Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Los Verbos en Inglés1 PDF
Uploaded by
LolyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Los Verbos en Inglés1 PDF
Uploaded by
LolyCopyright:
Available Formats
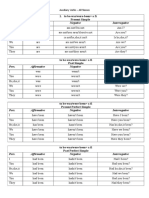
VERBOS TO BE y TO HAVE
1.- VERBO TO BE (ser o estar)
PRESENTE
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I am (Im) I am not (Im not) Am I?
You are (Youre) You are not (You arent) Are you?
He is (s) He is not (He isnt) Is he?
She is (s) She is not (She isnt) Is she?
It is (s) It is not (It isnt) Is it?
We are (re) We are not (We arent) Are we?
You are (re) You are not (You arent) Are you?
They are (re) They are not (They arent) Are they?
PASADO
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I was I was not (I wasnt) Was I?
You were You were not (You Were you?
werent)
He was He was not (He wasnt) Was he?
She was She was not (She wasnt) Was she?
It was It was not (It wasnt) Was it?
We were We were not (We werent) Were we?
You were You were not (You Were you?
werent)
They were They were not (They Were they?
werent)
El verbo to be se trata de un verbo auxiliar, por tanto, no precisa del auxiliar to do para la
forma negativa e interrogativa.
2.- VERBO TO HAVE (haber, tener o tomar)
PRESENTE
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I have (Ive) I have not (I havent) Have I?
You have (Youve) You have not (You Have you?
havent)
He has (Hes) He has not (He hasnt) Has he?
She has (Shes) She has not (She hasnt) Has she?
It has (Its) It has not (It hasnt) Has it?
We have (Weve) We have not (We havent) Have we?
You have (Youve) You have not (You Have you?
havent)
They have (Theyve) They have not (They Have they?
havent)
PASADO
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I had (Id) I had not (hadnt) Had I?
You had (Youd) You had not (hadnt) Had you?
He had (Hed) He had not (hadnt) Had he?
She had (Shed) She had not (hadnt) Had she?
It had (Id) It had not (hadnt) Had it?
We had (Wed) We had not (hadnt) Had we?
You had (Youd) You had not (hadnt) Had you?
They had (Theyd) They had not (hadnt) Had they?
En el caso de que no se ponga got habra que utilizar el auxiliar do.
PRESENTE SIMPLE/PRESENTE CONTINUO
(PRESENT SIMPLE/PRESENT CONTINUOUS)
1.- PRESENTE SIMPLE
a) AFIRMATIVA
Es igual que el verbo infinitivo sin to, excepto la tercera persona del singular, que termina
en s o es.
Para formar correctamente la 3 persona del singular hay que tener en cuenta las siguientes
reglas ortogrficas segn la terminacin del verbo:
En o, -ss, -sh, -ch, -sh o x aade es:
o Do Does
o Miss Misses
o Wish Wishes
o Touch Touches
o Fix Fixes
En vocal +y aade s:
o Say Says
En consonante +y cambia la y por la i antes de aadir es:
o Try Tries
b) NEGATIVA
Sujeto + do not (dont) o does not (doesnt) para la tercera persona del singular + verbo
en infinitivo sin to
c) INTERROGATIVA
Do o does + sujeto + infinitivo sin to
HAVE GOT, TO BE y los VERBOS MODALES NO
NECESITAN EL AUXILIAR DO/DOES EN
NEGATIVA NI INTERROGATIVA
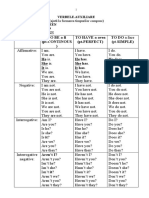
d) EJEMPLO
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I work I dont work Do I work?
You work You dont work Do you work?
He works He doesnt work Does he work?
She works She doesnt work Does she work?
It works It doesnt work Does it work?
We work We dont work Do we work?
You work You dont work Do you work?
They work They dont work Do they work?
Respuestas:
Yes, I do
No, he doesnt
e) USOS DEL PRESENTE SIMPLE
Hablar de verdades universales.
o The sun rises in the East El Sol sale por el este
Expresar acciones habituales.
Every morning, I wake up at 7 Me levanto a las 7 todos los das
Referirse a acciones permanentes.
My father works for IBM Mi padre trabaja en IBM
Referirse a medios de transporte, acontecimientos, etc; sujetos a un horario
determinado.
