Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formule Trigonometrice
Uploaded by
Andrei BratoloveanuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formule Trigonometrice
Uploaded by
Andrei BratoloveanuCopyright:
Available Formats
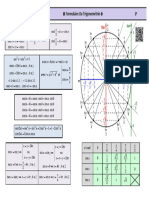
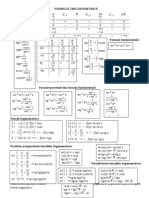
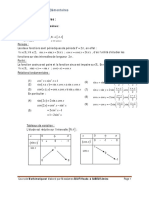
FORMULE TRIGONOMETRICE
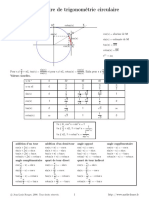
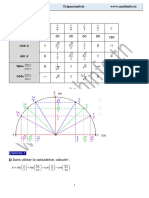
0 CI C II C III 3 C IV 2
2 2
sin x 0 + 1 + 0 - -1 - 0
cos x 1 + 0 - -1 - 0 + 1
tg x 0 + | - 0 + | - 0
ctg x | + 0 - | + 0 - |
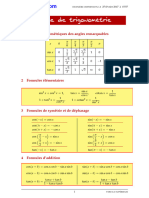
sin x Formula fundamental:
tgx= sin x =cosx
cos x 6 4 3 2 sin 2 x+cos 2 x=1
cos x sin 1 2 3
ctgx=
sin x 2 2 2 cos x =sinx
2
1 cos 3 2 1
tgx= tg x =ctgx
ctx 2 2 2
2
1 tg 3 1 3
ctgx= tgx
3 ctgx x =tgx
1 2
secx= ctg 3 1 3
cos x 3
1
cosecx=
sin x
Formule provenite din formula fundamental:
tg 2 x 1
cos 2 x =1- sin 2 x sin 2 x =1- cos 2 x sin 2 x = sin 2 x = 1 ctg 2 x
1 tg 2 x
sin 2 x 1 cos 2 x 1 ctg 2 x
tg 2 x = tg 2 x =
1 sin 2 x cos 2 x cos 2 x = 1 tg 2 x cos x =
2
1 ctg 2 x
1 sin 2 x cos 2 x 1 1
ctg 2 x = ctg 2 x = ctg 2 x = tg 2 x tg 2 x = ctg 2 x
sin 2 x 1 cos 2 x
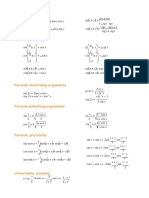
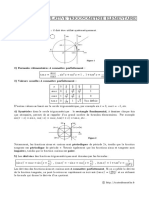
Funcii trigonometrice:
f: [-1,1], f(x) = sinx
f:[-1,1] , , f(x)= arcsin x
f: [-1,1], f(x) = cosx 2 2
f:[-1,1] [0, ], f(x)= arccos x
f: \ k / k Z , f(x) =tgx
2
f: ; , f(x)= arctg x
f: \ k / k Z
, f(x)= ctgx 2 2
f: ( 0; ) , f(x)= arcctg x
Paritatea i sin(-x) = - sinx arcsin(-x)= -arcsin x
imparitatea cos(-x) = cosx arccos(-x)= -arccos
funciilor
x , arcsin(sinx)=x tg(-x) = - tgx x
2 2 trigonometrice: ctg(-x) = - ctgx arctg(-x)= -arctg x
x [ 0, ] arccos(cosx)=x arcctg(-x)= -arcctg x
x [-1, 1] sin(arcsinx)=x sin(x+2k ) = sinx
x ; arctg(tgx)=x x [-1, 1] cos(arccosx)=x cos(x+2k ) = cosx
2 2
x tg(arctgx)=x tg(x+k ) = tgx
x ( 0; ) arcctg(ctgx)=x x ctg(arcctgx)=x ctg(x+k ) = ctgx, k Z
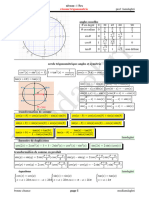
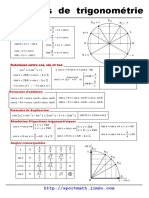
Reducerea la primul cadran: Deplasarea n punctul diametral opus:
1
x C II : x C III : x C IV : x :
sinx=sin( - x) sinx = - sin(x - ) sinx = - sin(2 - x) sin(x - ) =sin(x+ ) = - sinx
cosx= - cos( - cosx = - cos(x - cosx = cos(2 - x) cos(x - ) = cos(x+ ) = - cosx
x) ) tgx = - tg(2 - x) tg(x - ) = tg(x+ ) = tgx
tgx = - tg( - x) tgx = tg(x - ) ctgx = - ctg (2 - x) ctg(x - ) = ctg(x+ ) = ctgx
ctgx = - ctg( - ctgx = ctg(x - )
sin(x+y) = sinxcosy + cosxsiny sin(x-y) = sinxcosy cosxsiny sin2x = 2sinxcosx
cos(x+y) = cosxcosy sinxsiny cos(x-y) = cosxcosy + sinxsiny cos2x = cos 2 x-sin 2 x
tgx tgy tgx tgy =
tg(x+y) = 1 tgxtgy tg(x-y) = 1 tgxtgy
=2cos 2 x 1 =
ctgx ctgy 1 ctgxctgy 1 = 1 2sin 2 x
ctg(x+y) = ctx ctgy
ctg(x-y) = ctgx ctgy 2tgx
tg2x = 1 tg 2 x
x ctg 2 x 1
sin 2
= ctg2x =
2 2ctgx
1 cos x x
cosx-1 = - 2sin 2 sin3x = 3sinx 4sin 3 x
2 2
cos3x = - 3cosx + 4cos 3 x
2 x x
cos = cosx+1 = 2cos 2 3tgx tg 3 x
2 2 tg3x =
1 cos x 1 3tg 2 x
