Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thalassemia Table
Uploaded by
Meevie ToledoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thalassemia Table
Uploaded by
Meevie ToledoCopyright:
Available Formats
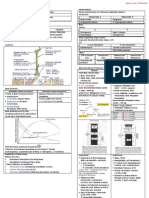
ALPHA THALASSEMIA
Barts Hydrops Fetalis Hb H Disease Hb H-Constant Spring Disease Thalassemia Minor The Silent Carrier
Infos Deletion of all four globin Deletion of three globin Consists of 2 normal Decrease in chain thalassemia
chains genes chains, 1 normal chain synthesis; maybe hetero or
and one abnormal chain homo but neither condition Associated with one gene
Observed in Southeast Widespread in Southeast that has 172 amino acids produces clinical disease deletion
Asians asia, Middle east and Benign
Mediterranean island Occurs in Orientals Common in Southereast
asia, Chinese and Filipinos Common in Asians, Chinese
Results from decreased and Filipinos
synthesis of chains and the Microcytosis in the
resultant formation of presence of normal Hb A
unstable Hb H () and Hb F (very suggestive of
thalassemia minor)
Clinical findings Underweight, edematous, Splenomegaly and anemia
st
demonstrate ascites tend to develop at 1 yr of life
(accumulation of serous fluid as well as mental
in the abdominal cavity), and retardation
disintended abdomens
Marked
hepatosplenomegaly
Laboratory findings Hypochromia Microcytic, hypochromic Microcytic and slightly Blood count is normal with
Variable reticulocytosis Detected microscopically hypochromic with slightly decreased MCV and
Nucleated red cell decreased MCV and MCH MCH
precursor Resemble golf ball (pitted
inclusions) & Hb H Target cells and other 1% to 2% Hb Barts but
inclusions occur in multiples poikilocytes are common normal in adults
Rare Hb H inclusions may
be found due to slight globin
imbalance
Tests Hb electrophoresis (alkaline Brilliant cresyl blue causes Hb CS migrates behind Hb A Modified BCB inclusion body
pH) shows fast-moving band the precipitation of Hb H in test enhances the
80% HbBarts& 20% Hb vitro Hemolysis should be precipitation of Hb H for it to
Portland and little or no Hb H applied to the electro support become more visible
(Both migrates faster than Hb electrophoresis (alkaline medium when Hb SC is
HbBarts) pH) shows 20-40% HbBarts suspected
then gradually replaced by
Hb H ()
Treatment Require no therapy; oxidant
drug should be avoided
TOLEDO, ML
BETA THALASSEMIA
Thalassemia Major Thalassemia Intermedia Thalassemia Minor Thalassemia Minima
Infos 4 genotypes Genes are less severely affected Asymptomatic No clinical or laboratory
0 : no globin chain production Impairment of -chain synthesis is less than the T. Little or no associated anemia abnormality detected
: decreased globin chain production major Peripheral blood erythrocyte: morphologically Usually discovered
1. 0/ 0 a. Homozygous + Thalassemia (+/ +) abnormal accidentally or during family
2. (/ (Mediterranean form) o Mild Black Form a. Heterozygous (/) or +( +/ ) studies
3. 0 / o American and African Blacks Thalassemia Genotype (SC/ ) indicated
4. ()Lepore/() Lepore (Hb Lepore) - 2 normal b. Homozygous Thalassemia (()/ ()) o Thalassemia trait or High-Hb A2 silent form (sc denotes silent
chains & 2 abnormal non- chains o American blacks, Arabs, Greeks, and Italians Thalassemia carrier) of an abnormal -
o Caused by the deletion of and structural o Caused by the combination of a normal globin gene
genes on the chromosome 11 pairs gene and either a or a + gene
c. Doubly Heterozygous Thalassemia Varieties b. Heterozygous Thalassemia ([] /)
o May be found in conjuction with , +, and Hb o Normal produced normal chains
Lepore o Deletion of the and genes on paired
chromosome 11
c. Heterozygous Hb Lepore ([] Lepore/ )
o One globin gene is normal
o Hb Lepore is produced from a second
fusion gene
Clinical findings Usually present with severe anemia w/in 1st year of life Growth and development of children: NORMAL Heterozygous Thalassemia: Hematocrit may be as
Excessive ineffective erythropoiesis bone marrow Adult: problems with iron overload low as 0.25 L/L during pregnancy
expansion marked skeletal deformities; distortion of ribs &
vertebrae; pathologic fractures of long bones
Protrusion of upper teeth & overbite dental & orthodontic
