Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Community Advocacy Rounds: A Cultural Competency and Health Disparity Curriculum (Carrie Mauras)
Uploaded by
AUCDOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Community Advocacy Rounds: A Cultural Competency and Health Disparity Curriculum (Carrie Mauras)
Uploaded by
AUCDCopyright:
Available Formats
Community Advocacy Rounds
A Cultural Competency and Health Disparity Curriculum
Carrie Mauras, PhD, Noelle Huntington, PhD, Alison Schonwald, MD
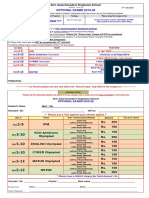
Background Data
Week Topic Preparation Activity Response Rate 80% (12/15)
Culturally competent care can reduce
disparities in health care
Medical education should include longitudinal 1 Cultural Competence 101 ---- Case Based Power Point
training in cultural competence as well as
successful engagement with community
partners Family Structure Article: Loss of a parent
2 Berg L, Rostila M, Saarela J, Hjern A. Parental Death During
Case & Discussion
Adult learning methods pair well with these Childhood and Subsequent School Performance. Pediatrics
2014;133;682.
topics, accounting for prior knowledge, Article: Children of Depressed
incorporating self-reflection and ongoing critical Parents
thinking
3 Impact of Parental Depression Wickramaratne P. et al. Children of Depressed Mothers 1 Year After
Case & Discussion
Remission of Maternal Depression: Findings From the STAR*D-
Child Study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168:593602.
Present disability awareness
Goals http://www.huffingtonpost.com/emily- unit
ladau/i-wont-disability-
Collaborating with Community Agencies: (Blind/Vision Impaired,
4 Understanding Our Differences
simulation_b_4936801.html
Deaf/Hard of Hearing,
Develop and evaluate a dynamic curriculum http://www.understandingourdifferences.or
using adult learning methods g/ Intellectual Disability,
Physical Disability)
Curriculum explores the social ecology of the
Article: Children of Parents with
patient, addressing health disparities, cultural Intellectual Disability
competence and other social-ecological factors 5 Impact of Parental Intellectual Disability Collings S, Llewellyn G. Children of parents with intellectual Case & Discussion
disability: Facing poor outcomes or faring okay? Journal of
Community Advocacy Rounds. (Strongly) Agree
influencing health outcomes in Developmental Intellectual & Developmental Disability, March 2012; 37(1): 6582.
Behavioral Pediatrics (DBP) Privilege Walk
6 Cultural Competence 201 ----- Increased my awareness of the disparities in care opportunities
for children from disadvantaged backgrounds
91%
Team Increased my awareness of my own biases and assumptions
100%
about families and communities
DBP: Alison Schonwald, MD
7 Cultural Competence 301 ----- Values Comparison
Increased my understanding of the influence of stigmatization
Psychologists: Carrie Mauras, PhD and Anna and discrimination on child health and development
91%
Chaves McDonald, PhD Present experience visiting
Social Workers: Katherine Engel, Julianna 8 Educational Environments Prepare to present
local school Will improve my ability to treat children with a wide range of
100%
backgrounds and life experiences effectively
Brody-Fialkin, Alison Rosenberg
Educators: Alexandra Fortuna, Lisyl Rigsby Article: Toxic Stress
9 Toxic Stress Shonkoff J, et al. The Lifelong Effects of Early Childhood Adversity Case and Power Point
Lessons Learned
and Toxic Stress. Pediatrics 2012;129;e232.