My plane leaves at 8.30 Mi avin sale a las 8:30
Dar un matiz de inmediatez a una retransmisin (por ejemplo deportiva) en
medios de comunicacin.
Peterson plays now, Smith doesnt catch the ball
Peterson juega ahora, Smith no coge la pelota
Referirse a acontecimientos que acaban de suceder, publicados en titulares de
peridico o noticias de televisin.
Bush wins Gana Bush
Con los verbos estticos que indican un estado ms que una accin.
Algunos indican tanto estado como actividad y pueden usarse en presente simple
y en presente continuo. Ejemplo:
Donna thinks the book is wonderful Donna cree que el libro es estupendo.
He is thinking about going to Malta in the summer Est pensando en irse a
Malta en verano.
El verbo see en presente continuo indica una accin futura fijada de antemano.
We are seeing Ann tonight Veremos a Ann esta noche.
Los verbos estticos estn relacionados con:
o Emociones y sentimientos:
Like gustar
Love amar
Hate odiar
Care cuidar
Hope esperar
Wish desear
Want querer
Admit reconocer
Enjoy disfrutar
Dislike - disgustar
o Pensamiento y la opinin:
Believe creer, cuestin de fe
Think creer razonablemente
Understand entender
Suppose suponer
Expect esperar
Agree estar de acuerdo
Know conocer/saber
Remember recordar
Forget olvidar
Mean significar
Imagine imaginar
Realize darse cuenta
Deserve merecer
Prefer preferir
Guess adivinar/suponer
o Percepcin y los sentidos:
Look mirar
Hear or
Taste probar
Smell oler
Feel sentirse
Hear or, escuchar
See ver
Sound sonar
Touch tocar/acariciar
o Precios y medidas:
Cost costar, valer
Measure medir, calibrar, sopesar, considerar
Weight aplastar, cargar
o Posesin y la esencia:
Belong pertenecer
Come from ser de
Own poseer
Have tener
Possess poseer
Contain contener
Depend on depender de
Need necesitar
Seem parecer
Appear - aparecer
f) EXPRESIONES UTILIZADAS EN PRESENTE SIMPLE (adverbios y expresionesde
frecuencia)
Always siempre
Usually generalmente, normalmente
Generally generalmente
Regularly con frecuencia, a menudo
Occasionally ocasionalmente, a veces
Hardly ever casi nunca
Frequently frecuentemente, a menudo
Often a menudo
Sometimes a veces
Rarely rara vez, pocas veces, casi nunca
Seldom raramente, pocas veces, casi nunca
Never nunca
At 1 oclock a las 1 en punto
At night de noche, por la noche
In the morning/evening en la maana/tarde
Every day, week todos los das, semanas
On Friday, Saturday el Viernes, Sbado
Once a month una vez al mes
Twice a week dos veces en semana
How often? - Con qu frecuencia?
Los adverbios de frecuencia van delante del verbo principal, pero si se trata del verbo to
be se colocan detrs.
He never recognises me Nunca me reconoce
Paul is always calm Paul siempre est tranquilo
Las expresiones temporales siempre van al principio o al final de la frase.
James uses his computer every day James usa su ordenador todos los das
Con how often? se pregunta con qu frecuencia se hace algo.
How often do you read? - Con qu frecuencia lees?
2.- PRESENTE CONTINUO
a) AFIRMATIVA
Se forma con el sujeto + verbo to be conjugado (am/are/is) + verbo principal terminado
en ing, siguiendo las siguientes reglas ortogrficas segn la terminacin de la forma base
del verbo:
En e muda pierde la e: ride riding // love loving
En y, la mantiene: pay paying
En ie, cambia la ie por y: die diying
En vocal + consonante (monoslabo) dobla la consonante, excepto w y x: run
runnig // show showing
En l o p (bislabo con acento llano) dobla esa letra: travel travelling
En vocal + consonante (bislabo con acento agudo), dobla la consonante: refer
referring // begin beginning
b) NEGATIVA
Se forma con el sujeto + el verbo to be conjugado en negativa (m not/isnt/arent) + verbo
terminado en ing.
c) INTERROGATIVA
Verbo to be conjugado (am/are/is) + sujeto + verbo principal terminado en ing
d) EJEMPLOS
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I am singing Im not singing Am I singing?
