Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BPMN Poster v1.0.10 (A2)
Uploaded by
calypso342Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BPMN Poster v1.0.10 (A2)
Uploaded by
calypso342Copyright:
Available Formats
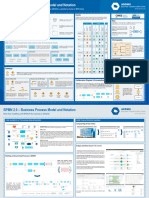
Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN) Poster baefg Check for the latest version at: http://bpmn.itposter.
net
Business Process Diagram Graphical Objects Business Process Diagram Connecting Objects
Sequence Flow and Message Flow rules
Events Activities Gateways Graphical connecting objects Only objects that can have an incoming and/or outgoing Sequence Flow / Message
An event is something that »happens« during the process. These events affect the An activity is a generic type of work that a company performs. An Flow are shown in the Tables Below.
A gateway is used to split or merge multiple process There are three ways of connecting Flow objects (Events, Activities,
flow of the process and usually have a cause (trigger) or an impact (result). activity can be atomic (task) or compound (process, sub-process).
flows. Thus it will determine branching, forking, Gateways) with each other or with other information – using sequence To: To:
Examples: 'Email received', '3 o'clock', 'Warehouse empty', 'Critical error',... Examples: 'Send a letter', 'Write a report', 'Calculate the interests',...
merging and joining of paths. Examples: 'Condition true? flows, message flows or associations.
A task is used to represent the – yes/no', 'Choose colour? – red/green/blue',...
Process Expanded
Intermediate
activity on the lowest abstraction Graphical connecting objects
sub-process
Event flow level.
Description Collapsed Normal A Sequence Flow is used to show the order In which the activities in a
sub-process Transaction Gateway control types sequence flow process will be performed.
Start
Event type More information about the
End
Conditional
From:
transaction and compensation A Sequence Flow can have condition expressions which are evaluated
From:
Data based exclusive decision or
Task attribute can be found under XOR merging. Both symbols have equal sequence flow at runtime to determine whether or not the flow will be used.
The Start Event indicates where a particular process will start. Intermediate (DATA) meaning. See also Conditional flow.
»Compensation Association«. Default For Data-Based Exclusive Decisions or Inclusive Decisions, one type
Events occur between a Start Event and an End Event. It will affect the flow of flow is the Default condition flow. This flow will be used only if all
General of the process, but will not start or (directly) terminate the process. The End sequence flow other outgoing conditional flows are NOT true at runtime.
Event indicates where a process will end. XOR Event based exclusive decision only.
A Message Flow is used to show the flow of messages between two
A message arrives from a participant and triggers the Event. This causes Task/Subprocess special attributes (EVENT) Message flow participants that are prepared to send and receive them. In BPMN,
two separate Pools in a Diagram can represent the two participants.
process to {start, continue, end} if it was waiting for a message, or changes
Message the flow if exception happens. End type of message event indicates that a
An Association (directed, non-directed) is used to associate
Looping The task or sub-process is repeated.
Data based inclusive decision or Association information with Flow Objects. Text and graphical non-Flow Objects
message is sent to a participant at the conclusion of the process.
The tasks in the sub-process can not be connected with
OR merging. can be associated with Flow objects.
A specific time or cycle can be set that will trigger the start of the Process Ad Hoc ~ sequence flows at design time.
Timer or continue the process. Intermediate timer can be used to model the time-
based delays. Multiple instances Multiple instances of task or sub-process will be created. COM- Complex condition (a combination of
PLEX basic conditions)
Error
This type of End indicates that a named Error should be generated. This
Error will be caught by an Intermediate Event within the Event Context.
Compensation The symbol represents a compensation task or sub-process.
Sequence flow mechanism Compensation Association
Parallel forking and joining
AND (synchronization). The Sequence Flow mechanisms is divided into types: Normal flow, Exception flow, In case of transactions it is desired that all activities which constitute
This type of Event is used within a Transaction Sub-Process. This type of
Event MUST be attached to the boundary of a Sub-Process. It SHALL be Conditional flow, Link Events and Ad Hoc (no flow). Refer also to specific a transaction are finished successfully. Otherwise the transaction fails
Cancel triggered if a Cancel End Event is reached within the Transaction Sub- »Workflow Patterns«. and rollback (compensation) activities occur which undo done
Process.
This is used for compensation handling--both setting and performing
Artefacts Normal sequence flow Ad Hoc –
activities.
compensation. It calls for compensation if the Event is part of a Normal Artefacts are used to provide additional information about the process. If No flow Task
Compensation Flow. It reacts to a named compensation call when attached to the
boundary of an activity. Very useful for modelling roll-back actions within
required, modellers and modelling tools are free to add new artefacts.