Intervention Article: Siblings of Children with
Disabilities
10 Siblings of Children with Disabilities Case based discussion Discussing uncomfortable topics and sharing
Content generated from DBP Boards content Walton K, Ingersoll B. Psychosocial Adjustment and Sibling
Relationships in Siblings of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder:
Risk and Protective Factors. J Autism Dev Disord, April 2015. personal viewpoints may be difficult, but can lead
specifications and previous challenging cases
to an effective and memorable learning experience
13 1-hour sessions Article: Mass Trauma
Interdisciplinary staff attendance 11 Mass Trauma Chrisman A, Joseph G. Dougherty J. Mass Trauma: Disasters,
Terrorism, and War. Child Adolesc Psychiatric Clin N Am 23 (2014)
Flipped Classroom
257279
Adult learning activities were engaging and
DBP and Psychology fellows
Case Discussion effective for many learners
LEND fellows
12 Fellow Case Review -----
Each session included a combination of
Sessions should be held regularly and group
preparation by participants, and/or case
Cultural Competence Self participants, including faculty, should be as
discussion, and/or active group learning Wrap Up
13 Self-Reflection ----- Assessment consistent as possible
activities
Letter to Self Letter to Self
15 trainees were surveyed about relevance
Sessions can be standalone or mixed in with other
and utility of the series for educational
learning session (e.g., M&M)
purposes Acknowledgement: DBP and Psychology fellows are supported in part by the LEND and MCHB Training Grants
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Increasing Access To Autism Spectrum Disorder Assessment Services For Children Under Three Through Part C ClinicsDocument32 pagesIncreasing Access To Autism Spectrum Disorder Assessment Services For Children Under Three Through Part C ClinicsAUCDNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Statewide Collaboration To Educate On Developmental and Behavioral Monitoring and ScreeningDocument1 pageStatewide Collaboration To Educate On Developmental and Behavioral Monitoring and ScreeningAUCDNo ratings yet
- Human-Centered Design For Community-Centered CollaborationDocument17 pagesHuman-Centered Design For Community-Centered CollaborationAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Test 71 02Document57 pagesTest 71 02AUCDNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Detecting Autism Early - A Pilot To Train Providers, Screen Toddlers, and Support Families With Autism Concerns in Primary CareDocument41 pagesDetecting Autism Early - A Pilot To Train Providers, Screen Toddlers, and Support Families With Autism Concerns in Primary CareAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Development and Utility of The Family-Centered Autism Navigation (Family CAN) Semi-Structured InterviewDocument1 pageThe Development and Utility of The Family-Centered Autism Navigation (Family CAN) Semi-Structured InterviewAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Access To Autism Information and Services in Wisconsin Is Enhanced by LEND Collaboration With State System InitiativeDocument1 pageAccess To Autism Information and Services in Wisconsin Is Enhanced by LEND Collaboration With State System InitiativeAUCDNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Addressing Access and Reach: Implementation of A Group CBT Intervention For Managing Anxiety in Students With ASD in Urban SchoolsDocument36 pagesAddressing Access and Reach: Implementation of A Group CBT Intervention For Managing Anxiety in Students With ASD in Urban SchoolsAUCD0% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- "And I Will Tell You This": Single, Black Mothers of Children With ASD/DD Using Cultural Capital in Special EducationDocument20 pages"And I Will Tell You This": Single, Black Mothers of Children With ASD/DD Using Cultural Capital in Special EducationAUCDNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Delaware's Autism Care Team: Autism CARES Meeting July 2019Document66 pagesDelaware's Autism Care Team: Autism CARES Meeting July 2019AUCDNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Evidence For The Use of Age-Based Diagnostic Tracks in Interdisciplinary Team Evaluation For Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument23 pagesEvidence For The Use of Age-Based Diagnostic Tracks in Interdisciplinary Team Evaluation For Autism Spectrum DisorderAUCDNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Influence of Race and Ethnicity On Vocational Rehabilitation Service Utilization and Outcomes of Transition-Age Young Adults With AutismDocument1 pageThe Influence of Race and Ethnicity On Vocational