Professional Documents
Culture Documents
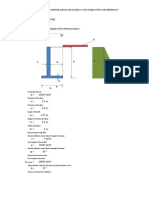
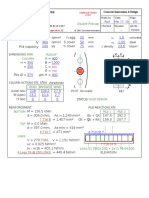
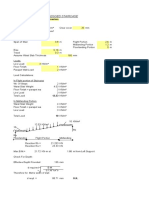
Soil Nailing
Uploaded by
Manash Protim Gogoi100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
90 views12 pagessoil
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsoil
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
90 views12 pagesSoil Nailing
Uploaded by
Manash Protim Gogoisoil
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Testing on Soil Nails
In the whole soil nail construction process, the
following tests must be carried out for quality
assurance.
Soil nail steel bar Tensile test, bending test, re-
bend test, galvanizing test.
Cement Grout Bleeding test, flow cone test,
compressive strength test.
SOIL NAIL STEEL BAR TEST
The soil nail steel bar is the most
essential element of soil nail system
and withstands tension, bending and
shear force in soil mass. Therefore, all
ranges of testing are needed to be
carried out before soil nail installation.
Tensile test, Bending test, Re-bend test,
Galvanizing test
Tensile Test
Tensile strength, yield stress and elongation are
given out in these tests.
According to Hong Kong Construction Standard 2
(1995), the tensile stress shall be at least 10%
greater than the actual yield stress measured in
tensile test.
The acceptable elongation shall not be over 12%
of 5 times the diameter of test piece in high stress
steel bar. (CEDD CS2, 1995)*
Civil Engineering and Development Department (CEDD), GEOTECHNICAL
ENGINEERING OFFICE .(1995). Construction Specification 2 ,Hong Kong.
BENDING TEST
This is the test for bending of a steel bar to meet the
bending requirements.
According to CEDD CS2 (1995) noted that the test
piece shall withstand being bent through 180
degrees around a former of a specific diameter.
The test specimens shall satisfy the requirement
which states that no sign of cracks on visual
examination are evident.
Re-bend Test
This test is for bending in opposite direction after
same process of bending test and acceptable
require the test specimens shall not break into two
pieces.
Galvanizing Test
This is the measure of the content of galvanized
material which has been painted or spread on the
steel bar (CEDD CS2, 1995). The galvanized material
can prevent the corrosion of the steel bar which may
be caused by ground water or saturated soil.
Cement Grout
O Cement grout is the surrounding material of
the soil nail which can protect the steel bar
against ground water and transfer the
frictional force from soil to steel bar.
Therefore, cement grout quality concrete is
essential.
O Bleeding test, Flow cone test, Compressive
strength test
Bleeding Test
This is the measure of water bleeding from cement grout.
According to CEDD CS2 (1992) & Australian Standard R64
mentioned that bleeding shall not exceed 1% of volume
at 60 minutes after mixing when measured at 20C
temperature in a covered 100mm diameter cylinder.
The bleeding rate is dependent on the humidity and
temperature. Therefore, a 20C constant temperature and
covered cylinder are necessary for this test. Moreover,
vibration should be avoided during the period of test.
Flow Cone Test
According to ASTM C939 (2002)
noted that this test is used to
determine the fluidity, or
viscosity, of the grout.
The fluidity is an indication of how
well the grout mix will flow when it is
pumped into the grout tube.
According to CEDD GS vol2 (1995),
the grout mix should pass
through this flow cone in at
least 15 seconds but should not
exceed 30 second.
If the grout mix that is too thick or
too viscous it may not be able to
pushed through the length of the
tendon, and if the grout mix that is
too thin it means the grout may
contain too much water and affect
the water/cement ratio.
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH TEST
Through the compressive strength test, the specimen sample
of cement grout can provide an indication of compressive
strength of material which provides an indication of the
mechanical and durability properties, in order to meet the soil
nail grout requirement. The specimen sample can be a 100 mm
sided square cube or 100 mm dia and 250 mm long
cylinder.