problems
Peripheral blood Hb: 2.5 6.5 g/dl Hemoglobin value: 7-10 g/dL (can be sustained so Increased erythrocyte count Electrophoresis, RBC
Numerous nucleated RBCs no need for routine transfusion) Marked decreased in MCV and MCH morphology and count, MCV
Microcytic& hypochromic Microcytic and hypochromic Normal or slightly decreased MCHC and MCH: NORMAL
Target cells & basophilic stippling Marked anisocytosis and poikilocytosis Microcytic and hypochromic, anisopoikilocytosis,
RPI: <3.0 Target cells are common target cells and basophilic stippling Slight decrease in -globin
Leucocytes: increased Peripheral blood film: basophilic stippling and Nucleated RBCs are ABSENT production that results in a
Platelet: normal nucleated RBCs Hb men: 12.9 g/dL; Women: 10.9 g/dL decrease / chain ratio
Reticuocyte counts is slightly elevated
Heterozygous Thalassemia: Hct women and
children: <0.31 L/L; Men: 0.37 L/L
Bone marrow Hypercellular Significant erythroid hyperplasia Slight erythroid hyperplasia
Marked erythroid hyperplasia
Special Hemoglobin Electrophoresis on Cellulose Acetate Hemoglobin electrophoresis at alkaline pH initial Special stains for erythrocyte inclusions are NEGATIVE
Hematologic Tests Acid elution technique for qualitative analysis of Hb F - screening procedure
helpful in differentiating thalassemia major disorders from
HPFH
Osmotic fragility test: markedly decreased
Chemistry Unconjugated bilirubin: mild elevation To differentiate microcytosis in Thalassemia minor
Urine urobilinogen & fecal urobilin: may be increased from IDA
Serum ferritin & iron: elevated
Transferrin often fully saturated (bec of iron overload
problem)
Treatment Blood transfusion Supportive; most patients have normal life span No treatment; Normal life span
Activation of globin gene expression
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation
Gene therapy
TOLEDO, ML
You might also like
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- January 11 January 25 February 6 February 22: Date SubjectsDocument3 pagesJanuary 11 January 25 February 6 February 22: Date SubjectsShams JailaniNo ratings yet
- Finals Trans (Hema)Document16 pagesFinals Trans (Hema)Ayesha CaragNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument2 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- Pedia - CNS Infection, Seizures, NMD (Agrava)Document30 pagesPedia - CNS Infection, Seizures, NMD (Agrava)Ivy Grace LimNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and NewbornDocument30 pagesHemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and Newbornkristine_camerinoNo ratings yet
- TRANS - Pediatric Patient ProblemsDocument4 pagesTRANS - Pediatric Patient ProblemsRencel Hope Bañez100% (1)
- Classification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical DiagnosisDocument25 pagesClassification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical Diagnosisayu rifqiNo ratings yet
- Pedia CardDocument4 pagesPedia CardPatricia Kate RegalaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsDocument9 pagesBronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsPGI Miayo, StephenNo ratings yet
- Neonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Document15 pagesNeonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Kurt ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Types of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesTypes of AnaemiaSuhaila NaemaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Pedia HandoutDocument2 pagesNotes For Pedia HandoutAiszel Angeli Pepito Ligo100% (2)
- IM Revalida Review 2019Document75 pagesIM Revalida Review 2019Nathaniel CamangonNo ratings yet
- GYNECOLOGY - 2.8 B&M Lesions of The OvariesDocument6 pagesGYNECOLOGY - 2.8 B&M Lesions of The OvariesAngela CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- Oncologic EmergenciesDocument3 pagesOncologic EmergenciesMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- PEDIA para 08AMDocument17 pagesPEDIA para 08AMpedia blue bookNo ratings yet
- Path Concept MapsDocument113 pagesPath Concept MapsAndleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: NeurologyDocument19 pagesCase Presentation: NeurologySydrex SarmientoNo ratings yet
