Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spinal Cord Transection
Uploaded by
Isak Shatika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesThis document describes the effects of spinal cord injuries at different levels. It outlines that injuries above C4 can cause tetraplegia and loss of sensation, while injuries from C5-T2 affect the upper extremities. Injuries from T3-T10 paralyze the lower extremities while sparing the upper extremities. Injuries from L1-S2 cause paraplegia and loss of sensation below the level of injury. Conus medullaris injuries below S3 cause saddle anesthesia and urinary/defecation issues. Cauda equina injuries below L1 also cause paraplegia, urinary issues, and impotence. Spinal centers for urination are located at S
Original Description:
THANK YOU
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the effects of spinal cord injuries at different levels. It outlines that injuries above C4 can cause tetraplegia and loss of sensation, while injuries from C5-T2 affect the upper extremities. Injuries from T3-T10 paralyze the lower extremities while sparing the upper extremities. Injuries from L1-S2 cause paraplegia and loss of sensation below the level of injury. Conus medullaris injuries below S3 cause saddle anesthesia and urinary/defecation issues. Cauda equina injuries below L1 also cause paraplegia, urinary issues, and impotence. Spinal centers for urination are located at S
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesSpinal Cord Transection
Uploaded by
Isak ShatikaThis document describes the effects of spinal cord injuries at different levels. It outlines that injuries above C4 can cause tetraplegia and loss of sensation, while injuries from C5-T2 affect the upper extremities. Injuries from T3-T10 paralyze the lower extremities while sparing the upper extremities. Injuries from L1-S2 cause paraplegia and loss of sensation below the level of injury. Conus medullaris injuries below S3 cause saddle anesthesia and urinary/defecation issues. Cauda equina injuries below L1 also cause paraplegia, urinary issues, and impotence. Spinal centers for urination are located at S
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
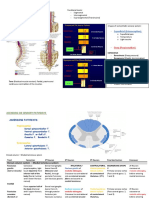
Spinal Cord
Complete transection Brown-Sequard
C1-C4 - Flaccid paralysis of diaphragm (dyspnea), radix of C4 -
-
Ipsilateral central paralysis
Ipsilateral deep sensation
- Central paralysis of extremities (tetraplegia) - Urination normal
- Loss of all kinds of sensation
- Central (suprasegmental) disturbances of urination
- Radicular pains in the neck to the nape
C5-T2 (zone of - Peripheral paralysis of upper extremities (peripheral Left part
innervation of
upper extremities)
paraplegia) - Ipsilateral peripheral of upper
- Central paralysis lower extremities (central paraplegia) extremities
- Loss of all kinds of sensation below level of lesions
- Ipsilateral central paralysis of
E.g. cervical lower extremities
spondyulosis - Central (suprasegmental) disturbance of urination.
- Ipsilateral deep sensation
- Radicular pains irradiating in upper extremities.
- Contralateral superficial sensation
(radiculopathy)
- Horners syndrome
- Urination normal
T3-T10 - Upper extremities are unaffected Right side
- Central paralysis of lower extremities (paraplegia)
- Upper extremities normal
- Loss of all kinds of sensation below level of lesions
- Ipsilateral central paralysis of leg
- Central (suprasegmental) disturbance of urination, usually
- Ipsilateral deep sensation
acute urinary retention - Contralateral superficial sensation
- Radicular pains have surrounding character. - Urination normal
L1-S2 (zone of - Peripheral paralysis of lower extremities (paraplegia) Left side
innervation of
lower extremities) - Loss of all kind sensation below level of lesions and in
- Ipsilateral peripheral paralysis
perineum - Urination normal
- Central (suprasegmental) disturbance of urination - Ipsilateral deep sensation
- Contralateral superficial sensation
Conus medullaris
(S3-S5)
- Paralyses are absent
- Loss of sensation in the field of a perineum (saddle- -
e.g. tumor, anesthesia)
ischemia, lumbar
disc herniation
- Peripheral (segmental) disturbances of urination
- Impotence and loss of anal reflex
Cauda equine
(involve fibers of
- Peripheral paralysis of the lower extremities (paraplegia)
L1,L2 and below) - Loss of all type of sensation on the lower extremities and in
a perineum -
- Peripheral (segmental) disturbances of urination
- Impotence and loss of anal reflex
- Severe radicular onychalgias (bladder pain worsen by
coughibg or sneezing)
- In lower cauda equine lesions (pseudo-conducting):
No paralysis of extremities
Saddle anesthesia
Urination, defecation and sexual dysfunction
5 variants of urination
disturbances
- Centrum vesicospinale and anospinale: located at level S3-S5 in grey substance the spinal centers of urination and defecation
- Their automatic reflex activity in normal adult is regulated to certain extent by cortex of brain via lateral columns (bilateral control, in frontal lobe). In unilateral lesion of
lateral column, communications with cortex are preserved, and disturbances of urination and defecation are not observed.
