Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cooling Water Control
Uploaded by
ivanrhs0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesCOOLING WATER CONTROL
Original Title
COOLING WATER CONTROL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCOOLING WATER CONTROL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesCooling Water Control
Uploaded by
ivanrhsCOOLING WATER CONTROL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Application Data Sheet
ADS 43-006/rev.B
August 2004
Theory
COOLING WATER CONTROL
BACKGROUND For cooling water containing a high level of suspend-
ed solids, a toroidal conductivity sensor such as the
The chemical process industry, petroleum refining, Model 228 and a fouling-resistant pH sensor such as
utilities, and many other industries, use large quanti- Model 396P are recommended.
ties of water for cooling.
Corrosion and scaling are further minimized by the
There is an increased emphasis being placed upon addition of chemical scale and corrosion inhibitors.
the re-use of cooling water by means of cooling tow- Inhibitors are fed based upon one of three methods: on
ers. The cooling effect is obtained by the evaporation acid demand, on opening the blow down valve, and on
of a small fraction of water and heat exchange with operating the make-up water valve. Inhibitors are fed
the air passing through the cooling tower. The prob- on acid demand when the acid pump runs and/or when
lems encountered in cooling systems are not usually the inhibitor pump runs. On opening the blow down
with the equipment, but with the water. As the water valve, the inhibitor pump adds the inhibitor to another
evaporates, the dissolved solids concentrate. These part of the system and precisely balances the loss of
impurities in water cause scale and corrosion in the inhibitor by blowdown.
heat exchange equipment.
The warm water and air also produce an ideal environ-
ment for biological growth. To control algae and slime
PROCESS growth, biocides (i.e., chlorine or bromine) are added
on a time basis, such as a given quantity once per day,
There are many variations in cooling towers and heat
twice per week, once per week, or by one of the above
exchange design. A common feature is the control of
methods. Chlorine levels can be monitored using the
the water quality with the use of continuous pH and
chlorine sensor Model 499ACL.
conductivity measurement while maintaining a given
set of conditions. This is done to further minimize cor- Dispersants are added to prevent coagulation or floc-
rosion and protect the equipment. Continuous recir- culation of suspended solids (dust, living microorgan-
culation of the cooling water causes the concentra- isms, dead cells, etc.). Dispersants are added in the
tion of the impurities to increase. The relative concen- same manner as inhibitors.
tration of the impurities in the water is measured by a Ozone treatment is a powerful alternative to chemical
contacting conductivity sensor, such as a Model 400 treatment and will reduce operating costs significantly
sensor. A conductivity controller initiates the opening while increasing safety. Unlike most chemicals, ozone
of a blowdown valve when the conductivity becomes has a half-life of only 20 minutes and will not be found
too high. This causes a demand for make-up water, in blow down water. The dissolved ozone sensor
which is less concentrated in impurities, and thus Model 499AOZ is intended for continuous measure-
lowers the conductivity. ment of dissolved ozone between 0 and 10 ppm. Use
Most of the impurities in cooling water are alkaline, of ozone treatment has seen a growing interest for
which is indicated. The alkaline impurities, especially cooling tower control and is a cost-effective solution for
calcium carbonate, are less soluble at high pH val- many applications.
ues. Therefore, a small quantity of sulfuric acid is
added to the circulating water to lower the pH value
and thus prevent the formation of solids (scale). The
ideal pH sensor for this application is the general pur-
pose Model 399. The Langelier Index is a factor
obtained from calcium hardness, alkalinity, pH, con-
ductivity, and temperature, and indicates scaling
potential.
INSTRUMENTATION
Model 1055 Dual Input Analyzer
Multi-parameter input instrument for pH, conductivity, chlorine, and ozone
Two (2) 4-20 mA outputs, plus three (3) fully programmable alarms
Choice of enclosures for pipe, surface, and panel mounting
NEMA 4X (IP65) enclosure
Model 400 Conductivity Sensor Model 399 pH/ORP Disposable Sensor
Fast and easy start up with predetermined Convenient and economical disposable
factory cal constant (not for 1055) design
Rugged titanium electrodes Chemically rugged Tefzel1 body completely
Versatile mounting configurations for screw-in, sealed to eliminate sensor leakage
retractable, or flow-through Double junction reference cell to protect reference from
poisoning ions
1
Tefzel is a registered trademark of E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.
Model 499ACL Free Chlorine Model 499AOZ Dissolved Ozone
Sensor Sensor
Measures free chlorine without sam- Rugged construction
ple pretreatment or reagent
Automatic pressure equalization
Automatic correction to 9.5 pH maintains correct membrane tension
Easily replaceable membrane with no special tools Quick cable to sensor disconnect Variopol option
required
For high solids or coating applications, use the following sensors:
Model 396P pH/ORP TUpH Sensor Model 228 Toroidal Conductivity
Patented1 polypropylene reference junction Sensor
and patented2 helical pathway mean longer Toroidal measurement principle greatly
sensor life in process solutions containing reduces sensor fouling problems.
heavy solids.
1 U.S. Patent No. 5,152,882, Foreign Patent Pending.
2 May be protected by U.S. Patent No. 6,054,031, Foreign Patents Pending.
FIGURE 1. Typical Cooling Water System
The right people,
the right answers,
right now.
ON-LINE ORDERING NOW AVAILABLE ON OUR WEB SITE
http://www.raihome.com
Credit Cards for U.S. Purchases Only.