- GI Diarrheal Micro ChartDocument3 pagesGI Diarrheal Micro ChartEvan MillerNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics:: History Taking and Physical Examination of AdolescentsDocument14 pagesPediatrics:: History Taking and Physical Examination of AdolescentsJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Clinpath - : Red Blood CellsDocument14 pagesClinpath - : Red Blood CellsYolanda Primrosa NurhanNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Supplement Pharmacology HandoutDocument1 pageTopnotch Supplement Pharmacology HandoutSanthosh RamasamyNo ratings yet
- 2023.LabDx - Trans02.Hemostasis and ThrombosisDocument4 pages2023.LabDx - Trans02.Hemostasis and ThrombosisstellaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension and Angina DrugsDocument158 pagesHypertension and Angina DrugsMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lectures 1 5 DR - TuyDocument10 pagesHematology Lectures 1 5 DR - TuyMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Philippine Adult Immunization Recommendation 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesPhilippine Adult Immunization Recommendation 2017 PDFLinius CruzNo ratings yet
- Pedia Bacte Table 08amDocument25 pagesPedia Bacte Table 08ampedia blue bookNo ratings yet
- Osce Cranial Nerves PDFDocument42 pagesOsce Cranial Nerves PDFriczen vilaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia 20-05-2020Document164 pagesThalassemia 20-05-2020Mohd Anas SheikhNo ratings yet
- Malassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinDocument48 pagesMalassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinNikki ValerioNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesClinical Case Tetralogy of FallotHedibertoAnzaNo ratings yet
- Pedia SummaryDocument10 pagesPedia SummaryBea GozaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplexDocument6 pagesPediatrics SamplexThea SansonNo ratings yet
- MED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinDocument5 pagesMED2 5.02 Oncologic Emergencies - Dr. F. AdefuinAra DiocosNo ratings yet
- 2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFDocument27 pages2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- History and PEDocument3 pagesHistory and PEBom TnaNo ratings yet
- 2016 CPG Ent PDFDocument21 pages2016 CPG Ent PDFCamelle CelisNo ratings yet
- BWH Hyperglycemia GuidelinesDocument7 pagesBWH Hyperglycemia Guidelinespmahesh107100% (1)
- Therapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDocument5 pagesTherapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDarnell DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Trans-Out Orders: NSVD Admitting Notes Postpartum OrdersDocument7 pagesTrans-Out Orders: NSVD Admitting Notes Postpartum OrdersDre ValdezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- MC NelsonsDocument31 pagesMC NelsonsNiñoTanNo ratings yet
- MHD Exam 5 MaterialDocument122 pagesMHD Exam 5 Materialnaexuis5467100% (1)
- Reviewer For Pedia Osce: 10.5 KG 45.16 CM / 17.8 in 75 CM SixDocument10 pagesReviewer For Pedia Osce: 10.5 KG 45.16 CM / 17.8 in 75 CM SixJamora ManilynNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesDocument9 pages5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesMaria roxanne HernandezNo ratings yet
- March 2022 Hybrid Full Course OFFICIAL Lecture Schedule - NOV-DEC UPLOADDocument3 pagesMarch 2022 Hybrid Full Course OFFICIAL Lecture Schedule - NOV-DEC UPLOADJhon PauloNo ratings yet
- Revalida Reviewer AsmphDocument237 pagesRevalida Reviewer AsmphShey ShocNo ratings yet
- Hematology SummaryDocument9 pagesHematology SummaryJovielle Hayden100% (1)
- JI RevalidaDocument61 pagesJI RevalidaAren LingadNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Surg TransDocument4 pagesPediatric Surg TransSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- CLINPATH Finals ReviewerDocument28 pagesCLINPATH Finals ReviewerVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2Document8 pagesPediatric Endocrinology Part 2: Pediatrics 2sarguss14No ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument51 pagesBlood ComponentsMandy A. Delfin100% (1)
- New Intern Guide Quick NotesDocument8 pagesNew Intern Guide Quick NotesTrisNo ratings yet
- Alpha ThalassemiaDocument4 pagesAlpha ThalassemiaNorman DamaaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableDocument3 pagesHematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableMeevie Toledo0% (1)
