Professional Documents
Culture Documents
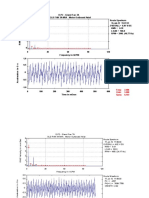
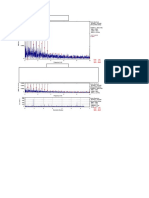
Vibration Sources Identification Guide
Uploaded by
DTNgo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views1 pagevibration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentvibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views1 pageVibration Sources Identification Guide
Uploaded by
DTNgovibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Vibration Sources Identification Guide
CAUSE FREQUENCY AMPLITUDE PHASE COMMENTS
Highest in Radial Direction-
Unbalance 1 x RPM Single Mark (Steady) A common cause of vibration.
Proportional to Unbalance
Velocity readings are highest at defective bearing.
Defective Anti-Friction Very High-Often From 10 to
Use Velocity Unstable As failure approaches, the amplitude of the velocity signal will increase and its frequency will
Bearings 100 x RPM
decrease. Cage frequency is approximately 0.6 x RPM x number elements.
High Axial Use phase analysis to determine relative movement of machine or bearings. Use a dial
Misalignment of Coupling or
1, 2 or 3 x RPM Axial 50% or more of Often 2, Sometimes 1 or 3 indicator if possible. Often diagnosed as a bent shaft.
Bearing
Radial Can be caused by misalignment of V belts.
Not Large
May appear to be unbalanced. Shaft and bearing amplitude should be taken. If shaft
Sleeve Bearing 1 x RPM Use Displacement Mode Up Single Reference Mark
vibration is larger than the bearing, vibration amplitude indicates clearance.
to 6000 CPM
Bent Shaft 1 or 2 x RPM High Axial 1 or 2 Similar to misalignment. Use phase analysis.
Use velocity measurement. Often affected by misalignment. Generally accompanied by side
Defective Gears High No. Gear Teeth x RPM Radial Unsteady band frequency. Pitting, scuffing and fractures are often caused by torsional vibrations.
Frequency sometimes as high as 1 million CPM or more.
2 x RPM
Check movement of mounting bolts in relation to the machine base. Difference between base
Mechanical Looseness Sometimes Proportional to Looseness 1 or 2
and machine indicates amount of looseness.
1 x RPM
Calculate the belt RPM using:
Use Strobe to Freeze Belt Pulley Diameter x 3.141
Defective Drive Belts 1 or 2 x Belt Speed Erratic Belt RPM = x Pulley RPM
in OSC Mode Belt Length
Look for cracks, hard spots, soft spots or lumps. Loose belt. Changes with belt tension.
1 or 2 x Line Frequency
(3600 or 7200 CPM for 1 or 2 Marks Sometimes
Electrical Usually Low Looks like mechanical unbalance until power is removed. Then drops dramatically.
60Hz Power) May appear at Slipping
1 x RPM
Caused by excessive clearance in sleeve bearings or by underloaded bearings. Will change
Oil Whip 45 - 55% RPM Radial Unsteady Unstable
with viscosity of oil (temperature).
Hydraulic-Aerodynamic No. Blades or Vanes x RPM Erratic Unsteady May excite resonance problems.
Beat Frequency Near 1 x RPM Variable at Beat Rate Rotates at Beat Frequency Caused by two machines, mounted on same base, running at close to same RPM.
Phase will shift 180 going through resonance (90 at resonance). Amplitude will peak at
Resonance Specific Criticals High Single Reference Mark resonance. Resonance in frame can be removed by changing rotor operating speed or by
changing the stiffness of the structure.
