Professional Documents
Culture Documents
24 HR Chick Reviewer
Uploaded by
Gail Amurao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views4 pagesEmbryo
Original Title
289904712-24-Hr-Chick-Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEmbryo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views4 pages24 HR Chick Reviewer
Uploaded by
Gail AmuraoEmbryo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
-2 layers of blastoderm:
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CHICK EMBRYO >epiblast (outer layer)
24-HR CHICK EMBRYO --will differentiate into ectoderm
and mesoderm
WHOLE MOUNT >hypoblast (inner layer)
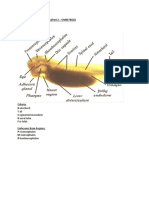
Area opaca Primitive streak
-peripheral region of chick blastodisc -longitudinal cleft formed on surface of amniote
-surounds the area pellucida blastodisc (convergence of cells)
-in direct contact with the yolk(renders the area -gastrulation begins as epiblast cells migrate
opaque) towards and into the streak
-differentiated into 3 zones: Primitive groove
>Peripheral zone -central furrow of the thickening
--margin of growth Primitive ridges
--cells have proliferated over the yolk -margins of the primitive streak
(w/o becoming adherent) -flanking primitive groove on either
>Zone junction Sides
--intermediate region Primitive pit
--cells cut free from yolk and added to -indented region of blastoderm
area pellucida -anterior end of the primitive streak
>Inner zone Hensens node (Primitive knot)
--germ wall -thickened area at anterior end of the
--cells originate from zone junction Streak
(contains yolk granules) -through which cells invaginate to form
--marks transition from area opaca to Notochord
the area pellucida -Homologous to dorsal lip of the
-area develops into 2 regions: blastopore (in amphibian embryos)
Area opaca vasculosa Proamnion
-Inner region of area opaca -anterior to developing avian embryo
-Thickenings of the splanchnic -surrounding the head
mesoderm from blood islands -endoderm and ectoderm
Area opaca vitellina -fate: will be invaded with mesoderm & become
-outer region of the area opaca incorporated into amnion
-initially lacks blood islands/blood Neural folds
vessels -margins of the neural plate (about to fuse at
Area pellucida the middorsal region)
-central region of the blastodisc Neural groove
-where primitive streak forms -median longitudinal groove
-lies directly over the subgerminal cavity -formed by rolling up of the neural plate
-appears translucent under the microscope Head fold
(owed to the thinness of the blastoderm) -folded region of the blastoderm
-dark crescentic line
-boundary of the heads of the embryo
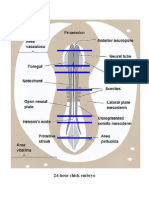
Notochord Head ectoderm
-longitudinal band of cells extending caudal -layers of cuboidal cells enclosing the head
-from regions of neural folds to hensens node -cells are cuboidal in origin
Foregut Neural folds
-1st part of digestive tract -margins of neural epithelium
-definite floor composed of endodermal cells Anterior neuropore
-Dome-shaped structure inside head -temporary external opening of neurocoel
Anterior intestinal portal Neural groove
-opening of foregut -median longitudinal groove
-appears like a prominent arched line beneath -formed by the rolling up of neural plate
the neural folds Prechordal plate
-continuous with lateral walls of the foregut -mass of chordamesodermal cells
-as development progresses, it moves -anterior to notochord
posteriorly & becomes part of the yolk stalk -will form head mesenchyme
Mesenchyme of the head Notochord
-lose network of cells -small medial mass of cells
-occupying space betweek foregut and -between foregut and neural plate
extoderm (head) Foregut
Mesoderm -dorsoventral flattened tube
Anterior border of the mesoderm -walls are made up of endodermal cells
-faint line -located beneath neural plate
-extends across area pellucida at the Oral plate (Oropharyngeal membrane)
level of anterior end of notochord -region where floor of foregut is in contact with
The thickened splanchnic mesoderm neural ectoderm of head
-darker line -will break open to form the mouth (in lateral
-lateral border of the anterior development)
intestinal portal Mesenchyme
-formed by delamination of lateral -loosely scattered cells
