Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flow in Pipes and Channels - Solved Examples
Uploaded by
Engr Ghulam MustafaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flow in Pipes and Channels - Solved Examples
Uploaded by
Engr Ghulam MustafaCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr. P.P.
Paily Flow in Pipes and Open Channels with
CVEN 3100: Fluid Mechanics Head Loss_Solved Examples
1. A laminar flow of SAE 30 oil at 20oC occurs in a 6 cm-diameter pipe inclined
at 40o to the horizontal. The pressure at the lower end is 350 kPa and it
decreases to 250 kPa over a 10 m length of pipe. Determine the flow rate in
the pipe and the direction of flow. Verify that the flow is laminar.
Given:
SAE 30 oil at 20 oC: laminar flow
To Find:
(1) Q
(2) direction of flow
(3) R ( if R 2100, flow is laminar)
Theory:
(1) Q = A V = (/4) d2 V
(2) Q1 = Q2 V1 = V2 = V
(3) for flow from 1 to 2: [ (p1/) + (V12/2g) + Z1 ] hL = [ (p2/) + (V22/2g) + Z2 ]
(4) hL = f (L/d) (V2/2g)
(5) for laminar flow, f = (64 / R)
(6) R = ( V d) /
Constant: for SAE 30 oil at 20 oC: = 912 kg/m3; = 8950 N/m3 (table 1.6)
= 0.17 N-s/m2 (figure B1)
Solution:
350 x1000 V 2 250 x1000 V 2
(2,3) [ + + 0 ] hL = [ + + (10 sin 40) hL = 4.745 m
8950 2g 8950 2g
since hL is positive, flow is from lower end to upper end.
(6) R = (912)(V)(0.06) / (0.17) = 321.9 V
(4,5) 4.745 = [ 64 / (321.9 V) ] (10 / 0.06) [V2 / (2x9.81) ] V = 2.809 m/s
(6) R = (321.9) (2.809) = 904.2 < 2100, the flow is laminar
(1) Q = (/4) (0.06)2 (2.809) = 7.101x10-3 m3/s
2. A fluid flows through a 10-mm diameter tube at a Reynolds number of 1800. If
the flow rate is 6.0 liters/min, what is the head loss in 100 m length of tubing ?
Given:
d = 10 mm
R = 1800
Q = 6.0 L/min
L = 100 m
To find:
(1) hL
Theory:
(1) hL = f (L/d) (V2/2g)
(2) f = 64 / R, since flow is laminar ( R < 2100)
(3) Q = A V = (/4) d2 V
Conversion: 1000 L = 1 m3
Solution:
(3) 6.0 / (1000 x 60) = (/4) (0.010)2 V V = 1.273 m/s
(2) f = 64 / 1800 = 0.0356
(1) hL = (0.0356) (100 / 0.010) [ (1.2732 / (2 x 9.81) ] = 29.40 m
3. Water at 20oC flows through a new cast iron pipe of 150 mm diameter at a
velocity of 2 m/s. What is the power loss over a 400 m length of pipe ?
Given:
Water at 20 C in cast iron pipe
d = 150 mm
V = 2 m/s
L = 400 m
To find:
(1) power loss, P
Theory:
(1) P = Q hL
(2) Q = A V = (/4) d2 V
(3) hL = f (L/d) (V2/2g)
(4) for turbulent flow, f = f ( R, e/d) read ( f ) from Moody chart
(5) R = ( V d) /
Constant: for water at 20 oC: = 998.2 kg/m3; = 9789 N/m3 ;
= 1.002 x 10-3 N-s/m2 (table B2)
for cast iron, e = 0.26 mm (table)
Solution:
(5) R = (998.2) (2) (0.150) / (1.002 x 10-3) = 2.989 x 105 3.0 x 105
(4) e/d = 0.26 /150 = 0.001733
for R = 3.0 x 105 and e/d = 0.001733, read from Moody chart: f = 0.023
(3) hL = (0.023) (400/0.150) [ (2)2 /(2 x 9.81) ] = 12.50 m
(2) Q = (/4) (0.150)2 (2) = 03534 m3/s
(1) P = (9789) (03534) (12.50) = 4334 W
4. A flow rate of 2.2 m3/s is to be carried in a rectangular open channel at a
velocity of 1.3 m/s. If Mannings n = 0.020, and the depth of flow is one-half
the channel width, what is the slope of the channel bed ?
