Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics::Gregor Mendel Used Garden Peas To Illustrate The Mechanisms of Heredity
Uploaded by
Maila Galimba CastilloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics::Gregor Mendel Used Garden Peas To Illustrate The Mechanisms of Heredity
Uploaded by
Maila Galimba CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics
Main idea:Gregor Mendel used garden peas to illustrate the mechanisms of heredity.
Gregor johann mendel (1822-1884) is the father of genetics. He entered the monastery at the
age of 21 and became a priest four years later. He presented his work in pea plants at the
society for the Study of natural Science in 1866. However, the scientific community paid little
attention to his work. He died in 1884, disappointed that his research had not been recognized.
In 1900s, however, the scientific community accepted and acknowledged the importance of his
work. To date, the basic principles of genetic inheritance, as laid down by Gregor Mendel, are
still valid and remain the cornerstone of the study of genetics.
The scientific study of heredity started with the experiments of the Austrian priest gregor
johann mendel . mendel bred different varieties of garden peas and cross-pollinated flowers
that had clearly different forms of traits. Such contrasting expression or alternative forms of a
trait called ALLELES.
His experiments were considered cutting edge during his time because he did not only observe
the kind of offspring produced by a particular cross but also counted the number of each kind
(use of quantitive approach to science), analyzed his data, made generilizations, and proposed
explanations for his results. In 1866, after almost a decade of breeding experiments with garden
peas(PISUM SATIVUM)
MONOHYBRID INHERITANCE
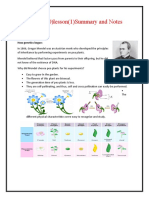
A monohybrid cross involves the inheritance of one trait only.Mendel cross-polinated
garden peas with contrasting expressions. Inheritance involving one pair of contrasting
characters (alleles) is called monohybrid inheritance. Mendel crossed two pure-breeding
garden peas, one with a purple flower, the other with a white flower. This type of cross is
called MONOHYBIRD CROSS. Pure-breeding plants produce only one form of a particular
trait when they self-fertilize. These pure breeding plants served as the parental generation
in Mendels experiments. The parental generation (represented as P) are the first two
organisms that are crossed in a breeding experiment.
In the study of genetics, symbols are used to represent individual organisms. The two
pure-breeding parents (P generation) are represented with PP and pp for purple and
white, respectively. Often the first letter of either alleles is used as a symbol. The symbol
P and p represent the genotype of the individual.
A genotype is the gene that is responsible for the observed trait.
A phenotype is the observable expressions of the trait.
You might also like
- Mendel's Laws of Inheritance (Notes) : CharactersDocument15 pagesMendel's Laws of Inheritance (Notes) : Characterssahoo&sahoo akashNo ratings yet
- Gregor Mendel The Father of GeneticsDocument2 pagesGregor Mendel The Father of GeneticsAnonymous BBs1xxk96VNo ratings yet
- Mendel and The Principles of HeredityDocument61 pagesMendel and The Principles of Heredityfae-ar_raziNo ratings yet
- Inheritance ChapterDocument26 pagesInheritance Chapterainaansari2212No ratings yet
- Gregor Johann MendelDocument18 pagesGregor Johann Mendeldeepthi k thomas100% (1)
- Lesson Plan..Document4 pagesLesson Plan..Yhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Mendelian genetics principles explainedDocument2 pagesMendelian genetics principles explainedAiki KajiuraNo ratings yet
- Genetics According to Mendel: Mendel's DiscoveriesDocument34 pagesGenetics According to Mendel: Mendel's DiscoveriesVaxo ChagalidzeNo ratings yet
- Classical (Mendelian) GeneticsDocument32 pagesClassical (Mendelian) GeneticsKOMAL FATIMANo ratings yet
- Fairbanks and Rytting (2001) Controversies On Mendel WorkDocument16 pagesFairbanks and Rytting (2001) Controversies On Mendel WorkCamilo Ernesto Araujo BarabasNo ratings yet
- Gregor Mendel - The Grandfather of GeneticsDocument8 pagesGregor Mendel - The Grandfather of GeneticsPogi BearNo ratings yet
- Abstract and I. Introduction (Lab Report)Document9 pagesAbstract and I. Introduction (Lab Report)Endaya Kristel D.No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument62 pagesGeneticsgwormtalaveraNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument32 pagesGeneticsriyanshis892No ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument3 pagesGregor MendelhdNo ratings yet
- Genetics Is The Study of Heredity. Heredity Is A Biological Process Where A ParentDocument1 pageGenetics Is The Study of Heredity. Heredity Is A Biological Process Where A ParentHannah Dela Cruz LayosaNo ratings yet
- Final Mendel Law 2Document9 pagesFinal Mendel Law 2ravip_29No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document35 pagesChapter 14nfacmaNo ratings yet
- Single Gene Inheritance HandoutDocument16 pagesSingle Gene Inheritance HandoutMarel LatawanNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Laws of Inheritance ExplainedDocument9 pagesMendel's Laws of Inheritance Explainedsaniya nanheNo ratings yet
