Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FN 170 MDG Handout
Uploaded by
Clarice Mae DacasinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FN 170 MDG Handout
Uploaded by
Clarice Mae DacasinCopyright:
Available Formats
MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS (MDG)
2015 PROGRESS REPORT
The Millennium Development Goals, created by the United Nations, are a global effort in addressing poverty, especially in developing countries. These are goals that promote human rights
and that are meant to be attained within 15 years. So far, this has been the most successful movement to reduce poverty. This has also paved way for the creation of the Sustainable Development
Goals.
Objectives of the MDGs:
To address extreme poverty and its aspects and put a stop to them To address issues related to education, health, gender, the environment, etc.
To address the needs of the poorest in the world and to save them from the abject and To protect our planet
dehumanizing conditions of extreme poverty
Goal Target Indicators Sub-indicators Status
1. Eradicate Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the Proportion of population below national Decreasing (Moderate pace)
Extreme Poverty proportion of people whose income poverty threshold
and Hunger is less than $1.00 a day Poverty gap ratio Decreasing (High pace)
Share of poorest quintile in national Increasing
consumption
Achieve full and productive Growth rate of GDP per person employed Increasing
employment and decent work for all, Employment-to-population ratio Increasing
including women and young people Proportion of employed population living Increasing
below the national poverty threshold
Proportion of own-account and contributing Proportion of own-account (self-employed) Decreasing
family workers in total employment workers in total employment
Proportion of contributing (unpaid) family Decreasing
workers
Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the Prevalence of underweight children under Decreasing (Moderate pace)
proportion of people who suffer from 5 years of age using Child Growth
hunger Standards (CGS)
Percent of household with per capita Proportion of population with mean one-day Decreasing (Slow pace)
energy less than 100% adequacy energy intake less than 100% adequacy
Proportion of population below national Decreasing (High pace)
subsistence (food) threshold
12. Achieve Universal Ensure that, by 2015, children Net enrolment ratio in primary education Increasing
Primary Education everywhere, boys and girls alike, will Population of pupils starting grade 1 who Primary completion rate Increasing (Slow pace)
be able to complete a full course of reach grade 6 (Cohort Survival Rate)
primary schooling Literacy rate of 15 to 24 years old Ratio of literate females to males of 15-24-year- Rate: Increasing (Slow pace)
olds Ration: Constant (High pace)
15. Promote Gender Eliminate gender disparity in primary Ratio of girls to boys in primary education Ratio of girls to boys in elementary participation Primary: Decreasing (Slow
Equality and and secondary education preferably rates pace)
Empower Women by 2005 and to all levels of education Elementary: Constant (High
no later than 2015 pace)
Ratio of girls to boys in secondary Ratio of girls to boys in secondary participation Decreasing (High pace)
education rates
Ratio of girls to boys in tertiary education Decreasing (High pace)
Share of women in wage employment in Increasing (Slow pace)
the non-agricultural sector
Proportion of seats held by women in Increasing (Slow pace)
national parliament
20. Reduce Child Reduce by two-thirds, between 1990 Under-five mortality rate Decreasing (High pace)
Mortality and 2015, the under-five mortality Infant mortality rate Decreasing (High pace)
rate Proportion of 1-year-old children Increasing (Moderate pace)
immunized against measles
23. Improve Maternal Reduce by three-quarters, between Maternal mortality ratio Increasing (Slow pace)
Health 1990 and 2015, the maternal Proportion of births attended by skilled Increasing (Moderate pace)
mortality ratio health personnel
Achieve, by 2015, universal access Contraceptive prevalence rate Increasing (Slow pace)
to reproductive health Adolescent birth rate Increasing (Slow pace)
Antenatal care coverage Antenatal care coverage (at least one visit) Increasing
Antenatal care coverage (at least four visits) Increasing
Unmet need for family planning Decreasing
30. Combat Have halted by 2015 and begun to
HIV/AIDS, Malaria reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS
and Other Achieve, by 2010, universal access
Diseases to treatment for HIV/AIDS for all
those who need it
Have halted by 2015 and begun to Prevalence associated with malaria Decreasing (High pace)
reverse the incidence of malaria and Death rate associated with malaria Decreasing (High pace)
other major diseases Prevalence associated with tuberculosis Increasing (Slow pace)
Death rate associated with tuberculosis Decreasing (Slow pace)
Proportion of tuberculosis cases detected Increasing (High pace)
under directly observed treatment short
course (DOTS)
Proportion of tuberculosis cases cured Increasing (High pace)
under directly observed treatment short
course (DOTS)
38. Ensure Integrate the principles of Proportion of land area covered by forest Increasing
