Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Fatigue
Uploaded by
KateLayaog100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views3 pagesFatigue NCP
Original Title
Ncp Fatigue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFatigue NCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views3 pagesNCP Fatigue
Uploaded by
KateLayaogFatigue NCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
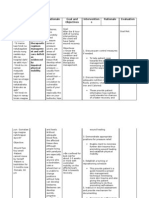
NURSING CARE PLAN NO.
Date Identified : June 16, 2017
Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives/Evaluation Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Criteria
Objective cues: Fatigue r/t to Within 6 hours of 1. Determine possible causes of fatigue, such 1. Identifying the related factors with Goal met
"kadtung sa una, maayo decreased nursing interventions as: fatigue can benefit in recognizing After 6 hours of
pa akong lawas kay haemoglobin count the patient will be potential causes and building a nursing interventions
Last physical illness
mahimo pa nako akong secondary to anemia able to report collaborative plan of care. the patient was able
Pain
gusto pero karun improved sense of to improved sense of
Emotional stress
limitado na kaayo akong energy. 2. Fatigue can restrict the patients ability energy as evidenced
Depression
lihok tungod sa akong to participate in self-care and do his or by patient
Side effects of medication
kondisyuon, kapoy her role responsibilities in the family and verbalization " arang
Anemia
permi akong lawas" society, such as working outside the arang naman akong
Sleep disorders
home. paminaw "
- unable to interact well - Oxygenation
2. Assess the patients ability to perform
with the examiner due to 3. Decreased RBC indexes are associated 97 % with o2
ADLs, instrumental activities of daily living
weakness of muscle with decreased oxygen-carrying capacity
(IADLs), and demands of daily living (DDLs).
strength of the blood. It is critical to compare
- cannot tolerate serial laboratory values to evaluate
3. Monitor hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC
maintain balance. (needs progression or deterioration in the client
counts, and reticulocyte counts.
assistance during and to identify changes before they
ambulation) become potentially life-threatening.
4. Assess the patients sleep patterns for
- capillary refill @ 3
quality, quantity, time taken to fall asleep and
seconds 4. Changes in the patients sleep pattern
feeling upon awakening and observe alteration
- weak as seen may be a contributing factor in the
in thought processes or behaviors.
- Speak in a slow, quiet development of fatigue. Numerous
and and hesitant manner. factors can exacerbate fatigue, together
Speak weakly 5. Identify energy conservation methods such with sleep deprivation, emotional
- drowsy as sitting and dividing ADLs into convenient distress, side effects of drugs, and
- dyspnoeic segments. Assist with movement or self-care progressing CNS disease.
- Hemoglobin : demands as appropriate.
71g/L (low) 5 Weakness can make ADLs almost not
- Erythrocytes: 6. Educate the patient and family about task possible for patient to finish. Being with
2.52 (low) organization methods and time organization the patient prevents the patient from
-Oxygenation methods. getting harm during activities.
94 % without o2
7. Anticipate the need for the transfusion of 6. Clients and caregivers may need to
packed RBCs. learn skills for delegating task to others,
setting priorities, and clustering care to
8. Aid the patient develop habits to promote use available energy to complete desired
effective rest/sleep patterns. activities. Organization and time
management can help the client conserve
9. Provide supplemental oxygen therapy, as energy and reduce fatigue.
needed.
7. Packed RBCs increase oxygen-
10. Administer ____________- carrying capacity of the blood.8.
Promoting relaxation before sleep and
providing for several hours of
uninterrupted sleep can contribute to
energy restoration.
9. Oxygen saturation should be kept at
90% or greater
10. Recombinant human erythropoietin, a
hematological growth factor, increases
hemoglobin and decreases the need for
RBC transfusions..
