Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE-465 Exercise 5
Uploaded by
Marko PetkovićCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE-465 Exercise 5
Uploaded by
Marko PetkovićCopyright:
Available Formats
EE-465 INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS I
S. Milovanovi, M. Petkovi
5. Space vector modulation for three-phase inverter
1 INTRODUCTION
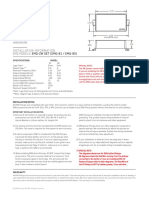
A three-phase 2L inverter is connected to the 3ph grid (400 V, 50 Hz) through a RL lter. By appropriately setting the phase and
magnitude of the voltage synthesized by the inverter, the power exchange with the AC grid can be modied or set.
IDC
VDC /2 Rg Lg i vga
a
vab ib vCM
O O
vbc vca ic N
va
VDC /2 vb vgc
Fig. 1 PV system output stage. The vc
input stage has been replaced by an
equivalent voltage source.
2 TASKS DESCRIPTION
1. Create a space vector PWM (SV-PWM) block following the implementation steps presented during the lecture according to
the following steps/subsystems:
(a) Determine the magnitude (M) of the reference space vector (given in the frame)
(b) Determine the angle () of the reference space vector
(c) Determine the sector (s) where the reference space vector is
(d) Calculate the duty-cycles () for the active and zero space vectors
(e) Assemble the switching pattern for odd and even sectors (cf. slide 22)
(f) Send the PWM signals out (sw)
2. As in the previous week determine the DC link voltage needed. Compare SV-PWM with CB-PWM with min/max common mode
injection for S = 3.5 kVA and = 3/4 in time and frequency domain. Whats the magnitude and angle of the converter
modulation index? Whats the magnitude of the fundamental of the grid current? Please add an initial condition to Lg in order
to get rid of the initial transient.
Tab. 1 Parameters set. Vg 400 Vl-l,rms fg 50 Hz
fsw 10 kHz Lg 10 mH Rg 20 m
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicsRahul Yadav100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Prevention of Accident and Safety Provision - 4thunit - PrintDocument7 pagesPrevention of Accident and Safety Provision - 4thunit - Printthilaga2009No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Gek 45375JDocument42 pagesGek 45375JBolivar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Brüel&Kjær 2607 - Measuring Amplifier - Instruction ManualDocument72 pagesBrüel&Kjær 2607 - Measuring Amplifier - Instruction ManualViktor DömeNo ratings yet
- Adf (Draft)Document15 pagesAdf (Draft)vanmorrison69100% (1)
- Henikwon Brochure 2Document23 pagesHenikwon Brochure 2Majho CanilangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 MPCDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 MPCMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- 7 robustMPCDocument57 pages7 robustMPCMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- 10 SplittingDocument59 pages10 SplittingMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- DQ TransformationDocument51 pagesDQ TransformationAili LuggymixNo ratings yet
- MPC Exercise 3 ReportDocument3 pagesMPC Exercise 3 ReportMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- EnStorage ScapsDocument43 pagesEnStorage ScapsMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- Report HVDocument8 pagesReport HVMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- PID Handout 2014Document3 pagesPID Handout 2014Marko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- Calibration of The Torquemeter (Getis)Document2 pagesCalibration of The Torquemeter (Getis)Marko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Lab BookDocument5 pagesSynchronous Machine Lab BookMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Epitaxial: ApplicationDocument6 pagesSilicon NPN Epitaxial: ApplicationDilJalaayNo ratings yet
- Zakk Wylde Set InstallationDocument4 pagesZakk Wylde Set Installationjohnsonaria22No ratings yet
- 9400TP Manual PDFDocument30 pages9400TP Manual PDFGilmar RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Build A Program Remote Control IR Transmitter Using HT6221Document2 pagesBuild A Program Remote Control IR Transmitter Using HT6221rudraNo ratings yet
- Mains Interruption Counter With Indicator Circuit DiagramDocument6 pagesMains Interruption Counter With Indicator Circuit DiagramSelvy SalfitriNo ratings yet
- Prospects of Wind Energy in Nigeria: # Ogbonnaya I.Okoro E. Chikuni P. GovenderDocument6 pagesProspects of Wind Energy in Nigeria: # Ogbonnaya I.Okoro E. Chikuni P. GovenderfumscoNo ratings yet
- EFSPL-1 ManualDocument7 pagesEFSPL-1 ManualALCALAB EL EQUIP TESTINGNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica MG 5000Document1 pageFicha Tecnica MG 5000mazzingerzNo ratings yet
- A Spin Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Using Half-Metallic-Ferromagnet Contacts For The Source and DrainDocument4 pagesA Spin Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Using Half-Metallic-Ferromagnet Contacts For The Source and DrainQueary OnlyNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For GFM-400Z Battery: Specifications Discharging Characteristics Curves (25 C)Document1 pageDatasheet For GFM-400Z Battery: Specifications Discharging Characteristics Curves (25 C)UCTT BLU MONo ratings yet
- v90 Operating InstructionsDocument349 pagesv90 Operating InstructionsTodor NakovNo ratings yet
- Windy Boy 5000A / 6000ADocument4 pagesWindy Boy 5000A / 6000ARomão OliveiraNo ratings yet
- AN4993Document10 pagesAN4993iskandarn_el5735No ratings yet
- FFT Based Differential Protection For Power Transformers: Suribabu & Sanker RamDocument14 pagesFFT Based Differential Protection For Power Transformers: Suribabu & Sanker RamTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- PC44 Pattern Control: Part 108 099DDocument164 pagesPC44 Pattern Control: Part 108 099DdannysionNo ratings yet
- ID-DCU-Marine DatasheetDocument4 pagesID-DCU-Marine DatasheetMaylen RivasNo ratings yet
- Antique Electronic Supply CatalogDocument156 pagesAntique Electronic Supply CatalogDaniele Greco50% (2)
- Allen & O'Brien - Electrical Resources - Conversion Tables - Reference Charts - Mathematical FormulaeDocument5 pagesAllen & O'Brien - Electrical Resources - Conversion Tables - Reference Charts - Mathematical Formulaeduuk73No ratings yet
- Chapter Four Basic Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDocument11 pagesChapter Four Basic Nodal and Mesh AnalysisTaufiqurrahman MczNo ratings yet
- GE Portascan Portable Bladder Scanner - Service ManualDocument18 pagesGE Portascan Portable Bladder Scanner - Service ManualHarold MartinezNo ratings yet
- AN2508 Digital Pulse Height AnalyserDocument10 pagesAN2508 Digital Pulse Height AnalyserAli ShaebaniNo ratings yet
- Design-Sm15 1Document4 pagesDesign-Sm15 1Ciro De SouzaNo ratings yet
- Solution: Given That, Supply Voltage, V: Fse LDocument20 pagesSolution: Given That, Supply Voltage, V: Fse LDeepak Gehlot100% (1)