Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System 1
Uploaded by
mei diana sara'is0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagessistem endikrin
Original Title
133867996 Endocrine System 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsistem endikrin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesEndocrine System 1
Uploaded by
mei diana sara'issistem endikrin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
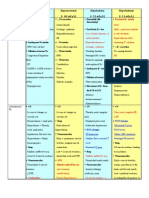
Endocrine System
System of glands(ductless) that release extracellular signaling molecules, known
as hormones to directly into the blood stream
Functions
1. Metabolism( The endocrine system regulates the rate of metabolism and
influences the maturation of tissues such as of the nervous system)
E.g Thyroid hormones
2. Ion Regulation( The endocrine system regulate blood ph as well as the
Na, K and Ca concentrations in the blood)
3. Water Regulation( regulates water balance in controlling the solute
concentration of the blood)
E.g Antidiuretic Hormone
4. Immune System Regulation
E.g Tyrosine
5. Heart rate and Blood pressure regulation
E.g. Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
6. Control of Blood Glucose and other nutrients
E.g. Insulin and Glucagon
7. Control of Reproductive functions
E.g. Testosterone and Estrogen
8. Uterine Contractions and milk release
E.g. Oxytocin
Organs of the Endocrine System
1. Hypothalamus
Part of the diencephalon located below the thalamus and is
connected to the pituitary gland
The highest center of the endocrine system that performs its functions
through hormonal and nervous system
It secretes Releasing Hormones for the pituitary gland
Secretes Oxtocin that is stored in the Posterior pituitary gland
Secretes Anti-Diuretic Hormone or Vasopressin that is also in the
posterior pituitary gland.
2. Pituitary Gland
The master gland
Located below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain
Divided into three parts
Anterior Pituitary gland
o Adenohypophisis
o Release and synthezise hormones
Growth hormone (GH)
Stimulates growth of bone and muscle,
promotes protein synthesis and fat
metabolism, decreases carbohydrate
metabolism
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of adrenal
cortical hormones
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid
hormones
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Female: stimulates growth of ovarian follicle,
ovulation
Male: stimulates sperm production
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Female: stimulates development of corpus
luteum, release of oocyte, production of
estrogen and progesterone
Male: stimulates secretion of testosterone,
development of interstitial tissue of testes
Posterior Pituitary Gland
o Neurohyphophisis
o Does not produce but stores and release
Antidiuretic hormone
Increase water reeabsorption by kidney
Oxytocin
Stimulates Uterine contraction and milk
ejection
Intermediate Pituitary Glands
Melanotropin
Skin colour regulations
Endhorpin
Pain receptors
3. Thyroid gland
Located in the anterior neck lateral to the trachea
Produces thyroid hormones by the thyroid follicles
primary function of the thyroid hormone is to control the
cellular metabolic activity.
stimulates oxidation
Stimulate Growth
Influence the development of the nervous system
4. Parathyroid gland
Located at the back of the thyroid gland (four in number)
Produces parathyroxine hormone
protein hormone from the parathyroid glands that regulates
calcium and phosphorus metabolism.
Increased secretion of parathormone results in
increased calcium absorption from the kidney, intestine,
and bones, thereby raising the blood calcium level
5. Timus Glands
Located in mediastinum behind os. Sternum
activate growth of the body
Reduce the activity of the sex glands
for the immunity of body
6. Adrenal Glands
Two small glands lying in the retroperitoneal region
Adrenal Medulla
o The adrenal medulla functions as part of the autonomic
nervous system.
o Stimulation of preganglionic sympathetic nerve
fibers,which travel directly to the cells of the adrenal
medulla, causes release of the catecholamine hormones
epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Adrenal Cortex
o promotes organic metabolism, regulates sodium and
potassium, response to stress, preadolescent growth
spurt
Glucocorticoids
Gluconeogenesis
Regulates blood sugar by conserving glucose
and cortisone
Mineralocorticoids
Aldosterone, corticosterone
Regulates electrolyte balance by Na retention
and K excretion
Androgens and Estrogens
Secondary sex characteristics
7. Pancreas
This retroperitoneal organ has both endocrine and exocrine
functions
The endocrine function resides in the Islets of Langerhans
The islets have three types of cells- alpha, beta and delta cells
The Alpha Cells Secrete Glucagon
The Beta Cells Secrete Insulin
The Delta Cells Secrete Somatostatin
8. Gonads
Responsible for secondary sex characteristics and reproductive
function
ovaries,
estrogen, progesterone, inhibin - decreases secretion of
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
testes
Produce testosterone hormone
Produces relaxin hormone
Location:
two ovaries are situated in the lower abdomen on each side
of the uterus.