You might also like
- Fatigue NCPDocument2 pagesFatigue NCPclydell joyce masiar100% (6)
- NCP - FatigueDocument3 pagesNCP - Fatigueitsmeaya100% (1)
- Anemia NCPDocument5 pagesAnemia NCPMel Christian Baldoz100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance R/T Generalized WeaknessDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance R/T Generalized Weaknesschanmin limNo ratings yet
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Document2 pagesAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- NCP FatigueDocument2 pagesNCP FatigueJon Eric G. Co100% (4)
- Activity Intolerance (NCP)Document3 pagesActivity Intolerance (NCP)Sonia Letran Singson100% (3)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerancejunex123No ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument7 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Casilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Document3 pagesCasilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Ynalie Casilan100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For InjuryBianca Freya Porral86% (7)
- Anemia NCPDocument6 pagesAnemia NCPApril Jumawan ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument10 pagesAnemia NCPCharmz_asherah100% (9)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceMaze Reyes40% (5)
- Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerDocument3 pagesRisk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerdanaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain - OBDocument5 pagesNCP Pain - OBSandra Guimaray50% (2)
- NCP For Ineffective Breathing Pattern - RMC CasepressDocument2 pagesNCP For Ineffective Breathing Pattern - RMC Casepressmissyuri08No ratings yet
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute PainEmman RamosNo ratings yet
- NCP (Fatigue)Document1 pageNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Pre NCP FatigueDocument2 pagesPre NCP Fatigueirisjabines67% (3)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Document1 pageNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocument4 pagesNCP Acute PainSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- NCP Gestational HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangNo ratings yet
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP Knowledge Deficit PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficit PDFskylertNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- N E E D S: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning/ Specific Outcome Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesN E E D S: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning/ Specific Outcome Intervention EvaluationArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocument2 pagesProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawNo ratings yet
- NCP Anxiety and PainDocument12 pagesNCP Anxiety and PainCazze Sunio100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- Immobility Care Plan For NursesDocument3 pagesImmobility Care Plan For NursesColleen Murray67% (9)
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- NCP ImbalancedDocument7 pagesNCP ImbalancedSasha FongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Risk For Falls (Antepartum)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Risk For Falls (Antepartum)kaimimiyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument4 pagesRisk For InjuryKatrina Denise TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ExampleDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ExampleBrittanyNo ratings yet
- NCP # 1 Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP # 1 Acute Painernst_bondoc50% (2)
- NCP 1 Addisons DiseaseDocument5 pagesNCP 1 Addisons DiseaseRenee RoSeNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824No ratings yet
- NCP Impaiered Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageNCP Impaiered Skin Integrityeiram2264% (11)
- NCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument9 pagesNCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionRYAN SAPLADNo ratings yet
- NCP AnxietyDocument2 pagesNCP Anxietyjae_lee_730% (1)
- NCP-Benign-Vertigo - Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP-Benign-Vertigo - Impaired Physical MobilityStephen S. Padayhag83% (6)
- Infection NCPDocument1 pageInfection NCPMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- NCP Multiple SclerosisDocument2 pagesNCP Multiple SclerosisJaylord Verazon100% (2)
- Health Center Duty: The Student Nurse Preparing For The Vaccines To Be AdministerDocument4 pagesHealth Center Duty: The Student Nurse Preparing For The Vaccines To Be AdministerKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Health Center Duty: The Student Nurse Preparing For The Vaccines To Be AdministerDocument4 pagesHealth Center Duty: The Student Nurse Preparing For The Vaccines To Be AdministerKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Apas XrayDocument1 pageApas XrayKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Pic 2Document3 pagesPic 2KateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Pic 1Document2 pagesPic 1KateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Butuan CityDocument1 pageFather Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Butuan CityKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Practising Clinical Instructor Submitted To: Supervising Clinical InstructorDocument2 pagesPractising Clinical Instructor Submitted To: Supervising Clinical InstructorKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Apol LMDocument3 pagesApol LMKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- DSM5Document3 pagesDSM5KateLayaog100% (1)
