Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IBPS SO Syllabus for Quantitative Aptitude, Reasoning & English
Uploaded by
vinayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IBPS SO Syllabus for Quantitative Aptitude, Reasoning & English
Uploaded by
vinayCopyright:
Available Formats
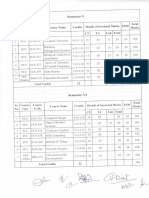
SYALLABUS FOR IBPS SO 2017
IBPS SO Syllabus for Quantitative Aptitude
1. Roots 16.Boats & Streams
2. Clocks 17.Pipes & Cisterns
3. Averages 18.Problems on Ages
4. Pie Charts 19.Time & Distance
5. Bar Graphs 20.Problems on trains
6. Logarithms 21.Stocks & Shares
7. Probability 22.Tabulation
8. Line Graphs 23.Decimal & Fractions
9. HCL & LCM 24.Ratio & Proportions
10.Percentages 25.Mixtures & Allegations
11.Mensuration 26.Volume & Surface Area
12.Simplification 27.Permutation & Combination
13.Profit & Loss 28.Simple & Compound Interest
14.Time & Work 29.Heights & Distance
15.Number System Relationships
IBPS Specialist Officer Syllabus for Reasoning
1. Logic 12.Blood Relation
2. Classification 13.Puzzle Test
3. Cubes and Dice 14.Direction Sense
4. Data Sufficiency 15.Logical Venn Diagrams
5. Syllogism 16.Alphabet & Alpha Numeric
6. Clocks & Calendars Sequence Test
7. Arithmetical Reasoning 17.Eligibility Test
8. Mathematical Operations 18.Arrangements-Linear & Circular
9. Input-Output 19.Series test
10.Coding-Decoding 20.Odd figures
11.Analogy 21.Miscellaneous test.
IBPS Specialist Officer Syllabus for English
1. Verb 12.Fill in the Blanks
2. Tenses 13.Sentence Completion
3. Adverb 14.Word Formation
4. Articles 15.Theme Detection
5. Grammar 16.Passage Completion
6. Homonyms 17.Rearrangement of Passage
7. Synonyms 18.Spelling
8. Antonyms 19.Sentence Framing
9. Vocabulary 20.Active-Passive Voice
10.Conclusion 21.Indirect-Direct Speech
11.Error Correction 22.Phrases and Idioms.
IBPS IT Officer Syllabus
Database Management System
1. File Based Data Management Disadvantages of file system
2. Database systems Need for Database, Advantages of using a database
3. Characteristics of data in a database Functions of DBMS, Components of a
database, Comparison between Database and file-processing systems
4. Data dictionary Data abstraction, Data independence Logical and Physical
data independence
5. Architecture: Overall Architecture of DBMS
6. Three level architecture Hierarchical, Networking, Relational Data Models (E-
R Model, E-R Diagrams, EER Model), Advantages and Disadvantages of each
model.
7. Advanced Concepts: Introduction to Data warehousing and Data mining
Different types
8. Client/Server Technology: Client Server Distributed and Co-operative
processing Peer- to Peer processing Application components
Transaction management.
9. Relational Structure Characteristics of Relational Database Model CODDs
rules Tables (Relations), Rows (Tuples), Domains, Attributes, Extension,
Intention.
10.Keys: Candidate Key, Primary Key, Foreign Key, Super Keys, Unique Keys.
11.Data Constraints: Referential Integrity Constraints, Entity Integrity Constraints,
Constraints like Primary key constraint, Unique, Check constraint strong Entity,
Weak Entity.
12.Normalization: Introduction Purpose of Normalization Definition of
Functional Dependence (FD) Relational database Design, Normal forms: 1NF,
2NF, 3NF, BCNF, 4Nf and 5 NF.
13.Database Administration: DBA Tasks DBA Tools User Privileges
Performance monitoring and tuning Query tracing Backup and Recovery
14.Introduction to SQL: Advantages of SQL Invoking SQL*PLUS, The Oracle Data-
types, Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation language (DML),
Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language ( DQL) and all related
commands.