2 ctg 3 x 3ctgx
1 cos x ctg3x =
2 x 3ctg 2 x 1
tg =
2 1 cos x
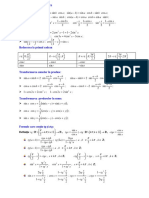
Transformarea produselor n sume: Transformarea sumelor n produse: Substituia
universal:
cosx cosy = x y x y
sinx+siny = 2sin cos
cos( x y ) cos( x y ) 2 2 x
t = tg
2 x y x y 2
sinx-siny = 2cos sin
sin( x y ) sin( x y ) 2 2 2t
sinx cosy = sinx =
2 x y x y 1 t2
cosx+cosy = 2cos cos
sinx siny = 2 2 1 t2
cos( x y ) cos( x y ) x y x y cosx =
cosx-cosy = - 2sin sin 1 t2
2 2 2 2t
x y sin( x y ) tgx =
arctg x arctg y = arctg tgx+tgy = ; tgx-tgy = 1 t2
1 m xy cos x cos y
1 t2
sin( xFunctiile
y) trigonometrice: ctgx =
Ecuaii trigonometrice: 2t
cos x cos y
sinx = a, a [-1, 1] x = (-1) k arcsin a + k , k arcsin x +arccos x =
Z 2
cosx = a, a [-1, 1] x = arccos a + 2k , k Z
tgx = a, a R x = arctg a + k , k Z arctg x +arcctg x =
2
ctgx = a, a R x = arcctg a+ k , k Z
sinx = sina, a R x = (-1) k a + k , k Z sinx = 0 x = k , k Z
cosx = cosa, a R x = a + 2k , k Z
cosx = 0 x = k , k Z
2
tgx = tga, a R\ k / k Z x = a+k , k Z tgx = 0 x = k , k Z
2
ctgx = ctgx, a R\ k / k Z x = a+k , k Z ctgx = 0 x = k , k Z
2
2
You might also like
- Formule TrigonometriceDocument2 pagesFormule TrigonometriceAnonymous e7xIuIYqdNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometriceDocument2 pagesFormule TrigonometriceremusNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometriceDocument4 pagesFormule TrigonometricegefinnaNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometriceDocument4 pagesFormule Trigonometriceirina100% (3)
- Formule Trigonometrice PDFDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometrice PDFAstrid XDNo ratings yet
- TrigonometrieDocument7 pagesTrigonometriecvacasa50No ratings yet
- TP TrigoDocument2 pagesTP TrigomichelprincesimbaNo ratings yet
- Formules Trigonometriques 1 4Document1 pageFormules Trigonometriques 1 4ahmed tounsiNo ratings yet
- Trig FormuleDocument1 pageTrig Formule514126No ratings yet
- Trigonometrie Sur Le Cercle - CoursDocument10 pagesTrigonometrie Sur Le Cercle - Courscharpz100% (1)
- Trigonometrie 1sm NJBDocument1 pageTrigonometrie 1sm NJBAl Amine DiopNo ratings yet
- Exercices: Les Équations Trigonométriques: Exercice 1Document4 pagesExercices: Les Équations Trigonométriques: Exercice 1Kabinet Camara100% (1)
- 3.resume Formulaire - TrigoDocument1 page3.resume Formulaire - TrigoAbidli IchrakNo ratings yet
- M.ka TS 2Document102 pagesM.ka TS 2Daro DiopNo ratings yet
- 492142984-03-Fiche-Trigonometrie-Superieur-Portrait (1) - Watermark-1Document3 pages492142984-03-Fiche-Trigonometrie-Superieur-Portrait (1) - Watermark-1gelb.dave666No ratings yet
- 03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur PortraitDocument3 pages03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur PortraitMix Santa100% (1)
- 03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur PortraitDocument3 pages03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur Portraitbadre100% (1)
