Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of Electrical Symbols
Uploaded by
Melissa MillerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Electrical Symbols
Uploaded by
Melissa MillerCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Electrical Symbols
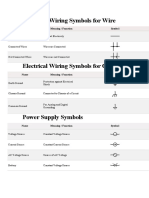
Symbol Component name Meaning
Wire Symbols
Electrical Wire Conductor of electrical current
Connected Wires Connected crossing
Not Connected Wires Wires are not connected
Switch Symbols and Relay Symbols
SPST Toggle Switch Disconnects current when open
SPDT Toggle Switch Selects between two connections
Pushbutton Switch (N.O) Momentary switch - normally open
Pushbutton Switch (N.C) Momentary switch - normally closed
DIP switch is used for onboard
DIP Switch
configuration
SPST Relay
Relay open / close connection by an
electromagnet
SPDT Relay
Close connection by jumper insertion
Jumper
on pins.
Solder Bridge Solder to close connection
Ground Symbols
Used for zero potential reference and
Earth Ground
electrical shock protection.
Chassis Ground Connected to the chassis of the circuit
Digital / Common Ground
Resistor Symbols
Resistor (IEEE)
Resistor reduces the current flow.
Resistor (IEC)
Potentiometer (IEEE)
Adjustable resistor - has 3 terminals.
Potentiometer (IEC)
Variable Resistor /
Rheostat(IEEE)
Adjustable resistor - has 2 terminals.
Variable Resistor /
Rheostat(IEC)
Trimmer Resistor Preset resistor
Thermal resistor - change resistance
Thermistor
when temperature changes
Photoresistor / Light Photo-resistor - change resistance
dependent resistor (LDR) with light intensity change
Capacitor Symbols
Capacitor
Capacitor is used to store electric
charge. It acts as short circuit with AC
and open circuit with DC.
Capacitor
Polarized Capacitor Electrolytic capacitor
Polarized Capacitor Electrolytic capacitor
Variable Capacitor Adjustable capacitance
Inductor / Coil Symbols
Coil / solenoid that generates
Inductor
magnetic field
Iron Core Inductor Includes iron
Variable Inductor
Power Supply Symbols
Voltage Source Generates voltage
Current Source Generates current.
AC Voltage Source AC (alternate) voltage source
Electrical voltage is generated by
Generator
mechanical rotation of the generator
Battery Cell Generates constant voltage
Battery Generates constant voltage
Generates voltage as a function of
Controlled Voltage Source voltage or current of other circuit
element.
Generates current as a function of
Controlled Current Source voltage or current of other circuit
element.
Meter Symbols
Measures voltage. Has very high
Voltmeter
resistance. Connected in parallel.
Measures electric current. Has near
Ammeter
zero resistance. Connected serially.
Ohmmeter Measures resistance
Wattmeter Measures electric power
Lamp / Light Bulb Symbols
Lamp / light bulb
Generates light when current flows
Lamp / light bulb
through
Lamp / light bulb
Misc. Symbols
Motor Electric motor
Change AC voltage from high to low
Transformer
or low to high.
Electric bell Rings when activated
Buzzer Produce buzzing sound
Fuse
The fuse disconnects when current
above threshold. Used to protect
circuit from high currents.
Fuse
Bus
Contains several wires. Usually for
Bus
data / address.
Bus
Optocoupler isolates onnection to
Optocoupler / Opto-isolator
other board
Converts electrical signal to sound
Loudspeaker
waves
Converts sound waves to electrical
Microphone
signal
Operational Amplifier Amplify input signal
Operates with hysteresis to reduce
Schmitt Trigger
noise.