Im singing
You are singing You arent singing Are you singing?
Youre singing
He is singing He isnt singing Is he singing?
Shes singing She isnt singing Is she singing?
Its singing It isnt singing Is it singing?
We are singing We arent singing Are we singing?
Were singing
Youre singing You arent singing Are you singing?
They are singing They arent singing Are they singing?
Yes, I am
No, I am not
e) USOS DEL PRESENTE CONTINUO
Referirse a una accin que est sucediendo en el momento en el que se habla
What are you doing John?
Qu ests haciendo, John?
Hablar de una accin presente que se sale de la norma
I get up at 8 every day but today Im staying at home
Me levanto a las 8 todos los das pero hoy me quedo (me estoy quedando) en
casa
Expresar lo que se har con toda seguridad en un futuro prximo porque se ha
fijado de antemano
Im going to the cinema tomorrow
Voy al cine maana
Con el adverbio always, para denotar una queja
She is always eating chocolate
Ella est comiendo siempre chocolate
f) ADVERBIOS Y EXPRESIONES DE TIEMPO UTILIZADOS EN PRESENTE
CONTINUO
Now ahora
Right now ahora mismo
At the momento en este momento
This year este ao
At present actualmente
Today hoy
These days estos das
This month este mes
This evening esta noche
Tonight esta noche
Tomorrow maana
Next Friday/ week/ year prximo viernes/semana/ao
Currently actualmente
Actually de hecho
LOS VERBOS ESTTICOS NO SUELEN
UTILIZARSE EN EL PRESENTE CONTINUO
PASADO PERFECTO SIMPLE / PASADO
PERFECTO CONTINUO
(PAST PERFECT SIMPLE / PAST PERFECT
CONTINUOUS)
1.- PASADO PERFECTO SIMPLE
a) AFIRMATIVA
Sujeto + had + participio del verbo que expresa la accin
b) NEGATIVA
Sujeto + hadnt + participio del verbo que expresa la accin
c) INTERROGATIVA
Had + sujeto + participio del verbo que expresa la accin
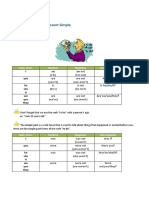
d) EJEMPLOS
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I had arrived I hadnt arrived Had I arrived?
You had arrived You hadnt arrived Had you arrived?
He had arrived He hadnt arrived Had he arrived?
She had arrived She hadnt arrived Had she arrived?
It had arrived It hadnt arrived Had it arrived?
We had arrived We hadnt arrived Had we arrived?
You had arrived You hadnt arrived Had you arrived?
They had arrived They hadnt arrived Had they arrived?
Respuestas:
Yes, I had
No, I hadnt
e) USOS DEL PASADO PERFECTO SIMPLE
Indicar que una accin ocurri antes que otra expresada en Pasado Simple.
By the time the police arrived, he had already left
Para cuando lleg la polica, ya se haba marchado
f) ADVERBIOS Y EXPRESIONES DE TIEMPO UTILIZADAS EN PASADO
PERFECTO SIMPLE
Already ya
By the time por el momento
After despus de
Before antes de
Until hasta/ hasta que
Never nunca/ jams
Just por poco/ acabar de
2.- PASADO PERFECTO CONTINUO
a) AFIRMATIVA
Sujeto + had been + verbo que expresa la accin en ing
b) NEGATIVA
Sujeto + hadnt been + verbo que expresa la accin en ing
c) INTERROGATIVA
Had + sujeto + been + verbo que expresa la accin en ing
d) EJEMPLOS
AFIRMATIVA NEGATIVA INTERROGATIVA
I had been working I hadnt been working Had I been working?
You had been working You hadnt been working Had you been working?
He had been working He hadnt been working Had he been working?
She had been working She hadnt been working Had she been working?
It had been working It hadnt been working Had it been working?
We had been working We hadnt been working Had we been working?
You had been working You hadnt been working Had you been working?
They had been working They hadnt been working Had they been working?
Respuestas:
Yes, I had been
No, I hadnt been
e) USOS DEL PASADO PERFECTO CONTINUO
Se utiliza para hacer referencia a acciones o situaciones que comenzaron en un momento
pasado, duraron un tiempo y se terminaron completamente antes del punto del pasado al
que se est refiriendo.