Given:
rectangular channel : y = b/2
Q = 2.2 m3/s
V = 1.3 m/s
n = 0.020
To find:
(1) channel bed slope, S
Theory:
n2 L 1
(1) hL = L S = 2 4/3
V2 k = 1.0 for m units
k Rh
(2) Rh = A / P = (b y) / (b + 2y) = (2 y2) / (4y) = y/2
(3) Q = A V = (2 y2) V
Solution:
(3) 2.2 = (2 y2) (1.3) y = 0.9199 m
(2) Rh = 0.9199 / 2 = 0.46 m
(1) S = [ (0.020)2 / (1)2 ] [1 / (0.46)4/3] (1.3)2 = 0.001904
5. A 2.0-m diameter semicircular channel carrying water has a bed slope of
0.0016. If Mannings n = 0.020, what is the discharge ?
Given:
semicircular channel
d = 2.0 m
S = 0.0016
n = 0.020
To find:
(1) Q
Theory:
(1) Q = A V = (/8) d2 V
n2 L 1 k
(2) hL = L S = 2 4/3
V 2 V = Rh3/2 S ; k = 1.0 for m units
k Rh n
2
(3) Rh = A / P = (/8) d / ( d/2) = d / 4
Solution:
(3,2) V = (1.0 / 0.020) (2.0 / 4)2/3 (0.0016) = 1.260 m/s
(1) Q = (/8) (2)2 (1.260) = 1.979 m3/s
6. Water at the rate of 11.66 m3/s flows in a finished concrete pipe so that it is
completely full and the pressure is constant at atmospheric pressure all along
the pipe. If the pipe slope is 0.005 what is the diameter ?
Given:
finished concrete pipe (with channel flow since pressure is atmospheric)
Q = 11.66 m3/s
S = 0.005
To find:
(1) d
Theory:
(1) Q = A V = (/4) d2 V
n2 L 1 k
(2) hL = L S = 2 4/3
V 2 V = Rh3/2 S ; k = 1.0 for m units
k Rh n
2
(3) Rh = A / P = (/4) d / ( d) = d / 4
Constant: for finished concrete, n = 0.012 (table)
Solution:
(1,2,3) 11.66 = (/4) d2 [(1.0) / (0.012) ] (d/4)2/3 (0.005)
d8/3 = 6.349 d = 2.0 m
You might also like
- Hydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsDocument42 pagesHydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsAsun RajaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 - Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesSheet 1 - Introduction To Fluid MechanicsMugiwara SparrowNo ratings yet
- Tshoga Lo PDFDocument11 pagesTshoga Lo PDFlehlabileNo ratings yet
- What Is Vena Contracta - How Vena Contracta Formed in Fluid Flow - Mecholic PDFDocument3 pagesWhat Is Vena Contracta - How Vena Contracta Formed in Fluid Flow - Mecholic PDFAmrut Raj PurohitNo ratings yet
- Prismoidal Formula 2Document11 pagesPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaNo ratings yet
- 5 6334648768108954434Document643 pages5 6334648768108954434Sanika TalathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document31 pagesChapter 6Camille LardizabalNo ratings yet
- Fox 7th ISM ch07-13Document1,079 pagesFox 7th ISM ch07-13Ismar GarbazzaNo ratings yet
- p γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Document4 pagesp γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- Area ConjugadaDocument30 pagesArea ConjugadaMiguel Delgadillo SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Homework 4Document7 pagesHomework 4Seifeldin Ali Marzouk100% (1)
- Chapter-7 Shear DesignDocument14 pagesChapter-7 Shear DesignAngelo RosNo ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesMariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringLyka Jane Tapia OpeñaNo ratings yet
- Problem 880 Moment Distribution MethodDocument2 pagesProblem 880 Moment Distribution MethodVirtual WizardNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFDocument32 pagesExam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFS. GreenNo ratings yet
- TG-Op1 Enunciados v01Document53 pagesTG-Op1 Enunciados v01VlmScarletQcaritaNo ratings yet
- Day 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Document51 pagesDay 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Free student100% (1)
- Drylab 3Document5 pagesDrylab 3Jejemon AntenorNo ratings yet
- DLSUD Soil Mechanics Lab ManualDocument49 pagesDLSUD Soil Mechanics Lab ManualblehNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #3 #ProblemsDocument5 pagesTutorial #3 #ProblemsAisha AbuzgaiaNo ratings yet
- V Notch WeirDocument14 pagesV Notch WeirPaul Ivan Asencio CasumpangNo ratings yet
