Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECG Lead Placement and Lead Reversal Guide
Uploaded by
alfurlaniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECG Lead Placement and Lead Reversal Guide
Uploaded by
alfurlaniCopyright:
Available Formats
ECG Lead Placement and
Identifying Lead Reversal
This quick reference guide is intended to show correct ECG electrode locations and
how to recognize inadvertent lead wire reversal.
Limb lead placement
For accurate 12-lead measurements and interpretation, limb leads must be placed on
the limbs, not the torso
For monitoring rhythm and rate, limb leads may be placed on the limbs or torso
Lead reversal
Ensuring that the ECG leads are connected to the correct ECG electrode position is
GDR 3323919_A
very important for acquiring accurate rhythm strips and 12-lead ECGs
Lead reversal usually produces recognizable ECG abnormalities
12-lead ECG: chest electrode locations
Frontal Image Lateral Image
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6
Electrode Location
V1 C1 4th intercostal space at right border of the sternum
V2 C2 4th intercostal space at left border of the sternum
V3 C3 Midway between V2 and V4
V4 C4 5th intercostal space at midclavicular line
V5 C5 Level with V4 at left anterior axillary line
V6 C6 Level with V4-V5 at left midaxillary line
AHA leadwire labels in first column, IEC labels in second column
12-lead ECG: additional chest electrode locations
Right-Side Leads Posterior Leads
5R 4R 3R 1 2 3 4 5 6 6 7 8 9
Electrode Location
V3R C3R Midway between V1 and V4R
V4R C4R 5th intercostal space, right midclavicular line
V5R C5R Level with V4R at right anterior axillary line
V7 C7 Level with V4-V6 at left posterior axillary line
V8 C8 Level with V4-V6 at left midscapular line
V9 C9 Level with V4-V6 at left spinal border
Note: automated interpretation may be invalid if V leads are moved to these locations
12-lead: limb electrode locations
Choose an ECG electrode site away
from areas with a large amount of
adipose tissue, major muscle groups or
bony prominences
Limb electrodes can be placed any-
where on the arms distal to the axillary
fold, and anywhere on the legs
RA LA
R L
Electrode Standard Location
RA R Right arm, near the wrist
LA L Left arm, near the wrist
RL N Right leg, above the
right ankle
LL F Left leg, above the
RL LL left ankle
N F
Rhythm monitoring ECG: limb electrode locations
RA LA
Limb leads may be placed on the torso
R L (pictured) or limbs
Choose an ECG electrode site away
from areas with a large amount of
adipose tissue, major muscle groups or
bony prominences
RL LL
N F
Electrode Torso Location (limb location also acceptable)
RA R Middle to outside end of the right clavicle, close to the bone
LA L Middle to outside end of the left clavicle, close to the bone
RL N Lower right trunk, just above the hip
LL F Lower left trunk, just above the hip
LA RA lead reversal LA LL lead reversal
If there is P wave inversion in lead I, If P waves or QRS complexes appear
check for LA RA reversal inverted in lead III, check for
LA LL reversal
Also, if the other complexes in lead I
appear inverted, check for However, be aware that physiologic left
LA RA reversal axis deviation can cause a negative QRS
in lead III
If P wave is larger in lead I than in lead II,
check for LA LL reversal
RL lead reversals
If lead II has extremely low amplitude,
check for RA RL reversal
If lead III has extremely low amplitude,
check for LA RL reversal
Additional Tips
LL RL reversal has almost no effect on the ECG; you cannot identify it from the
ECG, and it has little effect on ECG interpretation
If the RL electrode has poor skin contact, ECG artifact may occur
RL is used to minimize noise from common mode voltages, such as from power lines
Chest electrode reversal (V1V6)
Correct V leads
Normal R wave progression in leads V1V6
In a normal ECG, R wave amplitude should begin small in V1, then gradually increase
through about V4, then decrease, however loss of R wave amplitude can occur due to
