Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verb Tenses 2016
Uploaded by
siranthony44Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb Tenses 2016
Uploaded by
siranthony44Copyright:
Available Formats
VERB TENSES.
VERB: To speak spoke spoken. (INFINITIVE - SIMPLE PAST - PAST PARTICIPLE.
To be - was/were - been = estar.
To have - had - had = haber.
INFINITIVE.
To + verbo (to speak, to eat, etc.)
-ar, -er, -ir (amar, comer, rer)
To speak = Hablar.
To eat = Comer.
GERUND or -ING FORM.
-ando, -endo (estudiando, comiendo, riendo)
Studying = estudiando.
Eating = comiendo.
PAST PARTICIPLE. (3 columna de los verbos irregulares).
-ado, -ido, -ito, -oto, -cho, -so (amado, comido, redo, escrito, roto, hecho, impreso)
Written = escrito.
Eaten = comido.
CONTINUOUS or PROGRESSIVE
TO BE (am, is, are, was or were) + -ing.
Estar + -ando, -endo (amando, comiendo, riendo)
PERFECT.
TO HAVE (have / has / had) + Past Participle
Haber + -ado, -ido, -ito, -oto, -cho, -so (amado, comido, redo, escrito, roto, hecho, impreso)
We have spoken = Nosotros hemos hablado.
They had eaten = Ellos haban comido.
Verb Tenses, p.1
ACTIVE VOICE: MOODS AND TENSES.
VERB: To speak spoke spoken. (INFINITIVE - SIMPLE PAST - PAST PARTICIPLE.
-ar, -er, -ir (amar, comer, rer) Infinitive = To + verbo (to speak, to eat, etc.)
-ando, -endo (amando, comiendo, riendo) Gerund = -ing Form (speaking, eating, etc.)
-ado, -ido, -ito, -oto (amado, comido, redo, escrito, roto) Past participle (3 columna de los verbos, spoken, eaten, etc.)
CONTINUOUS = Progressive = To be + -ing. Estar + -ando, -endo (amando, comiendo, riendo)
PERFECT have / has / had + Past Participle (have spoken, had eaten, etc.) Haber + -ado, -ido (amado, comido, redo)
INDICATIVE MOOD.
The indicative is the mood of the verb used in objective statements or questions.
English Tense Form Translation
Tiempo en espaol
Infinitive Infinitive To speak Hablar
Infinitivo
Infinitive progressive To be speaking Estar hablando
Infinitivo progresivo
-ing form Gerund Speaking Hablando
Gerundio
Participle Past participle Spoken Hablado
Participio de pasado
Past participle progressive Be spoken Ser hablado
Participio de pasado progresivo
Present Simple present I speak Hablo
Presente Simple She speaks Ella habla
Present progressive I am speaking Estoy hablando / hablo
Presente progresivo
Present perfect I have spoken He hablado
Pretrito perfecto
Present perfect progressive I have been speaking He estado hablando
Pretrito perfecto progresivo
Past Simple past I spoke Habl, hablaba / hablara
Pasado simple
Past progressive I was speaking Estuve / estaba
Pasado progresivo hablando
Past perfect I had spoken Haba hablado
Pretrito pluscuamperfecto
Past perfect progressive I had been speaking Haba estado hablando
Pretrito pluscuamperfecto
progresivo
Future Simple future I will speak Hablar
Futuro simple
Verb Tenses, p.2
Simple future progressive I will be speaking Estar hablando
Futuro simple progresivo
Future perfect I will have spoken Habr hablado
Futuro perfecto
Future perfect progressive I will have been speaking Habr estado hablando
Futuro perfecto progresivo
Conditional Simple conditional I would speak Hablara
Condicional simple
Simple conditional progressive I would be speaking Estara hablando
Condicional simple progresivo
Perfect conditional I would have spoken Habra hablado
Condicional perfecto
Perfect conditional progressive I would have been speaking Habra estado hablando
Condicional perfecto progresivo
Verb Tenses, p.3
SUBJUNTIVE MOOD.