- ENSC 3233 HW #1 Solution PDFDocument10 pagesENSC 3233 HW #1 Solution PDFheem bashaNo ratings yet
- Tarea Unidad 5 - Flujo Variado - MARIANA FLORES LIZANODocument67 pagesTarea Unidad 5 - Flujo Variado - MARIANA FLORES LIZANOMariana FloresNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Pipes (With Pipe Network)Document68 pagesFlow Through Pipes (With Pipe Network)annashiyoNo ratings yet
- 12.57-The Dragster Starts From Rest and Travels Along A Straight Track With AnDocument6 pages12.57-The Dragster Starts From Rest and Travels Along A Straight Track With AnCristhian Edward Torres LoayzaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Andrew0% (1)
- Pplication of The Bernoulli Equation: Go Back To The Main Index PageDocument11 pagesPplication of The Bernoulli Equation: Go Back To The Main Index Page123habib123fikri100% (1)
- Geas IecepDocument32 pagesGeas IecepJenn BantilingNo ratings yet
- Ceng 231 Tutor 1Document11 pagesCeng 231 Tutor 1lawekushNo ratings yet
- CIEM5390 Problem Set 2 - SolutionDocument10 pagesCIEM5390 Problem Set 2 - SolutionMatthew LiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Document3 pagesModule 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- Ce 371 Homework 4 1) A Plug in The Bottom of A Pressurized TankDocument4 pagesCe 371 Homework 4 1) A Plug in The Bottom of A Pressurized TankSubhash KorumilliNo ratings yet
- War 2103 PrecipitationDocument52 pagesWar 2103 PrecipitationEgana IsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document21 pagesChapter 6Shida ShidotNo ratings yet
- Orifice, Nozzle and Venturi Flow Rate Meters: Water & Air FlowmetersDocument4 pagesOrifice, Nozzle and Venturi Flow Rate Meters: Water & Air Flowmeterssiva_nagesh_2No ratings yet
- Fluid Mech PaperDocument23 pagesFluid Mech Papertech2lifeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - BMCF 2223 - BuoyancyDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 - BMCF 2223 - BuoyancySekut TawarNo ratings yet
- CE365 Hydro, HW 1 SolutionDocument6 pagesCE365 Hydro, HW 1 SolutionbrayanNo ratings yet
- PRELIM EXAM - Docx QuestionnaireDocument1 pagePRELIM EXAM - Docx QuestionnaireLian HebronNo ratings yet
- 02 03ChapGereDocument16 pages02 03ChapGereXavier Pacheco PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Hydro HyrdoDocument16 pagesHydro HyrdoCherie Gold AccuhNo ratings yet
- Statics AnDocument13 pagesStatics AnIsaac Davy100% (1)
- Chap 2pdf 3 PDF FreeDocument23 pagesChap 2pdf 3 PDF FreeMarwa OmarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Elements of The Simple Circular CurvesDocument6 pages1.2 Elements of The Simple Circular CurvesJitendra BarandaNo ratings yet
- Irrigation EngineeringDocument18 pagesIrrigation EngineeringUmar NaveedNo ratings yet
- Problem 03 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesProblem 03 - Bernoulli's Energy Theorem - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problem 4 Heat TransferDocument3 pagesExercises Problem 4 Heat TransferMeeko TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document31 pagesChapter 5Sohail SakhaniNo ratings yet
- CE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020Document50 pagesCE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020SalmanNo ratings yet
- Numerical My BookDocument47 pagesNumerical My BookKiran Ghimire100% (1)
- Vertical Curves SWDocument1 pageVertical Curves SWvafdeleonNo ratings yet
- Refriger Ac I OnDocument15 pagesRefriger Ac I OnMiguel Angel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument6 pagesMachine DesignRen RenNo ratings yet
- EngineeringMechanics IBDocument157 pagesEngineeringMechanics IBGiovanni Gallardo MoranteNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument1 pageFluidsMary Joy Delgado33% (3)
- Chapter 9 Flow in Closed ConduitsDocument61 pagesChapter 9 Flow in Closed ConduitsNader Alaa56% (18)