an established myocardial infarction or other abnormality
V1 V2 reversal
Abnormal R wave progression in V1V3 is due to V1 V2 reversal
2015 Physio-Control, Inc., Redmond WA, USA.
You might also like
- ACLS Simplify AlgorithmDocument6 pagesACLS Simplify AlgorithmKristine Monforte Coma UritaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- West Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessDocument4 pagesWest Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessPhylum Chordata100% (1)
- Arrhythmias Teacher GuideDocument12 pagesArrhythmias Teacher GuideMayer Rosenberg100% (3)
- 8 Steps in ECG ReadingDocument3 pages8 Steps in ECG ReadingHosanna Gabrielle Dominguez-AbellaNo ratings yet
- Basic EcgDocument17 pagesBasic EcgJohn Vincent DerlaNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeDocument74 pagesBasic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeHazel Arcosa100% (1)
- Emergency Nursing 118 LECDocument11 pagesEmergency Nursing 118 LECboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care of PlanDbyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Note TakingDocument3 pagesFundamentals Note TakingJero BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDocument155 pagesElectrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- 18 NCP Ileal ConduitDocument11 pages18 NCP Ileal ConduitICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Teaching PackageDocument9 pagesCardiology Teaching PackageRicy SaiteNo ratings yet
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDocument6 pagesSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- HW InotropesDocument3 pagesHW InotropesNatalie YeohNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases: Kursk State Medical UniversityDocument88 pagesDepartment of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases: Kursk State Medical UniversityHendraDarmawanNo ratings yet
- ECG Changes in Myocardial InfarctionDocument25 pagesECG Changes in Myocardial InfarctionginaulNo ratings yet
- ICU Checklist For RoundingDocument1 pageICU Checklist For RoundingViolaNo ratings yet
- ECG Skill LabDocument37 pagesECG Skill LabNayyer Khan100% (1)
- Anatomy RespDocument57 pagesAnatomy RespGunawan SamosirNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Nursing OutlineDocument6 pagesSepsis Nursing OutlineSavannah Hayden100% (1)
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Script For EcgDocument14 pagesScript For EcgMonesa Badil LingasaNo ratings yet
- Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With DysrhythmiasDocument19 pagesSelected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With Dysrhythmiaslanie_jecielNo ratings yet
- Code Blue ManagemnetDocument36 pagesCode Blue ManagemnetPreethi BNo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument11 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-546355187No ratings yet
- Clinical Log Term II PDFDocument9 pagesClinical Log Term II PDFPriscilla S100% (1)
- HeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Document101 pagesHeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Putri NurlaeliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationLeirza OnibarNo ratings yet
- Acls LectureDocument15 pagesAcls LectureVincent BautistaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument85 pagesCritical Care NursinganreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Surgery, Hand Clinics, Volume 18, Issue 2, Pages 211-368 (May 2002)Document151 pagesCarpal Tunnel Surgery, Hand Clinics, Volume 18, Issue 2, Pages 211-368 (May 2002)alinutza_childNo ratings yet
- ECG PreparationDocument2 pagesECG PreparationShaheera Shamsudin100% (1)
- Basis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationDocument10 pagesBasis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationKristin SmithNo ratings yet
- Updated BLS Provider ManualDocument24 pagesUpdated BLS Provider ManualRaquel Bregita-RasNo ratings yet
- ECG BasicsDocument15 pagesECG Basicsrohitmeena2889No ratings yet
- Shock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Document41 pagesShock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Samjaisheel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Sut Ams Medical College, TVMDocument7 pagesSut Ams Medical College, TVMDIVYA R.S100% (1)
- DPN Icu PDFDocument1 pageDPN Icu PDFharoonNo ratings yet
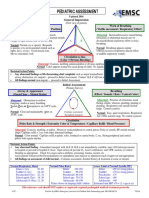
- Pediatric Assessment: General ImpressionDocument2 pagesPediatric Assessment: General ImpressionAghnia Nafila100% (1)
- Acute Stroke Nursing GuidelineFINAL 1 2Document5 pagesAcute Stroke Nursing GuidelineFINAL 1 2radanikmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocument55 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateEva PrimanandaNo ratings yet
- Bsn-Rs-Careplan 2Document9 pagesBsn-Rs-Careplan 2api-520841770No ratings yet
- CS ShockDocument5 pagesCS ShockJuliusSerdeñaTrapal0% (5)
- HO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesDocument7 pagesHO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesSteven Paul DaclesNo ratings yet
- Arterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNDocument34 pagesArterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNinuko1212No ratings yet
- Altered Mental Status: Clinical Reasoning ActivityDocument5 pagesAltered Mental Status: Clinical Reasoning ActivityTina TrippNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Notes (Second Year)Document6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Notes (Second Year)anette katrinNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Conquering The ECGDocument25 pagesConquering The ECGPankaj PatilNo ratings yet
- Patient AssessmentDocument3 pagesPatient AssessmentYemaya84100% (1)
- Pacemaker NotesDocument7 pagesPacemaker Notesrohit860No ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- FE Imbalance HandoutsDocument2 pagesFE Imbalance HandoutsPrasanth Kurien Mathew100% (2)
- ECG Rhythm InterpretationDocument16 pagesECG Rhythm InterpretationJanettNo ratings yet
- Acls Seminar MeDocument62 pagesAcls Seminar MeAbnet Wondimu100% (1)