It is used in subordinate clauses in which there is a change of subject and indicates that a situation is hypothetical, unreal, wished or
hoped for, or somehow speculative in nature. It is used in direct commands (except familiar) in which the third persons are usually
introduced by que.
In English it has only one form which coincides with the stem of the verb (infinitive without TO)
She demands that he speak (Ella solicita que el hable).
IMPERATIVE MOOD.
It is used to give a command or make a suggestion.
Imperative 2nd person singular & Speak Habla / Hablad
plural
1st person plural Let's speak Hablemos
CONDITIONAL MOOD.
It uses the construction "if... then..." It expresses the hypothetical, unreal, or speculative, and states the condition under which another
action or event may be realized.
Verb Tenses, p.4
USES.
SIMPLE PRESENT
For things that we do regularly and habits:
She goes to the beach every day.
Adverbs of frequency are often used with the simple present to talk about regular and habitual actions:
I never smoke.
To talk about facts or things that are always true:
The sun rises in the east.
To talk about a future, timetabled event:
My plane leaves at 10:15 a.m.
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
To talk about things that are in progress now:
Its raining now.
To talk about temporary situations:
We are staying in a hotel.
To talk about the future arrangements:
Im seeing the doctor on Thursday.
PAST SIMPLE
To talk about completed events or actions in the past:
My brother left school in 1998.
To talk about something that happened regularly in the past:
I walked to school every morning.
SIMPLE PAST WITH AGO
It tells us about the length of time between now and then:
I came to La Orotava eight years ago.
PAST CONTINUOUS
To talk about something that was in progress at a certain time in the past:
At 11:30 I was watching a film on TV.
To talk about an interrupted action in the past:
I was having a shower when the phone rang.
After WHILE or AS:
While I was waiting for the bus, a car stopped.
As he was walking past, he saw me.
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE
To talk about something that started in the past and continues in the present:
Ive lived here all my life.
To talk about experiences in our lives up to the present when no particular time is mentioned:
Ive visited Spain, but Ive never been to Portugal.
Use JUST + Present Perfect to talk about something which has happened recently and which is still true or important now:
Ive just spent 10,000 pts.
We dont use the present perfect if we know when something happened:
Tom just phoned 30 seconds ago (Tom has just phoned 30 seconds ago)
The Present Perfect with FOR or SINCE tells us about something which began in the past and is still true now. It answers the question:
How long ? FOR tells us the period of time. SINCE tells us when the time began:
Shes been blind for 30 years.
Shes been blind since birth.
Hes had his dog for 10 years.
Hes had his dog since 1990.
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
To talk about past activities that have a result in the present:
They have been working hard all morning. Now theyre tired.
It can be used for an action which began in the past, is still true now and which has been continuous or repeated. Because it looks at
actions over a period of time, it is often used with FOR or SINCE:
Surgeons have been performing operations for hundreds of years.
Doctors have been using anaesthetics since 1842.
PAST PERFECT SIMPLE
To talk about past actions or situations which happened before another past action or situation:
She looked in her bag. Shed forgotten her mobile phone!
To talk about events before a specific time in the past:
Verb Tenses, p.5
By 6:00 p.m. we had washed the dishes and cooked a pizza.
FUTURE WITH WILL
To talk about decisions at the moment of speaking:
I think I will cook something nice.
We also use it to talk about possibilities, often after MAYBE or PERHAPS:
Maybe Ill go on a diet.
To talk about general predictions:
I think people will live on the moon.
To talk about things that are certain to happen:
Ill be 18 in November.
FUTURE WITH GOING TO
To talk about our future intentions or plans when a decision has already been made:
I am going to have mushrooms.
We can also use it when we make predictions about the future which are based on present evidence:
Look at those clouds. Its going to rain.