15.Queries using Group by and Order by clause & Join: Querying a Single Table,
Ordering results, grouping the results, Joins, Types of Joins, Sub queries.
16.Operators: Logical, Value, Syntax and Query expression operators Set
operators.
17.Functions: Character, Arithmetic, Date and time, Group and Miscellaneous
Functions, Commit, Rollback, Savepoint.
18.Format models: Character, Numeric & Date Format models.
19.Views: Introduction Advantages of views The Create View Command,
Updating Views, Views and Joins, Views and Sub queries Dropping Views.
20.Sequences: Creating Sequences, Altering Sequences, Dropping Sequences.
21.Indexes: Index Types, Creating of an Index: Simple Unique and Composite
Index, Dropping Indexes.
22.Snapshots: Creating a Snapshot, Altering Snapshot, Dropping a Snapshot.
23.Introduction to PL/SQL: The PL/SQL Syntax, The PL/SQL Block Structure,
Fundamentals of PL/SQL, Advantages of PL/SQL data Types.
24.Control Structure: Conditional Control, Iterative Control, Sequential Control.
25.Exception handling: Predefined Exception User defined Exception.
26.Cursors: Implicit and Explicit Cursors
27.Procedures: Advantages Creating Executing and Deleting a Stored
Procedure.
28.Functions: Advantages Creating Executing and Deleting a Function.
29.Database Triggers: Use of Database Triggers How to apply database Triggers
Types of Triggers Syntax for Creating Trigger Deleting Trigger.
Data Communication and Networking
1. Data Communication: Components of a data communication Data flow:
simplex half duplex full duplex; Networks Definition Network criteria
Types of Connections: Point to point multipoint; Topologies: Star, Bus, Ring,
Mesh, Hybrid Advantages and Disadvantages of each topology.
2. Types of Networks: LAN MAN WAN CAN HAN Internet Intranet
Extranet, Client-Server, Peer To Peer Networks.
3. Transmission Media: Classification of transmission media Guided Twisted
pair, Coaxial, Fiber optics; unguided Radio waves Infrared LOS VSAT
cabling and standards
4. Network devices: Features and concepts of Switches Routers (Wired and
Wireless) Gateways.
5. Network Models: Protocol definition standards OSI Model layered
architecture functions of all layers..
6. Data Link Layer: Framing & its methods, Flow Control, Error control. DLL
Protocol, Piggybacking & Pipelining. MAC Sub layer, Media access control for
LAN & WAN, collision, IEEE 802 standards for LAN & MAN & their comparison.
Ethernet, Wireless LANs, Broadband Wireless, Bluetooth.
7. Network Layer: Routing, Congestion Control Algorithms, IP protocol, IP
Addresses, Comparative study of IPv4 & IPv6, Mobile IP.
8. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) User Datagram Protocol, Data Traffic,
Congestion Control and Quality of Service
9. Network Security: Cryptography, Message Security, Digital Signature, User
Authentication, Key Management, Security Protocols Internet,DNS,SMTP, FTP,
HTTP, WWW, Virtual Terminal Protocol.
Operating System
1. Introduction to System Programs & Operating Systems, Buffering & Spooling,
Types of Operating System.
2. File concepts, access methods, free space managements, allocation methods,
directory systems, protection, organization, sharing & implementation issues,
etc.
3. Process: Concept, Process Control Blocks (PCB), Scheduling criteria Preemptive
& non Preemptive process scheduling, Scheduling algorithms, algorithm
evaluation, multiple processor scheduling, real time scheduling, threads,
critical section problem, semaphores, and classical problems of
synchronization, etc.
4. Memory Hierarchy, logical and physical address space, swapping, contiguous
and non-contiguous allocation, paging, segmentation, Concepts of virtual
memory, Cache Memory Organization, demand paging, page replacement
algorithms, allocation of frames, thrashing, demand segmentation.
5. Distributed operating system:-Types, Design issues, File system, Remote file
access, RPC, RMI, Distributed Shared Memory(DSM), Basic Concept of Parallel
Processing & Concurrent Programming
6. Security & threats protection: Security violation through Parameter, Computer
Worms & Virus, Security Design Principle, Authentications, Protection
Mechanisms.
