Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Digital Communications Systems
Uploaded by
Ysrael M. Tatlonghari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesERCE
Original Title
Communication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentERCE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesIntroduction To Digital Communications Systems
Uploaded by
Ysrael M. TatlonghariERCE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Introduction to Digital Communications Systems
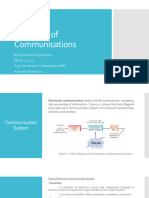
1. Communication the process of exchanging information.
2. Noise degrades or interferes with transmitted information
3. Transmitter is a collection of electronic components and circuits
that converts the electrical signal into a signal suitable
for transmission over a given medium
4. Communication the medium by which the electronic signal is sent from
channel one place to another
5. Receiver a collection of electronic components and circuits that
accepts the transmitted message from the channel and
converts it back into a form understandable by humans
6. Transceiver an electronic unit that incorporates circuits that both
send and receive signals
7. Attenuation Signal attenuation, or degradation, exists in all media
of wireless transmission. It is proportional to the square
of the distance between the transmitter and receiver
8. Noise random, undesirable electronic energy that enters the
communication system via the communicating medium
and interferes with the transmitted message
9. Simplex The simplest method of electronic communication is
referred to as simplex
10. Full duplex Most electronic communication is two-way and is
referred to as duplex
11. Half duplex The form of two-way communication in which only one
party transmits at a time is known as half duplex
12. Analog signals a smoothly and continuously varying voltage or current
13. Digital signals change in steps or in discrete increments
14. Modulation and electronic techniques for transmitting information
multiplexing efficiently from one place to another
15. Modulation makes the information signal more compatible with the
medium
16. Baseband information can be sent directly and unmodified over the medium
or can be used to modulate a carrier for transmission
over the medium
17. Carrier is a high frequency signal that is modulated by audio,
video, or data
18. Radio-frequency wave is an electromagnetic signal that is able to travel
long distances through space
19. Phase modulation the phase angle of the sine wave is varied
20. Broadband takes place when a carrier signal is modulated,
transmission amplified, and sent to the antenna for transmission
21. Frequency-shift keying takes place when data is converted to frequency-
(FSK) varying tones
22. Modems translate the data from digital to analog and back again
23. Demodulation or takes place in the receiver when the original baseband
detection (e.g. audio) signal is extracted
24. Multiplexing the process of allowing two or more signals to share
the same medium or channel
25. Electromagnetic The range of electromagnetic signals encompassing all
spectrum frequencies
26. Frequency is the number of cycles of a repetitive wave that occur
in a given period of time. (cps)(Hz)
Introduction to Digital Communications Systems
27. Cycle (frequency) consists of two voltage polarity reversals, current
reversals, or electromagnetic field oscillations
28. Wavelength is the distance occupied by one cycle of a wave and is
usually expressed in meters.
29. Bandwidth (BW) is that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
occupied by a signal.
30. Channel bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies required to transmit
the desired information
Introduction to Digital Communications Systems
ENUMERATION
2 MAIN Barriers of Communicaitons Methods of communication:
Language 1. Face to face
Distance 2. Signals
3. Written word (letters)
4. Electrical innovations:
Telegraph
Telephone
Radio
Television
Internet (computer)
Basic components of Communication Types of media include in Communication
Transmitter Channel
Channel or medium Electrical conductors
Receiver Optical media
Free space
System-specific media (e.g., water is the medium
for sonar).
Tranceivers (Examples) Classification of Electronics Communications
Telephones System
Fax machines One-way (simplex) or two-way (full
Handheld CB radios duplex or half duplex) transmissions
Cell phones Analog or digital signals.