Environmental sustainable development into country Consumption of ozone-depleting CFCs Decreasing
Sustainability policies & programs to reverse the (ODP tons)
loss of environmental resources
Reduce biodiversity loss, achieving, Ratio of area protected to maintain Increasing
by 2010, a significant reduction in the biological diversity to surface area
rate of loss Number of species threatened with Increasing
extinction
Halve, by 2015, the proportion of Proportion of families with access to safe Increasing (High pace)
population without sustainable water supply
access to safe drinking water and Proportion of families with sanitary toilet Increasing (High pace)
improved sanitation facility
By 2020, have achieved significant Proportion of families with access to Decreasing
improvement in the lives of at least secure tenure
100 million slum dwellers
39. Develop a Global Develop further an open, rule-based,
Partnership for predictable, non-discriminatory
Development trading and financial system
Deal comprehensively with the debt Debt service as a percentage of exports of Decreasing
problems of developing countries goods and services
thru national & international
measures in order to make debt
sustainable in the long term
In cooperation with pharmaceutical
companies, provide access to
affordable essential drugs in
developing countries
In cooperation with the private Telephone lines subscribers per 100 Increasing
sector, make available the benefits of population
new technologies, especially Cellular phone subscribers per 100 Increasing
information and communications population
Progress Rate:
Low = less than 0.5 pace of progress
Moderate = 0.5 0.9 pace of progress
High = >0.9 pace of progress
REFERENCES:
National Statistical Coordination Board. (2015). MDGWatch. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from http://www.nscb.gov.ph/stats/mdg/mdg_watch.asp
United Nations Development Programme. (2015). The Millennium Development Goals Report 2015. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from
http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/librarypage/mdg/the-millennium-development-goals-report-2015.html
United Nations. (n.d.). Overview. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from http://www.un.org/en/sections/about-un/overview/index.html
United Nations. (n.d.). What We Do. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from http://www.un.org/en/sections/what-we-do/index.html
United Nations Development Programme. (n.d.). A New Sustainable Development Agenda. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from
http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sdgoverview.html
United Nations Development Programme. (n.d.). Millennium Development Goals. Retrieved 4 September 2016 from
http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sdgoverview/mdg_goals.html
You might also like
- Neuromuscular Disorder Characteristics Signs and Symptoms: NMJ DisordersDocument1 pageNeuromuscular Disorder Characteristics Signs and Symptoms: NMJ DisordersClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- FN 165 ShowcardsDocument9 pagesFN 165 ShowcardsClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- TEWS - Edelia - First EntryDocument51 pagesTEWS - Edelia - First EntryClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- VIROLOGYDocument3 pagesVIROLOGYClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Market SurveyDocument33 pagesMarket SurveyClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Nutriclinic FORM ADocument1 pageNutriclinic FORM AClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- COLORESSSSSDocument1 pageCOLORESSSSSClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- As CM Pre Clerkship HandbookDocument164 pagesAs CM Pre Clerkship HandbookClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Disorder Characteristics Signs and Symptoms: NMJ DisordersDocument1 pageNeuromuscular Disorder Characteristics Signs and Symptoms: NMJ DisordersClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Focus Group Discussion (Pregnant and Lactating Women) : Registration SheetDocument5 pagesFocus Group Discussion (Pregnant and Lactating Women) : Registration SheetClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- DV and ConversionDocument3 pagesDV and ConversionClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Market Forms PDFDocument39 pagesMarket Forms PDFClarice Mae Dacasin0% (2)
- Physics Note SpicsDocument1 pagePhysics Note SpicsClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Nutriclinic FORM BDocument3 pagesNutriclinic FORM BClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Price List Group 1 Food Item Price/Unit NotesDocument3 pagesLaboratory: Price List Group 1 Food Item Price/Unit NotesClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Exer8 Nutricalc TableDocument2 pagesExer8 Nutricalc TableClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Expt. #14 - ATQDocument1 pageExpt. #14 - ATQClarice Mae Dacasin100% (1)