According to CEDD General Specification vol 2 (1992) and
AS R64 (2007)six samples are required for square cube samples
and three for cylindrical samples.
The compressive strength is calculated from the failure load
divided by cross-sectional area resisting the load and
reported in force per unit area.
SYLLABUS FOR MID SEMESTER
Length and cross-sectional area of reinforcing strip.
Applications of soil nailing.
Advantages of soil nailing.
Limitations of soil nailing.
Construction method of soil nails.
Components of the soil nails.
Soil nail construction equipment.
Soil nail construction procedure.
Testing on soil nails.
You might also like
- Tuned Liquid DampersDocument13 pagesTuned Liquid DampersMahaveer JanapalaNo ratings yet
- StormmgmtDocument22 pagesStormmgmtAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- DigiTech SDRUM Quick Start GuideDocument2 pagesDigiTech SDRUM Quick Start GuideOlivier CourantNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisDocument7 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisnhulugallaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Wind Turbine Design Analysis-A Twenty Year Progress ReviewDocument20 pagesThe Evolution of Wind Turbine Design Analysis-A Twenty Year Progress ReviewendoparasiteNo ratings yet
- Constant HeadDocument14 pagesConstant HeadmlakkissNo ratings yet
- Design of Long Span Exhibition Hall of Steel StructureDocument5 pagesDesign of Long Span Exhibition Hall of Steel StructureInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Moment FrameDocument16 pagesMoment FrameSanchithaNo ratings yet
- Clotan Steel - Purlin Span LengthsDocument3 pagesClotan Steel - Purlin Span LengthsColin SillmanNo ratings yet
- Speedy ConstructionDocument57 pagesSpeedy Constructionritika bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Canopy Report 07Document7 pagesCanopy Report 07Neha DasNo ratings yet
- Point Load TestDocument4 pagesPoint Load Testkiko auNo ratings yet
- Bolts Screws Hex Hexagon Nuts Washers Threaded Rods Din 933 934 7989 125 127 4034 975 555 IsoDocument43 pagesBolts Screws Hex Hexagon Nuts Washers Threaded Rods Din 933 934 7989 125 127 4034 975 555 IsoAli FikarNo ratings yet
- 3 Pilecap DesignDocument2 pages3 Pilecap DesignNyu123456No ratings yet
- Thesis On MLT and PDA TestDocument77 pagesThesis On MLT and PDA TestBMZNo ratings yet
- Lotsafee House: Bigbucks PLC Pilecap G14Document53 pagesLotsafee House: Bigbucks PLC Pilecap G14Nicholas ThompsonNo ratings yet
- 2 - 4 Gutter and Downspout Sizing and LocationDocument5 pages2 - 4 Gutter and Downspout Sizing and LocationansepachecoNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Slender Columns: Lecture # 4ADocument33 pagesAnalysis and Design of Slender Columns: Lecture # 4Apk khanNo ratings yet
- 1000m3 Reservoir CalcsDocument10 pages1000m3 Reservoir CalcschrisNo ratings yet
- RCC14 Crack WidthDocument1 pageRCC14 Crack WidthKha Phuc100% (1)
- Wind Actions On Canopy RoofsDocument8 pagesWind Actions On Canopy RoofsnenmilNo ratings yet
- Digitech TrioPlus Manual 5064509-A OriginalDocument63 pagesDigitech TrioPlus Manual 5064509-A OriginalAnonymous IhzuOnLNo ratings yet
- Design Sump PumpDocument2 pagesDesign Sump PumpAbdullah MofarrahNo ratings yet
- Group Members:: Prepared For: Pro - Dr. Yasmin AshaariDocument56 pagesGroup Members:: Prepared For: Pro - Dr. Yasmin Ashaarisadam mohamedNo ratings yet
- Purlin DesignDocument3 pagesPurlin DesignKNB KNNo ratings yet
- Stair Case Design: Say, 180 MM 164 MMDocument3 pagesStair Case Design: Say, 180 MM 164 MMShashankSinghNo ratings yet
- Design For TorsionDocument4 pagesDesign For TorsionChhim RothyNo ratings yet
- CYPECAD - User's Manual PDFDocument141 pagesCYPECAD - User's Manual PDFBelak1No ratings yet