Software Engineering
1. The Software Product and Software Process Models, Software Process
customization and improvement.
2. Requirement Elicitation, Analysis, and Specification Functional and Non-
functional requirements, Validation, Trace ability.
3. Software Design, Architectural Design, User Interface Design, Function-
oriented Design, SA/SD Component Based Design, Design Metrics.
4. Software Analysis and Testing, Software Test Process, Testing Levels, Test
Criteria, Test Case Design, Test Oracles, Test Techniques, Black-Box Testing, etc.
5. Software Maintenance & Software Project Measurement: Software
Configuration Management (SCM), Re-engineering, Reverse Engineering.
Project Management Concepts, Feasilibility Analysis, Project and Process
Planning, Resources Project Scheduling and Tracking, etc.
Data Structure
1. Introduction: Basic Terminology, Data types and its classification, Array
Definition, Representation and Analysis of Arrays, Single and Multidimensional
Arrays, etc.
2. Stack, Array Implementation of stack, Linked Representation of Stack, Queue,
Array and linked implementation of queues, Circular queues, D-queues and
Priority Queues. Linked list, Generalized linked list.
3. Trees: Basic terminology, Binary Trees, Complete Binary Tree, Extended Binary
Trees, Array and Linked Representation of Binary trees, etc.
4. Internal and External sorting ,Insertion Sort, Bubble Sort, selection sort Quick
Sort, Merge Sort, Heap Sort, Radix sort, Searching & Hashing: Sequential
search, binary search, Hash Table, Hash Functions, etc.
5. Graphs: Introduction, Sequential Representations of Graphs, Adjacency
Matrices, Traversal, Connected Component and Spanning Trees, Minimum Cost
Spanning Trees.
Compiler Design
1. Introduction to Compiler, Phases and passes, Bootstrapping, Implementation
of lexical analyzers, LEX: lexical analyzer generator, Input buffering, Recognition
of tokens, Error handling.
2. Basic Parsing Techniques: Parsers, Shift reduce parsing, operator precedence
parsing, top down parsing, predictive parsers, LR parsers , an automatic parser
generator
3. Syntax directed definitions, L-attributed definitions, Syntax directed
Translators, Intermediate code, etc.
4. Symbol Tables, Run-Time Administration, simple stack allocation scheme,
storage allocation in block structured language, Code Optimization and Code
Generation
5. Parsing control statements, syntax diagrams, Error Recovery, Interpreting
control statements, parsing programs, procedures and Functions.
Computer Organization and Microprocessor
1. Computer System: Basic Computer Operation, Machine Instructions,
Addressing Modes, DLX Architecture,
2. Computer Configuration, Memory organization, Memory Architecture and
Interface, DMA, Synchronization, etc.
3. Microprocessor As A CPU types of Microprocessor, Microcomputers,
Computer Languages, Flags, Program Counter(PC), Stack Pointer, OPCode
Format, etc.
4. Input-output System.
Object Oriented Programming (OOPS)
1. General concept OOPS Object, Classes, Data Abstraction, Encapsulation,
Inheritance, Polymorphism, Methods and Messages, Dynamic Binding.