Rehabilitation Service Utilization and Outcomes of Transition-Age Young Adults With AutismAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Autism Friendly Initiative at Boston Medical Center: Improving The Hospital Experience For Patients With AutismDocument41 pagesThe Autism Friendly Initiative at Boston Medical Center: Improving The Hospital Experience For Patients With AutismAUCDNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Preliminary Validation of The PROMIS® Pediatric Parent-Proxy Anxiety Measure in Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pagePreliminary Validation of The PROMIS® Pediatric Parent-Proxy Anxiety Measure in Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderAUCDNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The National Autism Data Center at Drexel University: Population-Level Data To Inform PolicyDocument1 pageThe National Autism Data Center at Drexel University: Population-Level Data To Inform PolicyAUCDNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- AUTISM 101: A Psychoeducational Intervention For Parents of Newly Diagnosed Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pageAUTISM 101: A Psychoeducational Intervention For Parents of Newly Diagnosed Children With Autism Spectrum DisorderAUCDNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Digital Media Exposure in Young Children With Disabilities, A Population Based SurveyDocument1 pageDigital Media Exposure in Young Children With Disabilities, A Population Based SurveyAUCDNo ratings yet
- Association Between Food Insecurity and Developmental Delay and Behavioral Problems in US Children 2-5 Years of AgeDocument1 pageAssociation Between Food Insecurity and Developmental Delay and Behavioral Problems in US Children 2-5 Years of AgeAUCDNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorder Prevalence in Diverse Communities in MinnesotaDocument1 pageAutism Spectrum Disorder Prevalence in Diverse Communities in MinnesotaAUCDNo ratings yet
- Building A Network of Community Leaders To Support Early Developmental Screening: Minnesota Act Early Delegate Network in Diverse Cultural CommunitiesDocument1 pageBuilding A Network of Community Leaders To Support Early Developmental Screening: Minnesota Act Early Delegate Network in Diverse Cultural CommunitiesAUCDNo ratings yet
- Susan M. Russell, M.S. and Betsy P. Humphreys, Ph.D. SuccessesDocument1 pageSusan M. Russell, M.S. and Betsy P. Humphreys, Ph.D. SuccessesAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- LEND Training in A Developmental-Behavioral Advanced Practice Nursing Fellowship: Increasing Access To Evaluation and Follow UpDocument1 pageLEND Training in A Developmental-Behavioral Advanced Practice Nursing Fellowship: Increasing Access To Evaluation and Follow UpAUCDNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Diversity in The Alaska LEND Program: Engaging Faculty From Rural AlaskaDocument1 pageStrengthening Diversity in The Alaska LEND Program: Engaging Faculty From Rural AlaskaAUCDNo ratings yet
- Autism Intervention Research Network On Physical Health (AIR-P) Addressing DisparitiesDocument1 pageAutism Intervention Research Network On Physical Health (AIR-P) Addressing DisparitiesAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- HRSA MCHB-Funded Autism CARES Programs Promote Equity and Increased Access To CareDocument1 pageHRSA MCHB-Funded Autism CARES Programs Promote Equity and Increased Access To CareAUCDNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Medication Use in Youth With Autism and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderDocument1 pagePsychotropic Medication Use in Youth With Autism and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderAUCDNo ratings yet
- Community-Partnered Participatory Research in Autism: Engaging Underresourced African American, Korean and Latino CommunitiesDocument1 pageCommunity-Partnered Participatory Research in Autism: Engaging Underresourced African American, Korean and Latino CommunitiesAUCDNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Site Randomized Control Trial of Family Navigation's Effect On Diagnostic Ascertainment Among Children at Risk For Autism: A DBPNet StudyDocument1 pageA Multi-Site Randomized Control Trial of Family Navigation's Effect On Diagnostic Ascertainment Among Children at Risk For Autism: A DBPNet StudyAUCDNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Diagnosis of Autism in An Ethnical Diverse, Community Sample: Who Refers and Why?Document1 pageDiagnosis of Autism in An Ethnical Diverse, Community Sample: Who Refers and Why?AUCDNo ratings yet