FUTURE CONTINUOUS
To talk about something in progress at a certain time in the future:
What will you be doing at 8 oclock this evening? --I will be watching the match on TV.
FUTURE PERFECT
To talk about something that will be complete by a certain time in the future:
By the time I am 21 I will have left home.
Verb Tenses, p.6
VERBS TENSE MAP.
SIMPLE CONTINUOUS PERFECT PERFECT CONTIN.
PRESENT PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS PRESENT PERFECT PRESENT PERFECT CONT.
I study every day. I am studying right now. I have already studied I have been studying for
lesson one. two hours.
PAST PAST SIMPLE PAST CONTINUOUS PAST PERFECT PAST PERFECT CONT.
I studied yesterday. I was studying when they I had already studied I had been studying for
arrived. lesson one, before I began two hours before my
to study lesson two. friends arrived.
FUTURE FUTURE SIMPLE FUTURE CONTINUOUS FUTURE PERFECT FUTURE PERFECT CONT.
I will study tomorrow. I will be studying when you I will already have studied I will have been studying for
arrive. lesson one, before I study two hours by the time you
lesson two. arrive.
Annotations:
= an action finished
= an action is continuing (it has taken longer time)
= results of an action persists (the action itself finished)
Verb Tenses, p.7
ENGLISH TENSES - GRAPHIC COMPARISON.
LEGEND:
action that takes place once, never or several times
actions that happen one after another
actions that suddenly take place
MOMENT OF TIME
action that started before a certain moment and lasts beyond that
moment
actions taking place at the same time
PERIOD OF TIME
action taking place before a certain moment in time
puts emphasis on the result
RESULT
action taking place before a certain moment in time
puts emphasis on the course or duration of the action
COURSE /
DURATION
Verb Tenses, p.8
You might also like
- Spanish English Verb Tenses 2015Document155 pagesSpanish English Verb Tenses 2015Fernando GarciaNo ratings yet
- Preterite Vs Imperfect - Part IDocument16 pagesPreterite Vs Imperfect - Part IMerecia SmithNo ratings yet
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Ingles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Document46 pagesIngles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Nicolás LaraNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 GR Reported SpeechDocument7 pages4 GR Reported Speechpaula y soniaNo ratings yet
- I Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolDocument11 pagesI Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolEmil FejzagićNo ratings yet
- 34 Verb Forms Prescribed For 3 TensesDocument24 pages34 Verb Forms Prescribed For 3 TensesbishwabengalitolaNo ratings yet
- Notas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Document9 pagesNotas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Anonymous thHFCANo ratings yet
- Diego Tierradentro Clavijo: 94507385 Leonor Vargas Herrera: 66987381Document9 pagesDiego Tierradentro Clavijo: 94507385 Leonor Vargas Herrera: 66987381leonorvhNo ratings yet
- Indicative Subjunctive: Pluperfect ImperfectDocument3 pagesIndicative Subjunctive: Pluperfect ImperfectErwin NuñezNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet English Verb TensesDocument76 pagesSpreadsheet English Verb TensesRamonaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - (Tenses)Document35 pagesLecture - (Tenses)Waqas HafeezNo ratings yet
- Simple Present - Present ProgressiveDocument11 pagesSimple Present - Present Progressivebenmehel abdelkrimNo ratings yet
- She Said, "I Am Tired." She Said That She Was TiredDocument6 pagesShe Said, "I Am Tired." She Said That She Was TiredfahrudinNo ratings yet
- Presente Continuo - InglesDocument14 pagesPresente Continuo - InglesMiyouba CarriganNo ratings yet
- Eng Verb Tenses PDFDocument8 pagesEng Verb Tenses PDFEnilda ReyesNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect ContinuousDocument9 pagesPast Perfect Continuousagnes febrianti putriNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument20 pagesVerb Tensesvpetrovaa23No ratings yet