2. Features, Advantages and Applications of OOPS
3. Aggregation and Association, Generalization, Multiple Inheritance.
IBPS Specialist Officer Syllabus for General Awareness
1. Sports 12.UNO
2. History 13.Marketing
3. Culture 14.Awards & Honors Sports
4. Indian Economy 15.Financial News
5. International Economy 16.Agriculture
6. Geography 17.Science & Technology
7. General Politics 18.Bills New & Amendments
8. Scientific Research 19.Memorandum of
9. Indian Constitution Understanding
10.Countries and Capitals 20.Appointments & Companies
11.Budget & Five Years Plans Mergers
You might also like
- Course FileDocument6 pagesCourse FilepthepronabNo ratings yet
- Finance, HR & IT Indicative Syllabus OverviewDocument10 pagesFinance, HR & IT Indicative Syllabus Overviewhaardik03No ratings yet
- Dcap204 Managing Database Dcap402 Database Management Systems PDFDocument265 pagesDcap204 Managing Database Dcap402 Database Management Systems PDFEr Hardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Olympiad winner’s skills by subjectDocument18 pagesOlympiad winner’s skills by subjectTameneNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument80 pagesSyllabusDhananjay JahagirdarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals fo Database Course outline 2023 for stdeuntsDocument4 pagesFundamentals fo Database Course outline 2023 for stdeuntsbeshahashenafe20No ratings yet
- DBMS - 3rd Year VI Semester - AICTE 2020-21 - 9 March 2021Document2 pagesDBMS - 3rd Year VI Semester - AICTE 2020-21 - 9 March 2021RAtnaNo ratings yet
- 3rd CSE IT New Syllabus 2019 20Document19 pages3rd CSE IT New Syllabus 2019 20Harsh Vardhan HBTUNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Syllabus CombinedDocument9 pages3rd Sem Syllabus CombinedARPITA ARORANo ratings yet
- MTE 1 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMTE 1 SyllabusMANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Post of Assistant Manager (MIS)Document1 pageSyllabus For The Post of Assistant Manager (MIS)Gonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- DBMS course syllabusDocument3 pagesDBMS course syllabuseswar pNo ratings yet
- Middleware Technologies Course OverviewDocument17 pagesMiddleware Technologies Course OverviewArunachalam SelvaNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument284 pagesDatabase Management Systemavinash pandeyNo ratings yet
- Dbms OutlineDocument6 pagesDbms OutlineGeorge Mbiriri MuindiNo ratings yet
- D B M SDocument4 pagesD B M SKutbuddin AmbawalaNo ratings yet
- (148182096) Ipsr Solutions PHP SyllabusDocument2 pages(148182096) Ipsr Solutions PHP Syllabusprabhujaya97893No ratings yet
- Mba IT BookDocument266 pagesMba IT BookDurgeshNo ratings yet
- 12 Computer Science and ApplicationsDocument5 pages12 Computer Science and ApplicationsSurya KameswariNo ratings yet
- Database Systems Course ContentDocument7 pagesDatabase Systems Course ContentAhmad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems - Course OutlineDocument5 pagesDatabase Management Systems - Course OutlineMuhammad AamerNo ratings yet
- NF) S ) JF Cfof) U G) KFN LJLJW ) JF, /fhkqflít T (Tlo ) 0Fl, Sdko'6/ Ol Hlgo/ KBSF) V'NF K - Ltof) Lutftds K/Liffsf) Kf7/Oqmd Låtlo KQDocument4 pagesNF) S ) JF Cfof) U G) KFN LJLJW ) JF, /fhkqflít T (Tlo ) 0Fl, Sdko'6/ Ol Hlgo/ KBSF) V'NF K - Ltof) Lutftds K/Liffsf) Kf7/Oqmd Låtlo KQNikesh NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument4 pagesDatabase Management SystemShruti PantNo ratings yet
- RGPV Mca V (5) Sem Grading SyllabusDocument14 pagesRGPV Mca V (5) Sem Grading SyllabusChetan NagarNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument2 pagesDatabaseamir100% (2)
- BTech CSE Third Year SyllabusDocument5 pagesBTech CSE Third Year SyllabusAnkush KumarNo ratings yet
- CS-2004 Database Management Systems Cr-4: Course Outcome: at The End of The Course, The Students Will Be Able ToDocument2 pagesCS-2004 Database Management Systems Cr-4: Course Outcome: at The End of The Course, The Students Will Be Able To089ASHUTOSH PATINo ratings yet