- 03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur PortraitDocument3 pages03 Fiche Trigonometrie Superieur PortraitSalma El MouldiNo ratings yet
- 4s Trigo CorDocument5 pages4s Trigo CorMatty DiopNo ratings yet
- Cesi Ets Cpi2Document9 pagesCesi Ets Cpi2Simon SeinturierNo ratings yet
- Formulaire TrigoDocument1 pageFormulaire TrigotheodibonaNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometrieDocument2 pagesFormule TrigonometriePol Martin100% (1)
- For Mulaire TrigoDocument2 pagesFor Mulaire TrigoRis Majdouline100% (1)
- SINTEZA - Formule Trigonometrie PDFDocument5 pagesSINTEZA - Formule Trigonometrie PDFGabriela LangNo ratings yet
- Formulaire Trigo +Document4 pagesFormulaire Trigo +Alae say100% (1)
- Formule TrigonometrieDocument6 pagesFormule TrigonometrieOlanuta Calin AndreiNo ratings yet
- TrigonométrieDocument1 pageTrigonométrieTrabi Le richeNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometrieDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometriezefelix100% (2)
- Résumé TrigonométrieDocument1 pageRésumé TrigonométrienapolilacasaNo ratings yet
- Formule TrigonometrieDocument2 pagesFormule TrigonometrieAleka HuzNo ratings yet
- Trigon Trigon Trigon Trigonometrie Ometrie Ometrie Ometrie: Fiche de CoursDocument2 pagesTrigon Trigon Trigon Trigonometrie Ometrie Ometrie Ometrie: Fiche de CoursBayrem jlklskj100% (1)
- TrigoDocument2 pagesTrigoMalek MesfarNo ratings yet
- Trigo NoRestrictionDocument2 pagesTrigo NoRestrictionMalek MesfarNo ratings yet
- 1re Primitives de Fonctions TrigonometriquesDocument7 pages1re Primitives de Fonctions TrigonometriquesHhamza Mmanouzi100% (1)
- Correction Série 2Document10 pagesCorrection Série 2youssef.bensalimNo ratings yet
- 6142fc4a8ae09ISE CL As 2021 CorrigesDocument16 pages6142fc4a8ae09ISE CL As 2021 CorrigesIvan AdouNo ratings yet
- Chapitre4 Maths1Document19 pagesChapitre4 Maths1hadjmoussanadir84No ratings yet
- FormulaireDocument4 pagesFormulaireBoubacar Yssouf Touré100% (1)
- Épreuves D'analyse Et Algèbre Niveau 1-1Document176 pagesÉpreuves D'analyse Et Algèbre Niveau 1-1tathumchrisNo ratings yet
- Formulaire TrigoDocument3 pagesFormulaire TrigoMehdi Majid100% (1)
- Exam 1 Nybh 13 SolDocument2 pagesExam 1 Nybh 13 SolAbdelmalkNo ratings yet
- Formule Trigonometrie PDFDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometrie PDFMarius Constantin100% (1)
- MAT1013 Rappels TrigoDocument4 pagesMAT1013 Rappels TrigoMoussa KonatéNo ratings yet
- Lim Fonc TrigDocument2 pagesLim Fonc TrigAnouar ChebbiNo ratings yet
- Formulaires de TrigonometrieDocument1 pageFormulaires de Trigonometriehitachi hadi100% (3)
- Ana 10Document21 pagesAna 10Fadi DaouNo ratings yet
- Mat2 FormuleDocument2 pagesMat2 FormuleMiljan NikolićNo ratings yet
- Correction TrigononmetriqueDocument11 pagesCorrection Trigononmetriqueskamina095No ratings yet
- 04 Trigonometrie PlancheDocument2 pages04 Trigonometrie Plancheagnanjeanbaptiste447No ratings yet
- TD 22 - TrigonometrieDocument2 pagesTD 22 - TrigonometrieguiguimuisansNo ratings yet
