Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculating Conduit Capacity PDF
Uploaded by
TTaanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculating Conduit Capacity PDF
Uploaded by
TTaanCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Reference
Calculating Conduit Capacity
One Cable Type in Conduit National Electrical Code, and is calculated on the area of the cable with 40% of the
conduit filled. For conduit runs of 50 to 100 feet, the installed number should be
The following information is to provide you with a quick and easy reference for conduit fill reduced by 15%, or use the next larger size conduit. If more than two 90 degree
requirements. This information is to be used as a general guideline. Each installation has bends are to be used in the conduit run, or if the run is to be over 100 feet in length,
different restrictions for installation environments and/or local codes to follow. insert a pull box.
The Conduit Capacity Chart provided on the following page is for applications when only An anti-friction agent is recommended in pulling operations.
one type of cable is to be used in a conduit. For example, if you know the diameter of the *CAUTION: Select an anti-friction agent which is suitable for the cable jacket material.
cable you will be installing, use the cable O.D. column, and find the exact or next largest The electronic characteristics of unjacketed cable may change due to the
diameter cable O.D.. Next, follow this row over to the number of cables you need to install application of anti-friction agents.
in a conduit. Then follow this column to the top of the chart and read the conduit size * COLD ENVIRONMENT PRECAUTION: Due to the nature of PVC compounds to
required for the number of cables you need to install. become non-pliable when stored or handled in ambient temperatures of
32 degrees F or less, we recommend the following:
"Prior to installation, condition the cable for at least 24 hours
Multiple Types of Cable in One Conduit at room temperature to provide the best flex properties
If you will be mixing various cable diameters in a conduit, then this overall chart does for ease of installation."
not apply. You will have to use the following guidelines to calculate the conduit fill Permissible area chart does not apply to metallic and non-metallic surface raceways;
requirements. consult the NEC for recommendations.
To determine the conduit size required for a particular installation of cable follow THE NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE FORBIDS
these steps: THE INSTALLATION OF COMMUNICATION CABLE
IN THE SAME CONDUIT AS POWER CABLE.
1. Square the O.D. of each cable and total the results.
2. Multiply the total by .7854*. This is the total area of
the cables in square inches. Pulling Tensions
3. From the Permissible Area row on the Conduit
Capacity Chart shown on the following page, select the Under the stress of approximately 15,000 lbs./sq. in. annealed copper will begin to
conduit size with an area equal to or greater than the permanently stretch. The table below lists the absolute maximum recommended pulling
total area you calculated. tensions for conductor sizes. For multiple conductor cable, multiply the appropriate value
* See Important Notes and by the total number of conductors. These pulling tensions must be equally distributed
Installation Suggestions among the conductors.
** Permissible Area to be occupied (sq. in.) is based on the
NEC standard of 40% fill, which applies to three or more THESE LIMITS MUST NEVER BE EXCEEDED
non-lead covered cable installed in the same conduit. EVEN MOMENTARILY!
DONT JERK THE CABLE!
The electronic characteristics of a cable may change due to
Important Notes and excessive tension and crushing.
Installation Suggestions
A single cable is permitted to occupy 53% and two cables are limited to 31% conduit Max. Pulling
Gauge
fill. For a single cable use .5927 in step 2, for two cables use 1.1034, and three Tension
or more cables use .7854. 24 AWG 4 lbs.
This chart is based on the maximum number of cable permitted in conduit under the 22 AWG 7 lbs.