- EC 3505: Introduction to Microprocessors and Digital Computer OrganizationDocument6 pagesEC 3505: Introduction to Microprocessors and Digital Computer Organizationrohit_rswNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) : RationaleDocument20 pagesRelational Database Management System (RDBMS) : Rationalepallavip10No ratings yet
- Syllabus For MPPSC IT EXAM 2016Document2 pagesSyllabus For MPPSC IT EXAM 2016Prashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Kerala PSC HSST Computer Science SyllabusDocument5 pagesKerala PSC HSST Computer Science SyllabusniyaNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDatabase Management Systems: Course Description and Objectivesash 3No ratings yet
- Int306:Database Management Systems: Course OutcomesDocument2 pagesInt306:Database Management Systems: Course OutcomesMadesh TurakaNo ratings yet
- CSE2004 - DATABASE-MANAGEMENT-SYSTEMS - ETH - 1.0 - 0 - CSE2004 Database Management System PDFDocument14 pagesCSE2004 - DATABASE-MANAGEMENT-SYSTEMS - ETH - 1.0 - 0 - CSE2004 Database Management System PDFArjun S 18BCE0236No ratings yet
- Computer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidDocument51 pagesComputer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidAyesha PervaizNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusrishabhtak16No ratings yet
- Database Management Quantum SebDocument284 pagesDatabase Management Quantum SebShivanshu Verma50% (4)
- Feedback 2017 18Document26 pagesFeedback 2017 18NikhilGuptaNo ratings yet
- 18-Computer Science SyllabusDocument5 pages18-Computer Science Syllabusmani_bushanNo ratings yet
- Master of Science (M.SC.) - Computer Science Curriculum - 2013Document50 pagesMaster of Science (M.SC.) - Computer Science Curriculum - 2013muralikrish14uNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lesson Plan With Out DatesDocument5 pagesDbms Lesson Plan With Out DatesKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Database Management System - 1 SyllabusDocument14 pagesDatabase Management System - 1 SyllabusRudrik BhattNo ratings yet
- Banking Batch - Syllabus Content Sheet: Quantitative Aptitude Logical ReasoningDocument1 pageBanking Batch - Syllabus Content Sheet: Quantitative Aptitude Logical ReasoningYASH HAJARENo ratings yet
- STA Syllabus PDFDocument10 pagesSTA Syllabus PDFselvaraj krishnaNo ratings yet
- Database Management System (Book)Document284 pagesDatabase Management System (Book)Mradul Dixit100% (2)
- APPGCET 2021 SYLLABUS COMPUTER SCIENCEDocument2 pagesAPPGCET 2021 SYLLABUS COMPUTER SCIENCEjNo ratings yet
- Database Fundamentals and Concepts ExplainedDocument1 pageDatabase Fundamentals and Concepts ExplainedSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- BSC CS-NEP III & IV SEMDocument19 pagesBSC CS-NEP III & IV SEMAkashNo ratings yet
- Computer Science and EngineeringDocument2 pagesComputer Science and EngineeringSurendra SuriNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidDocument57 pagesComputer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidAyesha PervaizNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidDocument58 pagesComputer Science: Instructor: Komal KhalidAyesha PervaizNo ratings yet
- Osou Syllabus DCA 2016 17Document10 pagesOsou Syllabus DCA 2016 17AVINASH RANANo ratings yet
- BCA Syllabus-III & IV SEMDocument23 pagesBCA Syllabus-III & IV SEMMukthaNo ratings yet
- TBC 302 Database Management SystemDocument2 pagesTBC 302 Database Management SystemViyan SinghNo ratings yet
- Mca-1 Rdbms SyllabusDocument3 pagesMca-1 Rdbms Syllabussanket shahNo ratings yet
- CSC2203 Database Systems: Course Information SheetDocument3 pagesCSC2203 Database Systems: Course Information SheetFaisal Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- C# Proramming LanguageDocument4 pagesC# Proramming LanguagemuhmmadzahidmiahNo ratings yet