Plate mesoderm -fills up space between foregut and neural plate
-will form: heart, part of circulatory Proamnion
System, and many other structure -region of blastoderm beneath embryos head
Somite -composed of ectoderm and endoderm layer
-division of dorsal mesoderm Subcephalic pocket
-3 or 4 pairs lie immediately lateral to the -cavity formed beneath the embryonic head (as
neural folds head folds develops)
Unsegmented mesoderm Somatopleure
-undivided region of mesoderm -membrane composed of ectoderm and somatic
-posterior to somites mesoderm
-forms part of body wall & chorion and amnion
TRANSVERSE SECTION
SECTION THROUGH THE PHARYNGEAL
MEMBRANE Splanchnopleure
-cellular layer Amnio-Cardiac vesicle
-consists of splanchnic mesoderm and -region of coelom
endoderm -will give rise to amnion and heart
-will form body wall & yolk sac and allantois -thickened splanchnic mesoderm, making up
Coelom proximal wall of semi-cardiac vesicle, is the
-cavity formed after separation of somatic forerunner of the heart
mesoderm and mesoderm -somatopleure, making up the dorsal wall of
Subgerminal cavity this vesicle, is involved in the formation of the
-space beneath hypoblast within area pellucida amnion
-give rise to midgut
SECTION THROUGH THE MIDGUT
SECTION THROUGH THE ANTERIOR INTESTINAL Note:
PORTAL *midgut- middle part of the gut that has the
Note: yolk for the floor of its cavity
*neural folds have come together to form the Midgut
neural tube -floorless region of the gut
*at the level of the open foregut -posterior to the anterior intestinal portal
*endoderm of the foregut is continuous with
the rest of the endoderm SECTION THROUGH THE SOMITE
*anterior intestinal portal- opening of the Note:
foregut *neural folds have no yet closed together
*region of thickened, splanchnic mesoderm is *somites develop from dorsal mesoderm & are
prospective cardiac mesoderm located on each side of the neural folds and
Neural tube notochord
-formed by thickening and rolling up of neural *later and adjacent to somites is the
plate (during embryonic neurulation) intermediate mesoderm (small region of
-will form the brain and spinal cord mesoderm)
Neural crest *Intermediate mesoderm will develop into
-found at the edges of the neural plate above kidneys
the neural tube *lateral plate mesoderm, lateral to
-migrate throughout the embryo to form intermediate mesoderm, will delaminate to
ganglia, pigment cells, part of gills arches, etc. form somatic and splanchnic mesodermal layers
Head fold Somite
-marked by downward bend of membranes -segmented mesodermal blocks
around the head region -located on either side of the developing spinal
Anterior intestinal portal cord
-opening of the foregut -arise from dorsal mesoderm
-as development progresses and gut elongates, Nephrotome (Intermediate
it moves posteriorly and becomes part of yolk mesoderm/mesomere/nephromere)
stalk -stalk-like connection between somites and
lateral plate mesoderm
-anteriorly:forms pronephros; posteriorly:forms
mesenchyme (will develop into mesonephros
and metanephros
Hypomere
-region of mesoderm distal to nephrotome
-subdivided into two layers:
>somatic
>splanchnic mesoderm
SECTION THROUGH THE PRIMITIVE STREAK
Primitive streak
-longitudinal cleft formed of the surface of the
amniote blastodisc by convergence of cells
-gastrulation begins as the epiblast cells migrate
towards and into the streak
Hensens node (primitive knot)
-thickened area at the anterior end of
the streak
-through which cells invaginates to form
Notochord
-homologous to dorsal lip of blastopore
Primitive pit
-depression slightly deeper than
primitive groove
-posterior to hensens node
Primitive groove
-central furrow more posterior to
primitive pit
Primitive ridges
-thickened margins on each side of the
primitive grovove
You might also like
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDocument18 pages24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerClarebelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Document17 pagesEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosNo ratings yet
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocument3 pages4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDocument8 pages24-Hr Chick EmbryopauNo ratings yet