20 AWG 12 lbs.
18 AWG 19 lbs.
16 AWG 30 lbs.
14 AWG 48 lbs.
12 AWG 77 lbs.
182
You might also like
- CABLES - Nexans - Lov Voltage CablesDocument112 pagesCABLES - Nexans - Lov Voltage CablesCET INGENIERIANo ratings yet
- Busbar CalDocument7 pagesBusbar Calajay cabreraNo ratings yet
- Catalogue TA Cable Plug RaychemDocument44 pagesCatalogue TA Cable Plug Raychemlehaphuong03100% (1)
- Grounding and Earthing For Genset - Reference Paper1 PDFDocument5 pagesGrounding and Earthing For Genset - Reference Paper1 PDFBrian RomanoNo ratings yet
- 1q07 Field Wiring PDFDocument8 pages1q07 Field Wiring PDFMWBABARNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar CalculationDocument13 pagesBus Bar CalculationاحمدرضاNo ratings yet
- Basic Nec Code Rules and Design PracticeDocument13 pagesBasic Nec Code Rules and Design PracticeSiswoyo Suwidji100% (1)
- Connector: 6.2mm Pitch/disconnectable Crimp Style ConnectorsDocument5 pagesConnector: 6.2mm Pitch/disconnectable Crimp Style ConnectorsRok HermanNo ratings yet
- Lowenberg1952 PDFDocument1 pageLowenberg1952 PDFKundan DuttaNo ratings yet
- Cable Carriers - Energy Chain Cable and Hose PackagesDocument5 pagesCable Carriers - Energy Chain Cable and Hose PackagesThomas VargheseNo ratings yet
- An 916Document10 pagesAn 916Socheat SonNo ratings yet
- Catalogue TE Raychem 24kV - 36kVDocument44 pagesCatalogue TE Raychem 24kV - 36kVTrần ChèNo ratings yet
- Bahrain Projects Important PointsDocument6 pagesBahrain Projects Important PointsDawoodNo ratings yet
- Underground Cable Ampacity With Neher McGrathDocument7 pagesUnderground Cable Ampacity With Neher McGrathJesus RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BusBar LiteratureDocument4 pagesBusBar LiteratureschaktenNo ratings yet
- ELR 02V JST Datasheet 62343639Document4 pagesELR 02V JST Datasheet 62343639etudiant.bouzekri.houdaNo ratings yet
- Electrical InstallationDocument47 pagesElectrical InstallationMalshi EkanayakaNo ratings yet
- E7D60B35 B2F4 4C42 F: (G) Corrosive Conditions. Conductors Exposed To OilsDocument1 pageE7D60B35 B2F4 4C42 F: (G) Corrosive Conditions. Conductors Exposed To OilsaharchtopiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument78 pagesUntitledZeri FalmizaNo ratings yet
- Cover MVDocument6 pagesCover MVFani Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- Busbar DetailsDocument12 pagesBusbar DetailsAjay SheeNo ratings yet
- Power Engineering: Sunday, 27 October 2013Document12 pagesPower Engineering: Sunday, 27 October 2013Ajay SheeNo ratings yet
- Busbar DetailsDocument12 pagesBusbar DetailsAjay SheeNo ratings yet
- Busbar DetailsDocument12 pagesBusbar DetailsAjay SheeNo ratings yet
- BUSBAR Size and CapacityDocument8 pagesBUSBAR Size and CapacityJohn Garnet50% (2)
- Cable Laying Techniques: Torrent Power (Surat)Document26 pagesCable Laying Techniques: Torrent Power (Surat)Sanju GohilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2a: Conductor Ampacity - Terminations and Derating FactorsDocument62 pagesLecture 2a: Conductor Ampacity - Terminations and Derating FactorsAntonNo ratings yet
- 11.4.1 Stringing: LS - "-Ca SystemDocument1 page11.4.1 Stringing: LS - "-Ca SystemErolNo ratings yet
- Bare Aluminum Wire and Cable Installation Practices PDFDocument28 pagesBare Aluminum Wire and Cable Installation Practices PDFtedNo ratings yet
- Voltage Supply Control Device LoadDocument37 pagesVoltage Supply Control Device LoadSyed Foysol IslamNo ratings yet
- Conductor Size, General: Table C-2 NEC References For Conductor SizingDocument4 pagesConductor Size, General: Table C-2 NEC References For Conductor SizingYashwanth NNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring Residential Canadian 7th Edition Mullin Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesElectrical Wiring Residential Canadian 7th Edition Mullin Solutions Manualallisondoylenqmsgyicjb100% (27)
- Fdok Ls Fdok RD DH JSFVR Oksyvst Osq LKFK Fo - QR Osqcy DH Vuq'Kaflr 'KKVZ Js VX Fof'Kf"VDocument9 pagesFdok Ls Fdok RD DH JSFVR Oksyvst Osq LKFK Fo - QR Osqcy DH Vuq'Kaflr 'KKVZ Js VX Fof'Kf"VAshish bhattNo ratings yet
- Low-Voltage Electrical Power Conductors and Cables SpecDocument9 pagesLow-Voltage Electrical Power Conductors and Cables SpecDenyNo ratings yet
- 1DB 38062 enDocument2 pages1DB 38062 enIkhuosho AbodeNo ratings yet
- OCC-206-3 Installation-Conduit Guidelines Rev A-1Document6 pagesOCC-206-3 Installation-Conduit Guidelines Rev A-1SAMNo ratings yet
- Helukabel 1DB 33054 enDocument2 pagesHelukabel 1DB 33054 enLaurentiu CatalinNo ratings yet