- Screening of Young Children For Autism Spectrum Disorders: Results From A National Survey of PediatriciansDocument1 pageScreening of Young Children For Autism Spectrum Disorders: Results From A National Survey of PediatriciansAUCDNo ratings yet
- ICEP CSS - PMS Institute, Lahore (MCQ'S Gender Studies)Document22 pagesICEP CSS - PMS Institute, Lahore (MCQ'S Gender Studies)Majid Ameer AttariNo ratings yet
- Resume CID200003017288368Document2 pagesResume CID200003017288368David Susilo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- In Virginia WoolfDocument4 pagesIn Virginia Woolfdalba14No ratings yet
- IELTS Listening Strategy and TacticsDocument41 pagesIELTS Listening Strategy and TacticsAhmed Mahmoud Yassin100% (6)
- Fractions and Mixed Numbers: Planning Guide: Grade 7 Addition and Subtraction of PositiveDocument27 pagesFractions and Mixed Numbers: Planning Guide: Grade 7 Addition and Subtraction of PositiveChet AckNo ratings yet
- Four ValuesDocument1 pageFour ValuesJohn Alvin SolosaNo ratings yet
- School Calendar 2010 - 11Document11 pagesSchool Calendar 2010 - 11Neil BradfordNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Pagtuturo NG Filipino Sa Elementarya IDocument5 pagesCourse Outline Pagtuturo NG Filipino Sa Elementarya IElma CapilloNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/12 February/March 2022Document17 pagesCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/12 February/March 2022shwetarameshiyer7No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Optional Exams 2019-20: Smt. Sulochanadevi Singhania SchoolDocument1 pageOptional Exams 2019-20: Smt. Sulochanadevi Singhania SchoolRamanand YadavNo ratings yet
- Exploring Literacy and Intergenerational Learning For Sustainable Development in Malawi PDFDocument34 pagesExploring Literacy and Intergenerational Learning For Sustainable Development in Malawi PDFteresaNo ratings yet
- What Elementary Teachers Need To Know About Language Lily Wong FillmoreDocument2 pagesWhat Elementary Teachers Need To Know About Language Lily Wong Fillmorekaren clarkNo ratings yet
- LWWR FinalsDocument23 pagesLWWR FinalsAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- E. The Duchamp Effect - Three Conversations in 1985 - Claes Oldenburg, Andy Warhol, Robert MorrisDocument23 pagesE. The Duchamp Effect - Three Conversations in 1985 - Claes Oldenburg, Andy Warhol, Robert MorrisDavid LópezNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Harian Sains Kanak-Kanak Pendidikan KhasDocument2 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Harian Sains Kanak-Kanak Pendidikan KhasnadiaburnNo ratings yet
- 18ME62Document263 pages18ME62Action Cut EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Sally Power (2012) From Redistribution To Recogniticon To RepresentationDocument21 pagesSally Power (2012) From Redistribution To Recogniticon To RepresentationMaster of ShadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Behavioral Theories of Learning: Educational PsychologyDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Behavioral Theories of Learning: Educational PsychologyTLambert89955294No ratings yet
- Syllabus in Assessment 1Document6 pagesSyllabus in Assessment 1Julius BalbinNo ratings yet
- ENG8 - Q2 - Mod5 Compare and Contrast The Presentation of The Same Topic in Different Multimodal Texts Grace ManuelDocument11 pagesENG8 - Q2 - Mod5 Compare and Contrast The Presentation of The Same Topic in Different Multimodal Texts Grace ManuelFreddy MarsucNo ratings yet
- Philippine Disaster Reduction and Management ActDocument22 pagesPhilippine Disaster Reduction and Management ActRhona Mae ArquitaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Kindergarten Curriculum Guide 20l7-20l8Document5 pagesDevelopmental Kindergarten Curriculum Guide 20l7-20l8api-311641812No ratings yet
- Scaffolding Practices For Effective Numeracy TeachersDocument1 pageScaffolding Practices For Effective Numeracy TeachersSizaza BruciaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math GAS Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesGen Math GAS Daily Lesson Logjun del rosario100% (2)
- Draft To Student Mse Oct 2014 - (Updated)Document4 pagesDraft To Student Mse Oct 2014 - (Updated)Kavithrra WasudavenNo ratings yet
- GMF Project and RubricDocument2 pagesGMF Project and RubriccaitilnpetersNo ratings yet
- Sptve - Techdrwg 8 - q1 - m9Document12 pagesSptve - Techdrwg 8 - q1 - m9MirtelShane-Ara Agustin SalesNo ratings yet
- Propaganda TechniquesDocument64 pagesPropaganda TechniquesSteffie Subiera ComodasNo ratings yet
- Jared M. Hansen: 1803 Anna ST Bellevue, NE 68005 Phone: C: (402) 709-1615 H: (402) 293-1565Document2 pagesJared M. Hansen: 1803 Anna ST Bellevue, NE 68005 Phone: C: (402) 709-1615 H: (402) 293-1565dcfan402No ratings yet