4 pagesInverse Trig Functions ExamplesAbdirazak Mohamed Haaji OmarNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry HWDocument26 pages4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.3. Bonding II HWDocument27 pages3.3. Bonding II HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 6.2. Gases and Their Properties NotesDocument14 pages6.2. Gases and Their Properties Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry NotesDocument9 pages4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Transcript: Honors Chemistry Chemical Compounds: Bonding I: Scene 1Document12 pagesTranscript: Honors Chemistry Chemical Compounds: Bonding I: Scene 1chunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.1. Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pages4.1. Chemical Reactions Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.3. Reaction Rates NotesDocument15 pages4.3. Reaction Rates Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.1. Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pages4.1. Chemical Reactions Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 5.1. Solutions HWDocument28 pages5.1. Solutions HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.1. Chemical Reactions HWDocument23 pages4.1. Chemical Reactions HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry NotesDocument9 pages4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.2. Bonding HWDocument22 pages3.2. Bonding HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.3. Reaction Rates HWDocument29 pages4.3. Reaction Rates HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry HWDocument26 pages4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.4. Acids and Bases NotesDocument12 pages3.4. Acids and Bases Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.4. Acids and Bases HWDocument30 pages3.4. Acids and Bases HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends HWDocument29 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.3. Bonding II NotesDocument12 pages3.3. Bonding II Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Transcripts For "Lecture: Lists: An Unordered List and We're Going To Add The Tags Between The Tags andDocument3 pagesTranscripts For "Lecture: Lists: An Unordered List and We're Going To Add The Tags Between The Tags andchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.2. Electronic Structure HWDocument29 pages2.2. Electronic Structure HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.1. Naming Chemical Compounds HWDocument21 pages3.1. Naming Chemical Compounds HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 3.1. Naming Chemical Compounds NotesDocument9 pages3.1. Naming Chemical Compounds Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends NotesDocument12 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Transcripts For "Lecture: Lists: An Unordered List and We're Going To Add The Tags Between The Tags andDocument3 pagesTranscripts For "Lecture: Lists: An Unordered List and We're Going To Add The Tags Between The Tags andchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.2. Electronic Structure HWDocument29 pages2.2. Electronic Structure HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends HWDocument29 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Making Text Headers With GIMPDocument5 pagesMaking Text Headers With GIMPchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Unit 6: Multimedia Part IIDocument9 pagesUnit 6: Multimedia Part IIchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends NotesDocument12 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- 5.3. Solubility HWDocument32 pages5.3. Solubility HWchunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Costara - Exercises Functional AnalysisDocument461 pagesCostara - Exercises Functional AnalysisJefferson Prada MárquezNo ratings yet
- Solving Trigonometric Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesSolving Trigonometric Equations and InequalitiesAshmit RanjanNo ratings yet
- QB - Signal & SystemDocument17 pagesQB - Signal & Systemerdeep2020No ratings yet
- CS681 Computational Number Theory: BCH CodesDocument5 pagesCS681 Computational Number Theory: BCH CodesChinmayee PaiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths 4 SyllabusDocument3 pagesEngineering Maths 4 SyllabusRanjan NayakNo ratings yet
- DR. A.P.J.ABDUL KALAM TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-IDocument3 pagesDR. A.P.J.ABDUL KALAM TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-IPranjal JalanNo ratings yet
- Trajectory Planning in Cartesian Space: Robotics 1Document21 pagesTrajectory Planning in Cartesian Space: Robotics 1Krisandi AgustoNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main + Adv.) Division Daily Practice Problems - BASIC MATHEMATICSDocument10 pagesJEE (Main + Adv.) Division Daily Practice Problems - BASIC MATHEMATICSAvijeet kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Comsats University Islamabad: Signals & SystemsDocument10 pagesComsats University Islamabad: Signals & SystemsFarid MalikNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2Yoradel RempilloNo ratings yet
- 12 Basic Functions PDFDocument18 pages12 Basic Functions PDFHans TurimtijaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Computer GraphicsDocument80 pagesUNIT 2 Computer GraphicsManikantaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Maths Selina Solutions Chapter 2 Exponents PowersDocument17 pagesICSE Class 8 Maths Selina Solutions Chapter 2 Exponents Powersva877396No ratings yet
- Programme 19: Integration ApplicationsDocument19 pagesProgramme 19: Integration ApplicationsDavid Hoktua Siregar siregarNo ratings yet
- SurdsDocument30 pagesSurdsSchizophrenic RakibNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - Maths Formula Sheet For CsecDocument6 pagesQdoc - Tips - Maths Formula Sheet For CsecKayla CoxNo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas: Reciprocal IdentitiesDocument2 pagesIntegration Formulas: Reciprocal IdentitiesCassandra AyadNo ratings yet
- IB Math Methods Exam SolutionsDocument15 pagesIB Math Methods Exam SolutionsFadi AyyoubNo ratings yet
- CAPE Pure Mathematics 2012 P2Document7 pagesCAPE Pure Mathematics 2012 P2steve hopeNo ratings yet
- 9 4 Rotation and Systems of Quadratic EquationsDocument15 pages9 4 Rotation and Systems of Quadratic Equationsapi-317140261No ratings yet
- Calculus - Improper IntegralsDocument9 pagesCalculus - Improper IntegralsNapoleon Son PoloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Ayush Kumar100% (1)
- DETERMINANT TARGET FinalDocument4 pagesDETERMINANT TARGET FinalambikaNo ratings yet
- Kontsevich Lefschetz NotesDocument22 pagesKontsevich Lefschetz NotesHuong Cam ThuyNo ratings yet
- MHR PreCal 12 Textbook CH 1 SolutionsDocument57 pagesMHR PreCal 12 Textbook CH 1 SolutionsBryan LowNo ratings yet