Examples of data objects: 'A letter', 'Email message', 'XML document',
Swimlanes Intermediate
link used as Task A
Compensation activity
the transaction. 'Confirmation',... Pools and lanes are used to represent organizations, ~
This type of event is triggered when the conditions for a rule
roles, systems and responsibilities. Examples: Intermediate link GOTO Transaction boundary
become true. Rules can be very useful to interrupt the loop process, for A
Rule example: 'The number of repeats = N'. Intermediate rule is used only for 'University', 'Sales division', 'Warehouse', 'ERP system',... used as GOTO Exception X Undo task A
Set of standardized artefacts
exception handling. A Pool MUST contain 0 or 1 Until Loop Looped subprocess Start Successfull
A Link is a mechanism for connecting the end (Result) of one Data objects provide information about what activities are required to be business process. transaction transaction
Lane Lane
Process to the start (Trigger) of another. Typically, these are triggered and/or what they produce. They are considered as Artefacts No Expanded sub-process Task B
Link Data object because they do not have any direct effect on the Sequence Flow or A Pool can contain 0 or more Error - compensation
Pool
two Sub-Processes within the same parent Process. It can be used, for A
example, when the working area (page) is too small – go to another page. Message Flow of the Process. The state of the data object should also be lanes. events cannot be
[state] set.
Exception flow Exception X Undo task B triggered
This type of event indicates that there are multiple ways of triggering the Two pools can only be connected Try again
Grouping can be used for documentation or analysis purposes. Groups
with message flows. B
Multiple Process. Only one of them will be required to {start, continue, end} the
Group can also be used to identify the activities of a distributed transaction that is
Process. shown across Pools. Grouping of activities does not affect the Sequence A Pool represents a participant in a process. It contains a business
or Message Flow. process and is used in B2B situations. Interrupt
This type of End indicates that all activities in the Process should be Exception X Transaction Handle through
Conditional flow loop rule
Terminate immediately terminated. This includes all instances of Multi-Instances. The
Annotation Description
Text Annotations are a mechanism for a modeller to provide additional A Lane is a sub-partition within a pool used to organize and exception other services
Process is terminated without compensation or event handling. information for the reader of a BPMN Diagram. categorize activities. ~ Failed transaction
B Collapsed adhoc sub-process Cancel - compensation events are triggered.
Wait a few minutes Cancel event can be used only with transaction.
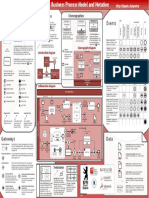
Business Process Diagram Notation - Common Patterns and Antipatterns
Wrong use of flows in/between (Wrong) Use of time events Use of flows within lanes Use of gateways Workflow patterns
There are two common mistakes when using time events. First,
pools starting events are often used instead of intermediate events.
Second, intermediate events are often used as a delay
Lanes are often wrongly used in similar ways as Pools. They Gateways are connected only with sequence flows. Also Avoid
potential deadlocks when using gateways.
Normal sequence flow
Multiple merge, uncontrolled flow
When modelling Pools, sequence flows and start/end events are wrongly contain more business processes or contain message
often missing, because it is wrongly presumed that message mechanism but modelled as an exception mechanism
flows between different lanes.
flows substitute sequence flows. Additionally, sequence flows (representing the duration of a task) and vice-versa (see the
are incorrectly used to connect pools. right use below).
A message flow is not Message flow cannot Exclusive choice with Simple merge,
A Pool can contain only one Parallel split, uncontrolled flow
Model the process in each Pool independently and afterwards allowed within a process influence the gateway decision gateway uncontrolled flow
Here a time event Is used as (1) process
define message flows between Pools.
Missing end event a DELAY mechanism.
Lane A
Task A
Missing sequence flows Task C
Pool B
Decision A conditional flow Is not
... Task A Task B ... Multiple choice
Lane B
information allowed (necessary) here
Task B Task C from Pool X
Delay Task A Discriminator,
Pool A
No output flow from the task Parallel split,
Task A Task B Task C forking gateway Synchronization merging gateway
... exists.