- 2 main groups
1. Suprasegmental (cental) disturbances
a. Incontinentio intermittens (periodic): Cortical regulation of urination is absent automatic reflex type of urination (independent activity of the spinal centers).
Usually observed in children.
b. Imperative incontinence
c. Urinary retention (retention urinae): marked in first few days of complete trasection of spinal cord when process develops acutely (trauma, inflammation) and
later is replaced by periodic incontinence.
2. Segmental (peripheral) disturbances
a. Incontinentio vera (true incontinence): typical in conus medullaris lesions. Urine is continuously allocated on drops in process of its entering into bladder, not
collecting in the bladder.
b. Ischuria paradoxa: hypertonicity of neck of the bladder remains cause resistance to pressure of urine and urine start to collect in bladder leads to over flown of
bladder urine is allocated on drops
You might also like
- Neuro Test Forebrain Mid-Caudal Brainstem Cerebellar C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 LMN BehaviourDocument2 pagesNeuro Test Forebrain Mid-Caudal Brainstem Cerebellar C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 LMN BehaviourZhi Ning CNo ratings yet
- Neurorehabilitation 1Document439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1Duncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- Medulla SyndromesDocument7 pagesMedulla Syndromesdisha1990No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy ClinicalsDocument9 pagesNeuroanatomy ClinicalsMuhammad Nabeel AbbasNo ratings yet
- Neurology in TableDocument93 pagesNeurology in TableHassan Bani SaeidNo ratings yet
- Umnl & LMNLDocument13 pagesUmnl & LMNLTammy BoudNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument5 pagesNeuroscienceChing MacarubboNo ratings yet
- Localisation in NeurologyDocument19 pagesLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Localisation in NeurologyDocument19 pagesLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Bns 1 SGD - Case Integration Case 2Document6 pagesBns 1 SGD - Case Integration Case 2KARL JUSTIN ANGNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex Cerebral CortexDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex Cerebral CortexMORGAN LAMBERTNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Thyroid GlandShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument30 pagesHemiplegiasarguss14100% (1)
- Lecture 37-Diseases of The Spine and Spinal Cord-Dr. Yudiyanta, SP.S (K) (2018)Document44 pagesLecture 37-Diseases of The Spine and Spinal Cord-Dr. Yudiyanta, SP.S (K) (2018)Chairul AmriNo ratings yet
- 1 Approach To A Neurologic DiagnosisDocument3 pages1 Approach To A Neurologic DiagnosisPatricia Anne ReyesNo ratings yet
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFDocument24 pages09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- WK 6 Entrapment Syndromes of The Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesWK 6 Entrapment Syndromes of The Upper Extremityapi-479720222100% (1)
- Injury NotesDocument15 pagesInjury NotesJaden MusclowNo ratings yet
- Tabla Brain SignsDocument4 pagesTabla Brain SignsAres Burballa TàrregaNo ratings yet
- Reda Note AnatomyDocument177 pagesReda Note Anatomymrcsexam.iranNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument33 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis DysarthriaDocument1 pageDifferential Diagnosis DysarthriaShruti KumarNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex Cerebral CortexDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex Cerebral CortexJ NNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 23 - Umn - LMN-2019Document30 pages23 - Umn - LMN-2019sara khanNo ratings yet
- Where Da Lesion atDocument5 pagesWhere Da Lesion atDeeWallyNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy TractsDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy TractsLola PNo ratings yet
- Vascular Disturbances (Module C) Cerebrovascular Accident (Cva)Document3 pagesVascular Disturbances (Module C) Cerebrovascular Accident (Cva)RosmaryNo ratings yet
- Res 113Document197 pagesRes 113Belinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- Localization of Motor 肖 (1) -for studentDocument41 pagesLocalization of Motor 肖 (1) -for studentmirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- QuizletDocument37 pagesQuizletnaimNo ratings yet
- Hacks Final FormattedDocument183 pagesHacks Final Formattedbhoj RAJNo ratings yet
- Potassium (K) 3.5 - 5.0 Meq/L (3.5 - 5.0 Mmol/L) : Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaDocument5 pagesPotassium (K) 3.5 - 5.0 Meq/L (3.5 - 5.0 Mmol/L) : Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaHenric CasimiroNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument27 pagesStrokeJASON KO CHIA SHENGNo ratings yet
- Frog AtlasDocument16 pagesFrog AtlasJAYHANNE PSYCHE MONDIANo ratings yet