I had been training eight hours a day for six moths
Yo haba estado entrenando ocho horas diarias durante seis meses
f) ADVERBIOS Y EXPRESIONES DE TIEMPO UTILIZADAS EN PASADO
PERFECTO CONTINUO
Already ya
By the time por el momento
After despus de
Before antes de
Until hasta/ hasta que
Never nunca/ jams
Just por poco/ acabar de
You might also like
- Afaraf (Afar Language) & Its Dictionary PreparationDocument19 pagesAfaraf (Afar Language) & Its Dictionary Preparationmichael_lheureux969780% (10)
- Interchange Intro Level Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesInterchange Intro Level Scope and SequencenaeemNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verb To Be : Affirmative NEGATIVE (+ Not) Interrogative (Reverse) PresentDocument2 pagesAuxiliary Verb To Be : Affirmative NEGATIVE (+ Not) Interrogative (Reverse) PresentChristina Selby100% (1)
- To Be (Present Tense Simple) : Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument2 pagesTo Be (Present Tense Simple) : Affirmative Negative Interrogativekasandra_style3751No ratings yet
- Inglese - Tempi VerbaliDocument4 pagesInglese - Tempi VerbaliAlessio ArmanniNo ratings yet
- Prezentul Simplu: Tobe Afi Afirmativa NegativaDocument15 pagesPrezentul Simplu: Tobe Afi Afirmativa NegativaBobina CristiNo ratings yet
- Upo de VerbosDocument4 pagesUpo de Verboskm p , njose luis varela taboadaNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument52 pagesSimple Pastcaio.pinheiro6681658851No ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument11 pagesBasic English Grammarloely mikrotik100% (1)
- BE, HAVE, DO Conjugation and UsageDocument3 pagesBE, HAVE, DO Conjugation and UsageSébastien Landais100% (1)
- Verbo To Be (Ser, Estar) en InglésDocument9 pagesVerbo To Be (Ser, Estar) en InglésAri RamirezNo ratings yet
- Starter Unit 2Document1 pageStarter Unit 2Kairós AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Interrogatives Et NégativesDocument4 pagesInterrogatives Et NégativesIla FornaNo ratings yet
- Grammar GuideDocument66 pagesGrammar GuidebeticabestNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be No Presente Simples: ADocument4 pagesVerb To Be No Presente Simples: ALiviaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To English To Be (Ser o Estar) : Tobe Se Utiliza en La Formación de Tiempos VerbalesDocument2 pagesWelcome To English To Be (Ser o Estar) : Tobe Se Utiliza en La Formación de Tiempos VerbalesAbdel QahharNo ratings yet
- VerbosDocument4 pagesVerbosAlexandra CostaNo ratings yet
- Activity 14-04-2023Document1 pageActivity 14-04-2023FERNANDO CAYAO VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple - Present Continuousanacarvalho_20074152No ratings yet
- English - Review Verbo To Be - PresentDocument1 pageEnglish - Review Verbo To Be - PresentPollyanna MeloNo ratings yet
- Gjuhe Angleze DetyratDocument14 pagesGjuhe Angleze DetyratLindaAr100% (1)
- I AM WAS Been YOU HE SHE IT WE They: ARE Were Been IS WAS Been IS WAS Been IS WAS Been ARE Were Been ARE Were BeenDocument4 pagesI AM WAS Been YOU HE SHE IT WE They: ARE Were Been IS WAS Been IS WAS Been IS WAS Been ARE Were Been ARE Were BeenEmmanuel Astaroth PaizaNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument5 pagesVerb TensesOnorina Sanchez Palacios100% (1)
- Conjugacion VerbosDocument8 pagesConjugacion VerbostrejanoNo ratings yet
- Have Some or AnyDocument12 pagesHave Some or AnyNawsaypo HtooNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verbs - All TensesDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Verbs - All TensesChiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- Verbos SencillosDocument4 pagesVerbos SencillosCarmen José Vázquez GóngoraNo ratings yet
