Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document
Uploaded by
Moira VilogCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document
Uploaded by
Moira VilogCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical growth study of correlation of organs and body growth pediatric anthropology
endocrinology nutrition and dentistry
Field of orthodontics
Behavioral development development of the child and interacts with the environment
Psychology,embryology
Methods of growth and development
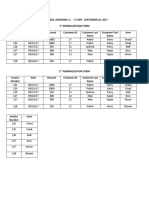
1type of data
1. Opinion crudest form of scientific knowledge
2. Not to be acceptable
3. Observation base on the and to step example eyeball and observe others
4. Quantitate measurements science deals with the quantitative minimizes
misunderstanding and permits the testing of hypothesis
Direct data derive from measurement taken on a loving or cadaver
CRANIOMETRY using dry skulls
ANTHROPOMETRY measurement of skeletal
Methods in studying bone and its development
VITAL STAINING belcher 1736 see when the bone started tetracycline
RADIOISOTOPE STUDYING BONE GROWTH
IMPLANTS
COMPARATIVE ANATOMY comparing human skull development with other animals
ROENTGEOGRAPHIC CEPHALOMETRY measure size of the skull determine the
amount of growth and its direction
NATURAL MARKERS done with serial radiograph used bony landmarks
3rd DERIVED DATA acquired comparing 2 measurements
GATHERING DATA
Longitudinal measure made by a same person or groupregilar intervals
Advantages
Variability development among individuals group is put in
Roper perspective
Specific development pattern of individual
Disadvantages
Time
Expense COSTLY
Attrition
Averaging
B. Crossectional study 1 period of time
Advantages
Faster
Less costly
Statistical treatment
Allows repeating Audie's more readily
Used of cadavers
Disadvantages
Obscures individual variation
Study of timing and development can be highly variable
C. Overlapping or semi longitudinal data
Heredity genes determine the amount of growth rate and onset
Nutrition role if the child does not it nutritious food, alteration of tooth reaction, delayed,
eruption has problems dentition becomes malocclusion malnourished
Illness debilitating patients becomes unable todo things
Race racial differences due to climate,nutritional and socioeconomic differences
Adult physique
Socioeconomic factors associated with nutrition
Family size and births order size of family of maturation
Secular trends trend of timed
Psychological disturbances stressful condition catch up growth
Exercise and climate change
Pattern, variability and timing
PATERN sets of constraine or process of organism certain pattern
Effect heredity and environmental factors
Applications of ortho
Pattern
Vertical growth pattern the face or bone grows technically
Aspects of normal growth pattern
1. Proportion body follow pattern over time
2. Differential growth rate
Organs does not actually develop mot all organs
3. Predictability pattern of growth when certain pattern at a certain time you can predict
Variability not everyone is the same
A concept or normality
A. Statistical central tendency of a group people
MEAN
MEDIAN
MODE
EVOLUTIONARY adaptation
FUNTIONAL spestablish homeostatic with the environment for survival
CLINICAL
AGE EQUIVALENCE
SIGNIFICANCE OF VARIABILITY something ther is abnormal
TIMING genetic but altered by the environment
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- HR Reviewer For MidtermsDocument41 pagesHR Reviewer For MidtermsMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- JAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 1Document41 pagesJAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 1Joe VaTa75% (4)
- Test Bank For Information Technology Auditing 4Th Edition by James A.HallDocument1 pageTest Bank For Information Technology Auditing 4Th Edition by James A.HallMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- UST Golden Notes 2011 ObliCon PDFDocument56 pagesUST Golden Notes 2011 ObliCon PDFEnnaid121100% (1)
- Varma Varmam Marma Book Full Color in English - VKRC Vol 2 Book S Ramesh Babu - Free PDF DownloadDocument14 pagesVarma Varmam Marma Book Full Color in English - VKRC Vol 2 Book S Ramesh Babu - Free PDF DownloadS Ramesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Pebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionDocument50 pagesPebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionZain zanzoonNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis SampleDocument77 pagesCholelithiasis Samplekrischamcute67% (3)