- Sample Problems Dec 05 2022Document30 pagesSample Problems Dec 05 2022JoYhCo OrPaPr100% (1)
- 1 85 Fluid MechDocument61 pages1 85 Fluid MechTomas Otero IIINo ratings yet
- 02 Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument14 pages02 Stoichiometric CalculationsDhavanLalNo ratings yet
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Report 122Document2 pagesReport 122Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- EXAM-4 (Final) ENVE 4410-5510 - F17 Equation SheetDocument6 pagesEXAM-4 (Final) ENVE 4410-5510 - F17 Equation SheetEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ayub ConstructionDocument1 pageAyub ConstructionEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- MS Al SiddiqueDocument1 pageMS Al SiddiqueEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ayub ConstructionDocument1 pageAyub ConstructionEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ayub ConstructionDocument1 pageAyub ConstructionEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Rakh Bhango ComplaintDocument1 pageRakh Bhango ComplaintEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Assistant Engineer 136 G 2018Document3 pagesAssistant Engineer 136 G 2018Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Interview 1Document2 pagesInterview 1Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Release LetterDocument1 pageRelease LetterEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.: P Is The Force Acting On A Body Whose Mass Is M and Acceleration Is F. The Equation P - MFDocument3 pagesA. B. C. D.: P Is The Force Acting On A Body Whose Mass Is M and Acceleration Is F. The Equation P - MFEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Rub-Nawaz S/o Pathana: Supervisor (Civil)Document2 pagesRub-Nawaz S/o Pathana: Supervisor (Civil)Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Payment CertificateDocument1 pagePayment CertificateEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Referencing at Least Two Chapters of The Main Text in This Class in Your Response To Each QuestionDocument1 pageInstructions: Referencing at Least Two Chapters of The Main Text in This Class in Your Response To Each QuestionEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Fin 330Document3 pagesFin 330Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.: P Is The Force Acting On A Body Whose Mass Is M and Acceleration Is F. The Equation P - MFDocument3 pagesA. B. C. D.: P Is The Force Acting On A Body Whose Mass Is M and Acceleration Is F. The Equation P - MFEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Sentence FormationDocument5 pagesSentence FormationEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Input DataDocument2 pagesInput DataEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Summer I I 2017Document5 pagesSyllabus Summer I I 2017Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Input DataDocument2 pagesInput DataEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- See ProblemDocument1 pageSee ProblemEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Friction Factor CalculationsDocument11 pagesPipe Flow Friction Factor CalculationsVictor ValenciaNo ratings yet
- AssgnDocument1 pageAssgnEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- RailwaysDocument14 pagesRailwaysEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- GAT1Document17 pagesGAT1Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1Engr Ghulam Mustafa100% (1)
- 4 2017 02 20!11 27 46 PMDocument36 pages4 2017 02 20!11 27 46 PMEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ex20 1Document3 pagesEx20 1barlosNo ratings yet
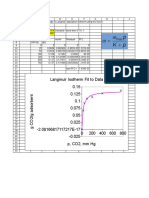
- Notes On Adsorption (Johnston) : KC C M X K M XDocument4 pagesNotes On Adsorption (Johnston) : KC C M X K M XBinyam KebedeNo ratings yet