- Reported Speech TeoriaDocument4 pagesReported Speech TeoriasilviaNo ratings yet
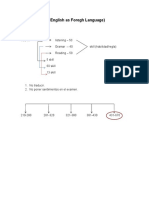
- TOEFL (Test of English As Foregh Language)Document22 pagesTOEFL (Test of English As Foregh Language)Armando SantosNo ratings yet
- BSN1 F - Eng100 Group2Document31 pagesBSN1 F - Eng100 Group2Jerreca DasasNo ratings yet
- Clase de InglesDocument17 pagesClase de InglesByron Bermello ToalaNo ratings yet
- Direct VS Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect VS Indirect SpeechKetua EE 2021 AndrianoNo ratings yet
- LIDIA VIANU Tabele de Gramatica English With A Key, English With A ChoiceDocument67 pagesLIDIA VIANU Tabele de Gramatica English With A Key, English With A Choicezerosapte100% (1)
- Miraa Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesMiraa Active and PassiveMira FebrianelNo ratings yet
- Basic 3: Additional GrammarDocument33 pagesBasic 3: Additional GrammarRamon CaceresNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDocument38 pagesPresent Perfect-Group 3 - CompressedDULCE MP100% (1)
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb TenseRose Bt MustafhaNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument33 pagesTenses of The VerbRyan ToledoNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument7 pagesPresent ContinuousGuadalupe AcostaNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb Tensemp SinghNo ratings yet
- Grammar in Use - Study NoteDocument13 pagesGrammar in Use - Study Noteosama aboualamNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewDocument78 pagesWeek 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewdewxoNo ratings yet
- Verbos AuxiliaresDocument12 pagesVerbos AuxiliaresalexanderNo ratings yet
- Verbs: State-Of-Being Verbs/ Verbs of BeingDocument4 pagesVerbs: State-Of-Being Verbs/ Verbs of BeingYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- Apuntes de Language IDocument11 pagesApuntes de Language ILuis PérezNo ratings yet
- Reporte D Speech: Discurso ReportadoDocument15 pagesReporte D Speech: Discurso ReportadoCarlosDavidAguirreRondinelNo ratings yet
- If Clauses: Type 1 - "RealDocument12 pagesIf Clauses: Type 1 - "RealRose SantosNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument19 pagesInglesBrian ShawNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: EstudiateDocument5 pagesReported Speech: EstudiateEduar Delgado Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Past Perfect and Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Past Perfect and Past ParticipleVu VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Documento PDFDocument6 pagesDocumento PDFJessica SchraderNo ratings yet
- صفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةDocument79 pagesصفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةbewarkootcher100% (1)
- Indicative and Imperative VerbsDocument16 pagesIndicative and Imperative VerbsChandaKundaNo ratings yet
- Engl111 Week 5Document53 pagesEngl111 Week 5Angelyn Grace TanNo ratings yet
- Actividad 3Document9 pagesActividad 3Juana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Tenses of Verb Pre-DemoDocument31 pagesTenses of Verb Pre-DemoMaridel DiamsayNo ratings yet
- 7 VerbsDocument94 pages7 VerbsAnda PopescuNo ratings yet
- Gramática Adverbs of Frequency (In Hierarchy Order) : Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument10 pagesGramática Adverbs of Frequency (In Hierarchy Order) : Gerunds and InfinitivesmmpmsNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide 3-2017 PDFDocument48 pagesGrammar Guide 3-2017 PDFRoberto Figueroa ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Communicative English: Listen, Learn, ApplyDocument180 pagesCommunicative English: Listen, Learn, ApplySindhu Manja100% (1)
- Indirect Speech: StatementsDocument4 pagesIndirect Speech: StatementsRosalía PlazaNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument12 pagesPresent ContinuousCristian Ramirez RodasNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech GrammarDocument5 pagesReported Speech GrammarJara Funez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Tense RevisionDocument78 pagesTense RevisionjoemacarraNo ratings yet
