Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dermoid cysts of the floor of the mouth: case report and literature review
Uploaded by
Jacky JunaediOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dermoid cysts of the floor of the mouth: case report and literature review
Uploaded by
Jacky JunaediCopyright:
Available Formats
Document downloaded from http://bjorl.elsevier.es day 15/07/2016. This copy is for personal use.
Any transmission of this document by any media or format is strictly prohibited.
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol.
2011;77(5):675.
CASE REPORT BJORL .org
Iatrogenic infection in dermoid cysts of the floor of the mouth
Thiago de Santana Santos1, Ana Cludia Amorim Gomes2, Riedel Frota3, Emanuel Dias de Oliveira e Silva4,
Paulo Ricardo Saquete Martins Filho5, Emanuel Svio de Souza Andrade6
Keywords: dermoid cyst, iatrogenic disease, mouth floor, surgery, oral.
INTRODUCTION evaluation, computed tomography, ultra-
sound, and biopsies may be used to clarify
Dermoid cysts are infrequent cystic the diagnosis.1 Upon careful palpation, der-
tumors with an epidermal epithelium lining moid cysts fluctuate or feel similar to dough;
and structures such as hair follicles, sweat ultrasound imaging adequately supplements
glands, and sebaceous glands. These cysts the physical examination. Thus, aspiration
are considered true teratomas, and their origin biopsies, which are not recommended in the
may be congenital or acquired. The incidence literature for the diagnosis of dermoid cysts,
is highest in male or female individuals aged may be avoided, and may be considered an
from 15 to 35 years1. iatrogenic procedure in this situation. An
altered physical status and the presence of
CASE REPORT poor dental health led to an initial diagnosis
of odontogenic infection involving the primary
A female patients aged 34 years fascial spaces.
reported a progressive bilateral growth in Therapy consists of surgical removal
the submentum and submandibular regions of lesions, either extra- or intraorally, depen-
during the past 6 years. She added that it had ding on the site and number of tumors2,5. In
worsened within the past seven days following the present case, removal was done through
needle aspiration biopsy in the floor of the an intraoral approach as the lesion was located
mouth (Figure 1A). The physical examina- above the geniohyoid muscle.
tion revealed fever, dysphonia, dysphagia,
and dyspnea. The patient was admitted into FINAL COMMENTS
the hospital for surgical drainage through
an intraoral approach; the drained material A careful physical examination may
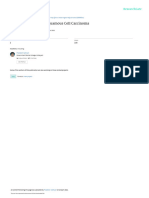
Figure 1. Dermoid cyst - A. Bilaterally enlarged submentual and
consisted of pus and a cyst containing hairs submandibular mass resulting in a double chin, limited opening avoid iatrogenic procedures when a dermoid
and a yellowish viscous material similar to of the mouth, and elevated floor of the mouth; B. Panoramic cyst is suspected; these lesions generally have
keratin. A panoramic radiograph of the jaws radiograph of the jaws; C. Ultrasound - arrows show a suggested well-defined features when located in the floor
revealed an extensive carious lesion with pulp cyst with a semiliquid content within the fascial spaces of the
muscles in the floor of the mouth; D. Surgical removal of the lesion
of the mouth.
involvement in unit 48, which suggested an through an intraoral approach; E. Histopathology. Note the wall
odontogenic infection (Figure 1B). Ultrasound of the cyst consisting of fibrous connective tissue, skin elements REFERENCES
showed a well-defined regularly contoured such as a hair follicle (PF), and sweat glands (SG) (H.E. 100x); F.
Postoperative aspect after 1 year and 6 months.
ecogenic mass in the submentum, suggesting 1. King RC, Smith BR, Burk JL. Dermoid cyst in
a cyst with viscous liquid content (Figure 1C). while those below this muscle may enlarge the floor of mouth: review of the literature and
The hypothesis was a dermoid cyst. Under the submentual region and generate a double case reports. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol.