- Diseases and disorders of the lymphatic, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systemsDocument1 pageDiseases and disorders of the lymphatic, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systemsClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Fil40 Manila PaperDocument1 pageFil40 Manila PaperClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Kotenbu Table of ContentsDocument4 pagesKotenbu Table of ContentsClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- A History of Composite Materials from Ancient TimesDocument2 pagesA History of Composite Materials from Ancient TimesClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- FN 11 Prelab 3Document2 pagesFN 11 Prelab 3Clarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Cultural Group - Script: Source: HTTP://WWW - Gly.Uga - Edu/Railsback/Cs/Csjapan - HTMLDocument1 pageCultural Group - Script: Source: HTTP://WWW - Gly.Uga - Edu/Railsback/Cs/Csjapan - HTMLClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
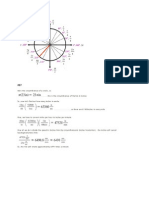
- Angle θ Values of the trigonometric functions in degrees in radians sin (θ) cos (θ) tan (θ) cot (θ) sec (θ) csc (θ)Document1 pageAngle θ Values of the trigonometric functions in degrees in radians sin (θ) cos (θ) tan (θ) cot (θ) sec (θ) csc (θ)Clarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- 87 Trig 3rdDocument1 page87 Trig 3rdClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Expt. #4 - RDRDocument7 pagesExpt. #4 - RDRClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Expt. #3 - FRDocument9 pagesExpt. #3 - FRClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Noli Me Tangere NotesDocument4 pagesNoli Me Tangere NotesClarice Mae Dacasin50% (4)
- Beowulf NotesyDocument1 pageBeowulf NotesyClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Modul English For Study SkillsDocument9 pagesModul English For Study SkillsRazan Nuhad Dzulfaqor razannuhad.2020No ratings yet
- Atlanta Pipes and FittingsDocument2 pagesAtlanta Pipes and Fittingsotadoyreychie31No ratings yet
- 1st ClassDocument18 pages1st Classchitl.23bi14075No ratings yet
- Eca Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesEca Important QuestionsSri KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Palo Alto Firewall VirtualizationDocument394 pagesPalo Alto Firewall VirtualizationRyanb378No ratings yet
- Lewis Carrol: Birth: DeathDocument21 pagesLewis Carrol: Birth: DeathmarialuvsjeffNo ratings yet
- Silyzer 300 - Next Generation PEM ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesSilyzer 300 - Next Generation PEM ElectrolysisSaul Villalba100% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentChristopher BellardNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Name: Bhupal Shrestha Address: Kamalamai Municipality-12, Sindhuli, Nepal. Email: ObjectiveDocument1 pageCurriculum Vitae: Name: Bhupal Shrestha Address: Kamalamai Municipality-12, Sindhuli, Nepal. Email: Objectivebhupal shresthaNo ratings yet
- Disk Electrostatic Automatic Coating System - OTSON - DM - OTS - 5000!3!0Document16 pagesDisk Electrostatic Automatic Coating System - OTSON - DM - OTS - 5000!3!0otsontek9227No ratings yet
- Hall Design For SpeechDocument1 pageHall Design For SpeechSarovar SaroNo ratings yet
- X TensoqaDocument2 pagesX TensoqaLeo CabelosNo ratings yet
- PremiumpaymentReceipt 10663358Document1 pagePremiumpaymentReceipt 10663358Kartheek ChandraNo ratings yet
- German BasicDocument60 pagesGerman BasicchahirNo ratings yet
- Austin's Cover Letter Example - Cultivated CultureDocument1 pageAustin's Cover Letter Example - Cultivated CultureYash SNo ratings yet
- Hempathane Topcoat 55219 Base 5521967280 En-UsDocument11 pagesHempathane Topcoat 55219 Base 5521967280 En-UsSantiago Rafael Galarza JacomeNo ratings yet
- Rules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveDocument12 pagesRules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveNd Reyes100% (2)
- Industrial/Organi Zational Psychology: Alday, Angeli Camille M. - 2P2Document51 pagesIndustrial/Organi Zational Psychology: Alday, Angeli Camille M. - 2P2SteffanyNo ratings yet
- Fixed Prosthodontics Provisional Materials: Making The Right Selection.Document7 pagesFixed Prosthodontics Provisional Materials: Making The Right Selection.veloso.rossana0% (1)
- Materials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneDocument10 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneVikrant Saumitra mm20d401No ratings yet
- 2017 Grade 9 Math Challenge OralsDocument3 pages2017 Grade 9 Math Challenge OralsGracy Mae PanganibanNo ratings yet
- CMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentDocument148 pagesCMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentZurab ChanturiaNo ratings yet
- Telecomm SwitchingDocument49 pagesTelecomm SwitchingTalha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Combined StressesDocument3 pagesMechanics of Materials: Combined StressesUmut Enes SürücüNo ratings yet
- Sequence TransformationDocument2 pagesSequence Transformationbrown222No ratings yet
- Openstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFDocument197 pagesOpenstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFBinank PatelNo ratings yet
- ATM ReportDocument16 pagesATM Reportsoftware8832100% (1)
- Rigor Mortis and Lividity in Estimating Time of DeathDocument2 pagesRigor Mortis and Lividity in Estimating Time of DeathfunnyrokstarNo ratings yet
- Purnanandalahari p3D4Document60 pagesPurnanandalahari p3D4anilkumar100% (1)