Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bearings-Designate The Direction of A Line by An Angle and
Uploaded by
John Paul Cuadero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views5 pagesBearings are used to designate the direction of a line using an angle and quadrant. True bearings are based on true north from the geographic poles, while magnetic bearings are based on magnetic north from the north magnetic pole, which shifts over time. The true meridian passes through the geographic poles and can be established through astronomical observation, while the magnetic poles are the points where the Earth's magnetic field points vertically upwards or downwards. Key surveying terms include the point of curvature where a curve begins, the point of tangency where a curve ends, the vertex where two lines meet to form an angle, and the center line which bisects a plane figure or divides a road.
Original Description:
ALL ABOUT TYPES OF STRESS
Original Title
Bearings
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBearings are used to designate the direction of a line using an angle and quadrant. True bearings are based on true north from the geographic poles, while magnetic bearings are based on magnetic north from the north magnetic pole, which shifts over time. The true meridian passes through the geographic poles and can be established through astronomical observation, while the magnetic poles are the points where the Earth's magnetic field points vertically upwards or downwards. Key surveying terms include the point of curvature where a curve begins, the point of tangency where a curve ends, the vertex where two lines meet to form an angle, and the center line which bisects a plane figure or divides a road.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views5 pagesBearings-Designate The Direction of A Line by An Angle and
Uploaded by
John Paul CuaderoBearings are used to designate the direction of a line using an angle and quadrant. True bearings are based on true north from the geographic poles, while magnetic bearings are based on magnetic north from the north magnetic pole, which shifts over time. The true meridian passes through the geographic poles and can be established through astronomical observation, while the magnetic poles are the points where the Earth's magnetic field points vertically upwards or downwards. Key surveying terms include the point of curvature where a curve begins, the point of tangency where a curve ends, the vertex where two lines meet to form an angle, and the center line which bisects a plane figure or divides a road.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Bearings- Designate the direction of a line by an angle and
quadrant letters. (e.g. N30 E). Bearings are never greater than
90. Bearings are referenced from north or south and the angle to
the east or west from the north-south meridian. True bearings are
based on true north. Magnetic bearings are based on magnetic
north.
True Meridian- is the north-south reference line through the
earthsgeographic poles. True meridian is defined as the plane
that passes through true north poles and true south poles at the
place of observation. True meridian can be established by
astronomical observation as it passes through true north and
south.
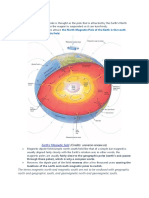
North Magnetic Pole- is the point on the surface
of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic
field points vertically downwards (in other words, if a magnetic
compass needle is allowed to rotate about a horizontal axis, it will
point straight down). There is only one location where this occurs,
near (but distinct from) the Geographic North Pole and
the Geomagnetic North Pole. The North Magnetic Pole moves
over time due to magnetic changes in the Earth's core.
South Magnetic Pole- is the wandering point on
the Earth's Southern Hemisphere where the geomagnetic
field lines are directed vertically upwards. It is the end of the
magnet, and the other end, pointing south because opposite
poles attract, the Earth's South Magnetic Pole is physically
actually a magnetic north pole. It is constantly shifting due to
changes in the Earth's magnetic field.
Geographic poles-
Are points on the earths surface that does not take
part in the earthsdiurnal rotation.The position of the earths axis o
f rotation relative to the earthsorbit is such that near the poles the
sun does not rise higher than 23. For this reason, the climateis
harsh, with low temperatures accompanied by strong winds and s
nowstorms.The instantaneous axis of earth rotation does not alwa
ysmaintain the same direction in the earth. As a result, the geogra
phic poles shift across the earthssurface, a phenomenon known
as polar motion.
Gradient- is another word for "slope". The higher the gradient of a
graph at a point, the steeper the line is at that point. A negative
gradient means that the line slopes downwards.. Horizontal plane:
A horizontal plane is a plane which is perpendicular to the
plumb line. Horizontal distance: In plane surveying, distance
measured along a level line termed as horizontal distance.
Center Line
Any line that bisects a plane figure.A painted line running along th
e center of a road or highway that divides it into two sectionsfor tr
affic moving in opposite directions, or, in the case of a divided hig
hway, for lines of traffic
moving in the same direction at different speeds.