- APOLGWAPADocument7 pagesAPOLGWAPAKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Bibliography BwesitDocument6 pagesBibliography BwesitKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Abstract LatestDocument3 pagesAbstract LatestKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Daily Recording of Activities 2Document3 pagesDaily Recording of Activities 2KateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Environmental SanitationDocument50 pagesEnvironmental Sanitationace_51891100% (7)
- Ebr 4Document1 pageEbr 4KateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Example 1 PDFDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Example 1 PDFKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Name: Group: Date: Week #:: Evidence-Based ResearchDocument2 pagesName: Group: Date: Week #:: Evidence-Based ResearchKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Bryle's MOADocument3 pagesBryle's MOAKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- ATTENDANCEDocument3 pagesATTENDANCEKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Resource Manual: Father Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Butuan CityDocument2 pagesResource Manual: Father Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Butuan CityKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Front and Apporval SheetDocument2 pagesFront and Apporval SheetKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Bryles On The Job Trainning FormDocument6 pagesBryles On The Job Trainning FormKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- DSM5Document4 pagesDSM5KateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of AgreementDocument3 pagesMemorandum of AgreementKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Fsuu Ojt FormDocument6 pagesFsuu Ojt FormKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument24 pagesSchizophrenia Case StudyRichard Sy100% (3)
- Nutrition Care Plan - Febrile Client With Hepatitis ADocument3 pagesNutrition Care Plan - Febrile Client With Hepatitis AElaine ArsagaNo ratings yet
- Olds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 10th Edition Davidson Test BankDocument33 pagesOlds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 10th Edition Davidson Test Bankstarostyadjustaged5p100% (29)
- Best Practice For Dental Hand Hygiene FacilityDocument1 pageBest Practice For Dental Hand Hygiene FacilityEsfandiary 121No ratings yet
- David Laid DUP ProgramDocument3 pagesDavid Laid DUP ProgramRyan MurphyNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Factors in Disease: AG Shand JPH WildingDocument28 pagesNutritional Factors in Disease: AG Shand JPH WildingcmncNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pain Clinic Referral Form Jpocsc: Fax: (604) 582-4591 PH: (604) 582-4587Document2 pagesChronic Pain Clinic Referral Form Jpocsc: Fax: (604) 582-4591 PH: (604) 582-4587Muhammed SamiNo ratings yet
- Andrea Larosa 4 Weeks Calisthenics Training Program (Beginner)Document26 pagesAndrea Larosa 4 Weeks Calisthenics Training Program (Beginner)Dimitry Donaire Flores100% (8)
- GTP MainGuide PDFDocument59 pagesGTP MainGuide PDFAhmed Seifelnasr100% (2)
- STS 2 Users GuideDocument145 pagesSTS 2 Users GuideTeoNo ratings yet
- Wash 1Document23 pagesWash 1Jeffrey DanabarNo ratings yet
- Part1 MSBDocument8 pagesPart1 MSBManuelNo ratings yet
- 2018 ENNS Dissemination Isabela ProvinceDocument162 pages2018 ENNS Dissemination Isabela ProvinceJoshua DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Desain Sentra Pangan Sesuai Penerapan Cara Produksi Pangan Olahan Yang Baik (Cppob) / Good Dak Kementerian Perindustrian Ta.2023Document74 pagesDesain Sentra Pangan Sesuai Penerapan Cara Produksi Pangan Olahan Yang Baik (Cppob) / Good Dak Kementerian Perindustrian Ta.2023Zaiful HamzahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory of Fundamental NursingDocument24 pagesNursing Theory of Fundamental NursingrerenrahmawatiNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosteraudrey.r.bedwellNo ratings yet
- Nurs21330 (Nursing Assess Me Nut Assignment)Document9 pagesNurs21330 (Nursing Assess Me Nut Assignment)Stella AshkerNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Olds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 11th Edition by DavidsonDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Olds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 11th Edition by DavidsonMartin Courser100% (32)
- (Updated) Recommended Routine Bodyweight Workout Log-2Document1 page(Updated) Recommended Routine Bodyweight Workout Log-2arthax123No ratings yet
- Class Note NUT 301 - 3 - ENERGY REQUIREMENTSDocument13 pagesClass Note NUT 301 - 3 - ENERGY REQUIREMENTSomonzejele jenniferNo ratings yet
- Phase 3 Week 4Document12 pagesPhase 3 Week 4justin wrightNo ratings yet
- Group Fitness Schedule MarcDocument1 pageGroup Fitness Schedule MarcbomoultonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patients With Multiple SclerosisDocument1 pageNursing Care For Patients With Multiple Sclerosis4gen_2No ratings yet
- 1-1 Mapeh 8Document2 pages1-1 Mapeh 8Jayson LabsanNo ratings yet
- FightReady 4D M 2Document15 pagesFightReady 4D M 2Jeffrey Xie100% (7)
- Faujifood Pakistan PortfolioDocument21 pagesFaujifood Pakistan PortfolioPradeep AbeynayakeNo ratings yet
- SPORTOVI SNAGE Weightlifting, Body Building I Power Lifting Kroz Teoriju I PraksuDocument271 pagesSPORTOVI SNAGE Weightlifting, Body Building I Power Lifting Kroz Teoriju I PraksuMiljan Nikolić50% (2)
- Somanabolic Weight TrainingDocument62 pagesSomanabolic Weight TrainingKhalid SaeedNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Test RecordDocument5 pagesPhysical Fitness Test Recordcristina tamonteNo ratings yet
- YoYo Intermittent Recovery Test Level 2Document12 pagesYoYo Intermittent Recovery Test Level 2Alexander Quiñones SánchezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NutritionDocument11 pagesIntroduction To NutritionKailash NagarNo ratings yet