- U W Electrical Wire, Cable and Terminations: Engineering Services Facility Design InformationDocument12 pagesU W Electrical Wire, Cable and Terminations: Engineering Services Facility Design InformationAhmed EzzatNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Cable SelectionDocument12 pagesPractical Guide To Cable Selectionazitagg100% (1)
- Experiment No. 5 Sizing and Selection of Neutral LinkDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 5 Sizing and Selection of Neutral LinkJude JohnNo ratings yet
- Man0799 01Document18 pagesMan0799 01Haris PolutanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Electrical Circuit in BuildingsDocument34 pagesLecture 4 - Electrical Circuit in BuildingsMar VenNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring Industrial Canadian 5th Edition Herman Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesElectrical Wiring Industrial Canadian 5th Edition Herman Solutions ManualKimCoffeyjndf100% (39)
- Anixter Minimum Bending Radius Wire Wisdom en PDFDocument1 pageAnixter Minimum Bending Radius Wire Wisdom en PDFAndrew Ixara AribowoNo ratings yet
- Basic Cable&Cable CareDocument45 pagesBasic Cable&Cable CarePrakhar Sarkar100% (1)
- Measure Distance for DSL DeliveryDocument2 pagesMeasure Distance for DSL Deliverybhaskar2000_inNo ratings yet
- Sizing of Protective Earthing ConductorDocument3 pagesSizing of Protective Earthing ConductorSarmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Sizing CircuitsDocument130 pagesSizing Circuitsinhenyeronerb100% (17)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Capacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsFrom EverandCapacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Radio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsFrom EverandRadio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- MV network design & devices selection guideDocument31 pagesMV network design & devices selection guideAnonymous kdFzbQ4jfNo ratings yet
- CB Vs ContactorDocument2 pagesCB Vs ContactorAmit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Right-of-Way Q&As For The Clean Power Call PDFDocument2 pagesRight-of-Way Q&As For The Clean Power Call PDFTTaanNo ratings yet
- Allen-Bradley - JACE 8000 IO Sell Sheet Tri 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesAllen-Bradley - JACE 8000 IO Sell Sheet Tri 2017 PDFTTaanNo ratings yet
- What's New in C37.113 - 2015, IEEE Guide For Protective Relay Applications To Transmission LinesDocument6 pagesWhat's New in C37.113 - 2015, IEEE Guide For Protective Relay Applications To Transmission LinesTTaan0% (1)
- Ger 4002Document14 pagesGer 4002Asanga HarshanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1sunny1725No ratings yet
- Alberta Environment Guidelines for Transmission Line R&RDocument5 pagesAlberta Environment Guidelines for Transmission Line R&RTTaanNo ratings yet
- Current TransformerDocument9 pagesCurrent TransformerRiyah_Rae80% (5)
- CIRED2011 0915 Final PDFDocument4 pagesCIRED2011 0915 Final PDFTTaanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document6 pagesLecture 4argari19No ratings yet
- What's New in C37.113 - 2015, IEEE Guide For Protective Relay Applications To Transmission LinesDocument6 pagesWhat's New in C37.113 - 2015, IEEE Guide For Protective Relay Applications To Transmission LinesTTaan0% (1)
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocument13 pagesThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingrajeshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus ProtectionDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus Protectionsunny1725No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocument13 pagesThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingrajeshNo ratings yet
- Electrical Relay Diagram SymbolsDocument5 pagesElectrical Relay Diagram SymbolsKARAM ZAKARIANo ratings yet
- Backup To Busbar Protection With Numerical Distance ProtectionDocument4 pagesBackup To Busbar Protection With Numerical Distance ProtectionTran Cong ThanhNo ratings yet
- Ger 4002Document14 pagesGer 4002Asanga HarshanNo ratings yet
- Ger 4002Document14 pagesGer 4002Asanga HarshanNo ratings yet
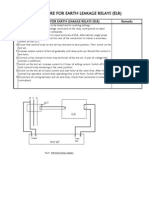
- Testing Procedure For Earth Leakage RelaysDocument1 pageTesting Procedure For Earth Leakage RelaysSimon Condor67% (3)
- Application of Peer-To-Peer Communication For Protective Relaying PDFDocument6 pagesApplication of Peer-To-Peer Communication For Protective Relaying PDFtobyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 323Document5 pagesLecture 323biswa217No ratings yet
- PA Open Book Reference 2015 PDFDocument1 pagePA Open Book Reference 2015 PDFTTaanNo ratings yet
- Relay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationDocument8 pagesRelay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationhariNo ratings yet
