Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biopharmaceutics
Uploaded by
Kaela LizadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biopharmaceutics
Uploaded by
Kaela LizadoCopyright:
Available Formats
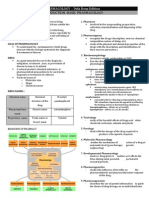
Biopharmaceutics: 1st Shifting GABs NOTES
Current drug interpretations are empirical BIOPHARMACEUTICS
PHARMACOGENOMICS
- Mapping out drug effects to individuals Area of study concerned with the formulation,
manufacture, stability and effectiveness of
PHYSICOCHEMICAL FACTORS pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Study of the factors (dosage form, formulation)
- Alter drug bioavailability influencing the bioavailability (in vivo, in vitro
- Particle size in solids dissolution testing) of a drug in man and animals
- Particle size in dispersed and the use of this information to optimize
- Tablet disintegration pharmaceutical or therapeutic activity of drug
- Tablet and capsule adjuncts products (vehicle) in clinical applications.
- Coatings Interrelationship of the physicochemical
- Crystalline drug properties properties (solubility, etc) of the drug, the dosage
form in which the drug is given, and the route of
Higher particle size = lower surface area covered administration on the rate and extent of drug
absorption (bioavailability in the systemic
PHARMACEUTICS: reducing particle size to increase circulation)
surface area Study of the relationship of the physicochemical
properties and in vitro behavior of the drug and
DISSOLUTION MEDIUM: penetrates para mas maging drug products on the delivery of the drug to the
bioavalaible body under normal conditions.
Examples of drug products that were reduced in particle size PHARMACOKINETICS drug movement in the body
and lead to higher dissolution
A process of how the body deals with the drug
1. Nitrofurantoin (macrocrystals) what your body does to your drug
- Modified in order to stay in the lumen
2. Spirinolactone PHARMACODYNAMICS - How drug changes your body
- Particles reduced to micro size (10^-6)
MICRONIZATION modern technique to A process of how your drug deals with your body.
reduce particle size what your drug does to your body
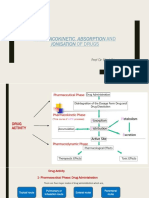
METHODS OF REDUCING PARTICLE SIZE: LADMER
- Trituration L biopharmaceutics
- Sieving (sieve # = higher means finer
squares) AD pharmacokinetics
- Micronization
- Sonication ME drug elimination (liver and kidney)
DISSOLUTION
Depends on intrinsic solubility PHARMACOKINETICS
Particle size is only a factor
Deals with the changes of drug concentration in a
EMULSIONS drug product inside the human or animal body
following administration
Oil in water
- Oil globules 500 mg IV bolus: 500 mg
- Oil + water + emulsifier
Water in oil 500 mg Tab PO: <500 mg metabolized in the liver before
- Water droplets reaching the systemic circulation : first-pass effect
*EFFECTS OF DOSAGE FORMS ON THERAPEUTIC After 2 hours, lesser some are excreted
SYSTEMS*
PHARMACODYNAMICS drug effect
Relationship between the drug concentration at
the site of action (Receptor- drug receptor
interaction may be good or bad) and
pharmacologic response including the biochemical Hepatic vein to inferior vena cava to heart
and physiologic effects that influence their then to the systemic circulation
interaction Bioavailable
Initiation of sequence of molecular events resulting DISTRIBUTION detour (on deposit sites or
in pharmacologic or toxic response storage) or to the target organ
o Deposit sites storage adipose,
Idiosyncracy- different effects to different people take muscles nerves, bones
effect, no effect, adverse effect. (DRUG TO GENES) peripheral tissues not the target
organ
- Difference in distribution different
affinity for tissue protein
DRUG PRODUCT - Can go back to systemic circulation from
the peripheral tissue when the drug in
Finished dosage form that contains an active the systemic circulation is eliminated.
