Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - Guidance Manual For Operators of Small Natural Gas Systems-2002 PDF
Uploaded by
gilberto garciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - Guidance Manual For Operators of Small Natural Gas Systems-2002 PDF
Uploaded by
gilberto garciaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
This chapter contains a simplified description of the pipeline safety requirements. The complete text can be
found in 49 CFR Part 192.
INTRODUCTION
Public Law 104-304 requires the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) to develop and
enforce minimum safety regulations for the transportation of gases by pipeline. The safety
regulations became effective in 1970, and are published in Title 49 of the Code of Federal
Regulations (CFR), Parts 190, 191, 192, and 199. The Office of Pipeline Safety of DOTs
Research and Special Programs Administration (RSPA) is charged with their enforcement.
The gas pipeline safety regulations apply to natural gas systems and operators of natural gas
master meter systems. The pipeline safety regulations require operators of natural gas systems
to: deliver gas safely and reliably to customers; provide training and written instruction for
employees; establish written procedures to minimize the hazards resulting from natural gas
pipeline emergencies; and, keep records of inspection and testing based on suggested forms
found in Appendix B.
Additionally, operators of all natural gas systems, except master meter systems, must test
employees in safety-sensitive positions for prohibited drugs and alcohol and provide an
employee assistance program. The requirements for drug and alcohol testing of pipeline
employees are found in 49 CFR Part 199, which incorporates the overall OPS drug testing
requirements found in 49 CFR Part 40.
Natural gas operators who do not comply with the safety regulations may be subject to civil
penalties, compliance orders, or both. If safety problems are severe, a "Corrective Action Order"
may be issued by OPS. This could result in the shutdown of the system.
State agencies may enforce pipeline safety regulations under certification by OPS. The state
agency is allowed to adopt additional or more stringent safety regulations for intrastate pipeline
transportation as long as such regulations are compatible with the federal minimum regulations.
However, if a state agency is not certified, the DOT retains jurisdiction over intrastate pipeline
systems.
Operators should check with the pipeline safety agency in their state (Appendix C) to determine:
whether a state agency has safety jurisdiction;
whether the state agency has pipeline safety requirements that exceed the federal
regulations;
the inspection and enforcement procedures of the state agency.
Revised May, 2002 I-1
OVERVIEW
The natural gas pipeline industry consists of transmission and distribution companies. These
pipeline systems can be simple or complicated. However, all gas pipeline companies are held to
the same safety standards.
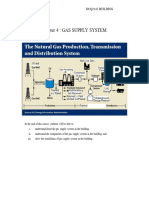
FIGURE I-1 represents one of the many possible configurations of natural gas transmission and
distribution systems. The natural gas:
Flows from the producing wells into gathering line(s).
Through gathering lines and compressors or compressor stations.
After the compressor(s), through transmission lines.
To a processing plant where the heavy ends, such as propane, butane, ethane or natural
gasoline, which are initially components of the gas stream, are removed.
Through the transmission line and additional compressors.
From the compressors to underground storage or a liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant
(where natural gas is liquefied by reducing its temperature to - 260 F), or directly to a
city gate station or master meter system.
FIGURE I-2 is an example of a distribution system that consists of mains and services operating at
different pressures, which are controlled by regulators. Ordinarily, industrial customers receive
gas service through high-pressure distribution mains. The small commercial and the residential
gas systems can be either low- or high-pressure distribution systems.