- Duo Pich Roof Closed Shed: Building Name:-Bearsand ApesDocument13 pagesDuo Pich Roof Closed Shed: Building Name:-Bearsand Apesadil_khan648No ratings yet
- CG 1 Anchor Block DesignDocument37 pagesCG 1 Anchor Block DesignGEOMAHESHNo ratings yet
- Dsign of Doglegged Staircase: Project: Worli QuartersDocument3 pagesDsign of Doglegged Staircase: Project: Worli Quartersd4891No ratings yet
- Construction of Marine and Offshore Structures, 3rd Edition - Page 276 PDFDocument1 pageConstruction of Marine and Offshore Structures, 3rd Edition - Page 276 PDFpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Types of Long Span TrussesDocument3 pagesTypes of Long Span TrussesPeter WhiteNo ratings yet
- Fluids - IIIDocument29 pagesFluids - IIINitin GandhareNo ratings yet
- Axial Load Column CapacityDocument3 pagesAxial Load Column Capacityaditya2053100% (1)
- Lecture Development of Reinforcement 24 November 2017Document40 pagesLecture Development of Reinforcement 24 November 2017valentina ayu100% (1)
- Silent PilerDocument5 pagesSilent PilerIkmal Ishak100% (1)
- Sewer Forced MainDocument32 pagesSewer Forced MainsachingadageNo ratings yet
- Drainage: Project BackgroundDocument9 pagesDrainage: Project BackgroundKwaku frimpongNo ratings yet
- Design of Sidewalls For Rain Water Tank-Case-1Document4 pagesDesign of Sidewalls For Rain Water Tank-Case-1Govendan GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Deep Beams FinalDocument13 pagesDeep Beams FinalNilesh Balkrishna Sunita ApteNo ratings yet
- BondekDocument52 pagesBondekTamilchelvam MurogayahNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - FoundationsDocument6 pagesLECTURE - FoundationsFazelah YakubNo ratings yet
- Harmer Drainage Price ListDocument144 pagesHarmer Drainage Price ListZuberYousufNo ratings yet
- Lateral-Torsional Buckling of Cold-Formed Zed-Purlins Partial-Laterally Restrained by Metal SheetingDocument11 pagesLateral-Torsional Buckling of Cold-Formed Zed-Purlins Partial-Laterally Restrained by Metal SheetingReaditReaditNo ratings yet
- How Fink Trusses WorkDocument4 pagesHow Fink Trusses WorkMansi PatelNo ratings yet
- Hinusdtan College of Science & Technology: ECE-064 Earthquake Resistant Design UNIT-5Document29 pagesHinusdtan College of Science & Technology: ECE-064 Earthquake Resistant Design UNIT-5Faraan KhanNo ratings yet
- 321 Sta R SP 001a Dam Stability - Main ReportDocument82 pages321 Sta R SP 001a Dam Stability - Main ReportnadraNo ratings yet
- LABC Typical Steel Beam SizesDocument1 pageLABC Typical Steel Beam SizesPetar ValevNo ratings yet
- Principle of PTDocument30 pagesPrinciple of PTJimmy ChungNo ratings yet
- Space Frame OptimisationDocument9 pagesSpace Frame OptimisationSreehari AshokNo ratings yet
- Pilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramDocument24 pagesPilegrp - Pile Group Analysis ProgramBabacar NIANGNo ratings yet
- Notes For Practical Construction Work (Civil) : Compiled By: Muhammad Imran ChaudharyDocument14 pagesNotes For Practical Construction Work (Civil) : Compiled By: Muhammad Imran ChaudharysarwarawNo ratings yet
- Tests of Self-Consolidating Concrete: ACI 237R-07Document53 pagesTests of Self-Consolidating Concrete: ACI 237R-07Ahmed GaziNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slump TestDocument4 pagesConcrete Slump TestyohanjNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slump Test: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesConcrete Slump Test: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJenny Ann ValderramaNo ratings yet
- CEB 711 - Structural Design II: Semester 2, 2020 2Document32 pagesCEB 711 - Structural Design II: Semester 2, 2020 2Asnil PrakashNo ratings yet