1994;78(5):567-76.
general anesthesia, the cyst was enucleated chin aspect2-4. In the present case, although 2. El-Hakim IE, Alyamani A. Alternative surgical
in an intraoral approach (Figure 1D). Histo- the lesion was above the geniohyoid muscle, approaches for excision of dermoid cyst of
pathology confirmed the hypothesis (Figure the initial infection and concomitant obesity the floor of mouth. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
1E). The tumor has not recurred 1 year and 6 of the patient resulted in a double chin, which 2008;37(5):497-9.
months after surgery (Figure 1F). 3. Armstrong JE, Darling MR, Bohay RN, Cobb G,
made for an atypical presentation of a tumor Lawen D, Daley TD. Trans-geniohyoid dermoid
located sublingually. cyst: considerations on a combined oral and
DISCUSSION The differential diagnosis of dermoid dermal surgical approach and on histogenesis. J
cysts in the floor of the mouth is made with se- Oral Maxillofac Surg.2006;64(12):1825-30.
veral other lesions, such as ranula, obstructed 4. Kim IK, Kwak HJ, Choi J, Han JY, Park SW. Co-
Dermoid cysts are generally asymp- existing sublingual and submental dermoid cyst
tomatic slow-growing tumors of varying size. submandibular/sublingual ducts, thyroglossal in an infant. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
The anatomical site is critical for its clinical duct cysts, odontogenic infection, benign and Radiol Endod. 2006;102(6):778-81.
presentation. Lesions above the geniohyoid malignant tumors, and even excessive fat in 5. Shaari C, Ho BT, Shah K, Biller HF. Lin-
muscle may enlarge the sublingual region, the submentual region. Besides the clinical gual dermoid cyst. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg.1995;112(3):476-8.
1
Spe ialist iu o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Brazilia College of Bu o a illofa ial Surger a d Trau atolog . Masters degree i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Per a u o
De istr S hool FOP , UPE.
2
Do toral degree i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Per a u o De istr S hool FOP , UPE. Adju t professor, Per a u o De istr S hool FOP , UPE.
3
Do toral degree i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Per a u o De istr S hool FOP , UPE. Staf of the reside progra i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Os aldo Cruz
U i ersit Hospital HUOC , UPE.
4
Spe ialist i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a. Head of the reside a d spe ializaio progra i u o a illofa ial surger a d trau a, Os aldo Cruz U i ersit Hospital HUOC , UPE.
5
Masters degree i health s ie es, Graduate Nu leus i Medi i e, Sergipe Federal U i ersit UFS . Su situte professor of oral patholog , Sergipe Federal U i ersit UFS .
6
Do toral degree i oral patholog , Rio Gra de do Norte Federal U i ersit UFRN . Adju t professor of oral patholog , Per a u o De istr S hool FOP , UPE.
Per a u o De istr S hool Fa uldade de Odo tologia de Per a u o - FOP .
Pernambuco University (Universidade de Pernambuco - UPE).
Se d orrespo de e to: Thiago de Sa ta a Sa tos - Fa uldade de Odo tologia, U i ersidade de Per a u o - A . Ge eral Ne to Ca al a i, . CEP: - . Ca aragi e, PE, Brazil.