(pararel join)
Exception time
(e.g. »after 2 hours«)
Lane A
Task B Simple merge,
Message Message Sequence flows are not Task A
Here it represents the uncontrolled flow
flow AD flow EB allowed between Pools
Pool A
DURATION of a task. The decision must Alter. 1
Lane B
Task B ... An intermediate event contain at least two
Task B Task C
Pool B
has to be used. Send message to output flows Alter. 2
Task D Task E Task F A message flow cannot be
Pool X
a gateway alternative
Alter. 3
Event based decision Complex decision
Missing start event (gateway)
Task C
Use of message events and Use of the sequence flow
message flows mechanism Task A
Use of tasks and events When using expanded sub-processes, sequence flows should
Analysing
decision
Starting and intermediate events can not be sources of information Multiple choice, inclusive
message flows. be connected to the boundaries of sub-processes. Processes
Analysts often wrongly model events and tasks. For Both examples are wrong - intermediate Task B decision gateway Synchronization merge, Example of a
example: events are wrongly modelled as tasks, task states ... and sub-processes should start and end properly!
merging gateway deadlock
message events can not produce
are modelled as new tasks. message flows. Events can be only Message
A sequence flow cannot cross from Pool X
This task is redundant. triggered by a message flow.
... the boundary of a sub-process Send message
This task is redundant. Document X Task A is automatically Message A to Pool X
Task automatically
starts at input
sequence flow
... finished at output
sequence flow.
Wrong positioning of
Sub-process »P« Message to Pool X About the BPMN Poster C
message event Message B
A Task A Task B Task C This poster is licensed under the
Receiving Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike (by-sa) License
Starting Performing Task A
...
task A
document
X
task A finished
...
... Task A Task B ...
The sub-process should The process should have an
Explanation of Poster Symbols
B
Authors:
have a start event end event
Important note, explanation Gregor Polančič & Tomislav Rozman
This task is redundant.The act of receiving Email: info@itposter.net
a document is a task itself.
... ...
Sub-process »P« Warning or error in the BPMN model University of Maribor
... Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... Task A Task B Task C Institute of Informatics
Recommendation
Message A Message B
Document X Document Y Exception flow Wrong model Poster version: 1.0.10 (6th October 2008)
Event Y Although it is recommended that a process has an explicit start and end
Literature used: BPMN Specification 1.0 @ http://www.bpmi.org
...
Task A
event, this is not a rule. In fact start and end events can be hidden in a sub Right (corrected) model
Normal flow Task A Task B ... process, if needed, or attached to the boundary of the task so as not to
...
interrupt the normal sequence flow between the sub-process and the rest of
http://bpmn.itposter.net
Event X the process.
B
You might also like
- BPMN Poster A4 Ver 1.0.10 PDFDocument1 pageBPMN Poster A4 Ver 1.0.10 PDFSatrio N. W. NotoamidjojoNo ratings yet
- BPMN Poster A3 Ver 1.0.10Document2 pagesBPMN Poster A3 Ver 1.0.10phischa kaewwimolNo ratings yet
- BPMN-Poster2019 FINAL en PDFDocument1 pageBPMN-Poster2019 FINAL en PDFsimdowNo ratings yet
- BPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business AnalystsDocument1 pageBPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business AnalystsinigomNo ratings yet
- BPMN Poster A3 Ver 1.0.7Document1 pageBPMN Poster A3 Ver 1.0.7philypeNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Presentation-Architecture For Personalized ContentDocument10 pagesAn Efficient Presentation-Architecture For Personalized ContentCarsten UllrichNo ratings yet
- Using BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldDocument6 pagesUsing BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldWonderware Skelta BPM100% (1)
- AWS Periodic TableDocument1 pageAWS Periodic Tabledouglas.dvferreiraNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Collections Processing WorkflowDocument1 pageCustomer Service Collections Processing WorkflowJancy KattaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3.11 Lab - Draw A Process DiagramDocument4 pages1.1.3.11 Lab - Draw A Process DiagramJoshua ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Rapid Object Detection Using A Boosted Cascade of Simple FeaturesDocument9 pagesRapid Object Detection Using A Boosted Cascade of Simple FeaturesYuvraj NegiNo ratings yet