- To Be: Am I ? Are You ? Is He ? Is She ? Is It ? Are We ? Are You ? (Plural) Are They ?Document2 pagesTo Be: Am I ? Are You ? Is He ? Is She ? Is It ? Are We ? Are You ? (Plural) Are They ?Grisel HiNo ratings yet
- The Verb TO BE: I Am Not Interested in Literature He Isn't Proud of His Friend. She Is Afraid of SpidersDocument2 pagesThe Verb TO BE: I Am Not Interested in Literature He Isn't Proud of His Friend. She Is Afraid of SpidersIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica BasicaDocument3 pagesGramatica Basicamoly083No ratings yet
- Superverbs vs Normal Verbs: The Two Main Types of VerbsDocument1 pageSuperverbs vs Normal Verbs: The Two Main Types of VerbsMaribel RockcuevaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Present Continuos - Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPresent Simple - Present Continuos - Past SimpleMónicaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH - Verb Tenses - Present and Past Simple - by Ricardo Vernaut JuniorDocument13 pagesENGLISH - Verb Tenses - Present and Past Simple - by Ricardo Vernaut JuniorSimei100% (1)
- Tabla de Conjugación Del Verbo To BeDocument11 pagesTabla de Conjugación Del Verbo To BeJanethDíazdePalaciosNo ratings yet
- 1) Form: - Ed ! ! ! Consoana + y - Ied Consoana AccentuateDocument25 pages1) Form: - Ed ! ! ! Consoana + y - Ied Consoana AccentuateAlexandra EvaNo ratings yet
- Verbo Have GotDocument1 pageVerbo Have GotgracielasudiNo ratings yet
- VERBS TO BE AND HAVE GOT - ChartsDocument1 pageVERBS TO BE AND HAVE GOT - ChartsPauNo ratings yet
- Question TagsDocument15 pagesQuestion TagsRita Patricia Patiño100% (1)
- Conjugación Del Verbo To BeDocument4 pagesConjugación Del Verbo To Bejose luis MataNo ratings yet
- Possessive adjectives and pronouns guideDocument7 pagesPossessive adjectives and pronouns guidePilarNo ratings yet
- El verbo to be en presenteDocument3 pagesEl verbo to be en presenteLICEO SAN MARTIN DE PORRESNo ratings yet
- Learn English verb tensesDocument12 pagesLearn English verb tensesBerta TutusausNo ratings yet
- English Alphabet and Grammar GuideDocument2 pagesEnglish Alphabet and Grammar GuideaygulNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument15 pagesEnglish TensesOvidiu Chiva100% (1)
- Verb TencesDocument18 pagesVerb TencesJMAKNo ratings yet
- Tiempos GramaticalesDocument18 pagesTiempos Gramaticalesgi naNo ratings yet
- CONJUGATION CHARTS (To Be)Document2 pagesCONJUGATION CHARTS (To Be)Gl ADNo ratings yet
- Conjugarea Verbelor La Diferite TimpuriDocument5 pagesConjugarea Verbelor La Diferite TimpuriChiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- A1 - Tenses I - The Present Simple: 1.to BeDocument6 pagesA1 - Tenses I - The Present Simple: 1.to BeTristan DevillersNo ratings yet
- Presente Perfecto, Presente Perfecto Continuo, Pasado Perfecto, Introducción A La PasivaDocument6 pagesPresente Perfecto, Presente Perfecto Continuo, Pasado Perfecto, Introducción A La PasivaIrene GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Side by Side Simple Present Simple Past Classroom Posters Grammar DrillsDocument1 pageSide by Side Simple Present Simple Past Classroom Posters Grammar DrillsEdita NiaurieneNo ratings yet
- Alex - VB de Repetat PDFDocument4 pagesAlex - VB de Repetat PDFMariusNo ratings yet
- Verbe EnglezaDocument4 pagesVerbe EnglezaMariusNo ratings yet
- Have Some or Any WorksheetDocument10 pagesHave Some or Any WorksheetNawsaypo HtooNo ratings yet
- Trabajo InglesDocument16 pagesTrabajo InglesRodrigo CapillaNo ratings yet
- Deberes de InglesDocument9 pagesDeberes de Inglesgemy loorNo ratings yet
- Verb to be conjugationsDocument1 pageVerb to be conjugationsAdrianaNo ratings yet
- RECAP Tenses Review Les Temps CONJUGAISONDocument12 pagesRECAP Tenses Review Les Temps CONJUGAISONSDubNo ratings yet