NOTE: There are several additional detailed articles that identify more complicated vibration sources at the Vibes Corp website titled:
1) LEARN ABOUT VIBRATION VOLUME 1: BASIC UNDERSTANDING OF MACHINERY VIBRATION
2) LEARN ABOUT VIBRATION VOLUME 2: ADVANCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS
3) LEARN ABOUT ELECTRICALLY INDUCED BEARING DAMAGE & SHAFT CURRENTS
2012 VIBES Corp
You might also like
- Fans Reference GuideDocument160 pagesFans Reference Guidekarthikraja21100% (13)
- Acoustic Signatures of Gear Defects Using Time-Frequency Analyses and A Test RigDocument22 pagesAcoustic Signatures of Gear Defects Using Time-Frequency Analyses and A Test RigKhalid F AbdulraheemNo ratings yet
- BalancingDocument138 pagesBalancingJeinnerCastroNo ratings yet
- Bearing BasicsDocument69 pagesBearing BasicsHashem Mohamed HashemNo ratings yet
- Vibration Diagnostic ChartDocument49 pagesVibration Diagnostic ChartAlex George100% (4)
- Basic Training Program On Vibration AnalysisDocument24 pagesBasic Training Program On Vibration AnalysisMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To Vibration DiagnosticsDocument72 pagesQuick Guide To Vibration DiagnosticsAbderrahim AbarayNo ratings yet
- Autocorrelation: 131 CAT IV Part 1 - Signal Processing SlidebookDocument8 pagesAutocorrelation: 131 CAT IV Part 1 - Signal Processing SlidebookLe Thanh Hai100% (2)
- EM104 - Orbital Analysis - Kelm - 0612Document16 pagesEM104 - Orbital Analysis - Kelm - 0612RobertoSlzr100% (1)
- Bypass Screw Conveyor Drive:: MotorDocument2 pagesBypass Screw Conveyor Drive:: MotorHosam Abd ElkhalekNo ratings yet
- A I RS: David G. Dorrell, William ThomsonDocument11 pagesA I RS: David G. Dorrell, William ThomsonEng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- Vibrasyon Electrical ProblemsDocument4 pagesVibrasyon Electrical ProblemsbbulutmmNo ratings yet
- Order Analysis ToolkitDocument16 pagesOrder Analysis ToolkitManuel Enrique Salas FernándezNo ratings yet
- ISO 18436 Category IV Vibration Analyst Training TopicsDocument1 pageISO 18436 Category IV Vibration Analyst Training TopicsDean LofallNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor Diagnostics Defect Frequencies and Data ColleDocument51 pagesElectric Motor Diagnostics Defect Frequencies and Data ColleSubrata Dubey50% (2)
- 7 - Gear DeffectDocument21 pages7 - Gear Deffectmohamed ghoneemNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Turbomachinery Using Startup and Coastdown Vibration DataDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Turbomachinery Using Startup and Coastdown Vibration DataAhtsham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Creating PeakVue Measurement PointsDocument2 pagesCreating PeakVue Measurement PointsNewman RiosNo ratings yet
- AMPLITUDE MODULATION Versus BEATSDocument5 pagesAMPLITUDE MODULATION Versus BEATSHaitham YoussefNo ratings yet
- Peakvue CaseDocument22 pagesPeakvue CaseNeopeakNo ratings yet
- SKF BRGDocument22 pagesSKF BRGVijeth99No ratings yet
- RMS Velocity in mm/Sec: Root Cause Analysis of High Vibration on Process Fan Using ODS ModelingDocument21 pagesRMS Velocity in mm/Sec: Root Cause Analysis of High Vibration on Process Fan Using ODS ModelingsatfasNo ratings yet
- Machinery Malfunction Diagnosis and Correction - Constant ContactDocument2 pagesMachinery Malfunction Diagnosis and Correction - Constant ContactLisan YanNo ratings yet
- High Vibration at Main Gear Box of Gas TurbineDocument9 pagesHigh Vibration at Main Gear Box of Gas TurbineJJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BalancingDocument102 pagesChapter 11 Balancingewfsd100% (1)
- Vibration Sources Identification GuideDocument1 pageVibration Sources Identification GuideMURALINo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Fans Using Vibration Analysis To Detect ProblemsDocument3 pagesCentrifugal Fans Using Vibration Analysis To Detect ProblemsGivon Da Anneista100% (1)
- Natural Frequency Testing GuideDocument12 pagesNatural Frequency Testing GuideRais RijalNo ratings yet
- CGL02 Blowers Report May 2009Document9 pagesCGL02 Blowers Report May 2009Hosam Abd Elkhalek100% (1)
- Timebase Plots ExplainedDocument18 pagesTimebase Plots ExplainedManuel L LombarderoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis For Machinery Health DiagnosisDocument12 pagesVibration Analysis For Machinery Health Diagnosiskoniks519No ratings yet