Revised May, 2002 I-2
FIGURE I-1
Producing Wells
Natural Gas Pipeline
System
Transmission Line
Gathering Lines
Processing
Plant
Compressor
Stations
LNG Plant
City
Underground Gate
Storage
Large Volume
Customer
DISTRIBUTION Meter
SYSTEM
Regulator
Revised May, 2002 I-3
Natural Gas Distribution System
FFigure 2
IGURE I-2
1/4 psig
Low
Pressure
Regulator System
High Pressure
Valve
Meter
Transmission Pipeline
City Gate
Station
60 psig
Distribution Main
Residential Service
Lines
450 psig
Commercial
60 psig
Industrial
1/4 psig
Revised May, 2002 I-4
You might also like
- Seminar Pemerkasaan Perundangan, Pelesenan Dan Keselamatan Gas 26 Sept 2018Document54 pagesSeminar Pemerkasaan Perundangan, Pelesenan Dan Keselamatan Gas 26 Sept 2018INSTECH Consulting100% (1)
- Becker T-Ball Control Valve: For Natural Gas ApplicationsDocument16 pagesBecker T-Ball Control Valve: For Natural Gas ApplicationsEduardo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Gas Distribution NetworkDocument31 pagesSession 3 Gas Distribution NetworkHugo Ruiz100% (2)
- Catalogue Regulators Tank Applications EN16129Document64 pagesCatalogue Regulators Tank Applications EN16129ARah AtilehNo ratings yet
- TrainingDocument17 pagesTrainingMathan Selva Kumar ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Gas Burner ConversionDocument35 pagesChapter 4 Gas Burner ConversionRanjani J DeepakNo ratings yet
- CGD Infrastructure & PNG DistributionDocument87 pagesCGD Infrastructure & PNG Distributiongrill100% (1)
- Gas DesighDocument81 pagesGas DesighNetra Nanda100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Design & Construction of Gas Distribution NetworkDocument81 pagesBasic Concepts of Design & Construction of Gas Distribution NetworkHoney NarangNo ratings yet
- Guide Vane Actuating Unit: Retrofit For Isotherm TurbocompressorsDocument4 pagesGuide Vane Actuating Unit: Retrofit For Isotherm TurbocompressorsHABINSHUTI FERDINANDNo ratings yet
- Gas Supply SystemDocument14 pagesGas Supply SystemSeye KareemNo ratings yet
- Gas DesighDocument81 pagesGas DesighNetra Nanda100% (1)
- Rolls Royce Avon MKDocument3 pagesRolls Royce Avon MKfrdnNo ratings yet
- Basic CGD Concept (Elaborative)Document81 pagesBasic CGD Concept (Elaborative)Shubhanker NandiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Leakage and Unaccounted For Gas PDFDocument13 pagesDetermination of Leakage and Unaccounted For Gas PDFMalouk CheniouniNo ratings yet
- City Gas Distribution PDFDocument80 pagesCity Gas Distribution PDFMoga Jagdish100% (1)
- Allison 501 KB CompressorDocument3 pagesAllison 501 KB CompressortaghiNo ratings yet
- Nirmal Products: Natural Gas Pre-Heaters Are Classified As Under: Direct Type Pre-HeatersDocument8 pagesNirmal Products: Natural Gas Pre-Heaters Are Classified As Under: Direct Type Pre-HeatersConcept -CEPLNo ratings yet
- Is 9798 1995Document25 pagesIs 9798 1995Vaishnav GireeshNo ratings yet
- CityGasDistributionDocument46 pagesCityGasDistributionsujaysarkar850% (1)
- RTA-19 - Oil Supply Monitoring For Geislinger Torsional Vibration DamperDocument5 pagesRTA-19 - Oil Supply Monitoring For Geislinger Torsional Vibration Damperdhilip87No ratings yet
- CRS 2-25 Diesel Common-Rail System With Solenoid Valve Injectors and 2,500 BarDocument3 pagesCRS 2-25 Diesel Common-Rail System With Solenoid Valve Injectors and 2,500 BarRooffNo ratings yet
- DS ProductDataSheet CRS3-27 ENDocument3 pagesDS ProductDataSheet CRS3-27 ENberbagidatakantor123No ratings yet
- Solar Saturn Gas Turbine Generator Drive Application Control PackageDocument3 pagesSolar Saturn Gas Turbine Generator Drive Application Control PackageSara VaccaNo ratings yet
- Pi 2000 Mahle PDFDocument8 pagesPi 2000 Mahle PDFHIDRAFLUIDNo ratings yet
- Webtec Products LimitedDocument20 pagesWebtec Products LimitedtecnicomanelNo ratings yet