- Lower Limb 0809Document59 pagesLower Limb 0809asdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Injuries To The Head, Neck, and Face Student NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 9 Injuries To The Head, Neck, and Face Student Notesapi-287615830No ratings yet
- Seac Sub AssoDocument6 pagesSeac Sub Assobeard007No ratings yet
- NEBOSH IGC 1 Home Work Element 8Document2 pagesNEBOSH IGC 1 Home Work Element 8sacham100% (1)
- Oral and Dental Aspects of Child Abuse: GoogleDocument48 pagesOral and Dental Aspects of Child Abuse: GoogleZuhrah Vitri YatiNo ratings yet
- Identifying Entrance GunshotDocument3 pagesIdentifying Entrance GunshotFajarPradhanaPutraNo ratings yet
- TEST CST 30 Seconds PDFDocument1 pageTEST CST 30 Seconds PDFMakmuriyah Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- ImpulseDocument76 pagesImpulseAsif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Cop 06Document98 pagesScaffolding Cop 06Marian Popescu100% (1)
- AxSOS 13Document28 pagesAxSOS 13Dan IonescuNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument19 pagesFirst AidheiraniaaelialuvsheesungNo ratings yet
- 24oct201912101307 Neetu Rani 192-197Document6 pages24oct201912101307 Neetu Rani 192-197Rtr Hasan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Tabel Exposure Dura PhilipsDocument4 pagesTabel Exposure Dura Philipsradiologi rsudtjpriokNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast EssayDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast Essayapi-201463200No ratings yet
- Starting Over Again - The True Comeback Player - David Brown - 2013Document14 pagesStarting Over Again - The True Comeback Player - David Brown - 2013lionello100% (1)
- 201706v3 YuanShiDian Booklet EnglishDocument98 pages201706v3 YuanShiDian Booklet Englishtehtehteh100% (2)
- Hope 2Document11 pagesHope 2Trisha Faye Tabuena PlanaNo ratings yet
- WOD - Mage - The Ascension - The Horizon War Trilogy Book 3 - War in Heaven PDFDocument378 pagesWOD - Mage - The Ascension - The Horizon War Trilogy Book 3 - War in Heaven PDFShanito Not'onbut'off67% (3)
- BandagingDocument2 pagesBandagingA CNo ratings yet
- Gym RulesDocument2 pagesGym Rulesapi-345233749No ratings yet
- 5 Surgery PreTest Self-Assessment and Review 13th Edition-Pages-47-57,39-43Document16 pages5 Surgery PreTest Self-Assessment and Review 13th Edition-Pages-47-57,39-43Mae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Zoomlion ZCC1100H Operators ManualDocument291 pagesZoomlion ZCC1100H Operators ManualERWINNo ratings yet
- 1.risk AssesmentDocument19 pages1.risk AssesmentIbrahim EsmatNo ratings yet
- 85 CRIM1 - People V Madali G.R. Nos. 67803-04. July 30, 1990Document3 pages85 CRIM1 - People V Madali G.R. Nos. 67803-04. July 30, 1990Bea Crisostomo0% (1)
- Infraction ToothDocument45 pagesInfraction ToothanmolNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument49 pagesNeuro AnatomyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- PorosityDocument26 pagesPorositymostafaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Spine CPT Code Changes: Kim Pollock, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDPDocument4 pages2017 Spine CPT Code Changes: Kim Pollock, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDPZakariaAwaludinNo ratings yet
- In Service Thoracic OutletDocument22 pagesIn Service Thoracic Outletapi-549232349No ratings yet
- Yas Technique 3Document5 pagesYas Technique 3sachiel77No ratings yet
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsFrom EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (97)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessFrom EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableFrom EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (788)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayFrom EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNo ratings yet
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (67)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Yin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesFrom EverandYin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesNo ratings yet
- Pranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingFrom EverandPranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!From EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- True Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentFrom EverandTrue Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)
- Strength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymFrom EverandStrength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Tibetan Yoga: Magical Movements of Body, Breath, and MindFrom EverandTibetan Yoga: Magical Movements of Body, Breath, and MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (133)
- Fascial Training: With Easy Exercises To More Mobility And Less Pain (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)From EverandFascial Training: With Easy Exercises To More Mobility And Less Pain (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Which Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseFrom EverandWhich Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (47)
- Easy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportFrom EverandEasy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Wheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemFrom EverandWheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Music For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicFrom EverandMusic For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5-Minute Yoga: A More Energetic, Focused, and Balanced You in Just 5 Minutes a DayFrom Everand5-Minute Yoga: A More Energetic, Focused, and Balanced You in Just 5 Minutes a DayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceFrom EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Mind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeFrom EverandMind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Calisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesFrom EverandCalisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Somatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindFrom EverandSomatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindNo ratings yet