ingredient, generally, but not necessarily, in
association with inactive ingredients (vehicle)
Formulation or matrix in which the drug is
contained
Term may also include a dosage form that does
not contain an active ingredient intended to be
used
o Placebo answers the question: if a
drug took effect by chance
DRUG DISPOSITION
Description of drug distribution and elimination
Tablet (oral)
No activity in esophagus
Disintegration in the stomach (liberation
/release)
Small intestine only accept the drug if its already
a solution
o Delay when not disintegrated)
o Absorption in the small intestine
Pass through a semi
permeable membrane
(involves diffusion) Ficks
Law of Diffusion
Should be lipid soluble,
nonionized, nonpolar, small
particle size fewer
absorption
Large surface area (villi), good
perfusion (good blood supply)
(should pass through veins)
Drain to portal vein
First-pass effect in the liver drug
metabolized before reaching the systemic
circulation
Deactivation efficacy may be reduced
(disadvantage)
Also known as first-pass metabolism or
presystemic elimination
Inactive (prodrug) active (ex. Aspirin,
prednisone methyl prednisolone)
Active parent (prolongs action of the drug in
the body) active metabolite (ex.
Diazepam oxazepam)
You might also like
- Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics: PCT400 (AY 2021-2022)Document7 pagesBiopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics: PCT400 (AY 2021-2022)Shaira MuksanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharma (Chapter 2 - Pharmaco & Pharmady)Document1 pageNursing Pharma (Chapter 2 - Pharmaco & Pharmady)Jemima GasconNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics: GSDMSFI - BS Pharmacy 3Document11 pagesBiopharmaceutics: GSDMSFI - BS Pharmacy 3Majeddah Aliudin TalambunganNo ratings yet
- Pharma MidtermDocument24 pagesPharma MidtermBethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Physicochemical Properties of The Drug Dosage Form Route of AdministrationDocument10 pagesPhysicochemical Properties of The Drug Dosage Form Route of AdministrationFfs AccsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsSyeda Eshaal JavaidNo ratings yet
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- PHBP Prelims - ReviewerDocument39 pagesPHBP Prelims - ReviewerAia RohaNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics Note 7th SemDocument38 pagesBiopharmaceutics Note 7th Semmj.vinoth@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Pharma TransDocument12 pagesPharma TransAesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- m2 Pharmacology Handout 8-25-21Document7 pagesm2 Pharmacology Handout 8-25-21Sheila May SantosNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument84 pagesPharmacology Handoutnanashimii100% (4)
- Fundamentals of Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsGopi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionDocument15 pagesPharmacokinetics 1: AbsorptionCecilia GrayebNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Pharma LecDocument11 pagesWeek 4 - Pharma LecJayla MarieNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument36 pagesPharmacokineticsRochelle RagoNo ratings yet
- Sources of New Drugs: Molecular Pharmacology Combinatorial SynthesisDocument14 pagesSources of New Drugs: Molecular Pharmacology Combinatorial SynthesisJasper JangNo ratings yet
- Pilapil PharmacologyDocument6 pagesPilapil PharmacologyIza FaboresNo ratings yet
- 4.1 BiopharmaceuticsDocument8 pages4.1 BiopharmaceuticsAzech Yam Ü100% (1)
- BioPharm Midterms ReviewerDocument26 pagesBioPharm Midterms ReviewerCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- FNP - Oral Medication NotesDocument23 pagesFNP - Oral Medication NotesOliver DiamaeNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document3 pagesPharma 2Trisha ApalisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Summary NotesDocument11 pagesPharmacology Summary Notesnurhana faudziNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction - Basic PharmacologyDocument4 pagesI. Introduction - Basic Pharmacologymdgayas70100% (2)