- 2023 07 14 BPMN 20 Poster ENDocument2 pages2023 07 14 BPMN 20 Poster ENAntonio BritoNo ratings yet
- Projmatic Case StudyDocument1 pageProjmatic Case Studyk4gs62x9vdNo ratings yet
- Meralco Bill SampleDocument3 pagesMeralco Bill SampleHarris BalbinNo ratings yet
- Modelbuilder - Automate ProcessingDocument7 pagesModelbuilder - Automate ProcessingKhalid ChadliNo ratings yet
- Otn Fec Po Opt TM AeDocument1 pageOtn Fec Po Opt TM Aenobita3No ratings yet
- Org Process MGMT Plan Blank CL1Document1 pageOrg Process MGMT Plan Blank CL1johnoo7No ratings yet
- MTC Ims Fo 14e Starrt CardDocument1 pageMTC Ims Fo 14e Starrt CardsouravrobinNo ratings yet
- Vendor Compliance: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioDocument1 pageVendor Compliance: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioMrito ManobNo ratings yet
- Software Testing at A Glance or TwoDocument1 pageSoftware Testing at A Glance or TwoRajarajan100% (1)
- E Busi8Document12 pagesE Busi8Prof. S. ShinyNo ratings yet
- Online Insurance Sales WorkflowDocument1 pageOnline Insurance Sales WorkflowFaisal AzizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost Risk Analysis Risk MitigationDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Cost Risk Analysis Risk Mitigationpa20060No ratings yet
- Order Management Ecommerce WorkflowDocument1 pageOrder Management Ecommerce WorkflowElena EnacheNo ratings yet
- Analisa Dan Perancangan Sistem: Activity DiagramsDocument25 pagesAnalisa Dan Perancangan Sistem: Activity DiagramsDiyah Chamdi AliNo ratings yet
- Portfolio DashboardDocument234 pagesPortfolio DashboardRNo ratings yet
- Collections Credit Cards Workflow PDFDocument1 pageCollections Credit Cards Workflow PDFBea LadaoNo ratings yet
- BizTalk Server 2010 Runtime Architecture PosterDocument1 pageBizTalk Server 2010 Runtime Architecture PosterascsaNo ratings yet
- Dmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01Document1 pageDmaic 12873122766122 Phpapp01quycoctuNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Your Portfolio Dashboard!: Instruct IonsDocument227 pagesWelcome To Your Portfolio Dashboard!: Instruct IonsVignesh MohanNo ratings yet
- Workflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-LtdDocument6 pagesWorkflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-Ltdluan_ba100% (1)
- Sccurriculumresultsreport 2Document1 pageSccurriculumresultsreport 2api-392364749No ratings yet
- Sejal Divekar Resume1Document2 pagesSejal Divekar Resume1Jason StanleyNo ratings yet
- Delloite Operator Value MapDocument1 pageDelloite Operator Value MapDiogo Pimenta Barreiros0% (1)
- Bpmn2 0 Poster enDocument1 pageBpmn2 0 Poster enBanu AysolmazNo ratings yet
- SmallgroupresultsreportDocument1 pageSmallgroupresultsreportapi-392364749No ratings yet
- Activities Events: Conversations ChoreographiesDocument1 pageActivities Events: Conversations ChoreographiesMoataz BelkhairNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Managers SolutionDocument2 pagesConcurrent Managers SolutionMukarram KhanNo ratings yet
- S IC: Unleashing The Emergent Correspondence For In-Context SegmentationDocument11 pagesS IC: Unleashing The Emergent Correspondence For In-Context SegmentationdrewqNo ratings yet
- DFMEA Examples 29JUN2020 7.2.19Document24 pagesDFMEA Examples 29JUN2020 7.2.19Mani Rathinam RajamaniNo ratings yet
- The Search EcosystemDocument1 pageThe Search EcosystemOmar CorralNo ratings yet
- Ayushi Patel Resume 1Document2 pagesAyushi Patel Resume 1api-710831774No ratings yet
- SWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Document1 pageSWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Nedra DebbechNo ratings yet
- Cert Study PlanDocument3 pagesCert Study PlanLiquan YangNo ratings yet
- School Counseling Example Action Plan TemplateDocument1 pageSchool Counseling Example Action Plan TemplateMJNo ratings yet
- Apex Triggers in SalesforceDocument3 pagesApex Triggers in Salesforceumaaruna uma11144No ratings yet
- Power Pivot Client Server ArchitectureDocument2 pagesPower Pivot Client Server ArchitectureBalakrishna SappaNo ratings yet
- App. Algorithms SummaryDocument37 pagesApp. Algorithms SummaryaliNo ratings yet
- Autos PoolDocument8 pagesAutos PoolPARASCADD Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- DataBase Jobs To Be MonitoredDocument28 pagesDataBase Jobs To Be MonitoredSurendraNo ratings yet