Pho e: + - Fa : + - E- ail: thiago. t f@ ahoo. o . r
Paper su ited to the BJORL-SGP Pu lishi g Ma age e t S ste Brazilia Jour al of Otorhi olar golog o Ma , ;
and accepted on July 20, 2010. cod. 7063
Brazilian Journal of otorhinolaryngology 77 (5) SeptemBer/octoBer 2011
http://www.bjorl.org / e-mail: revista@aborlccf.org.br
675
You might also like
- Advances in Oral Biology: Volume 3From EverandAdvances in Oral Biology: Volume 3Peter H. StapleNo ratings yet
- Pyogenic Granuloma of The Larynx A Case Report PDFDocument7 pagesPyogenic Granuloma of The Larynx A Case Report PDFpaolaNo ratings yet
- Rare Case of Large Peripheral Ossifying FibromaDocument5 pagesRare Case of Large Peripheral Ossifying FibromaSwab IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Ojsadmin, 1340Document4 pagesOjsadmin, 1340Dr NisrinNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1808869415307175 Main PDFDocument1 page1 s2.0 S1808869415307175 Main PDFKharismaNisaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cellulitis and Mediastinitis Caused by Odontogenic Infections. Report of Two Cases and Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesCervical Cellulitis and Mediastinitis Caused by Odontogenic Infections. Report of Two Cases and Review of LiteratureJC QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Okc PDFDocument6 pagesOkc PDFanggiNo ratings yet
- Thomas K, Gupta M, Gaba S, Gupta M. Tubercular Retropharyngeal Abscess With Pott's Disease in An Elderly Male Patient. Cureus. 2020 12 (5) .Document6 pagesThomas K, Gupta M, Gaba S, Gupta M. Tubercular Retropharyngeal Abscess With Pott's Disease in An Elderly Male Patient. Cureus. 2020 12 (5) .Imam Taqwa DrughiNo ratings yet
- A Giant Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of The - 2024 - International Journal of SDocument5 pagesA Giant Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of The - 2024 - International Journal of SRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology April 2021Document5 pagesPrimary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology April 2021ASJADI SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- Cabt 12 I 3 P 330Document4 pagesCabt 12 I 3 P 330abeer alrofaeyNo ratings yet
- Ejpd 2018 19 3 9Document3 pagesEjpd 2018 19 3 9Ismail YusufNo ratings yet
- Radicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RarDocument5 pagesRadicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RargarciadeluisaNo ratings yet
- Adult Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis With A Rare BRAF - 2022 - Advances in Oral ADocument3 pagesAdult Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis With A Rare BRAF - 2022 - Advances in Oral Ag.abdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- Gardner Syndrome-The Importance of Early Diagnosis A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesGardner Syndrome-The Importance of Early Diagnosis A Case Report and Review of LiteratureHarsh ChansoriaNo ratings yet
- Report on Two Cases of Gingival Epulis LesionsDocument5 pagesReport on Two Cases of Gingival Epulis LesionsAnandNo ratings yet
- Konjungtivitis GonoreDocument2 pagesKonjungtivitis Gonorefk unswagatiNo ratings yet
- hasson2007Document3 pageshasson2007Ankita GuravNo ratings yet
- Marsupialization With Enucleation of Mandibular Lateral Periodontal CystDocument1 pageMarsupialization With Enucleation of Mandibular Lateral Periodontal CystSkyeNo ratings yet
- Focal Reactive OvergrowthsDocument5 pagesFocal Reactive OvergrowthsLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Artículo 3Document4 pagesArtículo 3Ruby QuirozNo ratings yet
- Alternative Surgical Approaches For Excision of Dermoid Cyst of The Floor of MouthDocument3 pagesAlternative Surgical Approaches For Excision of Dermoid Cyst of The Floor of MouthKharismaNisaNo ratings yet
- Ars Lan 2019Document3 pagesArs Lan 2019khadidja BOUTOUILNo ratings yet
- Foreign Body Esophagus: When Endoscopic Removal FailsDocument3 pagesForeign Body Esophagus: When Endoscopic Removal FailsgheaastridgayatriNo ratings yet
- Case Report: A Large Extragnathic Keratocystic Odontogenic TumourDocument8 pagesCase Report: A Large Extragnathic Keratocystic Odontogenic TumourShinta Dewi NNo ratings yet