- Abrasion ResistanceDocument37 pagesAbrasion ResistanceNabeel WasimNo ratings yet
- TN 39 - Testing For Engineered Brick Masonry-Brick and Mortar - 2001 PDFDocument8 pagesTN 39 - Testing For Engineered Brick Masonry-Brick and Mortar - 2001 PDFAnonymous PjmE9RJcghNo ratings yet
- Tests On AggregatesDocument22 pagesTests On AggregatesMeg TNo ratings yet
- SCCJR Causes of CrimeDocument9 pagesSCCJR Causes of CrimejerinNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With OneDrive PDFDocument1 pageGetting Started With OneDrive PDFmegaNo ratings yet
- Criminal Behavior PDFDocument29 pagesCriminal Behavior PDFGohar Yaseen100% (2)
- Road Estimates SheetDocument11 pagesRoad Estimates SheetAmal PremachandranNo ratings yet
- SFD and BMDDocument18 pagesSFD and BMDManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Checklist For ExcavationDocument4 pagesChecklist For ExcavationMohaiminul Islam ShovonNo ratings yet
- Influence Line Chap.6Document71 pagesInfluence Line Chap.6Manash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Notice 05102015Document2 pagesNotice 05102015Manash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- 17 Paper SR Synchronisation Grid Tech 2015 FinalDocument11 pages17 Paper SR Synchronisation Grid Tech 2015 FinalManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- DetailDocument1 pageDetailManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- SOR Civil Works Assam PWD Schedule 2013 14Document2 pagesSOR Civil Works Assam PWD Schedule 2013 14Manash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- SOR Vol1 PrintDocument233 pagesSOR Vol1 Printranendra sarmaNo ratings yet
- AP Buildings SORDocument288 pagesAP Buildings SORgvramanaNo ratings yet
- Government of AssamDocument102 pagesGovernment of AssamManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- AMMOJM 2018 NoticeDocument1 pageAMMOJM 2018 NoticeManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- VIP MIL Structural Loads UFC 2004 PDFDocument62 pagesVIP MIL Structural Loads UFC 2004 PDFnimdew02No ratings yet
- SOR For Rural RoadsDocument189 pagesSOR For Rural RoadsDebajit ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- ISO CertificateDocument1 pageISO CertificateManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- EQTip 22Document2 pagesEQTip 22boubressNo ratings yet
- Bus Timing Nov17Document2 pagesBus Timing Nov17Manash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Transmission TowerDocument23 pagesAnalysis and Design of Transmission TowerIJMER100% (1)
- Commercial Egg Production GuideDocument46 pagesCommercial Egg Production GuideManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Tower Design: Bracing SystemsDocument49 pages7.4 Tower Design: Bracing SystemsBoisterous_Girl100% (1)
- Cause - Evaluation - Repair of Crack in ConcreteDocument9 pagesCause - Evaluation - Repair of Crack in Concretect_0011No ratings yet
- Tensile Strength in SoilDocument13 pagesTensile Strength in SoilManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Manash Protim Gogoi: ProfileDocument1 pageManash Protim Gogoi: ProfileManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- K K Chitkara - Construction Project ManagementDocument290 pagesK K Chitkara - Construction Project ManagementPrak Ba76% (21)
- Handling of Concrete PDFDocument89 pagesHandling of Concrete PDFManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Payment - Response of SSCDocument1 pagePayment - Response of SSCManash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- Powershift TransmissionDocument6 pagesPowershift TransmissionSuprastowo Bin SarinoNo ratings yet