- Pediatric Physiology 2007Document378 pagesPediatric Physiology 2007Andres Jeria Diaz100% (1)
- Cultural Essence UPLOADDocument1 pageCultural Essence UPLOADMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument43 pagesPartnershipIvhy Cruz EstrellaNo ratings yet
- At Pre Week 8602Document14 pagesAt Pre Week 8602Moira VilogNo ratings yet
- CPALE Syllabi 2018 PDFDocument32 pagesCPALE Syllabi 2018 PDFLorraine TomasNo ratings yet
- Transcript Celticandgermaniceurope AC501Document3 pagesTranscript Celticandgermaniceurope AC501Moira VilogNo ratings yet
- Cpar b86 Preweek - MasDocument20 pagesCpar b86 Preweek - MasMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- SKY Fiber Super Speed PlansDocument1 pageSKY Fiber Super Speed PlansMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- LG2 - Audit of Cash (S)Document8 pagesLG2 - Audit of Cash (S)Moira VilogNo ratings yet
- D1Document13 pagesD1Anonymous bljN91No ratings yet
- DatabaseNormalization BenavidezDocument2 pagesDatabaseNormalization BenavidezMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- Amazing RaceDocument3 pagesAmazing RaceMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- Common ProgrammingErrors StringsDocument11 pagesCommon ProgrammingErrors StringsMoira VilogNo ratings yet
- 17q21.31 Microdeletions FTNWDocument8 pages17q21.31 Microdeletions FTNWjohavenbNo ratings yet
- CVDocument3 pagesCVMaria InayatNo ratings yet
- Bishara, R. - Qualification Versus ValidationDocument4 pagesBishara, R. - Qualification Versus ValidationLuis Gustavo PachecoNo ratings yet
- Pha 613 Unit 1 Part 1 Terms - 10 StarDocument56 pagesPha 613 Unit 1 Part 1 Terms - 10 StarBernadette ArnanteNo ratings yet
- Crisis HiperglicémicaDocument31 pagesCrisis HiperglicémicaMelany Esteban BarzolaNo ratings yet
- AP Research PresentationDocument26 pagesAP Research PresentationCameron SherryNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs Are: Hepatoprotective Drugs E.g.: Silymarin Antibiotics E.G.Document2 pagesClassification of Drugs Are: Hepatoprotective Drugs E.g.: Silymarin Antibiotics E.G.Navya Sara SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of OcclusionDocument23 pagesPhilosophy of OcclusionAnil SukumaranNo ratings yet
- (2012) - Psychosis and GenderDocument2 pages(2012) - Psychosis and GenderChoko DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Laser Application in Medicine & LASER SAFETY5Document62 pagesPrinciple of Laser Application in Medicine & LASER SAFETY5melisandrianaNo ratings yet
- Crystal Aromatherapy Lesson 1Document9 pagesCrystal Aromatherapy Lesson 1crystals21No ratings yet
- Inguinal HerniaDocument9 pagesInguinal HerniaAmanda RapaNo ratings yet
- Oral Alerting ActivitiesDocument3 pagesOral Alerting ActivitiesAnn VillablancaNo ratings yet
- Raja Sir CampDocument6 pagesRaja Sir CampNivedan KothekarNo ratings yet
- D. Santhi Krupa, Et Al IJAPRDocument6 pagesD. Santhi Krupa, Et Al IJAPRAtraoNo ratings yet
- 1 15 AstrovirusDocument16 pages1 15 AstrovirusRizal Hery100% (1)
- A New Lingual Straight-Wire Techique: Journal of Clinical Orthodontics: JCO February 2010Document11 pagesA New Lingual Straight-Wire Techique: Journal of Clinical Orthodontics: JCO February 2010Hafaifa TaiebNo ratings yet
- Current Management of LabourDocument48 pagesCurrent Management of Labourapi-3705046100% (4)
- Ebook - Yoga - The Science of BreathDocument2 pagesEbook - Yoga - The Science of BreathGabriel CiocanNo ratings yet
- Corpal Nindya Duri IkanDocument10 pagesCorpal Nindya Duri IkanRadianNasutionNo ratings yet
- Flip Chart 06 IUDDocument12 pagesFlip Chart 06 IUDLamyaa Ali HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Essay NegligenceDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Essay NegligenceVladimir Hechavarria100% (1)
- HFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgatedDocument8 pagesHFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgateddanexrainierNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Situation in RizalDocument23 pagesCovid19 Situation in RizalToni Quitalig GamezNo ratings yet
- Tanzania STG 052013-Copy 1544379670122Document220 pagesTanzania STG 052013-Copy 1544379670122Waqar WikiNo ratings yet
- ABR Workout GuideDocument13 pagesABR Workout GuideGJONES80100% (1)