- Pharmacology (Intro-Drug Calculation)Document46 pagesPharmacology (Intro-Drug Calculation)May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology TrancesDocument27 pagesPharmacology TrancesMAZON, DHANYCIA XYREENNo ratings yet
- Clinical Veterinary PharmacologyDocument4 pagesClinical Veterinary PharmacologyLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Ladmer SystemDocument3 pagesLadmer Systemjihan febriyantiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Prelims ReviewerDocument21 pagesPharmacology Prelims ReviewerAntonette Africa MercadoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesPharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaVijungcoNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction - Basic Pharmacology PDFDocument4 pagesI. Introduction - Basic Pharmacology PDFdrrajbanerjeesdch88% (8)
- Trans 1 Medication Administration 1Document23 pagesTrans 1 Medication Administration 1Germin CesaNo ratings yet
- Melismichelle PharmacologyDocument2 pagesMelismichelle PharmacologyDr. Mariam AANo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsDocument31 pagesPharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsAli ElmehdawiNo ratings yet
- Conchem Q4 RevDocument15 pagesConchem Q4 RevReigne Daniella OgatisNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of PharmacologyDocument75 pagesBasic Principles of PharmacologyJessica Febrina Wuisan100% (1)
- Learning Packet in Level 1-NCM 106 NURSING PHARMACOLOGY: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Document15 pagesLearning Packet in Level 1-NCM 106 NURSING PHARMACOLOGY: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Nur Sanaani100% (1)
- Responses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseDocument4 pagesResponses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseThea GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Biofarmasetika Dan FarmakokinetikaDocument13 pagesBiofarmasetika Dan FarmakokinetikakhafifahNo ratings yet
- Lectura FX Cinética1Document7 pagesLectura FX Cinética1Jeraldiin BeltranNo ratings yet
- GRH - 1aph - 1Document9 pagesGRH - 1aph - 1Grace HernandezNo ratings yet
- NCM 106-CompDocument26 pagesNCM 106-Compprincess pantinopleNo ratings yet
- 1 PHA6120 IntroductionDocument86 pages1 PHA6120 Introductionchristian redotaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction Tophysical Pharmacy and Principles of Biopharmaceutics I. Physical PharmacyDocument13 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction Tophysical Pharmacy and Principles of Biopharmaceutics I. Physical PharmacyAi LoveeiNo ratings yet
- Basics of PharmacologyDocument33 pagesBasics of Pharmacologyshruti boseNo ratings yet
- Cc2lab TDM Part1Document3 pagesCc2lab TDM Part1Krisiah Anne HernandezNo ratings yet
- NCM 212 - Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument11 pagesNCM 212 - Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsLYRIZZA LEA BHEA DESIATANo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Principles Part 1Document43 pagesPharmacologic Principles Part 1studentme annNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanDocument6 pagesIntroduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanAmirah AnfNo ratings yet
- 1-Pharmacology. IntroductionpptxDocument59 pages1-Pharmacology. IntroductionpptxYoueel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MergedDocument18 pagesPharmacology MergedJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The LADMER SystemDocument4 pagesThe LADMER SystemCheryl ChiuNo ratings yet
- Review Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDocument6 pagesReview Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDela Cruz, Maria Roanne M.No ratings yet
- Pharma CompilationDocument113 pagesPharma CompilationGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- 3.bASIC Pharmacologic PrinciplesDocument2 pages3.bASIC Pharmacologic PrinciplesBenjie Balisi0% (1)
- Reviewer PharmaDocument5 pagesReviewer PharmaRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessJasmin AdoraNo ratings yet
- Essential Pharmacokinetics: A Primer for Pharmaceutical ScientistsFrom EverandEssential Pharmacokinetics: A Primer for Pharmaceutical ScientistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1Kaela LizadoNo ratings yet