Emerson Process Management
Liquid Division
2400 Barranca Parkway
Irvine, CA 92606 USA
Tel: (949) 757-8500
Fax: (949) 474-7250
http://www.raihome.com
Rosemount Analytical Inc. 2004
You might also like
- Effect of Chlorine Vs Chloramine Treatment Techniques On Materials Degradation in Reclamation InfrastructureDocument19 pagesEffect of Chlorine Vs Chloramine Treatment Techniques On Materials Degradation in Reclamation InfrastructureivanrhsNo ratings yet
- Open Cooling System Guide ALP 25 July 2013 Final VerDocument42 pagesOpen Cooling System Guide ALP 25 July 2013 Final VerivanrhsNo ratings yet
- TB R61P13 PDFDocument16 pagesTB R61P13 PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- IRENA-ETSAP Tech Brief I12 Water-Desalination PDFDocument28 pagesIRENA-ETSAP Tech Brief I12 Water-Desalination PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- TB R61P13 PDFDocument16 pagesTB R61P13 PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- Icd PDFDocument6 pagesIcd PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- Ctii 01a PDFDocument4 pagesCtii 01a PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- IRENA-ETSAP Tech Brief I12 Water-Desalination PDFDocument28 pagesIRENA-ETSAP Tech Brief I12 Water-Desalination PDFivanrhsNo ratings yet
- NIDI - StainlessSteels and Specialty Alloys For Modern Pulp and Paper Mills - 11025Document152 pagesNIDI - StainlessSteels and Specialty Alloys For Modern Pulp and Paper Mills - 11025srtools1980yNo ratings yet
- Adventures of Sludge Bugs: Microorganisms that Power Wastewater TreatmentDocument108 pagesAdventures of Sludge Bugs: Microorganisms that Power Wastewater Treatmentivanrhs100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lime Neutralization Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesLime Neutralization Wastewater TreatmentMehrdad AminkazemiNo ratings yet
- Revised NEQSDocument10 pagesRevised NEQSKhalid Masood GhaniNo ratings yet
- Physics 10 - SLIP TESTDocument2 pagesPhysics 10 - SLIP TESTrehanrehan2190No ratings yet
- Coo Seg Cat CDC Eqf 0002 0Document182 pagesCoo Seg Cat CDC Eqf 0002 0Ricardo VerdugoNo ratings yet
- G9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pagesG9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsCherrilyn Enverzo33% (3)
- Built Up Rate ReinforcementDocument25 pagesBuilt Up Rate Reinforcementsyazwan_badboyzNo ratings yet
- Aroclor 1232Document48 pagesAroclor 1232mcreadmailNo ratings yet
- 18.J.K.mitchell&K.soga - Fundamentals of Soil BehaviourDocument505 pages18.J.K.mitchell&K.soga - Fundamentals of Soil BehaviourJose Eduardo Murillo Fernandez88% (17)
- Load Cell & Its Application in TextileDocument27 pagesLoad Cell & Its Application in TextileSoumyajit Sarkar100% (1)
- Lab Manual-Total AlkalinityDocument4 pagesLab Manual-Total AlkalinitySuvanka DuttaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 NeutralizationDocument32 pagesLec 8 Neutralizationhaseeb tahirNo ratings yet
- Astm C1602-06Document4 pagesAstm C1602-06Gustavo Bances Herrera0% (1)
- Final ReviewDocument43 pagesFinal ReviewKaththi KathirNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To PVDF Coatings: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesAn Introduction To PVDF Coatings: Product Data SheetAnonymous DJrec2No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Vinavil 5406 enDocument2 pagesVinavil 5406 enVladimir Delgado B.No ratings yet
- Anna University ME2303 Design of Machine Elements Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnna University ME2303 Design of Machine Elements Exam QuestionssathurvedhaNo ratings yet
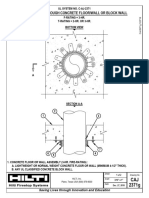
- Firestop System Details ASSET DOC LOC 2135392Document2 pagesFirestop System Details ASSET DOC LOC 2135392Amir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process-Ii: Lab Manual 01Document8 pagesManufacturing Process-Ii: Lab Manual 01Abdul Rehman FaisalNo ratings yet
- B 474 - 99 Qjq3nc05oqDocument5 pagesB 474 - 99 Qjq3nc05oqMarceloNo ratings yet
- Wa0036.Document2 pagesWa0036.GMHSS VehariNo ratings yet
- Free Electron Gas in 2D and 1DDocument16 pagesFree Electron Gas in 2D and 1DTurin TurambarNo ratings yet
- Honda Pump BrochureDocument18 pagesHonda Pump Brochurefser04No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETEDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- The Graphite FutureDocument21 pagesThe Graphite FutureEdgard Vásquez100% (1)
- Thermodynamic Considerations in The Interactions of Nitrogen Oxides and Oxy Acids in The AtmosphereDocument5 pagesThermodynamic Considerations in The Interactions of Nitrogen Oxides and Oxy Acids in The AtmosphereKing Ray TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Cis-Diamminediiodoplatinum (II)Document2 pagesPreparation of Cis-Diamminediiodoplatinum (II)Najwa ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- FEM Varification: ProblemDocument11 pagesFEM Varification: Problemandi0610bNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Soal Gas Insulation Santos EdunDocument5 pagesJawaban Soal Gas Insulation Santos EdunLuthfi Arif FadillahNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Reviewer BIOKMAN 1T AY2019-2020-1Document2 pagesFinal Exam Reviewer BIOKMAN 1T AY2019-2020-1Macy MarianNo ratings yet