Analog-to-digital converter Converts analog signal to digital
(ADC) numbers
Digital-to-Analog converter Converts digital numbers to analog
(DAC) signal
Used to generate precise frequency
Crystal Oscillator
clock signal
You might also like
- Measuring InstrumentDocument86 pagesMeasuring InstrumenteddoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols and Functionsara jelitaNo ratings yet
- Cluster 2 Study GuideDocument17 pagesCluster 2 Study GuideShavoy RichardsonNo ratings yet
- 7.Faults-Protection and Protective DevicesGDocument16 pages7.Faults-Protection and Protective DevicesGmola znbuNo ratings yet
- 5 Wiring Calculations For Other Loads and Servcie EntranceDocument23 pages5 Wiring Calculations For Other Loads and Servcie EntranceEdryanPoNo ratings yet
- DET 1022 Consumer BoxDocument5 pagesDET 1022 Consumer BoxLienie Azhar100% (1)
- Cable Selection and Wiring SystemDocument34 pagesCable Selection and Wiring SystemMuhammad Faiz bin Ahmad Shafi0% (1)
- Protection Devices1Document45 pagesProtection Devices1sivaNo ratings yet
- Electronically Controled Electric Fan RepairDocument4 pagesElectronically Controled Electric Fan RepairNij JinNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument5 pagesElectrical SymbolsMarc Bryan MappalaNo ratings yet
- Diode: Is An Electronic Device That Allows The Flow of Current in Only One Direction Other Term IsDocument7 pagesDiode: Is An Electronic Device That Allows The Flow of Current in Only One Direction Other Term IsLeunam SalpadNo ratings yet
- Installation and Estimation of Electrical Load PDFDocument59 pagesInstallation and Estimation of Electrical Load PDFMohd AliNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical/ Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesTable of Electrical/ Electronic Symbolscarmelle de lunaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring PlanDocument6 pagesElectrical Wiring PlanKenji BretaniaNo ratings yet
- 2007 Electrical Workshop ManualDocument99 pages2007 Electrical Workshop ManualRajneesh Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Electric LoadDocument58 pagesElectric LoadShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument10 pagesTransistorLeunam SalpadNo ratings yet
- Wires and Cables Used For Residential Electrical SystemsDocument3 pagesWires and Cables Used For Residential Electrical SystemsNurul ShathirahNo ratings yet
- ECM346 1.2.3 Function of Protection Devices HBI 02Document50 pagesECM346 1.2.3 Function of Protection Devices HBI 02Tiffany's LoveNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument18 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Install Electrical Metallic - Nonmetallic (PVC Conduit)Document13 pagesInstall Electrical Metallic - Nonmetallic (PVC Conduit)Rex Chambers LadaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Aircond & VentilationDocument54 pagesChapter 1 - Aircond & Ventilationepy87No ratings yet
- Reviewr 10 3rdDocument8 pagesReviewr 10 3rdMoises Marra EmbuidoNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument8 pagesQuestion BankCriselva Eupeña Pabrigal100% (1)
- ElectricalDocument35 pagesElectricalvinomalai100% (1)
- MDPE WORK PROCEDURE For GailDocument59 pagesMDPE WORK PROCEDURE For GailSaravanan100% (1)
- Excel Tutorial 3 Working With Formulas and Functions: ComprehensiveDocument28 pagesExcel Tutorial 3 Working With Formulas and Functions: ComprehensiveAmitNo ratings yet
- Bab 2-DC MOTORDocument35 pagesBab 2-DC MOTORAfieza TumijanNo ratings yet
- Wire Fuse and SwitchDocument47 pagesWire Fuse and SwitchMacy RiegoNo ratings yet
- Lamps: Lamp DiagnosisDocument16 pagesLamps: Lamp DiagnosisArt DoeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezDocument11 pagesElectrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezMary Jessica UyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electricity-1Document41 pagesBasics of Electricity-1anandancholaNo ratings yet
- Protective DevicesDocument4 pagesProtective DevicesKantharaj ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- Module 1A3 G12Document14 pagesModule 1A3 G12Flamin RogonNo ratings yet
- House WiringDocument8 pagesHouse WiringUncle DrewNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Current ProtectionDocument20 pagesTopic 3 - Current ProtectionVictorNo ratings yet
- Electricals Supplies and MaterialsDocument25 pagesElectricals Supplies and MaterialsROWEL T. REYESNo ratings yet
- ETM3final PDFDocument83 pagesETM3final PDFEnirethac Llrettoc0% (1)
- Ohms LawDocument40 pagesOhms Lawsrikalyani2k9No ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop: Tools Required: Insulated Combinatiom PlierDocument10 pagesElectrical Workshop: Tools Required: Insulated Combinatiom PlierhussainsaifeeNo ratings yet
