Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Mechanics
Uploaded by
Kriss Tita MontajesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil Mechanics
Uploaded by
Kriss Tita MontajesCopyright:
Available Formats
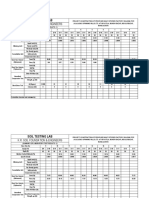
PARTICLE-SIZE DISTRIBUTION CURVE type of distribution of various-size
particles.
Use to determine the following four parameters:
1. Effective size (D10)
- The diameter in the particle size
distribution curve corresponding to
10 % finer.
- The effective size of a granular soil is I. Poorly Graded Soil: type of soil in
a good measure to estimate the which most of the soil grains are the
hydraulic conductivity and drainage same size.
through soil. II. Well Graded: represents a soil in
2. Uniformly Coefficient (Cu) which the particle sizes are
distributed over a wide range.
60 III. Gap Graded: a combination of two
=
10 or more uniformly graded fractions.
3. Coefficient of Gradiation (Cc)
2
30
=
60 10
4. Sorting Coefficient (So)
- Generally encountered in geologic
works but is not frequently used as a
parameter by geotechnical
engineers.
75
=
25
- The particle size distribution curve
shows not only the range of particle
sizes present in a soil but also the
Bulky particles - formed mostly by mechanical
weathering of rock and minerals.
Geologists use these terms to describe
the shapes of bulky particles:
Angularity and Sphericity Formula of
Bulky Particles, are defined as
PARTICLE SHAPE
- The shape of particles present in soil
Flaky Particles have very low sphericity
mass equally important as the
usually 0.01 or less. These particles are
particle-size distribution because it
predominantly clay minerals.
has a significant influence on the
physical properties of a given soil. Needle-shaped particles are much less
common than the two particle types.
Three major categories:
1. Bulky
2. Flaky
3. Needle Shaped
You might also like
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Document32 pagesAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Danilo NeryNo ratings yet
- Timber AssignmentDocument13 pagesTimber AssignmentKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- CE 60 - Project 2 Department of Civil Engineering College of Engineering and Design Silliman University Appendix W: Pert - CPMDocument1 pageCE 60 - Project 2 Department of Civil Engineering College of Engineering and Design Silliman University Appendix W: Pert - CPMKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- StepsDocument2 pagesStepsKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Timber AssignmentDocument13 pagesTimber AssignmentKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Passport RequirementsDocument1 pagePassport RequirementsKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Code of EthicsDocument1 pageCivil Engineering Code of EthicsKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4: Grain Size Analysis Part II: Hydrometer AnalysisDocument9 pagesExperiment No.4: Grain Size Analysis Part II: Hydrometer AnalysisKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- L3b Hydrometer AnalysisDocument5 pagesL3b Hydrometer Analysisjesus_vitangcolNo ratings yet
- CE 43A - Determine Soil Shrinkage LimitDocument5 pagesCE 43A - Determine Soil Shrinkage LimitKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Laying of reversed curve fieldworkDocument4 pagesLaying of reversed curve fieldworkKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- Ce35a SheetDocument1 pageCe35a SheetKriss Tita MontajesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Linear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocument91 pagesLinear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsFaith Reyna TanNo ratings yet
- RRR Media Kit April 2018Document12 pagesRRR Media Kit April 2018SilasNo ratings yet
- Soil Testing Lab Results SummaryDocument2 pagesSoil Testing Lab Results SummaryMd SohagNo ratings yet
- MATH Concepts PDFDocument2 pagesMATH Concepts PDFs bNo ratings yet
- Johnson 1999Document20 pagesJohnson 1999Linh Hoàng PhươngNo ratings yet
- معامل الاسفلتDocument32 pagesمعامل الاسفلتMohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting OperationDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting Operationchandan kumar100% (1)
- Adapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumDocument3 pagesAdapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumVini PezzinNo ratings yet
- (The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)Document72 pages(The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)BlackFlix Legendas em PortuguêsNo ratings yet
- VANSINA, Jan. Art History in AfricaDocument250 pagesVANSINA, Jan. Art History in AfricaRaphaelTim100% (1)
- PoiconverterDocument2 pagesPoiconvertertaco6541No ratings yet
- Open MPDocument30 pagesOpen MPmacngocthanNo ratings yet
- Agitators: Robert L. Bates, President Chemineer, IncDocument24 pagesAgitators: Robert L. Bates, President Chemineer, InctenshinomiyukiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Metacognitive Reading Report 1Document2 pagesUnderstanding The Self Metacognitive Reading Report 1Ako Lang toNo ratings yet
- IntegrityDocument5 pagesIntegrityPritam Kumar100% (1)
- 360 PathwaysDocument4 pages360 PathwaysAlberto StrusbergNo ratings yet
- Generate Ideas with TechniquesDocument19 pagesGenerate Ideas with TechniquesketulNo ratings yet
- Technical Bro A4 UK LR NEW v2Document45 pagesTechnical Bro A4 UK LR NEW v2Roxana NegoitaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleDocument1 pageAssessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleJoao JoseNo ratings yet
- ccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookDocument30 pagesccpc15 Supportive and Preventive WorkbookJeremy HamptonNo ratings yet
- Footprints 080311 For All Basic IcsDocument18 pagesFootprints 080311 For All Basic IcsAmit PujarNo ratings yet
- Lorain Schools CEO Finalist Lloyd MartinDocument14 pagesLorain Schools CEO Finalist Lloyd MartinThe Morning JournalNo ratings yet
- DOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinDocument3 pagesDOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinFredo NLNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3ADocument69 pagesHong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3AMARENG BERNABENo ratings yet
- Osprey, Men-At-Arms #008 The Black Watch (1971) (-) OCR 8.12Document48 pagesOsprey, Men-At-Arms #008 The Black Watch (1971) (-) OCR 8.12mancini100% (4)
- The Ideal Structure of ZZ (Alwis)Document8 pagesThe Ideal Structure of ZZ (Alwis)yacp16761No ratings yet
- Case Analysis of CriminologyDocument12 pagesCase Analysis of CriminologyinderpreetNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Citrix XenAppDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts of Citrix XenAppAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- 2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilDocument2 pages2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Disciple Making PaperDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Disciple Making Paperapi-665038631No ratings yet