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3From EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3No ratings yet
- Latin Verb-Conjugations: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandLatin Verb-Conjugations: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Say What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.From EverandSay What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.No ratings yet
- Basic Level Chinese - Ultimate ChartDocument12 pagesBasic Level Chinese - Ultimate ChartDeea DiaconuNo ratings yet
- English TodayDocument60 pagesEnglish TodayAlfin DivaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Translation As A Process SupplementDocument3 pagesSummary of Translation As A Process SupplementAumnia JamalNo ratings yet
- What Are ArticlesDocument12 pagesWhat Are ArticlesAlok BagriNo ratings yet
- Assimil Phasebook Cuban SpanishDocument9 pagesAssimil Phasebook Cuban Spanishrobertocarmur0% (1)
- English Review IVDocument5 pagesEnglish Review IVAnel Viridiana Alfonso BocarandoNo ratings yet
- Writing SkillsDocument3 pagesWriting SkillsDubravka KovacevicNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument18 pagesReported SpeechArnau EscolàNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 5 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1 - Modul 5 ProfesionalTaufik Ansyari85% (13)
- UNIT 3 How Much Is ItDocument22 pagesUNIT 3 How Much Is ItCelis LópezNo ratings yet
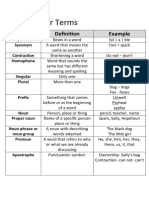
- Grammar Terms Vocab ListDocument3 pagesGrammar Terms Vocab ListMollyNo ratings yet
- BSCS Functioanl EnglishDocument5 pagesBSCS Functioanl Englishfizzabasharat44No ratings yet
- Learning Singular Plural Possessive Nouns WorksheetDocument1 pageLearning Singular Plural Possessive Nouns WorksheetNick AnthonyNo ratings yet
- GrammerDocument2 pagesGrammerHotBrosNo ratings yet
- Different Grammatical Forms of The Same WordDocument1 pageDifferent Grammatical Forms of The Same WordSri HariNo ratings yet
- List of 100 Most Commonly Used Hindi WordsDocument7 pagesList of 100 Most Commonly Used Hindi Wordsp_srib4uNo ratings yet
- Lisa Kahlen - German Grammar Made Easy. 2-Routledge (2017)Document275 pagesLisa Kahlen - German Grammar Made Easy. 2-Routledge (2017)Dang Hoang My100% (2)
- Suffixes: 1. FUL: Change Nouns Into Adjectives Indicating FULL OF, HAVING, OR CHARACTERIZED BYDocument4 pagesSuffixes: 1. FUL: Change Nouns Into Adjectives Indicating FULL OF, HAVING, OR CHARACTERIZED BYFernEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Structural TypologyDocument8 pagesLecture 10. Structural Typologybermet tursunbaevaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions or Prepositions ExerciseDocument4 pagesConjunctions or Prepositions ExerciseChareeshma SajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3THẢO NGUYỄN TRẦN PHƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- Genitive Case: Both NamesDocument3 pagesGenitive Case: Both NamesEveli AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- (New) Unit-6.1-Relative-ClauseDocument40 pages(New) Unit-6.1-Relative-ClauseTrangNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1 - Subject Verb AgrementDocument15 pagesMeeting 1 - Subject Verb AgrementInsignificant DustNo ratings yet
- Prepositions: ExampleDocument27 pagesPrepositions: ExampleVanshNo ratings yet
- What Is A SentenceDocument7 pagesWhat Is A SentenceAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Adjective DerivationDocument4 pagesAdjective DerivationVictoriaVacarițaNo ratings yet
- Adjektivdeklination Ohne ArtikelDocument6 pagesAdjektivdeklination Ohne ArtikelbijunpcmNo ratings yet
- La Marea Academy: Second Quarter Examination Language 4Document2 pagesLa Marea Academy: Second Quarter Examination Language 4Francisca CalamiongNo ratings yet
- Beginner English With Cover 6 July 2021Document130 pagesBeginner English With Cover 6 July 2021siti masturaNo ratings yet