Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE203 Fluid Mechanics I PDF
Uploaded by
Balagopal VOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE203 Fluid Mechanics I PDF
Uploaded by
Balagopal VCopyright:
Available Formats
Year of
Course Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits
Introduction
CE203 FLUID MECHANICS - I 3-1-0-4 2016
Pre requisite : Nil
Course Objectives
1. To understand the basic properties of the fluid, fluid statics, kinematics, and fluid dynamics so as to
analyse and appreciate the complexities involved in solving the fluid flow problems.
2. To give an introduction to the fundamentals of fluid flow and its behavior so as to equip the students
to learn related subjects and their applications in the higher semesters.
3. To develop the skill for applying the fluid statics, kinematics and dynamics of fluid flow concepts for
solving civil engineering problems.
Syllabus
Fluid Statics, Fluid pressure, Buoyancy and floatation, Fluid Kinematics, Dynamics of fluid flow, Flow
through orifice and notches, Flow through pipes, Boundary layer, Drag and lift on Immersed bodies
Course Outcomes:
1. Students will be able to get a basic knowledge of fluids in static, kinematic and dynamic equilibrium,
so as to solve real life problems in fluid mechanics.
2. Students will gain the knowledge of the applicability of physical laws in addressing problems in
hydraulics.
Text Books
1. Modi P. N. and S. M. Seth, Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics, S.B.H Publishers, New Delhi, 2002.
2. Subramanya K., Theory and Applications of Fluid Mechanics, Tata McGraw-Hill, 1993.
References
1. Streeter.V.L. Fluid Mechanics, Mc Graw Hill Publishers.
2. Bruce R Munson, Donald F Young . Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics, John Wiley & sons, 2011.
3. Jain A. K., Fluid Mechanics, Khanna Publishers, Delhi, 1996.
4. Joseph Katz, Introductory Fluid Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, 2015
5. Arora.K.R. Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machines, Standard Publishers, 2005.
6. Narasimhan S., A First Course in Fluid Mechanics, University Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., 2006.
7. Frank.M.White, Fluid Mechanics, Mc Graw Hill, 2013.
8. Mohanty.A.K. Fluid Mechanics, Prentice Hall, New Delhi, 2011
9. Narayana Pillai,N. Principles of Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Machines, University Press, 2011.
10. Kumar.D.N. Fluid Mechanics and Fluid power Engineering, S.K.Kataria & sons, 2013.
COURSE PLAN
Sem. Exam Marks
Module Contents Hours
%
Fluid properties - density specific gravity - surface
tension and capillarity - vapour pressure - viscosity and
compressibility - Classification of Fluids (No questions
to be asked) .
Fluid statics: Fluid pressure, variation of pressure in
a fluid, measurement of pressure using manometers-
simple manometers, differential manometers,
I Pressure head. Forces on immersed plane and 8 15
curved surfaces. Pressure distribution diagram for
vertical surfaces, Practical application of total
pressure (spillway gates).
Buoyancy and Floatation: Buoyant force, stability of
floating and submerged bodies, metacentre and
metacentric height, Analytical and experimental
determination of metacentric height.
Kinematics of fluid flow: Methods of describing
fluid motion, Lagrangian and Eulerian methods,
Types of fluid flow: steady and unsteady flow,
uniform and non-uniform flow, one, two and three
dimensional flow, laminar and turbulent flow,
rotational and irrotational flow. Types of flow lines:
stream line, path line, streak lines, conservation of
mass, equation of continuity in one, two and three
II 8 15
dimensions, (Derivation in Cartesian co-ordinate
system only)
Velocity & Acceleration of fluid particle, convective
and local acceleration, Deformation of fluid
elements: circulation and vorticity, velocity
potential, stream function, equipotential lines, flow
net, uses of flow net; Vortex motion, free and forced
vortex (no problems).
FIRST INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Dynamic of fluid flow: Eulers equation of motion and
integration of Eulers equation of motion along a
streamline. Bernoullis Equation, Energy correction
factors, Applications of Bernoullis equation : Pitot
III tube, Venturimeter and orifice meter. 8 15
Momentum Principle- Steady flow momentum
equation- Momentum correction factor, Force
computation on a pipe bend
Flow through orifices: Different types of orifices,
IV Flow over a sharp edged orifice, Hydraulic 8 15
coefficients Experimental determination of these
coefficients, flow through large rectangular orifice,
Flow through submerged orifices, flow under
variable heads, time of emptying.