- GE Multilin Relay Selection GuideDocument40 pagesGE Multilin Relay Selection GuideSaravanan Natarajan100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionpata nahi hai mujeNo ratings yet
- Contact SystemDocument52 pagesContact SystemdrivetecNo ratings yet
- Relay DefinitionsDocument16 pagesRelay DefinitionsAamir BalochNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1sunny1725No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus ProtectionDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus Protectionsunny1725No ratings yet
- Bank StatementDocument23 pagesBank StatementKundan Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Training MatrixDocument4 pagesTraining MatrixJennyfer Banez Nipales100% (1)
- Ilo MLCDocument66 pagesIlo MLCcarmenNo ratings yet
- The Cucumber Book Behaviour-Driven Development For Testers and DevelopersDocument28 pagesThe Cucumber Book Behaviour-Driven Development For Testers and DevelopersGursharan AulakhNo ratings yet
- Spo2 M1191aDocument247 pagesSpo2 M1191ashashibiya33No ratings yet
- III International Congress on Teaching Cases Related to Public and Nonprofit Marketing: Nestlé's CSR in Moga District, IndiaDocument8 pagesIII International Congress on Teaching Cases Related to Public and Nonprofit Marketing: Nestlé's CSR in Moga District, IndiaIshita KotakNo ratings yet
- Over 20 free and paid Pathfinder 2E character sheet optionsDocument1 pageOver 20 free and paid Pathfinder 2E character sheet optionsravardieresudNo ratings yet
- Drilling and Demolition: Hilti. Outperform. OutlastDocument48 pagesDrilling and Demolition: Hilti. Outperform. OutlastVinicius CoimbraNo ratings yet
- ERP ImplementationDocument47 pagesERP Implementationattarjaved100% (1)
- Natural DyeDocument21 pagesNatural Dyesanjay shettiNo ratings yet
- Catalogue: See Colour in A Whole New LightDocument17 pagesCatalogue: See Colour in A Whole New LightManuel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Grasshopper VB Scripting Primer IntroductionDocument28 pagesGrasshopper VB Scripting Primer Introductionfagus67No ratings yet
- Enter The Data Below: Sample PDF Only From Excel CalculationDocument1 pageEnter The Data Below: Sample PDF Only From Excel CalculationWilson (Electrical Engineer)No ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques For Implementing Integrated Performance Management Systems PDFDocument36 pagesTools and Techniques For Implementing Integrated Performance Management Systems PDFDobu KolobingoNo ratings yet
- CIA Interview GuideDocument14 pagesCIA Interview GuideCody ToebbickeNo ratings yet
- Jameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryDocument4 pagesJameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryKarthikmds ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Action Research HandoutDocument2 pagesAction Research HandoutgeethamadhuNo ratings yet
- Unified HSE Passport Standard LRDocument60 pagesUnified HSE Passport Standard LRSHRISH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Communicating Corporate Social Responsibility: Perspectives and PracticeDocument26 pagesCommunicating Corporate Social Responsibility: Perspectives and PracticeAndiMuhammadIrwanNo ratings yet
- Politische StrategiesEnd 2012 de en FINALDocument405 pagesPolitische StrategiesEnd 2012 de en FINALFomeNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The Third International Conference On Computational Intelligence and InformaticsDocument881 pagesProceedings of The Third International Conference On Computational Intelligence and InformaticsJanes DstNo ratings yet
- Municipal Tax Dispute Over Petroleum Refinery in PilillaDocument5 pagesMunicipal Tax Dispute Over Petroleum Refinery in PilillaDaphne Jade Estandarte PanesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Value at Risk with F&S Investments PortfolioDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Value at Risk with F&S Investments Portfolio7aadkhan100% (2)
- الصراع التنظيمي وأثره...Document25 pagesالصراع التنظيمي وأثره...mohmod moohNo ratings yet
- RLE Journal CoverDocument2 pagesRLE Journal Coverrchellee689No ratings yet
- Pe-501003-009 STPDocument9 pagesPe-501003-009 STPJeyakumar ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 72-76 kW 310SK/310SK TC Compact Track Loader SpecsDocument10 pages72-76 kW 310SK/310SK TC Compact Track Loader SpecsPerrote Caruso PerritoNo ratings yet
- QRHDocument12 pagesQRHNwe OoNo ratings yet
- Completing The Accounting Cycle: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDocument57 pagesCompleting The Accounting Cycle: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedPham Thi Hoa (K14 DN)No ratings yet
- Jan 2012Document40 pagesJan 2012Daneshwer Verma100% (1)