Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note Payable and Debt Restructuring
Uploaded by
louvelleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note Payable and Debt Restructuring
Uploaded by
louvelleCopyright:
Available Formats
Note Payable and Debt Restructuring
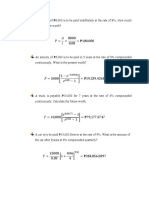
1. Note Payable is initially measured at fair value which is equal to the present value and
subsequently measured at amortized cost
2. When the note is issued solely for cash, the cash proceed is the present value using a discount
rate. Straight line method of depreciation is used. Using 12%, the entry is:
Cash 880,000
Discount on N/P 120,000
Note payable 1,000,000
3. If a promissory note is interest-bearing, the purchase price is the present value. Example: an
entity acquired equipment for 1,000,000 payable in 5 annual equal installments every dec.31 of
each year. Interest is 10percent on the unpaid balance.
1/1/11:
Equipment 1M
Note payable 1M
12/31 Interest Expense 100T
Note payable 200T
Cash 300T
12/31/12:
Interest Expense 80T
Note Payable 200T
Cash 280T
4. When a noninterest-bearing note is issued for a property with cash price, the cash price is
assumed to be the present value of the note issued. Entity acquired an equipment with a cash
price of 350T for 500T, 100T down and the balance payable in 4 equal annual installments:
1/1 Equipment 350T 12/31 NP 100T
Discount on N/P 150T Cash 100T
Cash 100T
N/P 400T Interest Exp 60T
Disc. On NP 60T
* Bond outstanding method is used to amortize discount.
* the cash paid is not added to the cost of equipment since the 350T cash value includes already
the 100T cash paid. So the 400T note payable applies to the 250T portion of the equipment.
Thus, 400-250=150T discount on note payable.
5. If there is no cash price in a noninterest bearing note, present value/cash price is determined
by multiplying the annual installment by the present value factor. Entity acquired an equipment
for 1M payable in 5 annual installments on every dec.31 of each year. Using 10percent
prevailing market interest, the entry is:
1/1 equipment 758,160 12/31 NP 200T
Discount on N/P 241,840 Cash 200T
Note payable 1,000,000 Interest exp 75,816
Disc.on NP 75,816
*Effective interest method is used.
You might also like
- Rental-Property Profits: A Financial Tool Kit for LandlordsFrom EverandRental-Property Profits: A Financial Tool Kit for LandlordsNo ratings yet
- Pei 135 - Pei300Document13 pagesPei 135 - Pei300Anonymous Rwa38rT8GVNo ratings yet
- 50 Common Money MistakesDocument124 pages50 Common Money MistakesLanre Tuase E Tal100% (2)
- 50cb2fca 1597910723873pdf PDF FreeDocument10 pages50cb2fca 1597910723873pdf PDF FreefarandiNo ratings yet
- Notes Payable and Bonds Payable - Quiz - With Answers - For PostingDocument8 pagesNotes Payable and Bonds Payable - Quiz - With Answers - For PostingWinny PoeNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Ia CH 6 & 7 NR LR 2020Document112 pagesIa CH 6 & 7 NR LR 2020Jm Sevalla57% (14)
- Module 5-NOTE PAYABLE AND DEBT RESTRUCTUREDocument13 pagesModule 5-NOTE PAYABLE AND DEBT RESTRUCTUREJeanivyle Carmona100% (1)
- Treasury Alliance Cash Pooling White PaperDocument16 pagesTreasury Alliance Cash Pooling White PaperShilpa KogantiNo ratings yet
- 16Document23 pages16Alex liao0% (1)
- Module 2 - Notes Payable Debt RestructuringDocument39 pagesModule 2 - Notes Payable Debt RestructuringJoshua Cabinas100% (1)
- Year Ahead 2022Document72 pagesYear Ahead 2022Dan CraneNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Note Payable and Debt RestructureDocument15 pagesModule 5 Note Payable and Debt Restructuremmh100% (1)
- Note Payable: Feu - IabfDocument5 pagesNote Payable: Feu - IabfDonise Ronadel SantosNo ratings yet
- Auditing Problems, CRC-ACEDocument9 pagesAuditing Problems, CRC-ACESannyboy Paculio Datumanong100% (1)
- 2009 Annual ReportDocument264 pages2009 Annual ReportasangasdNo ratings yet
- NISM Exam MaterialDocument51 pagesNISM Exam Materialgauravmonga15100% (2)
- Note PayableDocument6 pagesNote PayablemmhNo ratings yet
- Exam For Managerial AccountingDocument8 pagesExam For Managerial Accountingសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍No ratings yet
- Ppe IntDocument6 pagesPpe IntlouvelleNo ratings yet
- Receivables Part 2 AsuncionDocument65 pagesReceivables Part 2 AsuncionRica Jane Mariano100% (1)
- m7PRPTTY PDFDocument4 pagesm7PRPTTY PDFAshley De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- FakeDocument13 pagesFakePedroNo ratings yet
- Buy the Dip?: Investing in Decentralized Finance and Trading Cryptocurrency, 2022-2023 - Bull or bear? (Smart & profitable strategies for beginners)From EverandBuy the Dip?: Investing in Decentralized Finance and Trading Cryptocurrency, 2022-2023 - Bull or bear? (Smart & profitable strategies for beginners)No ratings yet