Flow over weirs: flow over rectangular, triangular and
trapezoidal sharp crested weir, Cipolletti weir, Broad
crested weir, Submerged weirs, Proportional weir.
SECOND INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Flow through pipes: Viscous flow - Shear stress,
pressure gradient relationship - laminar flow between
parallel plates - Laminar flow through circular tubes
(Hagen Poiseulle's Eqn) - Hydraulic and energy gradient
12 20
V - flow through pipes - Darcy -Weisbach's equation -
pipe roughness -friction factor- Moody's diagram- Major
and minor losses of flow in pipes - Pipes in series and in
parallel.
Boundary layer theory-no slip condition, boundary
layer thickness, boundary layer growth over long thin
plate, laminar, turbulent boundary layer, laminar sub
layer, Momentum integral equation of boundary layer
(no derivation), Blasius boundary layer equations for
VI 12 20
laminar and turbulent boundary layer.
Drag and lift on Immersed bodies-Pressure drag and
friction drag, profile drag, Drag and lift co-efficient-
computation of drag on a flat plate. Separation of
boundary layer and control.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
QUESTION PAPER PATTERN (End semester exam)
Maximum Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs
The question paper shall have three parts.
Part A - Module I & II : Answer 2 questions out of 3 questions (15 marks each)
Part B - Module III & IV: Answer 2 questions out of 3 questions (15 marks each)
Part C - Module V & VI: Answer 2 questions out of 3 questions (20 marks each)
Note: 1.Each part should uniformly cover the two modules in that part.
2. Each question can have a maximum of 4 subdivisions (a,b,c,d), if needed.
You might also like
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985From EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985No ratings yet
- Ce 442 Foundation Engineering II - Tedu s1617 - SyllabusDocument8 pagesCe 442 Foundation Engineering II - Tedu s1617 - SyllabusRex MayabangNo ratings yet
- Slide 7 - Shallow FoundationDocument49 pagesSlide 7 - Shallow FoundationfiorentinhNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: MR Wan Afnizan Bin Wan MohamedDocument82 pagesHydrology: MR Wan Afnizan Bin Wan MohamedSky FireNo ratings yet
- Autocad - R GreenleeDocument97 pagesAutocad - R GreenleekarimNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering Handout 2012-2013Document3 pagesSoil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering Handout 2012-2013Tushar GuptaNo ratings yet
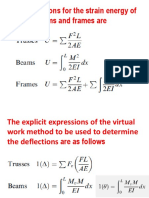
- Perbandingan Strain Energy-Virtual Work-CastiglianoDocument36 pagesPerbandingan Strain Energy-Virtual Work-Castiglianonurul saniyyahNo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument24 pagesEngineering HydrologyPrince Vince100% (1)
- Ce 401Document2 pagesCe 401MæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- 6 Stresses in SoilsDocument23 pages6 Stresses in SoilsJenina LogmaoNo ratings yet
- Capiz State University: WWW - Capsu.edu - PH Roxas@capsu - Edu.phDocument23 pagesCapiz State University: WWW - Capsu.edu - PH Roxas@capsu - Edu.phCarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- CE325 - 07 Consolidation SettlementDocument61 pagesCE325 - 07 Consolidation SettlementRobert PrinceNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDocument17 pagesLecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDrRoja A RNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2010 IntermediateDocument337 pagesAutoCAD 2010 IntermediateSinisa KusnjirNo ratings yet
- DRC Important QuestionsDocument11 pagesDRC Important QuestionsAdithya31No ratings yet
- Chal 1 Slides of Fluid MechanicsDocument54 pagesChal 1 Slides of Fluid MechanicsMohammad ShahrukhNo ratings yet
- Determine Water Content of Soil by Oven Dry and Pycnometer MethodsDocument6 pagesDetermine Water Content of Soil by Oven Dry and Pycnometer Methodsvenkateswara rao pothinaNo ratings yet
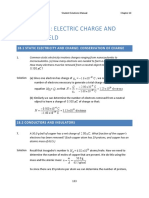
- Static Electricity and Charge Conservation of Charge PDFDocument9 pagesStatic Electricity and Charge Conservation of Charge PDFDavid I. Chamorro AriasNo ratings yet