- Guaifenesin Flemaxir Guaifenesin Flemaxir: Expectorant ExpectorantDocument1 pageGuaifenesin Flemaxir Guaifenesin Flemaxir: Expectorant ExpectorantKaela LizadoNo ratings yet
- FG Flow ChartDocument2 pagesFG Flow ChartKaela LizadoNo ratings yet
- First Shifting Practical #2Document6 pagesFirst Shifting Practical #2Kaela Lizado0% (1)
- Ranibizumab Vs BufazisumabDocument9 pagesRanibizumab Vs BufazisumabaditzNo ratings yet
- J MCQsDocument6 pagesJ MCQsF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Buy Codeine..........Document5 pagesBuy Codeine..........Shakilur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Contents and List of Drug Profiles in The Book Lay Person's Guide To MedicinesDocument5 pagesContents and List of Drug Profiles in The Book Lay Person's Guide To MedicinesS.Srinivasan ('Chinu'); Renu KhannaNo ratings yet
- Name Brand Names: International: SucralfateDocument10 pagesName Brand Names: International: Sucralfatenurul husnaNo ratings yet
- Biowaivers & BiosimilarsDocument11 pagesBiowaivers & BiosimilarsomicspublishinggroupNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures For Pharmaceutical Care Delivery in Health FacilitiesDocument7 pagesStandard Operating Procedures For Pharmaceutical Care Delivery in Health FacilitiesNhu0% (1)
- Stok Opname Tablet Di Apotek: NO. Nama Obat Principal Jumlah Stok EDDocument4 pagesStok Opname Tablet Di Apotek: NO. Nama Obat Principal Jumlah Stok EDAriza SetyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Perspective 1Document11 pagesPerspective 1Jesus is The LightNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Medicine Price List MPL Oncology November 2020Document13 pagesMedicine Price List MPL Oncology November 2020karar hussainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutics (And Pharmacokinetics)Document14 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceutics (And Pharmacokinetics)Kim MoranoNo ratings yet
- Simcyp PBPK V23 2024 Final v2Document5 pagesSimcyp PBPK V23 2024 Final v2backup.data.drive.03No ratings yet
- Analogue-Based Drug Discovery: Edited by Jdnos Fischer and C. Robin GanellinDocument12 pagesAnalogue-Based Drug Discovery: Edited by Jdnos Fischer and C. Robin GanellinronyNo ratings yet
- Zeway ReportDocument8 pagesZeway Reportbereket rikitaNo ratings yet
- Stock 18 Feb 20Document29 pagesStock 18 Feb 20alfath ramaNo ratings yet
- Pharma 4Document5 pagesPharma 4Uday kumarNo ratings yet
- Feb Recalls 3Document3 pagesFeb Recalls 3reethu mammenNo ratings yet
- European School of Medicinal Chemistry (XXXII Advanced Course of Medicinal Chemistry And"e. Duranti" National Seminar For PHD Students)Document3 pagesEuropean School of Medicinal Chemistry (XXXII Advanced Course of Medicinal Chemistry And"e. Duranti" National Seminar For PHD Students)Università degli Studi di Urbino Carlo BoNo ratings yet
- DOH DPRI As of July 2023Document42 pagesDOH DPRI As of July 2023Ronald Elnar100% (2)
- Regulatory Requirements For Product ApprovalDocument13 pagesRegulatory Requirements For Product Approval50KMKDIVYA RAJPALNo ratings yet
- List of Abbreviations Used in Medical Prescriptions - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesList of Abbreviations Used in Medical Prescriptions - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaffsdfsfdftrertNo ratings yet
- Codigo Cidigo de BarraDocument58 pagesCodigo Cidigo de BarraLuis Augusto Castro GNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae ToxicologyDocument6 pagesCurriculum Vitae Toxicologyvenkata gangadharNo ratings yet
- Daftar Permintaan Obat Bakti Sosial Bulan K3 Pltu Barru 2018Document2 pagesDaftar Permintaan Obat Bakti Sosial Bulan K3 Pltu Barru 2018Faradhillah Adi SuryadiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management PlanRoxanneGailBigcasGoleroNo ratings yet
- 0 1Document30 pages0 1iik abdulkholikNo ratings yet
- OBTL Dispensing 1 2022 23Document11 pagesOBTL Dispensing 1 2022 23Jaden GonzagaNo ratings yet
- What Is Route of Administration?Document4 pagesWhat Is Route of Administration?Quách Việt HoàngNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaDocument13 pagesModule 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaKelsey MacaraigNo ratings yet