Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 2 Study Guide
Uploaded by
api-342334216Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 2 Study Guide
Uploaded by
api-342334216Copyright:
Available Formats
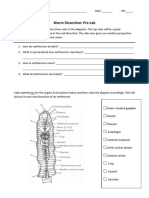
Name Date Class
CHAPTER 2
Study Guide
Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B.
Column A Column B
1. made up of individual organisms of the same species A. abiotic factors
2. all nonliving things in an environment B. biosphere
3. made up of the organisms and nonliving things in an area C. biotic factors
4. portion of Earth that supports life D. ecosystem
5. all living organisms in an environment E. population
Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B.
Column A
Column B
1. get energy by eating other organisms
A. autotrophs
2. eat both plants and animals
B. carnivores
3. eat only animals
C. detritivores
4. collect energy to produce their own food
D. herbivores
5. eat only plants
E. heterotrophs
6. eat or break down dead things
F. omnivore
Label the food chain below to identify each trophic level. Use these choices:
carnivore herbivore omnivore Producer
GRASS GRASSHOPPER RACCOON COYOTE
7. 8. 9. 10.
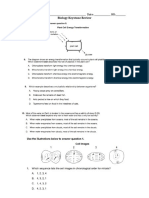
Name Date Class
CHAPTER 2:
Study Guide
Label the ecological pyramid. Use these choices:
primary consumers producers secondary consumers
Respond to each statement.
Recall the name for the total amount of living matter in each trophic level of an ecological pyramid.
Explain why an ecological pyramid is smaller at the top than at the bottom.
Number the steps of the water cycle in the order in which they occur.
Beginning with the collection of water in lakes or oceans.
Groundwater and runoff from land surfaces flow into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Water returns to Earth as rain or snow through the process of precipitation.
Through evaporation, water changes from a liquid to a gas that becomes part of the air.
Through condensation, water in the air changes from a gas to tiny droplets of liquid.
Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage about the carbon cycle.
atmosphere carbon cycles water
living organisms photosynthesis respiration
is a part of all organic compounds, which make up living things.
It through the environment due to the flow of energy in ecosystems.
The carbon cycle is made of several processes, including and
. During these processes, carbon moves between its major reservoirs.
These major reservoirs include , , and .
Name Date Class
CHAPTER 2:
Study Guide
Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage about the nitrogen cycle
ammonia atmosphere consumers decay decomposers
denitrification nitrogen fixation plants proteins urinate
Nitrogen is a nutrient that organisms need to produce .
Plants and animals cannot use the nitrogen that makes up a large percentage of the
. The nitrogen is captured and converted into a form that is usable
by plants in a process called . Nitrogen enters the food web when
absorb nitrogen compounds from the soil and use them to make
proteins. get nitrogen by eating plants or animals that contain
nitrogen. Nitrogen is returned to the soil when animals or when
organisms die and . break
down organic matter found in organisms into . This compound is
changed by organisms in the soil into other nitrogen compounds that can be used by plants. Finally, some
soil bacteria convert nitrogen compounds into nitrogen gas, which returns to the atmosphere in a process
called .
Label the diagram of the phosphorus cycle. Use these choices:
long-term cycle new rock short-term cycle soil and groundwater
22.
23.
24.