- Set 01Document161 pagesSet 01ashishjakateNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 5 Insitu StressDocument41 pagesKuliah 5 Insitu StressFat-hanna Marami SaNo ratings yet
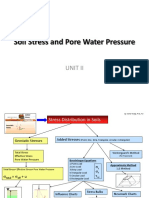
- Soil Stress ConditionDocument32 pagesSoil Stress ConditionSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- BE Syllabus Civil Engineering 2008-2012 Anna UniversityDocument127 pagesBE Syllabus Civil Engineering 2008-2012 Anna UniversitydepakmunirajNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument29 pagesLateral Earth Pressurewgr392100% (2)
- Unconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Document8 pagesUnconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Carmela Ayessa PiguerraNo ratings yet
- Surveying Model QuestionDocument2 pagesSurveying Model QuestionMahesh Kumar K BNo ratings yet
- Som PDFDocument105 pagesSom PDFanon_10845568100% (1)
- Advance Geotechnical EngineeringDocument21 pagesAdvance Geotechnical EngineeringWalterNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement: ................................................ (2.5 Weeks)Document33 pagesFlexible Pavement: ................................................ (2.5 Weeks)Cristian MaloNo ratings yet
- Content Question Bank 111U07CE604Document3 pagesContent Question Bank 111U07CE604manisaibabaNo ratings yet
- MTPPT4 - Design of Isolated FootingDocument19 pagesMTPPT4 - Design of Isolated FootingMineski Prince GarmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics SolutionDocument312 pagesMechanics SolutionManon VerhoevenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hydrostatic Forces On SurfacesDocument41 pagesChapter 1 Hydrostatic Forces On SurfacesFauzan Pojan100% (1)
- Chapter No. 01 and 02 Introduction To Hydrology. PrecipitationDocument96 pagesChapter No. 01 and 02 Introduction To Hydrology. PrecipitationRahat ullah0% (1)
- Soil PermeabilityDocument85 pagesSoil PermeabilityMavenNo ratings yet
- Strength of Metirials QUSDocument5 pagesStrength of Metirials QUSraviNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology Unit 4Document30 pagesConcrete Technology Unit 4sainathNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Manual (4-13-2022)Document26 pagesFDN Engg Manual (4-13-2022)ANGELICA SAHAGUNNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis NotesDocument166 pagesStructural Analysis NotesdunyNo ratings yet
- Hardened ConcreteDocument33 pagesHardened Concretechicku_iwayNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration SeeDocument39 pagesSoil Exploration SeeRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Plate Theory WikiDocument12 pagesPlate Theory Wikiletter_ashish4444No ratings yet
- OSH Situation in The Global and Local LevelsDocument11 pagesOSH Situation in The Global and Local LevelsLORENZ DAVE MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Atterberg LimitDocument6 pagesLab 2 - Atterberg LimitAmirah ShafeeraNo ratings yet
- Rate of Consolidation Terzaghi'sDocument7 pagesRate of Consolidation Terzaghi'sLava SatNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Earth DamDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Earth DamMojtaba Mohebinia100% (2)
- Chapter 8 Spread Footings SynthesisDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Spread Footings SynthesispkNo ratings yet
- Analisis Struktur C6Document47 pagesAnalisis Struktur C6Hazyema HarunNo ratings yet
- In-Situ Stresses (Class)Document22 pagesIn-Situ Stresses (Class)Mohd Asis LatipNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations: MR Mohd Faiz B Mohammad ZakiDocument24 pagesPile Foundations: MR Mohd Faiz B Mohammad ZakiMohammad Hafiz MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Soil MechanicsDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Soil Mechanicsbashiir warsameNo ratings yet
- Dam and Reservoir: Geological InvestigationDocument19 pagesDam and Reservoir: Geological InvestigationGadige ChandraNo ratings yet
- Indetermine StructureDocument8 pagesIndetermine Structuremaloy100% (1)
- Physical and Mechanical Properties of Some Common Nigerian Timber Species Based On Limit State Design ApproachDocument8 pagesPhysical and Mechanical Properties of Some Common Nigerian Timber Species Based On Limit State Design ApproachSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument15 pagesLateral Earth PressureLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- MEL203 2019 Lab ManualDocument72 pagesMEL203 2019 Lab ManualDharm-astra :The Weapon of Righteousness100% (1)