- Unbalance IdentificationDocument22 pagesUnbalance IdentificationAV100% (1)
- Sleeve Bearing Diagnostics R1Document75 pagesSleeve Bearing Diagnostics R1Daniel_Ali_bNo ratings yet
- Vib Screen - Vib Analysis PDFDocument16 pagesVib Screen - Vib Analysis PDFAngka SubaronNo ratings yet
- ISO 10816-1 Normativa VibracionesDocument10 pagesISO 10816-1 Normativa Vibracionesumendibil100% (1)
- PeakvueDocument68 pagesPeakvueLe Thanh Hai100% (1)
- 05-Fault Analysis 4Document17 pages05-Fault Analysis 4Hatem Abdelrahman100% (1)
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument22 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationJGD123No ratings yet
- Detection of Ski Slopes in Vibration SpectrumsDocument7 pagesDetection of Ski Slopes in Vibration SpectrumsjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Orbit ReferenceDocument25 pagesOrbit ReferenceIlku100% (1)
- Balancing Without Phase ReadingDocument2 pagesBalancing Without Phase Readingvirtual_56No ratings yet
- Why Industrial Bearings Fail: Analysis, Maintenance, and PreventionFrom EverandWhy Industrial Bearings Fail: Analysis, Maintenance, and PreventionNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Common Vibration Problems: Prof. Dr. Fawkia RamadanDocument13 pagesDiagnosis of Common Vibration Problems: Prof. Dr. Fawkia Ramadanفرح تامر100% (1)
- Low Frequency EvaluationDocument13 pagesLow Frequency EvaluationthrillerxNo ratings yet
- Design & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneDocument57 pagesDesign & Fabrication of a Cost-Effective Agricultural DroneFatima Nasir R:29No ratings yet
- Phase Analysis: How to Use Phase Readings to Diagnose FaultsDocument27 pagesPhase Analysis: How to Use Phase Readings to Diagnose FaultsShawn RuhlNo ratings yet
- Transient Speed Vibration AnalysisDocument34 pagesTransient Speed Vibration AnalysistylerdurdaneNo ratings yet
- MisalignmentDocument13 pagesMisalignmentZeeshan Sajid100% (1)
- Shaft Vibration EUDocument24 pagesShaft Vibration EUWildan Harun100% (1)
- Centrifugal FanDocument9 pagesCentrifugal FanDTNgoNo ratings yet
- Manual Vibration Case StudiesDocument18 pagesManual Vibration Case StudiesSomil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phase AnalysisDocument3 pagesPhase Analysisk_shah_777No ratings yet
- Fan TemplateDocument9 pagesFan TemplateHaitham YoussefNo ratings yet
- Machinery VibrationsDocument33 pagesMachinery VibrationsDanish AfrozNo ratings yet
- Structural Health MonitoringFrom EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasNo ratings yet
- 20 - Sample Machinery Vibration Analysis ReportDocument12 pages20 - Sample Machinery Vibration Analysis ReportBawaInspectorNo ratings yet
- CM3141 en Bump Test ModuleDocument2 pagesCM3141 en Bump Test ModuleLuisSilvaNo ratings yet
- Vibration AnalysisDocument10 pagesVibration AnalysisYasser BayoumyNo ratings yet
- Detect Misalignment with Vibration Analysis and ThermographyDocument5 pagesDetect Misalignment with Vibration Analysis and ThermographyTamer EmamNo ratings yet
- Vibration Monitoring and AnalysisDocument8 pagesVibration Monitoring and AnalysishashimtkmceNo ratings yet
- Petronas OGC Cooler Fan Vibration AnalysisDocument3 pagesPetronas OGC Cooler Fan Vibration AnalysisfazzlieNo ratings yet
- Cracked or Broken Tooth in a Gearbox: Diagnosing High 1X Radial VibrationDocument2 pagesCracked or Broken Tooth in a Gearbox: Diagnosing High 1X Radial VibrationHURRYSTARNo ratings yet
- Chandra Gupt Porwal, CMD, NIMDC PVT LTD.Document13 pagesChandra Gupt Porwal, CMD, NIMDC PVT LTD.CHANDRA GUPT PORWALNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Gear Box.5-MilosprokoDocument3 pagesVibration Analysis of Gear Box.5-MilosprokoRavikiran Hegde100% (2)
- Time Waveform Analysis TechniquesDocument2 pagesTime Waveform Analysis TechniquesManel Montesinos100% (1)
- Pulley Diameter X 3.141 Belt Length X Pulley RPM Belt RPM : WWW - Vibescorp.caDocument1 pagePulley Diameter X 3.141 Belt Length X Pulley RPM Belt RPM : WWW - Vibescorp.cahasen kushlafNo ratings yet
- Section2 Roller BearingsDocument118 pagesSection2 Roller BearingsDTNgo0% (1)
- Guidance For Mounting 4-20ma Sensors On FansDocument5 pagesGuidance For Mounting 4-20ma Sensors On FanskochicommNo ratings yet