- Língua Inglesa Aula Verb To Be Conjugação - AutomaçãoDocument10 pagesLíngua Inglesa Aula Verb To Be Conjugação - AutomaçãoDarlan Henrique100% (1)
- Verbs in English LanguageDocument16 pagesVerbs in English LanguageStanilaEmilNo ratings yet
- Verbs in English LanguageDocument17 pagesVerbs in English LanguageGabriel PlugaruNo ratings yet
- Does your brother used to come by usDocument1 pageDoes your brother used to come by ussimfora29No ratings yet
- Military Grammar WorkbookDocument16 pagesMilitary Grammar WorkbookInfernoBogdan ™No ratings yet
- English 6 q4 Module 4 1Document12 pagesEnglish 6 q4 Module 4 1minminlubay13No ratings yet
- PR2 Module 5 Research TitleDocument9 pagesPR2 Module 5 Research TitleRubylhyn Medalla100% (1)
- Fill in Verb Forms ExerciseDocument2 pagesFill in Verb Forms ExerciseHanadiaYuristaNo ratings yet
- Engaging English lessons for elementary studentsDocument6 pagesEngaging English lessons for elementary studentsPauline Erika CagampangNo ratings yet
- Skill 1-48Document45 pagesSkill 1-48Yoga AuliaNo ratings yet
- Answer: (1) A. Attitude MarkerDocument2 pagesAnswer: (1) A. Attitude MarkerKpop ChannelNo ratings yet
- The Normal Rule Is To Add-Ed.: 6.1 Past Simple - Spelling of Regular VerbsDocument6 pagesThe Normal Rule Is To Add-Ed.: 6.1 Past Simple - Spelling of Regular VerbsIsmael VazquezNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Examples from EnglishClubDocument1 pageParts of Speech Examples from EnglishClubStylishPower KingNo ratings yet
- Lexical Gaps: Defining and Illustrating Different TypesDocument10 pagesLexical Gaps: Defining and Illustrating Different Typesnour assiNo ratings yet
- 6 Easy Ways To Write Complex Sentences in IELTS Task 2Document8 pages6 Easy Ways To Write Complex Sentences in IELTS Task 2Raman KumarNo ratings yet
- SYNTAX AnalyzerDocument29 pagesSYNTAX Analyzeripo ipoNo ratings yet
- 11 Face2face Starter Students Book 11Document2 pages11 Face2face Starter Students Book 11Tika VirginiyaNo ratings yet
- FLIPPED TASK # 2.2P - Week 10 - Unit 8B - Shopping, Reporting Verbs, and Verb PatternsDocument7 pagesFLIPPED TASK # 2.2P - Week 10 - Unit 8B - Shopping, Reporting Verbs, and Verb PatternsMerly IbarraNo ratings yet
- Hull HouseDocument2 pagesHull HouseJeanie Wangsa100% (6)
- Punctuation Revisited - A Strategic Guide For Academics Wordsmiths and Obsessive PerfectionistsDocument155 pagesPunctuation Revisited - A Strategic Guide For Academics Wordsmiths and Obsessive Perfectionistsrenjithkr01100% (2)
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument10 pagesGrammar Translation MethodNilufar AbduvaliyevaNo ratings yet
- Simple tENSES OF VERBSDocument4 pagesSimple tENSES OF VERBSChinley FabrigaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of LanguageDocument2 pagesThe Nature of LanguageLanz NicoleiNo ratings yet
- IF-SENTENCES: ZERO TO THIRD CONDITIONALSDocument7 pagesIF-SENTENCES: ZERO TO THIRD CONDITIONALSarmindoNo ratings yet
- Handout I CasDocument1 pageHandout I Casdacho26No ratings yet
- What Is a Determiner? Types and ExamplesDocument6 pagesWhat Is a Determiner? Types and ExamplesAdelina Elena GhiuţăNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FIVE - ADocument14 pagesCHAPTER FIVE - AAgustina CanonicaNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Lesson 1. Masculino o FemeninoDocument4 pagesLevel 1 Lesson 1. Masculino o FemeninoSpanishlessonswMartaNo ratings yet
- AffixationDocument7 pagesAffixationRandy AgustianNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Second Half TestDocument2 pages9th Class Second Half TestAli UsmanNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares en Inglés - BristoleñDocument8 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares en Inglés - BristoleñCarlos PeraltaNo ratings yet