- HEMA PracticalDocument14 pagesHEMA PracticalNanik AndianiNo ratings yet
- Virology: EnterovirusesDocument40 pagesVirology: EnterovirusesMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableDocument3 pagesHematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableMeevie Toledo0% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry: NPNsDocument1 pageClinical Chemistry: NPNsMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Mycobacteria To Spirochetes SummaryDocument8 pagesMycobacteria To Spirochetes SummaryMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Community and Public Health PortfolioDocument90 pagesCommunity and Public Health PortfolioMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Coagulation DisordersDocument42 pagesHemorrhagic Coagulation DisordersGirum TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Blood Lymphatic and Immune System TerminologyDocument3 pagesBlood Lymphatic and Immune System TerminologySoniyaJI84No ratings yet
- Case 1Document11 pagesCase 1Kent MaravillosaNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Typing StudentDocument21 pages1 Blood Typing Studentapi-217623200No ratings yet
- Radiatus) Terhadap Peningkatan Kadar ProfilDocument10 pagesRadiatus) Terhadap Peningkatan Kadar ProfilDhilaNo ratings yet
- LP 10 Anemia 3Document43 pagesLP 10 Anemia 3Anonymous elq7jZiSNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Case SampleDocument7 pagesBleeding Case SampleNikko CabrestanteNo ratings yet
- USMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyDocument21 pagesUSMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyMatt McGlothlinNo ratings yet
- Lab HemostasisDocument29 pagesLab HemostasisTingLi Lucia Lorigiano100% (2)
- LabReports 1Document1 pageLabReports 1Ishpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument19 pagesInternship ReportumaihaNo ratings yet
- Haemtology QuestionDocument5 pagesHaemtology QuestionKumar KP100% (1)
- Rapid Review Hematology PDFDocument155 pagesRapid Review Hematology PDFBaguma Michael100% (3)
- Blood TypingDocument8 pagesBlood TypingAbby Umali-HernandezNo ratings yet
- Жинхэнэ полицитемиDocument14 pagesЖинхэнэ полицитемиАминаа ТавинбэхNo ratings yet
- Severity Anemia Pregnancy Adverse Maternal Fetal Outcomes Tertiary CareDocument8 pagesSeverity Anemia Pregnancy Adverse Maternal Fetal Outcomes Tertiary CareSSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Sunshine Hospitals: Department of PathologyDocument2 pagesSunshine Hospitals: Department of PathologyVarun reddyNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion LectureDocument8 pagesBlood Transfusion LectureCamille Cirineo Arensol100% (2)
- 10 1016@j Blre 2019 100638 PDFDocument40 pages10 1016@j Blre 2019 100638 PDFHugo HectorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Examination of The Peripheral Blood Film and Correlation With The Complete Blood CountDocument7 pagesChapter 15 - Examination of The Peripheral Blood Film and Correlation With The Complete Blood CountNathaniel SimNo ratings yet
- Capacity of Hospita101 2Document45 pagesCapacity of Hospita101 2kneou dojolesNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis Universi T Y - Hospital of The Sacred Heart Department of Pediat RicsDocument2 pagesSaint Louis Universi T Y - Hospital of The Sacred Heart Department of Pediat RicsKrystel Jaravata BatinoNo ratings yet
- Clinicalresearchfocus: The Research QuestionDocument4 pagesClinicalresearchfocus: The Research QuestionNiputu CintyadewiNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Resource Handbook 2018 PDFDocument30 pagesTransfusion Resource Handbook 2018 PDFPratama PuteraNo ratings yet
- Hematologic ManagementDocument17 pagesHematologic ManagementAlyssa MontimorNo ratings yet
- Study Questions BASIC AND APPLIDE Chapetr 1Document134 pagesStudy Questions BASIC AND APPLIDE Chapetr 1Anas AlkhateebNo ratings yet
- Drug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsDocument4 pagesDrug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsYusoff RamdzanNo ratings yet
- HBDocument4 pagesHBDattatreyaNo ratings yet
- Neo ThrombocytopeniaDocument10 pagesNeo ThrombocytopeniaOleOhhNo ratings yet