- Limit State Design TheoryDocument3 pagesLimit State Design TheoryEvans KishNo ratings yet
- Onyancha - Geological and Geotechnical Conditions of NairobiDocument234 pagesOnyancha - Geological and Geotechnical Conditions of NairobichristopherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Introduction To Deep Foundation Design: SolutionDocument24 pagesChapter 4. Introduction To Deep Foundation Design: SolutionAlejandro CasallasNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercise (Solution)Document6 pagesAdditional Exercise (Solution)abdul al muhaiminNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of CE203 Fluid Mechanics - I 3-1-0-4 2016Document3 pagesCourse Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of CE203 Fluid Mechanics - I 3-1-0-4 2016AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering S7 & S8-72Document1 pageCivil Engineering S7 & S8-72Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering S7 & S8-75Document1 pageCivil Engineering S7 & S8-75Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering S7 & S8-74Document1 pageCivil Engineering S7 & S8-74Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering S7 & S8-67Document1 pageCivil Engineering S7 & S8-67Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation PDFDocument9 pagesDifferential Equation PDFmarvinNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering S7 & S8-73Document1 pageCivil Engineering S7 & S8-73Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- Engg GraphicsDocument10 pagesEngg GraphicsBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- CE208 Geotechnical Engineering - IDocument3 pagesCE208 Geotechnical Engineering - IBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Engg CollegesDocument1 pageEngg CollegesBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics B (For Non-Circuit Branches) : Category L T P Credit Year ofDocument10 pagesEngineering Physics B (For Non-Circuit Branches) : Category L T P Credit Year ofBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- CE204 Construction TechnologyDocument3 pagesCE204 Construction TechnologyBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- CE202 Structural AnalysisDocument3 pagesCE202 Structural AnalysisBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Causes of MeanderingDocument1 pageCauses of MeanderingBalagopal V50% (2)
- SI. NO - Item Description 1 Course Diary/Attendance RegisterDocument2 pagesSI. NO - Item Description 1 Course Diary/Attendance RegisterBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Pre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsDocument3 pagesPre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Civil Engg 2013Document136 pagesCivil Engg 2013Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- KTU-S5 To S8-draftsyllabus-CIVILENGG-Final PDFDocument130 pagesKTU-S5 To S8-draftsyllabus-CIVILENGG-Final PDFBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- s6 Btech 2008Document46 pagess6 Btech 2008Ansad AzizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- IS 10262 - 2009 - RevisionDocument18 pagesIS 10262 - 2009 - RevisionSampathKumara Swamy K100% (4)
- Ass AsDocument10 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Btech Degree 2013 Scheme 13Document57 pagesBtech Degree 2013 Scheme 13Balagopal VNo ratings yet
- NagercoilDocument1 pageNagercoilBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Commercial Licence PDFDocument2 pagesCommercial Licence PDFBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Cse 2002 - Forensic Engineering: SL No Lecture Topics No of HoursDocument4 pagesCse 2002 - Forensic Engineering: SL No Lecture Topics No of HoursBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Nterview TipsDocument4 pagesNterview TipsBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- College CertificateDocument1 pageCollege CertificateYateesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accountability VsDocument3 pagesAccountability VsBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Commercial LicenceDocument2 pagesCommercial LicenceBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption: Operating Calibrated Operating CalibratedDocument4 pagesGas Absorption: Operating Calibrated Operating CalibratedAuzaNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa - PMCA - LevelDocument40 pagesYokogawa - PMCA - Levelhon choong chongNo ratings yet