Computer modems
The two most common methods of modulation The three basic types of multiplexing are:
are: Frequency division
Amplitude Modulation (AM) Time division
Frequency Modulation (FM) Code division
You might also like
- Nec 4106 Module 1Document28 pagesNec 4106 Module 1Jessie Rey MembreveNo ratings yet
- PRINCOMM ReviewerDocument4 pagesPRINCOMM Reviewerrick reyNo ratings yet
- 01 Handout 1Document4 pages01 Handout 1Eleomar P. HalamanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronic CommunicationDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Electronic CommunicationKrish RaghunundhunNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.0Document35 pagesChapter One 1.0Arazim Olorundare SheuNo ratings yet
- Basic CommunicationDocument24 pagesBasic CommunicationSiam hasanNo ratings yet
- Eec 128Document23 pagesEec 128Adetayo Salawu67% (3)
- Lesson 1 Com02Document3 pagesLesson 1 Com02cipher polNo ratings yet
- ICT Note For Grade 10Document5 pagesICT Note For Grade 10Sosina TilahunNo ratings yet
- 1introduction To Communications - For LectureDocument32 pages1introduction To Communications - For LectureKathleen Jhoren ReglosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument123 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemMichael Tesfaye100% (1)
- EEC 128 TheoryDocument73 pagesEEC 128 TheoryHuu Uu100% (1)
- Introductinon: 1.1. Elements of A Communication SystemDocument4 pagesIntroductinon: 1.1. Elements of A Communication SystemLij Girmachew Tekel HawariatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronic CommunicationsDocument97 pagesIntroduction To Electronic CommunicationsEcaNo ratings yet
- Introtoelectives2 Part4Document5 pagesIntrotoelectives2 Part4Joyce MillanNo ratings yet
- PCOM ReviewerDocument14 pagesPCOM ReviewerMARCELO PELAYONo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electronic CommunicationDocument17 pagesFundamental of Electronic CommunicationLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Pendahuluan PDFDocument81 pagesBab 1 Pendahuluan PDFalfianNo ratings yet
- 1st ChapterDocument15 pages1st ChapterMd Raton AliNo ratings yet
- DEE 072 Telecommunication Notes FinalDocument118 pagesDEE 072 Telecommunication Notes FinalFilbert Ombongi100% (1)
- 4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. CollegeDocument5 pages4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. Collegeajaykumar988No ratings yet
- INTRo TO COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS 10675Document58 pagesINTRo TO COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS 10675KelvinNo ratings yet
- DCB30082 Topic 5Document39 pagesDCB30082 Topic 5Aiman NaimNo ratings yet
- Book ReviewDocument70 pagesBook ReviewMonique QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introd 2015Document19 pagesChap1 Introd 2015semakulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1kedirNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemDocument9 pagesCommunication Systemvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Tomasi OutlinedDocument76 pagesTomasi OutlinedNyeng NathanNo ratings yet
- A1!04!502E - Sto. Tomas, ShairaDocument4 pagesA1!04!502E - Sto. Tomas, ShairaSTO. TOMAS SHAIRA FRESCONo ratings yet
- ET-353, Lecture 03 (Communication System)Document34 pagesET-353, Lecture 03 (Communication System)Jahanzaib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Source Transmitter Receiver RecipientDocument2 pagesSource Transmitter Receiver RecipientsyaziraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document53 pagesChapter 1Renz Benhar Ocon BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesCommunication SystemsMT๛ LUCIFERNo ratings yet
- Affiah Telecommunication Systems IDocument286 pagesAffiah Telecommunication Systems IKrista JacksonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer FecnDocument2 pagesReviewer FecnNathan ash ClintonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Communications SystemsDocument6 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Communications SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Unit-I 17.07Document41 pagesUnit-I 17.07radhika.22210203No ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument59 pagesCommunication Systemsulul azmiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Communication SystemmDocument17 pagesTopic 1 Communication SystemmRoneline LizadaNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCommunication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringAyad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- Communication Is The Basic Process of Exchanging InformationDocument20 pagesCommunication Is The Basic Process of Exchanging InformationMary Grace CuevaNo ratings yet
- Electronics QuestionDocument13 pagesElectronics QuestionAkash NegiNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Notes EEE400 Wk1Document5 pages02 Lecture Notes EEE400 Wk1Wafula DerrickNo ratings yet
- Electronics Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectronics Interview QuestionsEhsan FirdausNo ratings yet
- And Control. The Computer Segment Is The Largest Communications Is TheDocument4 pagesAnd Control. The Computer Segment Is The Largest Communications Is TheEren YeagerNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication (Written Report)Document12 pagesTelecommunication (Written Report)Wafa L. AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FinalDocument80 pagesUnit 1 FinalDeepika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Communications VITEEE PDFDocument19 pagesCommunications VITEEE PDFSemiu AdelekeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Systems-1Document32 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systems-1joeykenyattaNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Communication System With DetaileDocument5 pagesBlock Diagram of Communication System With Detaileravikumar rayalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Communication DefinitionsDocument27 pagesIntroduction: Communication DefinitionsThangaPrakashPNNo ratings yet