- Central Odontogenic Fibromyxoma of Mandible: An Aggressive Odontogenic PathologyDocument7 pagesCentral Odontogenic Fibromyxoma of Mandible: An Aggressive Odontogenic PathologyWesley RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 2017 FrogDocument4 pages2017 FrogUma DatarNo ratings yet
- Early Management and Wound Dressing Selection For Cervical Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesEarly Management and Wound Dressing Selection For Cervical Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case ReportDeka Dharma PutraNo ratings yet
- Ijos 201375 ADocument4 pagesIjos 201375 AIsmail YusufNo ratings yet
- Removal of Foreign Body (Denture) in Esophagus With Rigid EsophagoscopeDocument6 pagesRemoval of Foreign Body (Denture) in Esophagus With Rigid EsophagoscopetaagrettaaNo ratings yet
- Kimura Disease, Pott'S Puffy - XXXXXDocument28 pagesKimura Disease, Pott'S Puffy - XXXXXHossam ThabetNo ratings yet
- Pulpitis JurnalDocument2 pagesPulpitis JurnalIsmail YusufNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of The Hard Palate Secondary To Actinomycosis: A Case ReportDocument2 pagesOsteomyelitis of The Hard Palate Secondary To Actinomycosis: A Case ReportPeter SalimNo ratings yet
- Paradental CystDocument2 pagesParadental CystAyoubNo ratings yet
- Diode Laser Aided Excision of Pyogenic Granuloma On Tongue: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesDiode Laser Aided Excision of Pyogenic Granuloma On Tongue: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Rare Paediatric Ossifying Fibroma CaseDocument7 pagesRare Paediatric Ossifying Fibroma CaseRika Sartyca IlhamNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Sialometaplasia of The Palate: A Case Report: Ashwarya Trivedi, Mysore K Sunil, Sonam Gupta, Shaveta GargDocument4 pagesNecrotizing Sialometaplasia of The Palate: A Case Report: Ashwarya Trivedi, Mysore K Sunil, Sonam Gupta, Shaveta Gargandrianiputri916No ratings yet
- Article Thyroglose 1Document2 pagesArticle Thyroglose 1Jessica Paulina Salazar RuizNo ratings yet
- Kumar I 2018Document3 pagesKumar I 2018bm100% (1)
- Duplication of The External Auditory Canal Two CasDocument5 pagesDuplication of The External Auditory Canal Two CasIvana SupitNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument46 pagesCase PresentationCareer Guide with Dr ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Absesparafaring4 PDFDocument3 pagesAbsesparafaring4 PDFnataliayobeantoNo ratings yet
- Kista TiroglosusDocument2 pagesKista TiroglosusKhairuman FitrahNo ratings yet
- Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising in A Previous Calcifying CystDocument8 pagesGhost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising in A Previous Calcifying CystAntonio Álvarez FloresNo ratings yet
- Irritational Fibroma A Case ReportDocument2 pagesIrritational Fibroma A Case ReportquikhaaNo ratings yet
- 9-Traumatic FibromaDocument3 pages9-Traumatic Fibromaasal bakhtyariNo ratings yet
- Pindborg Tumor Presenting in Early Adolescent - A Rare Case ReportDocument7 pagesPindborg Tumor Presenting in Early Adolescent - A Rare Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Rare Genital Disseminated Superficial Porokeratosis in Immunocompetent ManDocument3 pagesRare Genital Disseminated Superficial Porokeratosis in Immunocompetent ManMostafaAhmedNo ratings yet
- Excision of An Atypical Case of Palatal Bone Exostosis: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesExcision of An Atypical Case of Palatal Bone Exostosis: A Case ReportdrgsaifullahNo ratings yet
- Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst - Report of Case Found - in Routine Imaginological Examinations and An Update of The LiteratureDocument8 pagesBotryoid Odontogenic Cyst - Report of Case Found - in Routine Imaginological Examinations and An Update of The LiteraturePo PowNo ratings yet
- Perioral and Gingival Hyperpigmentation Seco - 2021 - International Journal of WDocument2 pagesPerioral and Gingival Hyperpigmentation Seco - 2021 - International Journal of WBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- True Versus Bay CystDocument11 pagesTrue Versus Bay Cystjorefe12No ratings yet
- Ijcmr 692 Jun 14Document2 pagesIjcmr 692 Jun 14Jeyachandran MariappanNo ratings yet