- Electric Shop ManualDocument22 pagesElectric Shop ManualRohith NaniNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- Grade9 - Rat Tail SpliceDocument6 pagesGrade9 - Rat Tail SpliceEu NiceNo ratings yet
- Sharp Dcinverter Ac Service ManualDocument43 pagesSharp Dcinverter Ac Service ManualAbdorrahim DahdouhNo ratings yet
- Interpret Technical Drawings and PlansDocument10 pagesInterpret Technical Drawings and PlansDarvin Manet SecillanoNo ratings yet
- How To Copy The Content in NotepadDocument17 pagesHow To Copy The Content in NotepadDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- GE6162 EPL Lan Manual - ElectricalDocument42 pagesGE6162 EPL Lan Manual - ElectricalDhamu DharanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document68 pagesUnit 4Abdul MuhaiminNo ratings yet
- 45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFDocument7 pages45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Wiring DiagramDocument27 pagesWiring DiagramMayeth Silva GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Creating A Effective PresentationDocument14 pagesCreating A Effective PresentationSherwin SantosNo ratings yet
- WiringDocument35 pagesWiringHanifNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument12 pagesNetworkingcaseyfarmerNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Series. Sec 1Document130 pagesParallel and Series. Sec 1Mahra AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 Written Test T.L.E: Directions: Read The Statement Carefully and Choose One That BestDocument3 pages1 Written Test T.L.E: Directions: Read The Statement Carefully and Choose One That BestJDNo ratings yet
- Grounding PresentationDocument113 pagesGrounding PresentationPrashant ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring Practical 1Document12 pagesElectrical Wiring Practical 1liza zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsMegu MeguNo ratings yet
- KSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument12 pagesKSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAmendaNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsDocument15 pagesSimple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsCiprian MihailaNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesElectrical SymbolsJulia Veatrice PerezNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Thyristor ConvertersDocument24 pagesThyristor ConvertersAishuNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Vehicle LabDocument24 pagesSustainable Vehicle LabMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell Integrated Unified Power Quality Conditioner For Voltage and Current Reparation in Four-Wire Distribution GridDocument9 pagesFuel Cell Integrated Unified Power Quality Conditioner For Voltage and Current Reparation in Four-Wire Distribution GridMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument1 pageLicenseMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Installer InputDocument6 pagesInstaller Input'Andres TorregrosaNo ratings yet
- MDocument1 pageMMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- C 5 Ee 02573 GDocument18 pagesC 5 Ee 02573 GMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- IEEE Outline FormatDocument3 pagesIEEE Outline FormatAlex HerrmannNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Compensation Using UpqcDocument9 pagesPower Quality Compensation Using UpqcMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Application of Fuzzy LogicDocument22 pagesApplication of Fuzzy LogicMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- MdmgrappDocument18 pagesMdmgrappMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- 07898543Document6 pages07898543Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KDocument1 pageJJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols 3Document9 pagesCircuit Symbols 3Kiran SomayajiNo ratings yet
- ZIDt KLPeDocument21 pagesZIDt KLPeMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Load Compensation and Voltage Regulation in Three-Phase Fourwire Distribution System Using Photovoltaic Supported Custom Power DeviceDocument15 pagesLoad Compensation and Voltage Regulation in Three-Phase Fourwire Distribution System Using Photovoltaic Supported Custom Power DeviceMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Haiii.. All 222aaaaaaaaaaaa 3222aaaaaaaaaaaaa 4222222222AAAAAAAAAA 5222222222AAAAAAAAAAAA 5222222222 &&Document1 pageHaiii.. All 222aaaaaaaaaaaa 3222aaaaaaaaaaaaa 4222222222AAAAAAAAAA 5222222222AAAAAAAAAAAA 5222222222 &&Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Double Freq TransientDocument22 pagesDouble Freq TransientMelissa Miller100% (1)