Point of Curvature- It is the point where the circular curve
begins. The back tangent is tangent to the curve at this point.
Point of Tangency- It is the end of the curve. The forward
tangent is tangent to the curve at this point.
Vertex - a point where two lines meet to form an
angle; especially: the point on a triangle that is opposite to
the base.
Solo Data Collector-
Geodimeter is an instrument which works based on the
propagation of modulated light waves, was developed by E.
Bergestand of the Swedish Geological Survey in collaboration
with the manufacturer M/s AGA of Swedish. The instrument is
more suitable for night time observations and requires a prism
system at the end of the line for reflecting the waves.
Surveying Altimeter
-It is used in barometric leveling in which vertical difference
between two points is determined based on the atmospheric
pressure. In olden days, aneroid barometer is used for barometric
leveling but it had so many errors. Now altimeter replaced the
aneroid. Altimeter shows accurate response against atmospheric
pressure changes. Sometimes, air-recorder is also used to take
photographs of survey area. The major effecting factor for an
altimeter is temperature variation since it is dependent of air
density. Generally, altimeter is calibrated at 10oC. If the
observational temperature is more than 10oC, then the difference
in elevation is too. If it is more than 10oC t hen elevation
difference is more. So, a correction 0.2ft is applied for every 100ft
elevation difference when temperature is above 10oC.
You might also like
- Navigation Basics: Fundamental Concepts in Aeronautical NavigationDocument15 pagesNavigation Basics: Fundamental Concepts in Aeronautical NavigationRichard Pedraja100% (3)
- ATPL VivaDocument71 pagesATPL Vivacarltonfenandes100% (1)
- A Cartographic Map Projection Is A Systematic TransformationDocument34 pagesA Cartographic Map Projection Is A Systematic TransformationShamanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Earth Basic Magnetism SPLDocument3 pagesEarth Basic Magnetism SPLROHIT REDDYNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Declination - WikipediaDocument37 pagesMagnetic Declination - Wikipediapilot digitalNo ratings yet
- Gnav TheoryDocument9 pagesGnav TheoryMNo ratings yet
- Navigation IDocument29 pagesNavigation Imohamed100% (1)
- Gnav PDFDocument7 pagesGnav PDFMoslem GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Magnetic Field - Basics PDFDocument15 pagesThe Earth's Magnetic Field - Basics PDFAntonio Jose da CostaNo ratings yet
- Navigation Chapter-1: Direction, Latitude and LongitudeDocument76 pagesNavigation Chapter-1: Direction, Latitude and LongitudeAnusher Ansari100% (1)
- Polaris Fun 1 MainDocument20 pagesPolaris Fun 1 MainJayesh Solaskar100% (1)
- IAFS - Basic Aerial NavigationDocument27 pagesIAFS - Basic Aerial Navigationioannaknt622No ratings yet
- Astronomical Coordinate SystemsDocument11 pagesAstronomical Coordinate SystemsObby Dwi Syahputra100% (1)
- Surveying Lecture-2Document28 pagesSurveying Lecture-2Bittu BittuNo ratings yet
- Social Note (2) For Grade 7Document3 pagesSocial Note (2) For Grade 7Melkamu YigzawNo ratings yet
- 1 - Navigation Theory QuestionsDocument21 pages1 - Navigation Theory QuestionsShruti PrakasenNo ratings yet
- Satellite Orbits: Kepler's LawDocument18 pagesSatellite Orbits: Kepler's LawhelenNo ratings yet
- General Navigation Handbook: Compiled By: Akshey SoodDocument59 pagesGeneral Navigation Handbook: Compiled By: Akshey SoodManas Batra100% (2)
- Lec 6Document44 pagesLec 6SUHAYB 96No ratings yet
- Nav 3 Activity#4Document2 pagesNav 3 Activity#4CLIJOHN PABLO FORDNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 2.2 PDFDocument8 pagesATPL Inst 2.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - The Form of The EarthDocument7 pagesChapter 01 - The Form of The EarthIludiran Kola100% (2)
- Navigation... : Longitude and LatitudeDocument16 pagesNavigation... : Longitude and LatitudeSv. Ante100% (1)