- Abstract and Introduction (Lab Report)Document9 pagesAbstract and Introduction (Lab Report)Endaya Kristel D.No ratings yet
- Mendel's Genetics Experiments on Pea PlantsDocument13 pagesMendel's Genetics Experiments on Pea PlantsResna N K ResiNo ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument5 pagesGregor MendelMihret GelanNo ratings yet
- Mendel GregorDocument3 pagesMendel GregorTricia AvilaNo ratings yet
- MAJORSHIP BiosciDocument109 pagesMAJORSHIP BiosciMary Rose DasallaNo ratings yet
- MendelDocument2 pagesMendelGADY VELAG VECABNo ratings yet
- How Gregor Mendel's pea plant experiments uncovered principles of inheritanceDocument7 pagesHow Gregor Mendel's pea plant experiments uncovered principles of inheritanceMichael SopranoNo ratings yet
- RPP - Pewarisan Sifat Inggris Silabus RsbiDocument14 pagesRPP - Pewarisan Sifat Inggris Silabus RsbiAgus Joko SungkonoNo ratings yet
- m4- Patterns of Mendelian InheritanceDocument32 pagesm4- Patterns of Mendelian InheritanceDaisy RamaNo ratings yet
- Gregor Mendel: ND THDocument2 pagesGregor Mendel: ND THAnonymous w5Sc1OpHtKNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Topic 4 Hand OutDocument23 pagesCytogenetics Topic 4 Hand OutJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- Gregor Johann Mendel: 20 July 1822-6 January 1884Document4 pagesGregor Johann Mendel: 20 July 1822-6 January 1884Yuki NakataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Notes 2014Document15 pagesChapter 14 Notes 2014Adeela AashiNo ratings yet
- GregormendelandhispeasreadingandquestionsDocument2 pagesGregormendelandhispeasreadingandquestionsapi-248015505No ratings yet
- That Deals With Heredity and Variation of Organisms.: GENETICS - Branch of BiologyDocument8 pagesThat Deals With Heredity and Variation of Organisms.: GENETICS - Branch of BiologyBenedict OcampoNo ratings yet
- MedilianismDocument16 pagesMedilianismYujin AhnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 OutlineDocument16 pagesChapter 14 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument7 pagesReportMax RosadoNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument23 pagesMendelian GeneticsPallavi Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Law of SegregationDocument3 pagesLaw of SegregationMichael SopranoNo ratings yet
- Mendel'S Experiments and The Laws of Probability: Openstax CollegeDocument12 pagesMendel'S Experiments and The Laws of Probability: Openstax CollegeSantiagoNo ratings yet
- MELC 1&2 Phenotype-GenotypeDocument38 pagesMELC 1&2 Phenotype-GenotypeMary Rose Jusay GumapacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Pedigree AnalysisDocument4 pagesLesson 1. Pedigree AnalysisSheryl Lou AngelesNo ratings yet
- History of Genetics - BargayoDocument14 pagesHistory of Genetics - BargayoDarling Jen Saranillo BargayoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyEngr. Christopher Lennon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- REPORT 1 Patterns of InheritanceDocument41 pagesREPORT 1 Patterns of InheritanceJeanette FormenteraNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Lesson ScriptDocument7 pagesMendelian Genetics Lesson ScriptCamille AquinoNo ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument7 pagesGregor MendelMitkoNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Genetics ExplainedDocument25 pagesHeredity and Genetics ExplainedPhilpNil8000No ratings yet
- Lab 02 - Mendelian GeneticsDocument13 pagesLab 02 - Mendelian Genetics13ucciNo ratings yet
- Mendel LegacyDocument1 pageMendel LegacyrosaspukekonakulayNo ratings yet
- Genetics Study GuideDocument7 pagesGenetics Study GuideAanav MittalNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument7 pagesMendelian GeneticsChiqui Caday JimenezNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Laws: Genetics Principles from Pea Plant ExperimentsDocument6 pagesMendel's Laws: Genetics Principles from Pea Plant ExperimentsAhmad AlabdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Pre Post MendelianDocument5 pagesPre Post Mendeliansakshi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument10 pagesGregor Mendelapi-262000934No ratings yet
- How Mendel's Pea Experiments Laid the Foundation of Modern GeneticsDocument4 pagesHow Mendel's Pea Experiments Laid the Foundation of Modern GeneticsRazvan RzNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Principles: Laws of Inheritance and Genetics ExperimentsDocument26 pagesMendelian Principles: Laws of Inheritance and Genetics ExperimentsbjkopparNo ratings yet
- I Got It from My Mama! Gregor Mendel Explains Heredity - Science Book Age 9 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandI Got It from My Mama! Gregor Mendel Explains Heredity - Science Book Age 9 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species by Charles Darwin - Delphi Classics (Illustrated)From EverandThe Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species by Charles Darwin - Delphi Classics (Illustrated)No ratings yet
