Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Claude PeñaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Claude PeñaCopyright:
Available Formats
NERVOUS SYSTEM
NS 102
- the system of cells, tissues and organs that regulates the bodys responses to internal and external stimuli
- it is the master controlling and communicating system of the body
Functions:
- receiving sensory input - performing integrations - generating motor output
2 divisions of nervous system
A. central nervous system - Includes the brain and spinal cord; all of the activities of the body
Parts:
1. spinal cord - transmits neural signal between the brain and other body parts
2. brain the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ
Parts of the brain
A cerebrum largest part of human brain; associated with higher brain function such as thought and action
4 sections of cerebrum
1. frontal lobe 2. occipital lobe 3. temporal lobe 4. parietal lobe
Corpus callosum bundle of axons which connects the two cerebral hemispheres
B - Cerebellum associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture and balance
C Brain Stem responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure
D Diencephalon superior to the brain stem
Major structures of diencephalons
1. thalamus 2. hypothalamus 3. epithalamus
B peripheral nervous system consists mainly of nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord
Types of nerves
1. spinal nerves
2. cranial nerves
Neurons or nerve cells functional unit of nervous system
- are cells in the body that transport messages from the brain to the cells
Parts of neurons
1. axon main branch that conducts a nerve impulse away from the cell body
2. dendrites refers to the branches that carry impulses toward a cell body
3. cell body the central portion of a nerve cell which includes a cytoplasmic mass and a nucleolus
kinds of neurons
1. sensory neuron sensory receptors to CNS; carries out impulses from receptors
2. interneuron carries impulses from sensory nerves to motor nerves
3. motor neuron carries impulses from CNS to muscles and organs
2 divisions of peripheral nervous system (PNS)
1. somatic nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements
2. autonomic nervous system acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and
controls visceral functions
2 subdivisions of autonomic nervous system
1. parasympathetic nervous system Rest and Digest System; lowers heartbeat, breathing rate and blood pressure
2. sympathetic nervous system fight or flight response; increases heart rate and blood pressure
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- CH 17 WorkbookDocument13 pagesCH 17 WorkbookClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- C17D1 Homework 3Document8 pagesC17D1 Homework 3Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- CH 12 WorkbookDocument18 pagesCH 12 WorkbookClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Term Exam 1Document2 pagesTerm Exam 1Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CH 16 WorkbookDocument14 pagesCH 16 WorkbookClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- FTP - Corporation 2021Document2 pagesFTP - Corporation 2021Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- CH 16 WorkbookDocument14 pagesCH 16 WorkbookClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ch16D2 Workbook 3Document5 pagesCh16D2 Workbook 3Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- C16D1 Workbook 3Document9 pagesC16D1 Workbook 3Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Joint Cost Allocation MethodsDocument19 pagesJoint Cost Allocation MethodsClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Reserves Bad Debts Types of Corporation CCPCDocument2 pagesReserves Bad Debts Types of Corporation CCPCClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 WorkbookDocument33 pagesCH 11 WorkbookClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Clyde Ian Brett C. ZEN115 - 2MB January 28, 2015 "What Does That Imply?"Document3 pagesClyde Ian Brett C. ZEN115 - 2MB January 28, 2015 "What Does That Imply?"Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- SpeechDocument2 pagesSpeechClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- K+12 Program in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesK+12 Program in The PhilippinesClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- No Pardon for a Wrongfully Convicted PrisonerDocument1 pageNo Pardon for a Wrongfully Convicted PrisonerClaude Peña0% (1)
- Merrill Lynch Futures Inc Vs Court of Appeals Spouses Pedro M Lara and Elisa G LaraDocument2 pagesMerrill Lynch Futures Inc Vs Court of Appeals Spouses Pedro M Lara and Elisa G LaraClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Unforgettable Experience in ZEN 115 Speech ClassDocument1 pageUnforgettable Experience in ZEN 115 Speech ClassClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Zuiden V GVTLDocument2 pagesZuiden V GVTLClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis and OogenesisDocument14 pagesSpermatogenesis and OogenesisClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BBL 112 012715Document3 pagesBBL 112 012715Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Case Digests - Corporation LawDocument134 pagesCase Digests - Corporation LawLemuel R. Campiseño80% (10)