- 3directional Measuring InstrumentsDocument34 pages3directional Measuring InstrumentsEmmanuel RapadaNo ratings yet
- Stuvia 848773 Atpl G Nav ResumeDocument9 pagesStuvia 848773 Atpl G Nav ResumeAnuar SNo ratings yet
- DR & Maps & Charts CombineDocument118 pagesDR & Maps & Charts Combinefalcon21152115100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Alberto NeriNo ratings yet
- What Is Marine NavigationDocument3 pagesWhat Is Marine NavigationOli Colmenares100% (1)
- Renewable Energy Systems The Solar Resource Source: Masters (Chapter 7)Document106 pagesRenewable Energy Systems The Solar Resource Source: Masters (Chapter 7)Shadan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Latitude: Navigation SearchDocument20 pagesLatitude: Navigation SearchEduciti MumbaiNo ratings yet
- Pyranometer and PyrheliometerDocument10 pagesPyranometer and PyrheliometerHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus KosmonautikasseDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus Kosmonautikassegirithik14No ratings yet
- Solar Radiation: Fig. 1 The Sun Earth RelationshipDocument10 pagesSolar Radiation: Fig. 1 The Sun Earth Relationshipsmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- Physics Project. FinalDocument22 pagesPhysics Project. Finalforchat759No ratings yet
- 11-Prof - Ishraque Ahmad NCESDocument24 pages11-Prof - Ishraque Ahmad NCES592000hivaNo ratings yet
- LatitudeDocument16 pagesLatitudealysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Time - Astrology, Astronomy and The Solar System PDFDocument24 pagesEarth and Time - Astrology, Astronomy and The Solar System PDFJude21No ratings yet
- Geog Ch. 1 SummaryDocument7 pagesGeog Ch. 1 SummaryScion McKinleyNo ratings yet
- SC Unit1Document15 pagesSC Unit1apollo eceNo ratings yet
- Earth MagnetismDocument24 pagesEarth MagnetismAyush Srivastava50% (2)
- Module 3Document26 pagesModule 3madhu.ammu112No ratings yet
- Satellite CommunicationDocument3 pagesSatellite CommunicationNuuradiin Xasan DhaqaneNo ratings yet
- GENERAL NAVIGATION 3m PDFDocument12 pagesGENERAL NAVIGATION 3m PDFfarryNo ratings yet
- Cartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesCartography Unit 3: Basic Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletTJ CabatinganNo ratings yet
- CLIMATE AND BUILT FORM II Module 2 ADocument67 pagesCLIMATE AND BUILT FORM II Module 2 ADHEESHNA DILEEP 200545100% (1)
- Nav TriangleDocument20 pagesNav Triangleeboy14No ratings yet
- Engineering AstronomyDocument13 pagesEngineering AstronomyFayaz S NabilNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter3 PDFAdithyan GowthamNo ratings yet
- Satcom My PresentationDocument84 pagesSatcom My PresentationSachinSachdevaNo ratings yet
- Yug Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesYug Physics Investigatory ProjectyugpalsanawalaNo ratings yet
- Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletDocument11 pagesGeodesy Flashcards - QuizletTJ CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Principles of NavigationDocument58 pagesPrinciples of NavigationNguyễn Thao80% (5)
- Climatology: RAR-309 By:-Abhijeet SinghDocument32 pagesClimatology: RAR-309 By:-Abhijeet SinghAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- General Navigation Revision NotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Navigation Revision NotesKartavya Patel100% (1)
- Magnetic Pole Geomagnetic PoleDocument7 pagesMagnetic Pole Geomagnetic Poleravi rathodNo ratings yet
- Astronomical SurveyDocument13 pagesAstronomical SurveyAtiqur Rahman SakibNo ratings yet
- NavigationDocument3 pagesNavigationShashikaNo ratings yet