- Paralysis in Dogs and CatsDocument56 pagesParalysis in Dogs and Catscat clinic pdhbNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord DiseaseDocument77 pagesSpinal Cord Diseasemirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- CN Summary FinalDocument2 pagesCN Summary FinalNur NajminaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: Afferents and EfferentsDocument4 pagesCranial Nerves: Afferents and Efferentsmay_74846422No ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document3 pagesChapter 36Samantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Tachdjian's Pediatric Orthopaedics v.4Document660 pagesTachdjian's Pediatric Orthopaedics v.4Leonardo Garay QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes: Hemiparesis (Faciobrachiocrural Weakness)Document7 pagesStroke Syndromes: Hemiparesis (Faciobrachiocrural Weakness)eko aNo ratings yet
- Common Conditions of The Lumbar SpineDocument4 pagesCommon Conditions of The Lumbar SpineJames KNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Cad Question TablesDocument4 pagesWeek 6 Cad Question Tablesapi-479499469No ratings yet
- Neuropati Jepitan (Entrapment Neuropathy)Document38 pagesNeuropati Jepitan (Entrapment Neuropathy)Lukman HakimNo ratings yet
- Localization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020Document49 pagesLocalization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Paediatric PEDocument2 pagesPaediatric PEAzizi RafieNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb NeuroDocument2 pagesLower Limb Neuroquojo041No ratings yet
- Neurological HX TakingDocument3 pagesNeurological HX Takingbloo tomartoNo ratings yet
- MoinaDocument43 pagesMoinaMoo MinNo ratings yet
- LMN Disease - DiagnosisDocument6 pagesLMN Disease - DiagnosisIqi Siti RizkiahNo ratings yet
- Paraplegia-Types, Causes and DiagnosisDocument59 pagesParaplegia-Types, Causes and Diagnosiskashmala afzalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex and Speech NajeebDocument27 pagesCerebral Cortex and Speech NajeebchawkatNo ratings yet
- Acute Focal Neurological SignsDocument27 pagesAcute Focal Neurological SignsKayman SpartanNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Saraf Di Lower LimbDocument1 pageKelainan Saraf Di Lower Limbyulia margarethNo ratings yet
- CerebullamDocument2 pagesCerebullamMahmoud Abu MayalehNo ratings yet
- Test - 20 Dental ImplantsDocument5 pagesTest - 20 Dental ImplantsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 4 Intensive Therapy of Somatic Complicaton. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Document6 pagesTest - 4 Intensive Therapy of Somatic Complicaton. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 18 Specific Diseases - Actinomycosis, TB, Syphilis, HIVDocument4 pagesTest - 18 Specific Diseases - Actinomycosis, TB, Syphilis, HIVIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 14 Diseases of The TMJ PDFDocument4 pagesTest - 14 Diseases of The TMJ PDFIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- CV Example - 2019 Issak1Document3 pagesCV Example - 2019 Issak1Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 8 Retension, Dystopia, PericoronitisDocument5 pagesTest - 8 Retension, Dystopia, PericoronitisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 12 Odontogenic Maxillary SinusitisDocument5 pagesTest - 12 Odontogenic Maxillary SinusitisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Schedule Classes 5th Years 1st SemesterDocument1 pageSchedule Classes 5th Years 1st SemesterIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 6 Methods of Extractions (Tooth Removal)Document4 pagesTest - 6 Methods of Extractions (Tooth Removal)Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 9 Chronic PeriodontitisDocument5 pagesTest - 9 Chronic PeriodontitisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning: Major Infectious Causes of Acute DiarrheaDocument7 pagesFood Poisoning: Major Infectious Causes of Acute DiarrheaIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 13 Odontogenic Osteomyelitis of The Jaws, Furuncles, Carbuncles, ErysipelasDocument5 pagesTest - 13 Odontogenic Osteomyelitis of The Jaws, Furuncles, Carbuncles, ErysipelasIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Test - 10 Root (Radicular) CystsDocument5 pagesTest - 10 Root (Radicular) CystsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- TularemiaDocument5 pagesTularemiaIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Schedule Classes 4th Years Ist SemesterDocument1 pageSchedule Classes 4th Years Ist SemesterIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Salmon Ellos IsDocument5 pagesSalmon Ellos IsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Medicine Study Notes PDFDocument764 pagesUndergraduate Medicine Study Notes PDFSHAKEEL1991No ratings yet