- BET Surface Are MeasurementsDocument16 pagesBET Surface Are MeasurementsKwan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Glass Handbook 2010 English For Eastern Europe PDFDocument300 pagesGlass Handbook 2010 English For Eastern Europe PDFAnthony Thaddeus AntonioNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Capacity FractionatorsDocument26 pagesUltimate Capacity Fractionatorsrvkumar61No ratings yet
- Chung - 2010 - Confinement of Rectangular Reinforced Concrete ColDocument406 pagesChung - 2010 - Confinement of Rectangular Reinforced Concrete ColkbkshanakaNo ratings yet
- Avalanche PhotodiodeDocument5 pagesAvalanche PhotodiodeChiranth ErappaNo ratings yet
- Shock-Induced Collapse of A Gas Bubble in Shockwave LithotripsyDocument10 pagesShock-Induced Collapse of A Gas Bubble in Shockwave LithotripsyemadinscribdNo ratings yet
- MLDocument23 pagesMLSunil KNo ratings yet
- What Is Quantum Mechanics - Quantum Physics Defined, ExplainedDocument6 pagesWhat Is Quantum Mechanics - Quantum Physics Defined, ExplainedIsabel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic Loading-Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic LoadingDocument6 pagesComposite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic Loading-Composite Action of Ferrocement Slabs Under Static and Cyclic LoadingKarrar MonarchNo ratings yet
- Electric Iron Doe - PresentationDocument12 pagesElectric Iron Doe - Presentationapi-568978327No ratings yet
- Liftoff TechniquesDocument4 pagesLiftoff TechniquesSwarnava SanyalNo ratings yet
- Straub Flex 1L Coupling Data SheetDocument1 pageStraub Flex 1L Coupling Data SheetTrEnD SeT vicky rioNo ratings yet
- CabreraRyanM ES230-PS4Document7 pagesCabreraRyanM ES230-PS4Tim AcostaNo ratings yet
- Thermo QualsDocument26 pagesThermo QualsLuc LeNo ratings yet
- 1 Condition AssessmentDocument40 pages1 Condition AssessmentManideep DoddaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1.2 Beam Deflection: Preliminary Lab Calculations To Determine Beam Modulus of ElasticityDocument8 pagesActivity 2.1.2 Beam Deflection: Preliminary Lab Calculations To Determine Beam Modulus of ElasticityJulius PaganNo ratings yet
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1Document6 pages(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1Arhum AliNo ratings yet
- Pre Engineering Class Schedule 2023 24Document1 pagePre Engineering Class Schedule 2023 24abelendalew93No ratings yet
- Gaining Confidence With GD T - Part 2Document22 pagesGaining Confidence With GD T - Part 2Abraham ThomasNo ratings yet
- PotentiometryDocument48 pagesPotentiometryapi-19959578No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - A: F M M Multiphase FlowDocument44 pagesTopic 2 - A: F M M Multiphase FlowAnjo VasquezNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 1 - Electrochemistry SCI 401 - Chemistry For EngineersDocument14 pagesElectrochemistry: 1 - Electrochemistry SCI 401 - Chemistry For EngineersAMLU Law OfficesNo ratings yet
- Grinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainDocument8 pagesGrinding+uit 1-s2.0-S092401361500179X-mainMd MehtabNo ratings yet
- 115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDocument2 pages115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Keyada wangNo ratings yet
- Ps 00000 1165 0004 E - Rev 0 - Piping Material SpecificationDocument877 pagesPs 00000 1165 0004 E - Rev 0 - Piping Material SpecificationThirunavukkarasu ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument4 pagesAnswer SheetDanny Lanos100% (1)
- Inverted T BeamsDocument234 pagesInverted T BeamsAnna GNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Self Compqcting ConcreteDocument86 pagesProject Report On Self Compqcting Concreteassssad20000No ratings yet