- LSB Personnel Contact Numbers: Lsb-Engrng. Head SecretaryDocument1 pageLSB Personnel Contact Numbers: Lsb-Engrng. Head SecretaryJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Home For The ElderlyDocument1 pageA Proposed Home For The ElderlyJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1Document57 pagesWorkshop 1John Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Biography of Maupassant and Robert FrostDocument2 pagesBiography of Maupassant and Robert FrostJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Conclusions: 6.1 Concluding RemarksDocument4 pagesConclusions: 6.1 Concluding RemarksJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Notebook: Name: Jbench Swadel Mangueran Grade & Section: 4-Love Advisor: Honey Del CoroDocument1 pageAssignment Notebook: Name: Jbench Swadel Mangueran Grade & Section: 4-Love Advisor: Honey Del CoroJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute Technology UniversityDocument3 pagesCebu Institute Technology UniversityJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Biography of Famous PoetsDocument6 pagesBiography of Famous PoetsJohn Paul CuaderoNo ratings yet
- Hurley CVDocument5 pagesHurley CVBrendan HurleyNo ratings yet
- Human-Induced Threats To Bio-Diversity in North-East India With Special Reference To MajuliDocument10 pagesHuman-Induced Threats To Bio-Diversity in North-East India With Special Reference To MajuliIJBSS,ISSN:2319-2968No ratings yet
- TP876E - Study & Ref Guide Glider PilotDocument20 pagesTP876E - Study & Ref Guide Glider PilotbahbahaNo ratings yet
- Impact of UrbanizationDocument11 pagesImpact of UrbanizationZama Mahmood100% (1)
- 350Document36 pages350kathleenjaneNo ratings yet
- First Edition - Geography, Economics and Economic GeographyDocument190 pagesFirst Edition - Geography, Economics and Economic GeographyDr Swaamee Aprtemaanandaa Jee100% (2)
- Data InterpretationDocument2 pagesData Interpretationkosuru_rajuNo ratings yet
- Cebis Lex510 560 RussianDocument103 pagesCebis Lex510 560 RussianAndriyNo ratings yet
- Kashmir Earthquake Case Study 29024 2Document10 pagesKashmir Earthquake Case Study 29024 2Ketan DhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Trimble Dimensions 2006 Conference at A GlanceDocument2 pagesTrimble Dimensions 2006 Conference at A GlanceTrimbleDimensionsNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - MeteorologyDocument86 pagesVolare Questions - Meteorologypontoo100% (5)
- Design Brief - Ivth Year - Mass HousingDocument5 pagesDesign Brief - Ivth Year - Mass Housingj0hn5n50% (2)
- Week 7 - Task Assignment 1Document2 pagesWeek 7 - Task Assignment 1Rspbrry SprklNo ratings yet
- Fetch PDFDocument5 pagesFetch PDFPatricio Castillo ManquecoyNo ratings yet
- Purd 1 - 12 - 09Document9 pagesPurd 1 - 12 - 0955shadowNo ratings yet
- A GIS Approach For Evaluating MunicipalDocument141 pagesA GIS Approach For Evaluating MunicipalSopheak PenNo ratings yet
- Compro2013 GE PDFDocument12 pagesCompro2013 GE PDFgammaepsilon77100% (1)
- Site Analysis: Triveni Kalasangam, DelhiDocument1 pageSite Analysis: Triveni Kalasangam, DelhidivyaNo ratings yet
- Municipalities - Zip Codes of Broward County 2014: Boca RatonDocument1 pageMunicipalities - Zip Codes of Broward County 2014: Boca RatonJenn092No ratings yet
- NeupaveDocument9 pagesNeupaveHHTNo ratings yet
- Michael Danko ResumeDocument1 pageMichael Danko Resumeapi-244853425No ratings yet
- Chaplain Schmitt Island Master Plan - 201712211237348868Document109 pagesChaplain Schmitt Island Master Plan - 201712211237348868JORGE MARTIN DEL CAMPONo ratings yet
- Meghalaya - The Abode of CloudsDocument4 pagesMeghalaya - The Abode of CloudsThomas ArbenzNo ratings yet
- 5-6 Acre Plan Khet-ModelDocument1 page5-6 Acre Plan Khet-Modelrapc80No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Abbottabad DistrictDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 1 Abbottabad DistrictTaimur Hyat-KhanNo ratings yet
- Geology 1010 Self-Guided Field Trip InvestigationDocument11 pagesGeology 1010 Self-Guided Field Trip Investigationapi-317455186No ratings yet
- Biodiversity News #72 - SpringDocument34 pagesBiodiversity News #72 - SpringThomasEngstNo ratings yet
- Kurnool 2015Document289 pagesKurnool 2015singam v reddyNo ratings yet
- 29 (A Math CD)Document13 pages29 (A Math CD)Qhayyum HakiemNo ratings yet
- Engineering ProfessionDocument26 pagesEngineering ProfessionTyn MaturanNo ratings yet