- Organ Description How Is It Formed? PurposeDocument6 pagesOrgan Description How Is It Formed? PurposeAnna Nicole LazaroNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo ReviewerDocument9 pagesChick Embryo ReviewerKeana TapangNo ratings yet
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDocument7 pagesEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- 24 33 Hour ChickDocument9 pages24 33 Hour ChickMary Grace Tuazon100% (1)
- 01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainDocument5 pages01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainAsh CansanayNo ratings yet
- 33 HR Chick EmbryoDocument12 pages33 HR Chick EmbryoErvin AblazaNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Chick EmbryoDocument95 pagesChick EmbryoAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFDocument3 pages48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachNo ratings yet
- Tail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeDocument2 pagesTail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabDocument3 pages7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- Neural Tube Formation 4-8 WeeksDocument56 pagesNeural Tube Formation 4-8 WeeksLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- 33-Hour Chick Development StagesDocument5 pages33-Hour Chick Development StagesJedd VirgoNo ratings yet
- Ex4 Frog EmbryoDocument20 pagesEx4 Frog EmbryoJan Leightton Laxamana100% (2)
- EARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd WeekDocument4 pagesEARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd WeekNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Development of the Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesDevelopment of the Nervous SystemAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- Failure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsDocument6 pagesFailure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsMargo Roth SpiegelmanNo ratings yet
- Head FactoidsDocument17 pagesHead FactoidsENo ratings yet
- Development of CNSDocument84 pagesDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankNo ratings yet
- Brain and MeningesDocument5 pagesBrain and Meningesr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Embryo Lab Org 2Document14 pagesEmbryo Lab Org 2pauNo ratings yet
- Development of FaceDocument19 pagesDevelopment of FaceAkhila ReddyNo ratings yet
- 33HR ChickDocument7 pages33HR ChickJasper PanosoNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Document9 pagesChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- 3rd Week of Development 2022Document36 pages3rd Week of Development 2022aameena nadaNo ratings yet
- 3 EmbryologyDocument19 pages3 EmbryologyKennVaneNo ratings yet
- 04 - Develpment Week 3Document12 pages04 - Develpment Week 3hiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy No.2Document71 pagesAnatomy No.2hendalzeer02No ratings yet
- Intro To NeurologyDocument10 pagesIntro To NeurologyShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Embryology TimelineDocument3 pagesEmbryology Timelinesayeda.raza24No ratings yet
- Nervous + Animal DiversityDocument7 pagesNervous + Animal DiversityMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- 48hr ChickDocument2 pages48hr ChickYeonruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, CAPUT: External Benchmarks. Supraorbital Edge of The Orbit, Inion, Tragus of EarDocument31 pagesChapter 5, CAPUT: External Benchmarks. Supraorbital Edge of The Orbit, Inion, Tragus of EarSyafiq KhalilNo ratings yet
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNo ratings yet
- Emrbyo Lab Whole Mount: 48 HR Chick ReviewerDocument6 pagesEmrbyo Lab Whole Mount: 48 HR Chick ReviewerChristine Mae DelimaNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation Somites and Folding TSRDocument27 pagesGastrulation Somites and Folding TSRAsia SattiNo ratings yet
- Gastrulationin MammalsDocument16 pagesGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal DevelopmentMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- 4 MM FrogDocument5 pages4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFTanya Tanu100% (1)