25.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Abe 412-Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Laboratory Exercise No. 5Document12 pagesAbe 412-Irrigation and Drainage Engineering Laboratory Exercise No. 5Jan James GrazaNo ratings yet
- Lau Biz202 Macro EnvironmentDocument9 pagesLau Biz202 Macro EnvironmentMai NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Anthony Biddle, Nigel D Cattlin Pests and Diseases of Peas and Beans A Colour HandbookDocument130 pagesAnthony Biddle, Nigel D Cattlin Pests and Diseases of Peas and Beans A Colour Handbookkjuan roaNo ratings yet
- Earthworm DissectionDocument5 pagesEarthworm Dissectionapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Frog PrelabDocument1 pageFrog Prelabapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Earthworm Pre LabDocument2 pagesEarthworm Pre Labapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 15-1 Darwins TheoryDocument15 pages15-1 Darwins Theoryapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 15-3 Shaping Evolutionary TheoryDocument25 pages15-3 Shaping Evolutionary Theoryapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 11-2 Complex Patterns of InheritanceDocument44 pages11-2 Complex Patterns of Inheritanceapi-342334216No ratings yet
- CH 14 NotesDocument23 pagesCH 14 Notesapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 10-3 Gene Linkage PolyploidyDocument14 pages10-3 Gene Linkage Polyploidyapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Pigeon GeneticsDocument1 pagePigeon Geneticsapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Spongebob-Genetics 2Document3 pagesSpongebob-Genetics 2api-342334216100% (1)
- Keystone ReviewDocument2 pagesKeystone Reviewapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Market Survey ReportDocument6 pagesMarket Survey ReportxulphikarNo ratings yet
- Soal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 Semester 1Document3 pagesSoal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 Semester 1yayangbanita100% (1)
- High Blood Sugar Levels Hyperglycemia. Diabetes Evaluation.Document3 pagesHigh Blood Sugar Levels Hyperglycemia. Diabetes Evaluation.Ibn SadiqNo ratings yet
- Deadpool - Samurai v02 (2022) (Digital) (1r0n)Document224 pagesDeadpool - Samurai v02 (2022) (Digital) (1r0n)dobof66532No ratings yet
- Handouts For 21st Century Literature Oct 9region7,8,10 and NCRDocument4 pagesHandouts For 21st Century Literature Oct 9region7,8,10 and NCRManuel J. RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Member Rewards Catalogue 2020/21 EditionDocument22 pagesMember Rewards Catalogue 2020/21 EditionNORMALA ABDUL RANINo ratings yet
- Elementary Unit 6b PDFDocument2 pagesElementary Unit 6b PDFPatrick VásquezNo ratings yet
- Dialogue Task 14Document5 pagesDialogue Task 14Fizri Adha0% (1)
- Present SimpleDocument6 pagesPresent SimpleKarlNo ratings yet
- Posessive Adjectives and Pronouns - ExercitiiDocument2 pagesPosessive Adjectives and Pronouns - ExercitiiGabriel CizmaritaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)Document18 pagesSyllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)api-19803189No ratings yet
- New Hope For Malnourished Mothers and ChildrenDocument12 pagesNew Hope For Malnourished Mothers and ChildrenthousanddaysNo ratings yet
- Text For No. 1 - 4: A. Choose One Correct Answer Out of The Four Options Given!Document7 pagesText For No. 1 - 4: A. Choose One Correct Answer Out of The Four Options Given!Lisa Aprilia AprisaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Semester Ganjil Kelas XiDocument6 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Semester Ganjil Kelas XiAchsien100% (1)
- GreenLine BrochureDocument12 pagesGreenLine BrochurekiwipumpsNo ratings yet
- Packing ListDocument3 pagesPacking ListLaura Daniela Romero RomeroNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension 2: DirectionsDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension 2: DirectionsFiorella Maria Montero OrtizNo ratings yet
- PENGARUH PEMBERIAN NAUNGAN DAN PUPUK ORGANIK CAIR TERHADAP PERTUMBUHAN DAN PRODUKSI TANAMAN STROBERI (Fragaria SP.) DI DATARAN RENDAHDocument13 pagesPENGARUH PEMBERIAN NAUNGAN DAN PUPUK ORGANIK CAIR TERHADAP PERTUMBUHAN DAN PRODUKSI TANAMAN STROBERI (Fragaria SP.) DI DATARAN RENDAHrudy hery syahfutroNo ratings yet
- Thesis Type PDFDocument35 pagesThesis Type PDFPrabid67% (6)
- (2xxx) What's Hot: New Year's EveDocument5 pages(2xxx) What's Hot: New Year's EveNorah LawlorNo ratings yet
- 4th Sibling Swap - WBDMMDocument6 pages4th Sibling Swap - WBDMMKareem TeekeyNo ratings yet
- Dark Kitchen Food Delivery App by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesDark Kitchen Food Delivery App by SlidesgoZalikal IlhamNo ratings yet
- World11 19 14Document39 pagesWorld11 19 14The WorldNo ratings yet
- Seed Quality Analysis of Ethiopian Mustard (Brassica Carinata A. Braun) by Near Infrared SpectrosDocument6 pagesSeed Quality Analysis of Ethiopian Mustard (Brassica Carinata A. Braun) by Near Infrared SpectrosAntonio Deharo BailonNo ratings yet
- Production of Modified Cassava Flour (Mocaf) : Bahrun Bin Mohd ShakirDocument24 pagesProduction of Modified Cassava Flour (Mocaf) : Bahrun Bin Mohd ShakirHACHALU FAYENo ratings yet
- Meniu Limba EnglezaDocument4 pagesMeniu Limba EnglezaDiana BotaNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Melly NH - EnglishDocument3 pagesSoal Pat Melly NH - Englishisman armanaNo ratings yet