- ACC 211 Week 10-12Document24 pagesACC 211 Week 10-12idontcaree123312No ratings yet
- Claims Supported by Formal Promises To Pay Usually in The Form of NotesDocument3 pagesClaims Supported by Formal Promises To Pay Usually in The Form of NotesCzar RabayaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Notes Payable & Debt Restructuring - Rev2Document44 pagesModule 2 - Notes Payable & Debt Restructuring - Rev2Bea Angelle CamongayNo ratings yet
- Derivatives ActivitiesDocument9 pagesDerivatives Activitiesjoong wanNo ratings yet
- 12 Acctg Ed 1 - Notes Receivable PDFDocument17 pages12 Acctg Ed 1 - Notes Receivable PDFNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- C8 Note PayableDocument28 pagesC8 Note PayableJoana RidadNo ratings yet
- 5 Investment AccountsDocument11 pages5 Investment AccountsBAZINGANo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument60 pagesFinancial AccountingSurajNo ratings yet
- BIP-Week-13-14-with NotesDocument8 pagesBIP-Week-13-14-with NotesgelNo ratings yet
- Residential Real Estate Introduction Slides - Student Version-1Document120 pagesResidential Real Estate Introduction Slides - Student Version-1Aaron HoardNo ratings yet
- Tugas ObligasiDocument15 pagesTugas Obligasiwahdah ulin nafisahNo ratings yet
- Catan Selina Mari Unit 2 Intacc3 099Document12 pagesCatan Selina Mari Unit 2 Intacc3 099Elc Elc ElcNo ratings yet
- LatihanDocument12 pagesLatihanSurameto HariyadiNo ratings yet
- PPE Lecture With Assignments COMPLETEDocument4 pagesPPE Lecture With Assignments COMPLETEsabina del monteNo ratings yet
- Fedillaga Case13Document19 pagesFedillaga Case13Luke Ysmael FedillagaNo ratings yet
- Finspeed Round 1 - Individuals FDocument7 pagesFinspeed Round 1 - Individuals FBảo Hân VũNo ratings yet
- Note Payable Irrevocably Designated As at Fair Value Through Profit or LossDocument4 pagesNote Payable Irrevocably Designated As at Fair Value Through Profit or Lossnot funny didn't laughNo ratings yet
- Bond Features: TI Interest Rates and Bond ValuationDocument19 pagesBond Features: TI Interest Rates and Bond ValuationSissyboiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Team ProblemDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Team ProblemRachel KleinNo ratings yet
- 02multiple ChoiceDocument12 pages02multiple ChoicePRINCESS MAY ADAMNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Notes and Loans ReceivableDocument6 pagesAccounting For Notes and Loans ReceivableBvreanchtz Mantilla CalagingNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Note PayableDocument24 pagesChapter8 Note PayableKristine Joy Peñaredondo BazarNo ratings yet
- Problem 14-4 (IAA)Document8 pagesProblem 14-4 (IAA)NIMOTHI LASE0% (1)
- Notes ReceivableDocument9 pagesNotes ReceivableJAPNo ratings yet
- MID - Test N03Document2 pagesMID - Test N03Vân Nhi PhạmNo ratings yet
- Bonds Payable ReviewDocument6 pagesBonds Payable ReviewJyasmine Aura V. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Notes Payable and Debt RestructuringDocument10 pagesNotes Payable and Debt RestructuringChrisus Joseph SarchezNo ratings yet
- Notes With Unrealist RateDocument6 pagesNotes With Unrealist RateLauNo ratings yet
- Week 4 AssignmentDocument6 pagesWeek 4 AssignmentJames Bradley HuangNo ratings yet
- MYOB Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesMYOB Sample QuestionsKay BMNo ratings yet
- FA of SPDocument8 pagesFA of SPShivangi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Impairment of Assets - 1Document18 pagesImpairment of Assets - 1techna8No ratings yet
- Jawaban UAS Akuntansi FirmansyahDocument3 pagesJawaban UAS Akuntansi Firmansyahfirmanpipit64No ratings yet
- Notes ReceivableDocument9 pagesNotes ReceivableJAPNo ratings yet
- Yıldız Technical University Civil Engineering Department Construction Management DivisionDocument36 pagesYıldız Technical University Civil Engineering Department Construction Management DivisionBulut ŞakirNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3 1. Chapter 4: Share-Based Payments (Part 2)Document5 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3 1. Chapter 4: Share-Based Payments (Part 2)happy240823100% (1)
- March Bill PDFDocument2 pagesMarch Bill PDFRaman kumarNo ratings yet
- Two Ways of Conducting Foreign ActivitiesDocument7 pagesTwo Ways of Conducting Foreign ActivitiesJustine VeralloNo ratings yet
- Module 2c Notes ReceivableDocument35 pagesModule 2c Notes ReceivableChen HaoNo ratings yet
- 0 Repayment Schedule 19-34-13Document1 page0 Repayment Schedule 19-34-13salan salanNo ratings yet
- Answers 9+10Document18 pagesAnswers 9+10Nguyễn Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting N5: National CertificateDocument9 pagesFinancial Accounting N5: National CertificateHonorine Ngum NibaNo ratings yet