- Seminar 2Document7 pagesSeminar 2gatorssoccer1313No ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocument23 pagesExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekDocument25 pagesEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Frog Embryology PDFDocument17 pagesFrog Embryology PDFHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument5 pagesNeuroembryology and NeurohistologyCZARINA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideDocument19 pagesAnatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideChetfalkNo ratings yet
- Major Divisions of the Nervous System ExplainedDocument38 pagesMajor Divisions of the Nervous System ExplainedVitor MartinsNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Love BunniesDocument3 pagesLove BunniesAquamarineeeNo ratings yet
- Examen InglésDocument10 pagesExamen InglésAntonio CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Endangered AnimalsDocument2 pagesEndangered Animalsyohanieca josephNo ratings yet
- Anatomy &physiology of Small Animals!!!Document107 pagesAnatomy &physiology of Small Animals!!!Bio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Digital NotesDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Digital NotesKshreeNo ratings yet
- Samuel Gelfan and Attie Yvonne Werner: Were A ContractDocument3 pagesSamuel Gelfan and Attie Yvonne Werner: Were A ContractThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Identifying Venomous and Nonvenomous Snakes in TexasDocument10 pagesIdentifying Venomous and Nonvenomous Snakes in TexasAttila KissNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument19 pagesTaxonomysenthilkumar_rNo ratings yet
- CH 42 Circulatory Systems: AP BiologyDocument27 pagesCH 42 Circulatory Systems: AP BiologyNelson TingalingNo ratings yet
- 24XX Dying Sun 1.1 SPREADSDocument2 pages24XX Dying Sun 1.1 SPREADSEvandro FormozoNo ratings yet
- STD 5 - English - Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonDocument4 pagesSTD 5 - English - Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonReshma KatariaNo ratings yet
- For This 1992 Adaptation of The AswangDocument2 pagesFor This 1992 Adaptation of The AswangAnn AcobaNo ratings yet
- Ferdinand SequencingDocument2 pagesFerdinand SequencingEFL Classroom 2.0No ratings yet
- English Exercise Book 3 Eso A: Ies Canónigo ManchónDocument36 pagesEnglish Exercise Book 3 Eso A: Ies Canónigo ManchónrobertoquinteiroNo ratings yet
- L1 A2 Communication Games StarterDocument1 pageL1 A2 Communication Games StarterMarcelo D'EliaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OverviewDocument23 pagesEndocrine System OverviewKimberly Joy GregorioNo ratings yet
- Tructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and CellmodificationDocument53 pagesTructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cellmodificationako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .DocxDocument17 pagesDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .Docxjoan100% (4)
- Test Bank For Operations Management 14th Edition William J StevensonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Operations Management 14th Edition William J Stevensonmasqueedenized8a43l100% (44)
- KIB Common Myth ConceptionsDocument4 pagesKIB Common Myth Conceptionscila111No ratings yet
- Baptist Health System Will Build New Hospital in BoerneDocument12 pagesBaptist Health System Will Build New Hospital in BoerneBrittany LudwigNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life Long TestDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Life Long TestMichelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Heaven & Earth Spa Treatments Under 40Document2 pagesHeaven & Earth Spa Treatments Under 40Janhavi SoniNo ratings yet
- Biological aspects of the dangerous jellyfish Physalia physalisDocument19 pagesBiological aspects of the dangerous jellyfish Physalia physalisbakin muNo ratings yet
- An, The or N/A (No Article)Document2 pagesAn, The or N/A (No Article)Yeimi Tatiana Rojas100% (2)
- Rectal ExaminationDocument21 pagesRectal ExaminationdrgbkhanNo ratings yet
- Dairy India 2007Document4 pagesDairy India 2007Rama Kr M100% (1)
- Making SausagesDocument225 pagesMaking Sausagestanoy vai100% (1)
- N 5 CF 0 Aec 4 C 415 eDocument47 pagesN 5 CF 0 Aec 4 C 415 eSachin NainNo ratings yet
- Animals and Young OnesDocument10 pagesAnimals and Young OnesAgrippa MungaziNo ratings yet