- Prist University: Advanced Learners ListDocument1 pagePrist University: Advanced Learners ListMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KDocument1 pageJJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KDocument1 pageJJJJJJJJJJ KKKKKKKKKKKKKKK KK K KMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- SymbolsDocument1 pageSymbolsMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Dec 4Document1 pageDec 4Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- DVRDocument14 pagesDVRMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Haiii.. All 11 222 3222 4222222222 5222222222 5222222222Document1 pageHaiii.. All 11 222 3222 4222222222 5222222222 5222222222Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- Haiii.. All 222111111111111 32221111111111111 42222222221111111111 5222222222111111111111 5222222222 &&Document1 pageHaiii.. All 222111111111111 32221111111111111 42222222221111111111 5222222222111111111111 5222222222 &&Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- THD 2Document1 pageTHD 2Melissa MillerNo ratings yet
- HID Kits Metal HalideDocument1 pageHID Kits Metal HalideEliasNo ratings yet
- Frigidaire 52876 Lghb2869tf Fr5202rgw2 Manual enDocument40 pagesFrigidaire 52876 Lghb2869tf Fr5202rgw2 Manual enJimmy ZettenbergNo ratings yet
- Calculul Inductantei Unei Bobine - OdtDocument3 pagesCalculul Inductantei Unei Bobine - OdtMihai TămagăNo ratings yet
- Control PanelDocument9 pagesControl PanelPEMELIHARAAN LISTRIKNo ratings yet
- 5100 ManualDocument33 pages5100 ManualamenstoNo ratings yet
- VDR DM100 VDRDocument4 pagesVDR DM100 VDRMarekMyszkaNo ratings yet
- 196000-3270 BOMBA INJETORA DENSO - pdf-4Document2 pages196000-3270 BOMBA INJETORA DENSO - pdf-4militar1968No ratings yet
- Tri EngDocument22 pagesTri EngAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Datasheet ECM 3508 Interface 4pgv1 A80401 PressDocument4 pagesDatasheet ECM 3508 Interface 4pgv1 A80401 Presslgreilly4No ratings yet
- 17-1 ALLU D Series Parts&Accessories Recommended Price ListDocument7 pages17-1 ALLU D Series Parts&Accessories Recommended Price ListKadir Koray BozyelNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument37 pagesDatasheetMohamad YahyaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Battery Performance On The Initial Sizing of Hybrid-Electric General Aviation AircraftDocument18 pagesImpact of Battery Performance On The Initial Sizing of Hybrid-Electric General Aviation AircraftNguyễn Tiến Minh KhôiNo ratings yet
- Folleto Lavadora Carga Superior YWNE5 ComercialDocument2 pagesFolleto Lavadora Carga Superior YWNE5 ComercialKarly OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 1607181570417713Document2 pages1607181570417713akhundbilalNo ratings yet
- Properties: Navigation 1/4" (6.55 MM) Monoconductor Corrosion ResistantDocument1 pageProperties: Navigation 1/4" (6.55 MM) Monoconductor Corrosion ResistantRaed fouadNo ratings yet
- Aim Spice Tutorial v3Document6 pagesAim Spice Tutorial v3Madalina HirbeaNo ratings yet
- DucatiOmaha 2019 Monster1200SDocument162 pagesDucatiOmaha 2019 Monster1200SandrzejgalantNo ratings yet
- MCSet - RollarcDocument4 pagesMCSet - RollarccatalinccNo ratings yet
- 01 10 Mercedes Benz EDocument4 pages01 10 Mercedes Benz EAnderson SousaNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheets: Page 1 of 19 210372 Proj. No.: Customer: Proj. Name: 13Document19 pagesTechnical Data Sheets: Page 1 of 19 210372 Proj. No.: Customer: Proj. Name: 13samirNo ratings yet
- Graphic Dot Matrix Chip in Glass VFD MN32032ADocument1 pageGraphic Dot Matrix Chip in Glass VFD MN32032AJoeMs2020No ratings yet
- W Section 1 Mma Welding Saf Fro General Catalogue68475045296859596Document8 pagesW Section 1 Mma Welding Saf Fro General Catalogue68475045296859596sarahrouNo ratings yet
- Moving DataDocument30 pagesMoving DataJoJoMoNo ratings yet
- Venezuela Graphic Design DrawingsDocument1 pageVenezuela Graphic Design DrawingsJose AlbarezNo ratings yet
- Australian/New Zealand StandardDocument8 pagesAustralian/New Zealand Standardfaneveslucas_4723330No ratings yet
- SP CV Truck Dump 2012 NEW Dump ENG4p PDFDocument2 pagesSP CV Truck Dump 2012 NEW Dump ENG4p PDFAl-kasid Commercial Agencies Company / MachineryNo ratings yet
- Indexer Cam Gear Kurvengetriebe HSG BWV - HEINZDocument20 pagesIndexer Cam Gear Kurvengetriebe HSG BWV - HEINZluiz cláudioNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta QMS Magicolor 7300 Service ManualDocument271 pagesKonica Minolta QMS Magicolor 7300 Service Manualimre657No ratings yet
- 1home Automation System Using A Simple Android App - DIY ProjectsDocument8 pages1home Automation System Using A Simple Android App - DIY ProjectsSagar ShindeNo ratings yet