- Input Data: Material PropertiesDocument2 pagesInput Data: Material PropertiesEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Reynold NumberDocument5 pagesReynold NumberFita Desti SenjaNo ratings yet
- Assign-5 - FM-II - Fall - 2019 - Turbomachinery - Pump Performance CurvesDocument2 pagesAssign-5 - FM-II - Fall - 2019 - Turbomachinery - Pump Performance CurvesJugnoo JNo ratings yet
- Vit SystemDocument10 pagesVit SystemVijeeshNo ratings yet
- FRANKLIN ELECTRIC Convertible - Jet - Manual - 06-16-FinalDocument32 pagesFRANKLIN ELECTRIC Convertible - Jet - Manual - 06-16-FinalRomankoNo ratings yet
- 12s1ry 12s1gy 12s1gy 12R 12s1gy 12RDocument11 pages12s1ry 12s1gy 12s1gy 12R 12s1gy 12RJohn Fredy Simancas FierroNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Main Control Valve (Type 1) : 1. StructureDocument60 pagesGroup 2 Main Control Valve (Type 1) : 1. Structurejulio cesarNo ratings yet
- Danfoss Hand Book - DKBDPS000A502Document99 pagesDanfoss Hand Book - DKBDPS000A502durimuk100% (1)
- Training - Flowserve Apm Pump CW Pump Part 2Document12 pagesTraining - Flowserve Apm Pump CW Pump Part 2hasan099No ratings yet
- Wet Well Pumping Station Design GuideDocument61 pagesWet Well Pumping Station Design Guideawhk2006100% (3)
- TDP 623B - Water Cooled - Chillers Omar Rojas PDFDocument106 pagesTDP 623B - Water Cooled - Chillers Omar Rojas PDFSNM100% (2)
- 345C PJW Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pages345C PJW Hydraulic SystemDANIEL VARGAS RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- 35-TCV-005 & 35-TCV-006 Control Valve Sizing Project - Pembangunan 2 Tangki Black Product Control Valve - Gas, Steam or Vapor FlowDocument1 page35-TCV-005 & 35-TCV-006 Control Valve Sizing Project - Pembangunan 2 Tangki Black Product Control Valve - Gas, Steam or Vapor FlowFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Diconelci 2020 PDFDocument22 pagesCatalogo Diconelci 2020 PDFnatalia-319206No ratings yet
- Hazop Worksheet Hazard Identification Study WorkDocument2 pagesHazop Worksheet Hazard Identification Study Workssat111No ratings yet
- NACA Airfoils Post Stall PDFDocument23 pagesNACA Airfoils Post Stall PDFEmilio BernyNo ratings yet
- Yukenmodularvalves Yuken CatDocument140 pagesYukenmodularvalves Yuken Catchidambaram kasi100% (1)
- Water Supply Network ArrangementDocument14 pagesWater Supply Network ArrangementHari RNo ratings yet
- CST-1 Design HistoryDocument2 pagesCST-1 Design HistoryJefferson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Osborne Reynolds DemonstrationDocument6 pagesOsborne Reynolds DemonstrationAzizul Hakim100% (1)
- Series G4000 Specification SheetDocument2 pagesSeries G4000 Specification SheetWattsNo ratings yet
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures LTDDocument2 pagesMegha Engineering & Infrastructures LTDrameshNo ratings yet
- Манипулятор распределитель D77005-en PDFDocument42 pagesМанипулятор распределитель D77005-en PDFИгорь ТерещенкоNo ratings yet
- Steam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles and TurbinesDocument39 pagesSteam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles and TurbinesVinay AnkolekarNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument7 pagesAir CompressorYemaneDibetaNo ratings yet
- S08 Diesel Power Pack PDFDocument166 pagesS08 Diesel Power Pack PDFIH MedranoNo ratings yet
- The Friction Factor It Is Denoted by F and Defined As The Ratio of The Wall Shear Stress To The Product of The Velocity Head (VDocument2 pagesThe Friction Factor It Is Denoted by F and Defined As The Ratio of The Wall Shear Stress To The Product of The Velocity Head (VJHuvieCLaireNo ratings yet
- Compresor Sullair 7500 en WordDocument164 pagesCompresor Sullair 7500 en WordPedro Huaman Lopez75% (8)
- Energy RatioDocument2 pagesEnergy RatioVinay MPNo ratings yet
- DimplesDocument20 pagesDimplesrajuNo ratings yet
- RTBNDocument1 pageRTBNAjay PrajapatiNo ratings yet