- Telecom-Chapter OneDocument7 pagesTelecom-Chapter Onetsegab bekele100% (2)
- Introduction To Electronics Communication SystemDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Communication SystemJOSHUA NEIL CARIGONo ratings yet
- Intro To Communication SystemsDocument61 pagesIntro To Communication SystemsRemuel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Communication Electronics Chapter Summary FrenzelDocument15 pagesCommunication Electronics Chapter Summary FrenzelMichelle Anne PerlasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 & 2Document69 pagesUnit 1 & 2Saiyma Fatima RazaNo ratings yet
- SECA1303Document250 pagesSECA1303rqfkypprjtNo ratings yet
- 16 - Principles of CommunicationDocument14 pages16 - Principles of CommunicationRome Bueno Jr.No ratings yet
- Mahendra Engineering College: Lecture HandoutsDocument3 pagesMahendra Engineering College: Lecture Handoutshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods Course SyllabusDocument20 pagesStatistical Methods Course SyllabusYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument22 pagesNewtonYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Carrier RecoveryDocument4 pagesCarrier RecoveryYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Geas 1Document91 pagesGeas 1Ysrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument15 pagesRRLYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- HEADERDocument14 pagesHEADERYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Manuel S. Enverga University Foundation College of Engineering and Technical DepartmentDocument4 pagesManuel S. Enverga University Foundation College of Engineering and Technical DepartmentYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- History of Control SystemDocument1 pageHistory of Control SystemYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Introduction Power SupplyDocument46 pagesIntroduction Power SupplyYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- My Own DesignDocument1 pageMy Own DesignYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- SMS Roaming Tutorial: March 22, 2006Document30 pagesSMS Roaming Tutorial: March 22, 2006FistailNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 703 Security GuideDocument424 pagesVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 703 Security GuideyonasNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 GSM Initial Configuration Guide (V900R013C00 - 03) (PDF) - enDocument168 pagesBSC6900 GSM Initial Configuration Guide (V900R013C00 - 03) (PDF) - enc2poyraz100% (2)
- Cisco 200 Series Smart SwitchesDocument38 pagesCisco 200 Series Smart SwitchesNikko BardeNo ratings yet
- 22 VoLTE Call StepsDocument94 pages22 VoLTE Call StepsManish Kumar100% (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent RRH2x60W: (RRH2x60-21, RRH2x60-21A, RRH2x60-850, RRH2x60-1900, RRH2x60-1900A)Document41 pagesAlcatel-Lucent RRH2x60W: (RRH2x60-21, RRH2x60-21A, RRH2x60-850, RRH2x60-1900, RRH2x60-1900A)cuongNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Iot Application Layer ProtocolsDocument63 pagesComparison of Iot Application Layer ProtocolsAditriNo ratings yet
- DR 138 438Document2 pagesDR 138 438P HandokoNo ratings yet
- GPS Synchronization Clock PCS-9785CDocument2 pagesGPS Synchronization Clock PCS-9785CganeshNo ratings yet
- Vodafone Standard Procedure For Microwave Swap Site - V1Document14 pagesVodafone Standard Procedure For Microwave Swap Site - V1ethosgrNo ratings yet
- COMMS 1 Modulation ANSWERSDocument5 pagesCOMMS 1 Modulation ANSWERSClyde Ann CantagoNo ratings yet
- GuiaDocument122 pagesGuiaMarlon AlbanNo ratings yet
- 02 Course OverviewDocument11 pages02 Course OverviewsreenathonwebNo ratings yet
- 38.LFDC Relay Testing With F6150-1Document89 pages38.LFDC Relay Testing With F6150-1Sristhi GanguliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes NBCAS511Document18 pagesChapter 3 Notes NBCAS511Zilly cocoNo ratings yet
- tl250 300 inst-ENDocument48 pagestl250 300 inst-ENsiteromNo ratings yet
- Carrier Balancing Between Multiple Carriers/BI Sectors & DRD Issues IdentificationDocument19 pagesCarrier Balancing Between Multiple Carriers/BI Sectors & DRD Issues IdentificationMd Irfan HussainNo ratings yet
- Error Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & ArchitectureDocument18 pagesError Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & ArchitectureAnirudh RamarajNo ratings yet
- Designing A Jitter Buffer For Qos Improvement in Voip NetworksDocument6 pagesDesigning A Jitter Buffer For Qos Improvement in Voip Networkshome kmsNo ratings yet
- Go2signals Analysis Suite Tech - Specs. 22.2-001Document16 pagesGo2signals Analysis Suite Tech - Specs. 22.2-001rolf.haenggiNo ratings yet
- ION M TechnologyDocument38 pagesION M TechnologyАндрій КорольовNo ratings yet
- EC-2 Brochure enDocument4 pagesEC-2 Brochure enJhon JairoNo ratings yet
- Intelligent GSM Care For Bus Finding SystemDocument7 pagesIntelligent GSM Care For Bus Finding SystemManasa ChikkalaNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 5 - NETWORK DESIGN - Conception Physique Reseau PDFDocument62 pagesChapitre 5 - NETWORK DESIGN - Conception Physique Reseau PDFit sonyNo ratings yet
- 矢量网络分析的基本原理Document16 pages矢量网络分析的基本原理Juan RenedoNo ratings yet
- Precision Clock Synchronization WP PDFDocument20 pagesPrecision Clock Synchronization WP PDFtimeking00No ratings yet
- 2.7V 12-Bit A/D Converter With SPI Serial Interface: Features Package TypesDocument20 pages2.7V 12-Bit A/D Converter With SPI Serial Interface: Features Package TypesYogesh KhollamNo ratings yet
- Tektone Tek-Care 160 System Layout: Central Equipment ModulesDocument1 pageTektone Tek-Care 160 System Layout: Central Equipment ModulesRafaelVillaNo ratings yet
- CV KansiimeDocument3 pagesCV KansiimeefsdfsdafsdNo ratings yet
- DB SCADA Interface Bluelog XM XC enDocument2 pagesDB SCADA Interface Bluelog XM XC enaladanh2000No ratings yet