- Run Chart - ThroughputDocument2 pagesRun Chart - ThroughputAndreea HavrișciucNo ratings yet
- Embedded Project WorksheetDocument4 pagesEmbedded Project WorksheetcammanderNo ratings yet
- Vendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioDocument1 pageVendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioLIGAYA SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- Modern Information Retrieval: ModelingDocument263 pagesModern Information Retrieval: ModelingahmadNo ratings yet
- Module7 QgansDocument13 pagesModule7 Qgansdr.hassanalqanaziNo ratings yet
- Training Topics: Day 0 (Monday)Document3 pagesTraining Topics: Day 0 (Monday)saurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is A GC Buffer Busy WaitDocument2 pagesWhat Is A GC Buffer Busy Waitmrstranger1981No ratings yet
- All Clear Kl7 Unit2 Basic Test BDocument3 pagesAll Clear Kl7 Unit2 Basic Test BKatarzyna Agata Krzyczmonik50% (2)
- Photoshop Normal Map FilterDocument7 pagesPhotoshop Normal Map FilterDarek CzarneckiNo ratings yet
- Evermotion Archmodels PDFDocument2 pagesEvermotion Archmodels PDFLadonnaNo ratings yet
- Functional Specifications - Openbravo Wiki Projects-AppraisalsDocument6 pagesFunctional Specifications - Openbravo Wiki Projects-AppraisalsJitesh SasiNo ratings yet
- Brava Enterprise Installation Guide 5.3 SP1Document106 pagesBrava Enterprise Installation Guide 5.3 SP1jazarja100% (2)
- The Engineering Design Revolution - CAD History - 13 IBM, Lockheed and DassaultDocument44 pagesThe Engineering Design Revolution - CAD History - 13 IBM, Lockheed and DassaultphamduyprojectNo ratings yet
- IED Configurator User ManualDocument36 pagesIED Configurator User ManualSayed SaadNo ratings yet
- Ritmurile LuniiDocument161 pagesRitmurile Luniimonica_vasilescu2008No ratings yet
- Saep 1610Document21 pagesSaep 1610Anonymous 4IpmN7OnNo ratings yet
- Brake ABS WabcoDocument2 pagesBrake ABS WabcoBudiNo ratings yet
- 11 - Hashing PDFDocument24 pages11 - Hashing PDFKealeboga Duece ThoboloNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control (With Comparison Chart) - Key DifferencesDocument5 pagesDifference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control (With Comparison Chart) - Key Differencescenkj100% (1)
- Editavel Gregory R Andrews - Concurrent Programming - Principles and Practice-The Benjamin - Cummings (1991)Document656 pagesEditavel Gregory R Andrews - Concurrent Programming - Principles and Practice-The Benjamin - Cummings (1991)Tiago Martins100% (1)
- Ppa CVDocument3 pagesPpa CVRashid Mahmood JaatNo ratings yet
- Inverse of A MatrixDocument10 pagesInverse of A MatrixcontactrnNo ratings yet
- PM Challenge '19 - XLRIDocument9 pagesPM Challenge '19 - XLRIRajat PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Internet: Submitted in Partial Fulfillement For The Degree of Masters of Business AdministrationDocument24 pagesSeminar Report On Internet: Submitted in Partial Fulfillement For The Degree of Masters of Business AdministrationVikash BhanwalaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Dec-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 29-Dec-2023kanishkakhanna.inboxNo ratings yet
- April 2 3,2016, Chennai, IndiaDocument3 pagesApril 2 3,2016, Chennai, IndiaCS & ITNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 8x1 MUX and 1X8 DMUX 4 5 6 7 SR, D, JK, T FF 8 4-Bit Binary, BCD Counters (Syn/asyn Reset) 9 FSMDocument25 pages1 2 3 8x1 MUX and 1X8 DMUX 4 5 6 7 SR, D, JK, T FF 8 4-Bit Binary, BCD Counters (Syn/asyn Reset) 9 FSMhari chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Nimcet 2009 PaperDocument17 pagesNimcet 2009 Paperanujdhanuka100% (1)
- Milling ProgramDocument20 pagesMilling ProgramSudeep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- GX Deloitte Lab Sap s4 Hana FinancDocument2 pagesGX Deloitte Lab Sap s4 Hana Financhoney_2132No ratings yet
- Sair e Natamam PDFDocument294 pagesSair e Natamam PDFHafiz Ihsan UllahNo ratings yet
- I-K Bus Codes v6Document41 pagesI-K Bus Codes v6Dobrescu CristianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document24 pagesLecture 05Abdul Ghani Khan100% (1)
- C++ Tutorials Chapter 01Document14 pagesC++ Tutorials Chapter 01darkclaw_aqpNo ratings yet
- PRISMAsync v5.1 For IPR C850 Series Settings Editor 070116Document98 pagesPRISMAsync v5.1 For IPR C850 Series Settings Editor 070116JustinAtkinsonNo ratings yet