- Me Cse Second SemesterDocument8 pagesMe Cse Second SemesterprabakaranbscNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Ch3 & Ch4Document9 pagesTest Bank Ch3 & Ch4Darrell NicholasNo ratings yet
- 2V0-21 23demoDocument7 pages2V0-21 23demoRony WeyNo ratings yet
- Masibus Scanner 85XX R6F 0814Document2 pagesMasibus Scanner 85XX R6F 0814Raj Kumar AhmedNo ratings yet
- BRKDCT-2081 Cisco FabricPath Technology and Design (2011 London)Document98 pagesBRKDCT-2081 Cisco FabricPath Technology and Design (2011 London)vimalm15No ratings yet
- How To Delete All Pictures or Other Objects in Excel EasilyDocument6 pagesHow To Delete All Pictures or Other Objects in Excel EasilySyed Fahad AliNo ratings yet
- Transmission EngineerDocument25 pagesTransmission EngineerStephen AdokwuNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Software Defined HF TransmitterDocument2 pagesNext Generation Software Defined HF TransmitterVIRENDRA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Cloudinfrastructureservices Co Uk Active Directory Security Best PracticesDocument51 pagesCloudinfrastructureservices Co Uk Active Directory Security Best PracticesWedesu EyobNo ratings yet
- 5.3.1.3 Lab - Observing DNS Name ResolutionDocument3 pages5.3.1.3 Lab - Observing DNS Name ResolutionMuhammad MusyawirNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Data CenterDocument26 pages4.1 Data CenterPramod PawarNo ratings yet
- Dhi xvr5204 08 16a s2 DatasheetDocument3 pagesDhi xvr5204 08 16a s2 DatasheetcitracandikaNo ratings yet
- Compatibility Matrix Solidus ECare 8.3Document12 pagesCompatibility Matrix Solidus ECare 8.3Udayanga Sanjeewa WickramasingheNo ratings yet
- ABAP Code - To Fetch SAP BI Qery DataDocument10 pagesABAP Code - To Fetch SAP BI Qery DatahemchanKNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5: 1. Aim: Implementation Wireless Network in NS-3. 2. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 5: 1. Aim: Implementation Wireless Network in NS-3. 2. ObjectivesAnil kadamNo ratings yet
- Cisco Callmanager Express 3.3 System Administrator Guide: Corporate HeadquartersDocument370 pagesCisco Callmanager Express 3.3 System Administrator Guide: Corporate HeadquartersDmitry DNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined NetworkingDocument11 pagesSoftware-Defined NetworkingAhmed Zehara (IDPP)No ratings yet
- Pan Os New FeaturesDocument156 pagesPan Os New Featuresalways_redNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth SimulationDocument17 pagesBluetooth Simulationtidus152No ratings yet
- Profesor: Matos Huaman, Jhoul Andy Sección: T5GB: Proyecto Final de Redes ConvergentesDocument16 pagesProfesor: Matos Huaman, Jhoul Andy Sección: T5GB: Proyecto Final de Redes ConvergentesKenneth AlaniaNo ratings yet
- Java Temenos Connector Server Plugin Isolistener - JarDocument5 pagesJava Temenos Connector Server Plugin Isolistener - JarBIDC EmailNo ratings yet
- NetworkSecurityISO Lesson Plan1Document3 pagesNetworkSecurityISO Lesson Plan1KarpagamSivakumarNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% FullDocument21 pagesCCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% FullLuis Blanco BelverNo ratings yet
- 1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1Document11 pages1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1edwinNo ratings yet
- Lte Ran Ericsson Nokia Parameter MappingDocument145 pagesLte Ran Ericsson Nokia Parameter MappingAlapanChakraborty86No ratings yet
- Cell Site Mobile CommunicationDocument355 pagesCell Site Mobile CommunicationMahendra singhNo ratings yet
- Efficient Priority Queue Hardware ImplementationDocument16 pagesEfficient Priority Queue Hardware ImplementationFaisal IrfanNo ratings yet
- How To Collect TSET and STEP InfoDocument3 pagesHow To Collect TSET and STEP InfoDaveClarkNo ratings yet
- Rt420 Datasheet enDocument11 pagesRt420 Datasheet enxandebarataNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: EIGRP: TopologyDocument7 pagesLab 3: EIGRP: TopologyJair VelasquezNo ratings yet
- It Era 4Document27 pagesIt Era 4jules200303No ratings yet