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery CasesDocument5 pagesOral and Maxillofacial Surgery Casesvaleria lindaNo ratings yet
- Phleboliths and The Vascular Maxillofacial LesionDocument4 pagesPhleboliths and The Vascular Maxillofacial LesionVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Actinomycose AmygdalienneDocument3 pagesActinomycose AmygdalienneOumaima Ben KhalifaNo ratings yet
- The Plunging Ranula Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management 1989Document4 pagesThe Plunging Ranula Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management 1989kaarlaamendezNo ratings yet
- Pseudo-Ankylosis Caused by Osteoma of The Coronoid Process: Case Report - Tumors/CystsDocument3 pagesPseudo-Ankylosis Caused by Osteoma of The Coronoid Process: Case Report - Tumors/CystsSaurabh SatheNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument4 pagesCasepika pikatwNo ratings yet
- Ijcpd 12 68Document5 pagesIjcpd 12 68lily oktarizaNo ratings yet
- A Case of Sepsis Caused by Odontogenic Infection With Temporal Fossa and Pericostal AbscessDocument1 pageA Case of Sepsis Caused by Odontogenic Infection With Temporal Fossa and Pericostal AbscessJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Muenke PaperDocument7 pagesMuenke PaperJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- VictoriaSchunemann ApertSyndromeDocument27 pagesVictoriaSchunemann ApertSyndromeJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Oral Cancer Diagnosis and TherapyDocument427 pagesOral Cancer Diagnosis and TherapyJacky Junaedi100% (2)
- 1 Hochman NYSDJDocument6 pages1 Hochman NYSDJJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- 6 Surgical Periodontal TherapyDocument38 pages6 Surgical Periodontal TherapyPriya SargunanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Reference Interval For Presepsin, An Early Marker For Sepsis - Biochemia MedicaDocument5 pagesDetermination of Reference Interval For Presepsin, An Early Marker For Sepsis - Biochemia MedicaJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument45 pagesInfectionJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- 10 1001@jama 2016 0287Document10 pages10 1001@jama 2016 0287ompardor7554No ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infections For SeminarDocument11 pagesOdontogenic Infections For SeminarJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Dental Flap DesignDocument31 pagesDental Flap Designgeethagm4No ratings yet
- Athraa A. Mahmood M.Sc. of Periodontics: Prepared byDocument22 pagesAthraa A. Mahmood M.Sc. of Periodontics: Prepared byJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Manual Abx055370Document4 pagesManual Abx055370Jacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Pathfast BrochureDocument6 pagesPathfast BrochureJacky Junaedi100% (1)
- PROSPEKT ENG Presepsin Time Is Survival ID 6153Document15 pagesPROSPEKT ENG Presepsin Time Is Survival ID 6153Jacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma of MaxillaDocument11 pagesPeripheral Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma of MaxillaJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Piis0901502717314777 2Document9 pagesPiis0901502717314777 2Jacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Circulation, Body Fluid and BasicDocument65 pagesDisorder of Circulation, Body Fluid and BasicJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Scoring Systems and Outcome Markers in ICU PatientsDocument2 pagesPrognostic Scoring Systems and Outcome Markers in ICU PatientsJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Ranula: A Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesRanula: A Review of LiteratureNicco MarantsonNo ratings yet
- Pre Album inDocument5 pagesPre Album inJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Presepsin FinalDocument5 pagesPresepsin FinalJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Sanggar BorneoDocument1 pageSanggar BorneoJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Tennison Type Lip Repair PDFDocument7 pagesTennison Type Lip Repair PDFJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Bang Hendi 3Document10 pagesBang Hendi 3Jacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Oral Oncology Diagnosis and ManagementDocument327 pagesContemporary Oral Oncology Diagnosis and ManagementJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Emergency Case TemplateDocument46 pagesEmergency Case TemplateJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- TN ErwinDocument13 pagesTN ErwinJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- TN NgadinoDocument16 pagesTN NgadinoJacky JunaediNo ratings yet