- Jasa Ocean Edit FINAL RevisiDocument5 pagesJasa Ocean Edit FINAL RevisiAtalariq BudihartoNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesCheat SheetKhushi RaiNo ratings yet
- Repayment ReportDocument1 pageRepayment ReportSANJAY KumarNo ratings yet
- Law FinalsDocument5 pagesLaw FinalslouvelleNo ratings yet
- Review Materials Used (4th Year)Document13 pagesReview Materials Used (4th Year)louvelleNo ratings yet
- D. Tender of Payment & Consignation: 2. Loss of Thing DueDocument2 pagesD. Tender of Payment & Consignation: 2. Loss of Thing DuelouvelleNo ratings yet
- QuantiDocument72 pagesQuantilouvelleNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Comprehensive Exam Coverage: Instruction: Please Arrange The Following Subjects in Its Order of Priority (From 1-5) Based On How YouDocument1 pageQualifying Comprehensive Exam Coverage: Instruction: Please Arrange The Following Subjects in Its Order of Priority (From 1-5) Based On How YoulouvelleNo ratings yet
- Mission StatementDocument1 pageMission StatementlouvelleNo ratings yet
- Bonds PayableDocument2 pagesBonds PayablelouvelleNo ratings yet
- Implementing Strategies: Management & Operations Issues: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred DavidDocument34 pagesImplementing Strategies: Management & Operations Issues: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred DavidlouvelleNo ratings yet
- Bonds PayableDocument2 pagesBonds PayablelouvelleNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Refers To The Relationship Between Goods or Services Produced and Resources UsedDocument1 pageEfficiency Refers To The Relationship Between Goods or Services Produced and Resources UsedlouvelleNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument2 pagesAccounting For Income TaxlouvelleNo ratings yet
- Assertions of Compliance With Accountability RequirementsDocument2 pagesAssertions of Compliance With Accountability RequirementslouvelleNo ratings yet
- Manual Data ProcessingDocument1 pageManual Data ProcessinglouvelleNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument1 pageMultiple ChoicelouvelleNo ratings yet
- Starbucks Company ProfileDocument2 pagesStarbucks Company Profilearaby_mhNo ratings yet
- Depletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)Document3 pagesDepletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)didit.canonNo ratings yet
- Wikimart: Building A Russian Version of AmazonDocument7 pagesWikimart: Building A Russian Version of Amazonapi-329688545100% (1)
- Nestle Multinational CompanyDocument3 pagesNestle Multinational CompanyShebel AgrimanoNo ratings yet
- OSIM International Annual Reoprt 2009Document198 pagesOSIM International Annual Reoprt 2009Ho Lun Tang0% (1)
- Financial Analysis - Planning NotesDocument49 pagesFinancial Analysis - Planning NotesMadhan Kumar BobbalaNo ratings yet
- Public Disclosure DocumentsDocument52 pagesPublic Disclosure DocumentsEdgar Arbey RomeroNo ratings yet
- Internship Report 5 SemDocument41 pagesInternship Report 5 SemAayush SomaniNo ratings yet
- ECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 1: Last NameDocument13 pagesECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 1: Last NameexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 SolutionDocument10 pagesTopic 3 Solutiontijopaulose00No ratings yet
- Under Armour Case Study AnalysisDocument42 pagesUnder Armour Case Study AnalysisAsif Ashraf100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - State Preference TheoryDocument19 pagesChapter 4 - State Preference TheoryK60 Đỗ Khánh NgânNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2: Strategic Financial Management Questions Future ContractDocument24 pagesPaper - 2: Strategic Financial Management Questions Future ContractRaul KarkyNo ratings yet
- B5Document35 pagesB5issa adiemaNo ratings yet
- Saral Gyan Stocks Past Performance 050113Document13 pagesSaral Gyan Stocks Past Performance 050113saptarshidas21No ratings yet
- The Law Commission: Working PaperDocument56 pagesThe Law Commission: Working PaperDiana Alexandra ComaromiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Report: I. Problems IdentificationDocument3 pagesCase Study Report: I. Problems IdentificationFeelya MonicaNo ratings yet
- AshokaDocument16 pagesAshokaManjesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Literature ReviewDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Literature Reviewcoolpeer91No ratings yet
- Iqt GovtDocument29 pagesIqt GovtEncee MianNo ratings yet
- 226-Article Text-601-1-10-20210702Document12 pages226-Article Text-601-1-10-20210702Leni NopriyantiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Bank Heist Trail Goes Cold in Manila As Probes FalterDocument17 pagesBangladesh Bank Heist Trail Goes Cold in Manila As Probes FalterRheinhart PahilaNo ratings yet