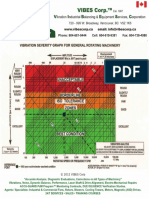
- Vibration Severity Graph Colour PDFDocument1 pageVibration Severity Graph Colour PDFDTNgoNo ratings yet
- Balance, Vibration, and Vibration Analysis: BalancingDocument4 pagesBalance, Vibration, and Vibration Analysis: BalancingGivon Da AnneistaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis ISO Cat III DLDocument7 pagesVibration Analysis ISO Cat III DLDTNgoNo ratings yet
- Slow Rpm.Document1 pageSlow Rpm.DTNgoNo ratings yet
- 2130 Measurement CautionsDocument8 pages2130 Measurement Cautionsjgb78uk8426No ratings yet
- Adv Gear AnalysisDocument15 pagesAdv Gear AnalysisDTNgoNo ratings yet
- CST10Document22 pagesCST10DTNgoNo ratings yet
- Gear Calculations XL SheetDocument5 pagesGear Calculations XL SheetkarthiktcdNo ratings yet
- Gear Calculations Rev3Document5 pagesGear Calculations Rev3ghostghost123No ratings yet
- Nso User Guide-5.3 PDFDocument178 pagesNso User Guide-5.3 PDFAla JebnounNo ratings yet
- VSD Operacion ControlDocument138 pagesVSD Operacion ControlLeon PerezNo ratings yet
- Employee performance factors analysis electronic companyDocument10 pagesEmployee performance factors analysis electronic companyAmrithaNo ratings yet
- Logic CHPT71Document27 pagesLogic CHPT71Eronjosh FontanozaNo ratings yet
- Baidu - LeetCodeDocument2 pagesBaidu - LeetCodeSivareddyNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design: Introduction & Motivation Introduction & MotivationDocument33 pagesVLSI Design: Introduction & Motivation Introduction & MotivationPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Astm A6 A6m-08Document62 pagesAstm A6 A6m-08Vũ Nhân HòaNo ratings yet
- Geotehnical Engg. - AEE - CRPQsDocument48 pagesGeotehnical Engg. - AEE - CRPQsSureshKonamNo ratings yet
- Instrument Resume OIL and GAS.Document3 pagesInstrument Resume OIL and GAS.RTI PLACEMENT CELLNo ratings yet
- Seksioni I Kabllos Per Rrymat e Lidhjes Se ShkurteDocument1 pageSeksioni I Kabllos Per Rrymat e Lidhjes Se ShkurteDukagjin Ramqaj100% (1)
- Algebra Translating Algebraic Phrases 001Document2 pagesAlgebra Translating Algebraic Phrases 001crazyomnislash25% (4)
- How Dna Controls The Workings of The CellDocument2 pagesHow Dna Controls The Workings of The Cellapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Eurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 ManualDocument88 pagesEurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 Manualfelix olguinNo ratings yet
- TIM Fungsi 1Document40 pagesTIM Fungsi 1lilikNo ratings yet
- Notes Measures of Variation Range and Interquartile RangeDocument11 pagesNotes Measures of Variation Range and Interquartile RangedburrisNo ratings yet
- Syllabi M.Tech. WRDMDocument114 pagesSyllabi M.Tech. WRDMMadhab KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Impeller: REV Rev by Description PCN / Ecn Date CHK'D A JMM Released For Production N/A 18/11/2019 PDLDocument1 pageImpeller: REV Rev by Description PCN / Ecn Date CHK'D A JMM Released For Production N/A 18/11/2019 PDLSenthilkumar RamalingamNo ratings yet
- LC IN SCIENCE and MathDocument14 pagesLC IN SCIENCE and MathCharity Anne Camille PenalozaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: The Fork at The End of NowDocument28 pagesClimate Change: The Fork at The End of NowMomentum Press100% (1)
- 997-3 CIP Safety Adapter: Single Point Lesson (SPL) - Configure CIP Safety Adapter and A-B PLCDocument18 pages997-3 CIP Safety Adapter: Single Point Lesson (SPL) - Configure CIP Safety Adapter and A-B PLCTensaigaNo ratings yet
- LyonDCCT Technology ReviewDocument4 pagesLyonDCCT Technology Reviewrajagopal gNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual MCSE 101Document35 pagesLab Manual MCSE 101Juan JacksonNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operacion de Bomba BlackmerDocument20 pagesManual de Operacion de Bomba BlackmerMorales EduardoNo ratings yet
- SUBstation Equipmens TLDocument12 pagesSUBstation Equipmens TLJecer Casipong NuruddinNo ratings yet
- Scoop Atlas Wagner ST1810Document4 pagesScoop Atlas Wagner ST1810Juan Manuel PerezNo ratings yet
- Example 1 LS Dyna - Bullet Model SimulationDocument6 pagesExample 1 LS Dyna - Bullet Model Simulationsunil_vrvNo ratings yet
- Sequelize GuideDocument5 pagesSequelize Guidemathur1995No ratings yet