- CatConPlu 1Document16 pagesCatConPlu 1Shyam Prasad K SNo ratings yet
- DIN Track Terminal Blocks: XW5 SeriesDocument5 pagesDIN Track Terminal Blocks: XW5 SeriesDaniloTurxiosNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Performance Testing of Single-Element Unbalanced Gas-Lift ValvesDocument8 pagesDynamic Performance Testing of Single-Element Unbalanced Gas-Lift ValvesIkramNo ratings yet
- Rotork ManpowerDocument4 pagesRotork Manpowermar mayoNo ratings yet
- Axial Piston PumpDocument36 pagesAxial Piston Pumpmurad850% (1)
- Katalog STAG Akcesoria ENDocument32 pagesKatalog STAG Akcesoria ENBELLO SAIFULLAHINo ratings yet
- Furnace Thermostat 95c-10024bDocument4 pagesFurnace Thermostat 95c-10024bBlow JoeNo ratings yet
- P66 Cataloge PDFDocument7 pagesP66 Cataloge PDFFerNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Gas Custody Transfer Flow Computers: Application NoteDocument4 pagesCalibrating Gas Custody Transfer Flow Computers: Application Notesurya chandraNo ratings yet
- Hwa YoungDocument43 pagesHwa Youngensi116No ratings yet
- 02 Gas Piping Systems at Launderettes and Similar Installations1Document47 pages02 Gas Piping Systems at Launderettes and Similar Installations1Human Development RISBNo ratings yet
- Qualitrol AP 900 910 RPRRDocument6 pagesQualitrol AP 900 910 RPRRJefe de PlantaNo ratings yet
- ManpowerDocument4 pagesManpowerabjithNo ratings yet
- AIR BLOWERS Calculation of Air Pipe SizeDocument30 pagesAIR BLOWERS Calculation of Air Pipe SizeEngFaisal Alrai100% (1)
- F125-3829 Hydraulic DiagramDocument3 pagesF125-3829 Hydraulic DiagramhacknoteNo ratings yet
- P66 Series Electronic Fan Speed Controls: Product BulletinDocument7 pagesP66 Series Electronic Fan Speed Controls: Product BulletinAlejandro AvilaNo ratings yet
- Additive Injection System Concept Native FileDocument3 pagesAdditive Injection System Concept Native FileAneeq WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 01-01 - LESER-The Safety ValveDocument36 pages01-01 - LESER-The Safety ValveAdrian PetrascuNo ratings yet
- Gasmultibloc Combined Regulator and Safety Shut-Off Valves Single-Stage Function Integrated Bypass Valve MB-D (Le) 405 - 412 B07Document6 pagesGasmultibloc Combined Regulator and Safety Shut-Off Valves Single-Stage Function Integrated Bypass Valve MB-D (Le) 405 - 412 B07TobiasAngererNo ratings yet
- Low Gas Pressure Regulator: Product HandbookDocument31 pagesLow Gas Pressure Regulator: Product HandbookmanishaliveNo ratings yet
- Resources Instrumentation Parker Pneumatic Prep Air II RegulatorsDocument29 pagesResources Instrumentation Parker Pneumatic Prep Air II RegulatorsAnonymous C05BLcNo ratings yet
- P 200 Series+CinDocument2 pagesP 200 Series+CinjovicatrpcevicNo ratings yet
- HP Boiler Control ValvesDocument32 pagesHP Boiler Control ValveshalloihrNo ratings yet
- ML Ind0037Document8 pagesML Ind0037alex escobarNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Troubleshooting Unit For HPI Engine, 6D170E-3Document4 pagesIntroduction of Troubleshooting Unit For HPI Engine, 6D170E-3frank_16No ratings yet
- Gas Transport Symposium: Lifetime of Electrical Equipment, Instrumentation & SCADADocument46 pagesGas Transport Symposium: Lifetime of Electrical Equipment, Instrumentation & SCADAEm GomezNo ratings yet
- Analisis en La Producción de Gas ABBDocument55 pagesAnalisis en La Producción de Gas ABBboa144No ratings yet
- Internship Report Kandhkot Gas Field: Submitted byDocument10 pagesInternship Report Kandhkot Gas Field: Submitted byMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Boiler Clearances: Peru Sourthern Peru S.ADocument2 pagesBoiler Clearances: Peru Sourthern Peru S.AJohan F. MonroyNo ratings yet
- Compressor Solutions For Hydrogen Trailer FillingDocument2 pagesCompressor Solutions For Hydrogen Trailer FillingamsukdNo ratings yet