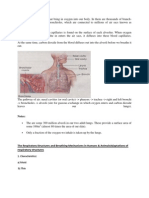
- Respiratory - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory - Circulatory SystemClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument27 pagesPartnershipRomel Gregg TorresNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Case 030615Document2 pagesCase 030615Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- BBL112 022415Document38 pagesBBL112 022415Claude PeñaNo ratings yet
- NS 102-Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageNS 102-Reproductive SystemClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Lymphatic and Excretory SystemsDocument3 pagesThe Lymphatic and Excretory SystemsClaude PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Document44 pagesThe Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8SunnyReduNo ratings yet
- CVD Q's & A'sDocument9 pagesCVD Q's & A'sAlan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Ethier Introductory Bio Mechanics From Cells To Organisms Cambridge 2007Document545 pagesEthier Introductory Bio Mechanics From Cells To Organisms Cambridge 2007hoplala100% (1)
- Science PPT Male Rep System 1.1Document70 pagesScience PPT Male Rep System 1.1Mathel ChavezNo ratings yet
- Student Thesis AssessmentDocument3 pagesStudent Thesis AssessmentAnggi Anggraeni Ratu GumelarNo ratings yet
- Our Lungs Are The Organs That Bring in Oxygen Into Our BodyDocument17 pagesOur Lungs Are The Organs That Bring in Oxygen Into Our BodySaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- Immunochemistry: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument41 pagesImmunochemistry: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Coreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Document13 pagesCoreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Issouf BertheNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Fitness SlidesDocument22 pagesCardiovascular Fitness SlidesFrancine RanadaNo ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 pagesUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramNo ratings yet
- ProcreationDocument55 pagesProcreationRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
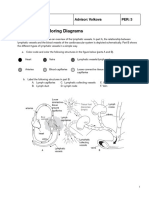
- 02 Anatomy PAK 9 - Coloring DiagramsDocument6 pages02 Anatomy PAK 9 - Coloring DiagramsMahek MotlaniNo ratings yet
- Bhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFDocument675 pagesBhatia LMR 2019 All Subjects PDFPrince Trambadiya100% (1)
- Case Ana CVD BleedDocument19 pagesCase Ana CVD BleedReymon Jan RodadoNo ratings yet
- MBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesMBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Study of Histopathological Pattern of Thyroid Lesions: International Journal of Biomedical and Advance ResearchDocument10 pagesStudy of Histopathological Pattern of Thyroid Lesions: International Journal of Biomedical and Advance ResearchAprilia Fani PNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus Maag DuodenographyDocument49 pagesOesophagus Maag DuodenographyEvan DionesiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Interaction in Critically Ill Patients: Major Determinants of Cardiovascular Responses to VentilationDocument48 pagesCardiopulmonary Interaction in Critically Ill Patients: Major Determinants of Cardiovascular Responses to VentilationAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Constraints PDFDocument4 pagesConstraints PDFArun Gopal100% (1)
- Neurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFDocument82 pagesNeurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFAnonymous oCjRxyBP100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of PCAPDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of PCAPMads0% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Differential Count ImportanceDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 - Differential Count ImportanceIra ReyNo ratings yet
- Iyengar Yoga For The Respiratory System-2020 PDFDocument13 pagesIyengar Yoga For The Respiratory System-2020 PDFSlice LeNo ratings yet
- Activity #11 Urogenital SystemDocument4 pagesActivity #11 Urogenital SystemNathaniel FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)
- Aumento de Reborde Con Tejido BlandoDocument8 pagesAumento de Reborde Con Tejido BlandoSilvia SolisNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument17 pagesBloodfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- Nakamura IIDocument10 pagesNakamura IIMairaMaraviChavezNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument6 pagesDigestive System GuideQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Compartments and ExchangeDocument21 pagesBody Fluids Compartments and ExchangeLIDIYA MOL P VNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)