- Air Release ValveDocument17 pagesAir Release Valvevikaskatheria100% (1)
- Dryer Level Endress HauserDocument112 pagesDryer Level Endress HauserraldavoodNo ratings yet
- Additional Course Material: Physical Properties of FluidsDocument43 pagesAdditional Course Material: Physical Properties of Fluidssilswal1988No ratings yet
- Cavitation in Restriction Orifices and Valves - NeutriumDocument5 pagesCavitation in Restriction Orifices and Valves - Neutriumمنير أحمدNo ratings yet
- Orifice and Chemical Tracer Flow Test Measurements On Production Geothermal Wells PDFDocument1 pageOrifice and Chemical Tracer Flow Test Measurements On Production Geothermal Wells PDFindeskeyNo ratings yet
- Carrier - Water Piping Systems and Pumps PDFDocument33 pagesCarrier - Water Piping Systems and Pumps PDFShaaban NoamanNo ratings yet
- Ambato Psv-13 High Performance Series Rev1-40cDocument8 pagesAmbato Psv-13 High Performance Series Rev1-40cAlfredo OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Level and Flow Measurement - AdnanDocument83 pagesLevel and Flow Measurement - AdnanMuzamilNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1Document44 pagesHydraulics 1Rhia Roxas100% (1)
- API Piping PlansDocument9 pagesAPI Piping PlansMohit MundraNo ratings yet
- Well-Performance Testing ProceduresDocument10 pagesWell-Performance Testing ProceduresJohn Ely Collado BantogNo ratings yet
- Selection and Sizing of Pressure Relief ValvesDocument21 pagesSelection and Sizing of Pressure Relief ValvesjoesuhreNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Detaction System CalculationsDocument44 pagesFire Protection and Detaction System CalculationsMohamedSaid100% (1)
- ESR0055024ACAL1004 0cDocument24 pagesESR0055024ACAL1004 0ckayaltharanNo ratings yet
- Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology Burla: Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesVeer Surendra Sai University of Technology Burla: Lesson Plansanthi saranyaNo ratings yet
- Halliburton API Calculations For OilDocument107 pagesHalliburton API Calculations For OilKhurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- LPG Sensor TechnologyDocument20 pagesLPG Sensor Technologyeddie eddNo ratings yet
- Pavc Complete Hy28 2662 CDDocument46 pagesPavc Complete Hy28 2662 CDMoein Emani100% (1)
- PDS Placas DANIEL DIC 17Document15 pagesPDS Placas DANIEL DIC 17Katia ArroyueloNo ratings yet
- EFS.10.05.01R.1 Design Basis For Instr PDFDocument49 pagesEFS.10.05.01R.1 Design Basis For Instr PDFSaravanan VaradarajanNo ratings yet
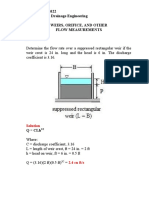
- ABE Review 2022 Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Weirs, Orifice, and Other Flow Measurements Problem 1Document8 pagesABE Review 2022 Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Weirs, Orifice, and Other Flow Measurements Problem 1Niel Crizza Chloe JandaNo ratings yet
- Zurn Install Instruc 2700Document2 pagesZurn Install Instruc 2700Rafyss RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pipe Routing InstructionsDocument37 pagesPipe Routing InstructionsDANLIN ENGINEERS100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering Technology - Higher National Diploma (HND)Document19 pagesElectrical Engineering Technology - Higher National Diploma (HND)Chibueze EzeokaforNo ratings yet
- Field Testing of CompressorsDocument12 pagesField Testing of CompressorsmishraenggNo ratings yet
- 11-4080 HYSYS Relief Valve Sizing Demo Guide FinalDocument18 pages11-4080 HYSYS Relief Valve Sizing Demo Guide FinalNoman Abu-FarhaNo ratings yet
- Spirax Sarco - Typical Steam Orifice Flowmeter Station PDFDocument3 pagesSpirax Sarco - Typical Steam Orifice Flowmeter Station PDFnasirmuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 Flow Through A Sluice Gate PDFDocument11 pagesExperiment No 1 Flow Through A Sluice Gate PDFMohamed Nageeb SalemNo ratings yet