- Hold Your Throat and SayDocument12 pagesHold Your Throat and SayMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Report in Science EducationDocument1 pageReport in Science EducationMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ecology InventoryDocument6 pagesEcology InventoryMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Rice Hay (Oryza Sativa, Linn) Fridge Deodorizer: Ilocos Sur Polytechnic State College - Graduate SchoolDocument2 pagesRice Hay (Oryza Sativa, Linn) Fridge Deodorizer: Ilocos Sur Polytechnic State College - Graduate SchoolMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Role Play - Rubric 1Document1 pageRole Play - Rubric 1Siti ShalihaNo ratings yet
- Why Conserve Trees and ForestsDocument3 pagesWhy Conserve Trees and ForestsMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Professional Development Plan To Improve Teaching and Learning Level IIIDocument3 pagesProfessional Development Plan To Improve Teaching and Learning Level IIIMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Honor Veterans Program EMCEE GuideDocument2 pagesHonor Veterans Program EMCEE GuideMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- SAG Horticulture NC II PDFDocument7 pagesSAG Horticulture NC II PDFMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Marine Ecosystems: Maila B. GalimbaDocument53 pagesMarine Ecosystems: Maila B. GalimbaMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Strategies Involving Transformation: Presented By: Maila B. GalimbaDocument14 pagesStrategies Involving Transformation: Presented By: Maila B. GalimbaMaila Galimba CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Log 7 (First Quarter)Document6 pagesLesson Log 7 (First Quarter)Maila Galimba Castillo90% (20)
- Life Sciences Part 2 Csir JRF Net Gate DBTDocument167 pagesLife Sciences Part 2 Csir JRF Net Gate DBTNOORUDDINNo ratings yet
- GregormendelandhispeasreadingandquestionsDocument2 pagesGregormendelandhispeasreadingandquestionsapi-248015505No ratings yet
- How Social Inequality Affects Different Groups in SocietyDocument42 pagesHow Social Inequality Affects Different Groups in SocietyMustaffa MansoorNo ratings yet
- Genetic Basis of Inheritance: Types of Phenotypic TraitsDocument16 pagesGenetic Basis of Inheritance: Types of Phenotypic TraitsknlsinhaNo ratings yet
- The Fetal MatrixDocument273 pagesThe Fetal MatrixMonica Surdu100% (1)
- Blending TheoryDocument7 pagesBlending TheoryM Zahid Gondal100% (3)
- CBSE CBSE Class 10 Science Solved Question Paper 2015Document13 pagesCBSE CBSE Class 10 Science Solved Question Paper 2015s k kumarNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Genetics ExperimentsDocument6 pagesMendel's Genetics ExperimentsnancamarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeneticsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To GeneticsCaptain WolfNo ratings yet
- Seerat e Ameer Al Momineen Mufti JafarDocument574 pagesSeerat e Ameer Al Momineen Mufti Jafarwww.alhassanain.org.english100% (5)
- Kendler 2005Document10 pagesKendler 2005MaximilianNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Vocabulary Literay - Student GuideDocument6 pagesActivity 1 Vocabulary Literay - Student Guideapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Bsczo 103 PDFDocument241 pagesBsczo 103 PDFNeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- AGB 121: Principles Of Animal GeneticsDocument299 pagesAGB 121: Principles Of Animal GeneticsDeep PatelNo ratings yet
- Preguntas InglesDocument18 pagesPreguntas InglesLalo GarduñoNo ratings yet
- Mendel'S Experiments and The Laws of Probability: Openstax CollegeDocument12 pagesMendel'S Experiments and The Laws of Probability: Openstax CollegeSantiagoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance & VariationsDocument59 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance & VariationsChandra VadanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mendelian InheritDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Mendelian InheritDiego Garcia67% (3)
- Mendelian Inheritance - 1Document22 pagesMendelian Inheritance - 1WONG JIE MIN MoeNo ratings yet
- We Spy: Is There Really So MuchDocument36 pagesWe Spy: Is There Really So MuchAldersgate Methodist Church SingaporeNo ratings yet
- The American Biology Teacher: About Our CoverDocument1 pageThe American Biology Teacher: About Our CoverMilawati U.No ratings yet
- How traits are inherited from parentsDocument6 pagesHow traits are inherited from parentsMEHUL SIRNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid CrossDocument2 pagesDihybrid CrossAditi KathaitNo ratings yet
- Assessing English Competence Using VocabularyDocument18 pagesAssessing English Competence Using VocabularyNovi FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Eng 306 - Doc 3 - 2020f - Extra ReadingDocument163 pagesEng 306 - Doc 3 - 2020f - Extra ReadingNguyen Anh TaiNo ratings yet
- Building A Better Teacher How Teaching Works, Green PDFDocument809 pagesBuilding A Better Teacher How Teaching Works, Green PDFluizdasilvaazevedoNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument9 pagesHereditysong MusicNo ratings yet
- Physical Basis of HeredityDocument24 pagesPhysical Basis of HeredityEniola abdullahi AduagbaNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments Reveal Laws of InheritanceDocument16 pagesMendel's Pea Plant Experiments Reveal Laws of InheritanceJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology as a Neuroscience - Four ThemesDocument37 pagesBiopsychology as a Neuroscience - Four ThemesJohnreih BanggaNo ratings yet