The testes are the pair of male sex organs that form within
the abdomen but descend into the scrotum
Reference : https://www.scribd.com/document/133867996/Endocrine-System
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 7B Reproduction WorksheetDocument11 pages7B Reproduction WorksheetSuttada0% (1)
- Test QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesTest QuestionnaireYkay RoaringNo ratings yet
- What's in Breast Milk?Document1 pageWhat's in Breast Milk?Sunny SideNo ratings yet
- Canine Handlers Trainer's TrainingDocument6 pagesCanine Handlers Trainer's TrainingCherry BepitelNo ratings yet
- MCQ MicrobDocument9 pagesMCQ Microbstationsectiontiga80% (5)
- Blood Culture CollectionDocument2 pagesBlood Culture CollectionNestor PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Pemasangan Kateter UrinDocument12 pagesPemasangan Kateter UrinYULI222100% (1)
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris NewDocument25 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Newmei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi WahyuniDocument7 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi Wahyunimei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris NewDocument25 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Newmei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- " Lung Cancer ": English PaperDocument3 pages" Lung Cancer ": English Papermei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Format Askep KMB Bhs. InggrisDocument13 pagesFormat Askep KMB Bhs. Inggrismei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- BingDocument4 pagesBingpifitputriNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument11 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggrismei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi WahyuniDocument7 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi Wahyunimei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument11 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggrismei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- B.inggris EnvyDocument1 pageB.inggris Envymei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi WahyuniDocument7 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Nebulizer Dan Batuk Efektifterhadap Status Pernapasan Pasien Copd Lutfi Wahyunimei diana sara'isNo ratings yet
- GuppyDocument2 pagesGuppymartynunez12345No ratings yet
- RatDocument2 pagesRatAriel ChouNo ratings yet
- Textile GlossaryDocument143 pagesTextile GlossaryRanjana RajanNo ratings yet
- 501 1267 1 SM PDFDocument8 pages501 1267 1 SM PDFyamahar1yr6No ratings yet
- Abdominal TB Causing Intestinal ObstructionDocument10 pagesAbdominal TB Causing Intestinal ObstructionCleoanne GallegosNo ratings yet
- HPNDocument26 pagesHPNI-Focus PhotosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2 PDFDocument33 pagesEndocrine System 2 PDFNadlif MuammarNo ratings yet
- Kelas 3 Kelas 2 Kelas 1Document4 pagesKelas 3 Kelas 2 Kelas 1RS Azzahra UjungbatuNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Diagram: Salivary GlandsDocument35 pagesDigestive System Diagram: Salivary GlandsJoyce DometitaNo ratings yet
- CH - 42 SodoiDocument15 pagesCH - 42 SodoiAnonymous 333No ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolyte Imbalancessccctutor100% (2)
- Minerva Anestesiol 2017 GruenewaldDocument15 pagesMinerva Anestesiol 2017 GruenewaldMarjorie Lisseth Calderón LozanoNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Term 2 Science Formative AssessmentDocument2 pagesYear 9 Term 2 Science Formative AssessmentAditya N WardhanaNo ratings yet
- SemenarDocument11 pagesSemenarMohammed Moosa JehadNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument27 pagesBiology Projectravifact0% (2)
- Parts of Speech KIPS Academy (Free Download)Document43 pagesParts of Speech KIPS Academy (Free Download)AyshahNo ratings yet
- Brain Natriuretic PeptideDocument9 pagesBrain Natriuretic PeptideRio Kristian NugrohoNo ratings yet
- SMNR - 4... Wound HealingDocument62 pagesSMNR - 4... Wound HealingDrAmar GillNo ratings yet
- Periodontal EmergenciesDocument13 pagesPeriodontal EmergenciesAmmar Aldawoodyeh50% (2)
- Jurnal GlaukomaDocument6 pagesJurnal GlaukomaIntan NarariaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To POW Eng IX 1st Term PDFDocument80 pagesSolutions To POW Eng IX 1st Term PDFTeena sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0735109786800183 Main PDFDocument252 pages1 s2.0 S0735109786800183 Main PDFdangthieuhoiNo ratings yet