- Paper On CGD NetworkDocument5 pagesPaper On CGD NetworkAnant RubadeNo ratings yet
- FAS VaporizerBooklet Rev03Document17 pagesFAS VaporizerBooklet Rev03jhaNo ratings yet
- Tổng hợp các tiêu chuẩn hiện cóDocument10 pagesTổng hợp các tiêu chuẩn hiện cóĐường LâmNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsDocument35 pagesElectronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsMuhammad Sohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- KMT - GLOBE - Manual (Ver0.2) - Eng - 16-2026 (2016.08.16)Document21 pagesKMT - GLOBE - Manual (Ver0.2) - Eng - 16-2026 (2016.08.16)Ozi Fawzi100% (1)
- Astm A324-73 (1992)Document2 pagesAstm A324-73 (1992)FeteneNo ratings yet
- Jupiter Band Instruments, Inc. PO Box 90249 Austin, TX 78709-0249 512.288.7400 Fax 512.288.6445Document12 pagesJupiter Band Instruments, Inc. PO Box 90249 Austin, TX 78709-0249 512.288.7400 Fax 512.288.6445frazNo ratings yet
- LPG System AccessoriesDocument4 pagesLPG System AccessoriesPatel KalingaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco - Scooptram ST18 (18t) PDFDocument4 pagesAtlas Copco - Scooptram ST18 (18t) PDFДмитрий АсташонокNo ratings yet
- Ancon - Wall Ties and Restraint FixingsDocument32 pagesAncon - Wall Ties and Restraint FixingsJoão Ricardo LopesNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Project Semester 2 StudentDocument3 pagesPLSQL Project Semester 2 Studentssmile50% (2)
- Java Gui Programming Using Swing I Solved Assignment Ip Class 11Document6 pagesJava Gui Programming Using Swing I Solved Assignment Ip Class 11vikas_20% (3)
- The Idoc Interface: - R/3, Release 4.5Document73 pagesThe Idoc Interface: - R/3, Release 4.5Preetam BiswalNo ratings yet
- FLP Temperature IndicatorDocument2 pagesFLP Temperature IndicatorNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Beads Zetag 7563 - 0410Document2 pagesChemicals Zetag DATA Beads Zetag 7563 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Theory of EstimationDocument2 pagesTheory of EstimationSushil Rana MagarNo ratings yet
- Syswan Duolinks SW24 Series Dual WAN Router User GuideDocument114 pagesSyswan Duolinks SW24 Series Dual WAN Router User GuideSyswan Technologies, Inc.No ratings yet
- Msds Aluminium FoilDocument7 pagesMsds Aluminium FoillatifahNo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 3037 2013 (Ect)Document20 pagesBS en Iso 3037 2013 (Ect)rob100% (1)
- Robinson Fan Manual 1Document26 pagesRobinson Fan Manual 1Aykut Avcı100% (2)
- En 1092-1 PN-10 Steel Pipe Flange - ValviasDocument5 pagesEn 1092-1 PN-10 Steel Pipe Flange - ValviasHoria ZecheruNo ratings yet
- List of Standards On Vibratory FoundationsDocument5 pagesList of Standards On Vibratory FoundationsMiminoRusNo ratings yet
- ERD97P21-U Receiver: Product SpecificationDocument2 pagesERD97P21-U Receiver: Product SpecificationSakerhetsNo ratings yet
- Nas 3610Document186 pagesNas 3610onur onurNo ratings yet
- Track Busway Plug in Units - Domestic 6Document68 pagesTrack Busway Plug in Units - Domestic 6TBS Máy Phát ĐiệnNo ratings yet
- Data Communications Networks: Provisioning GuideDocument174 pagesData Communications Networks: Provisioning Guidelong157No ratings yet
- TCS Video Interfon Model AVC11010-uk PDFDocument12 pagesTCS Video Interfon Model AVC11010-uk PDFrakacyuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Little Rethinking The HandpieceDocument3 pagesDr. Little Rethinking The Handpiecejessica_vukovichNo ratings yet
- I BeamDocument12 pagesI Beamnitouch3564No ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Calculate Measurement Uncertainty - IsobudgetsDocument17 pages7 Steps To Calculate Measurement Uncertainty - IsobudgetsJGlobex100% (1)
- Fourth Edition by William StallingsDocument22 pagesFourth Edition by William Stallingskstu1112No ratings yet