- Lecture: Erysipelas: Basic Clinical PrinciplesDocument15 pagesLecture: Erysipelas: Basic Clinical PrinciplesIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis (Part II)Document10 pagesViral Hepatitis (Part II)Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Yersiniosis: Yersinia Pathogenic Kinds and VariantsDocument7 pagesYersiniosis: Yersinia Pathogenic Kinds and VariantsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Cases InfectiousDocument20 pagesCases InfectiousIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Short Table of Infectious DiseasesDocument9 pagesShort Table of Infectious DiseasesIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- 2.5. The Identification Of Мвт Drug Resistance: Tuberculosis Course for English-speaking studentsDocument9 pages2.5. The Identification Of Мвт Drug Resistance: Tuberculosis Course for English-speaking studentsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Clinical Forms of Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis Course For English-Speaking StudentsDocument20 pagesChapter 3. Clinical Forms of Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis Course For English-Speaking StudentsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Cases InfectiousDocument20 pagesCases InfectiousIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Clinical Forms of Tuberculosis 3.1. Tubercular IntoxicationDocument14 pagesChapter 3. Clinical Forms of Tuberculosis 3.1. Tubercular IntoxicationIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument10 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- 00 0 Etio All 2014 - 1 PDFDocument88 pages00 0 Etio All 2014 - 1 PDFIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesNoella Marie BaronNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationDocument2 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationShalyn ArimaoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Lungnila Elizabeth School of Social Work, Senapati, Manipur August 2016-June 2018Document4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Lungnila Elizabeth School of Social Work, Senapati, Manipur August 2016-June 2018Deuel khualNo ratings yet
- Constitution & By-LawsDocument15 pagesConstitution & By-LawsMichael C. AndradeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringDocument32 pagesAdvanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringZhang ChaodongNo ratings yet
- Don'T Forget To Edit: Input Data Sheet For E-Class RecordDocument12 pagesDon'T Forget To Edit: Input Data Sheet For E-Class RecordCherry Lyn BelgiraNo ratings yet
- Spotify Strategig Possining and Product Life Cycle Four Basic Stages.Document5 pagesSpotify Strategig Possining and Product Life Cycle Four Basic Stages.Jorge YeshayahuNo ratings yet
- Creativity and AestheticDocument17 pagesCreativity and AestheticSyahirah Erahzs100% (1)
- Lab Exercise: 8Document5 pagesLab Exercise: 8Test UserNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Candelaria V RomeroDocument2 pagesHeirs of Candelaria V Romeromoniquehadjirul100% (1)
- 10 Applications in Engineering Mechanics PDFDocument10 pages10 Applications in Engineering Mechanics PDFWolf Lord100% (1)
- Cranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaDocument3 pagesCranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaSlavica JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Democracy in SomalilandDocument118 pagesDemocracy in SomalilandAbdirahman IsmailNo ratings yet
- Whats New PDFDocument74 pagesWhats New PDFDe Raghu Veer KNo ratings yet
- Filters SlideDocument17 pagesFilters SlideEmmanuel OkoroNo ratings yet
- Icivics MontesquieuDocument3 pagesIcivics Montesquieuapi-32806152578% (9)
- Time UntimeDocument10 pagesTime UntimeMacmillan Publishers11% (27)
- Kalki ProjectDocument3 pagesKalki ProjectMandar SohoniNo ratings yet
- The Prodigious MuseDocument466 pagesThe Prodigious Musesleepyninjitsu100% (1)
- New Memories by Ansdrela - EnglishDocument47 pagesNew Memories by Ansdrela - EnglishB bNo ratings yet
- HistogramDocument7 pagesHistogramTesfaye MinaleNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesMuhammad AdibNo ratings yet
- Slides - Simple Linear RegressionDocument35 pagesSlides - Simple Linear RegressionJarir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Class Program 2019 2020Document2 pagesClass Program 2019 2020Cristy Gongon100% (5)
- Adeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFDocument12 pagesAdeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFAngel SánchezNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar 2019-20 Odd Semester PDFDocument1 pageAcademic Calendar 2019-20 Odd Semester PDFPiyush ManwaniNo ratings yet
- CO - Config Sap Top JobsDocument81 pagesCO - Config Sap Top JobsAditya PakalaNo ratings yet
- A Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalDocument6 pagesA Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalJoko Cahyo BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Cri 192Document5 pagesCri 192Reyn CagmatNo ratings yet
- Alien Cicatrix II (Part 02 of 03) - The CloningDocument4 pagesAlien Cicatrix II (Part 02 of 03) - The CloningC.O.M.A research -stopalienabduction-No ratings yet