- Congenital Cystic Masses of The NeckDocument48 pagesCongenital Cystic Masses of The NeckEsraa El ShemeNo ratings yet
- Dermoid Cyst of Nasal Septum in An Adult Patient: 1. IntroductionDocument7 pagesDermoid Cyst of Nasal Septum in An Adult Patient: 1. IntroductionMANASA AswathNo ratings yet
- Differences Benign Malignant NeoplasmsDocument3 pagesDifferences Benign Malignant NeoplasmsMichtropolisNo ratings yet
- Limbal DermoidDocument4 pagesLimbal DermoidPranjali ChhayaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Atlas of Orbital Diseases-Email PDFDocument389 pagesSurgical Atlas of Orbital Diseases-Email PDFAmi Misici100% (1)
- Bhattacharya S K Short Cases in Surgery PDFDocument346 pagesBhattacharya S K Short Cases in Surgery PDFRadhika M100% (5)
- MCQ Shalya Tantra 170820Document59 pagesMCQ Shalya Tantra 170820Setu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Dermoid CystDocument13 pagesDermoid CystGaganaNo ratings yet
- Dermoid Cyst: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 pagesDermoid Cyst: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchfgfxgxNo ratings yet
- Dermoid CystDocument29 pagesDermoid CystAlik ChuaNo ratings yet
- Benign Lesions of The OvariesDocument12 pagesBenign Lesions of The OvariesdocjosmaNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Torsion of Dermoid CystDocument4 pagesGyne - Torsion of Dermoid CystroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument19 pagesOvarian Cyst Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentMuhammad AbeeshNo ratings yet
- Managing Adnexal Masses in PregnancyDocument6 pagesManaging Adnexal Masses in PregnancyRosália Coutada100% (1)
- Dermoid Sinus Surgery in DogsDocument6 pagesDermoid Sinus Surgery in DogsAvak JoshNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument26 pagesOvarian CystAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Brief Descriptions : Yusmafaziela BT Yusof 08-3-223 Group C Section 6 Pathology: Dermoid Cysts, OvaryDocument4 pagesBrief Descriptions : Yusmafaziela BT Yusof 08-3-223 Group C Section 6 Pathology: Dermoid Cysts, OvaryYusmafaziela YusofNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Various Gynecological and Obstetric TopicsDocument140 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Document on Various Gynecological and Obstetric TopicsjNo ratings yet
- Congenital Neck MassesDocument9 pagesCongenital Neck Massesjuita auglinaNo ratings yet
- Dermoid Cyst-Grand RoundsDocument13 pagesDermoid Cyst-Grand RoundsjojolilimomoNo ratings yet
- Mature Ovarian Cystic Teratoma Containing Well-Differentiated Cerebellar TissueDocument2 pagesMature Ovarian Cystic Teratoma Containing Well-Differentiated Cerebellar TissuedrelvNo ratings yet
- Dermoid CystDocument4 pagesDermoid Cystmicheal1960No ratings yet
- 144174d1376299459 Previous Years Question Papers Jipmer Staff Nurse Recruitment Exam Jipmer Question Paper 2012 PDFDocument12 pages144174d1376299459 Previous Years Question Papers Jipmer Staff Nurse Recruitment Exam Jipmer Question Paper 2012 PDFGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Neoplasia: Neoplasia: Gross & Histological PreparationsDocument30 pagesClassification of Neoplasia: Neoplasia: Gross & Histological PreparationsdostoviskyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Ovarian Cyst and InfertilityDocument7 pagesRelationship Between Ovarian Cyst and InfertilityiVriskNo ratings yet
- ENT NoseDocument18 pagesENT NosevkNo ratings yet
- IOTA - Simple - Rules - Susanne - Johnson 2 PDFDocument76 pagesIOTA - Simple - Rules - Susanne - Johnson 2 PDFBenyamin Rakhmatsyah TitaleyNo ratings yet
- 8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809Document8 pages8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809NenyNo ratings yet
- Ijo 67 1930Document19 pagesIjo 67 1930faraamirNo ratings yet
- Low-risk cystectomy technique for benign ovarian cystsDocument4 pagesLow-risk cystectomy technique for benign ovarian cystsBudi do Re miNo ratings yet