- Les Fonctions - Les Fonctions TrigonométriquesDocument10 pagesLes Fonctions - Les Fonctions Trigonométriquescaomeilin24No ratings yet
- Memo Actuar I atDocument16 pagesMemo Actuar I atKatia Jean-Etienne KoneNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Intégration Des Fonctions HyperboliquesDocument1 page3.9 Intégration Des Fonctions HyperboliquesIsmahane BenaliNo ratings yet
- Model TPDocument5 pagesModel TPassilainfo0No ratings yet
- Équations différentielles: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisFrom EverandÉquations différentielles: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisNo ratings yet
- Introduction À La PlasticitéDocument49 pagesIntroduction À La PlasticitéMellier100% (1)
- Cours Asservi Digital 2021Document40 pagesCours Asservi Digital 2021Maram MërïemNo ratings yet
- 11 L ComplexesDocument16 pages11 L ComplexesanasNo ratings yet
- Genie L1 LMD FASE 2Document22 pagesGenie L1 LMD FASE 2jessicampuangaNo ratings yet
- TD N°3 Avec SolutionDocument7 pagesTD N°3 Avec Solutionجمال طيبي100% (1)
- Te 10Document6 pagesTe 10armelo simbeNo ratings yet
- Cahier Poly Et Disque 2016Document36 pagesCahier Poly Et Disque 2016jackNo ratings yet
- Optique Non LinéaireDocument88 pagesOptique Non LinéaireDankov2No ratings yet
- TestF c1 2014 CorrigéDocument6 pagesTestF c1 2014 CorrigéOthmane ADNo ratings yet
- QCM Ptransfert 2018 CorrigeDocument4 pagesQCM Ptransfert 2018 CorrigeJules DecaesteckerNo ratings yet
- Exercice: 1: Année Scolaire 2022/2023Document22 pagesExercice: 1: Année Scolaire 2022/2023Adam StatiNo ratings yet
- Séance 1 Économétrie Financiére S6 Finance Et Banque Avril 2020Document13 pagesSéance 1 Économétrie Financiére S6 Finance Et Banque Avril 2020Moncef BARZANENo ratings yet
- Thermo Me TrieDocument2 pagesThermo Me TrieYASSINE LaachoubiNo ratings yet
- Cours Algo Et ExerciceDocument43 pagesCours Algo Et ExerciceMaa MatildNo ratings yet
- Cours - Determinant PDFDocument15 pagesCours - Determinant PDFYasser LamyasserNo ratings yet
- Chaines de CôtesDocument7 pagesChaines de Côtesajaikumar ShankarNo ratings yet
- Be9860 Technique IngénieurDocument34 pagesBe9860 Technique Ingénieurbertrand_0123456789No ratings yet
- Thème:: Mémoire de Fin D'Etudes Pour L'Obtention Du Diplôme de Licence ProfessionnelleDocument31 pagesThème:: Mémoire de Fin D'Etudes Pour L'Obtention Du Diplôme de Licence Professionnellekerim abdel-farroukNo ratings yet
- TP: Résolution Numérique Des Edps Par DF: - Équation de La ChaleurDocument7 pagesTP: Résolution Numérique Des Edps Par DF: - Équation de La Chaleurthrwalide433No ratings yet
- Chapitre2 Critère de Performance D'une RégulationDocument46 pagesChapitre2 Critère de Performance D'une RégulationAYOUB RIAD100% (2)
- Série Notion ArithmétiqueDocument1 pageSérie Notion ArithmétiqueM sbNo ratings yet
- TD5 Structure Des GroupesDocument1 pageTD5 Structure Des GroupesjoliuNo ratings yet
- Eva 2 CM1 Geometrie 2 1Document3 pagesEva 2 CM1 Geometrie 2 1mavy inaoNo ratings yet
- Klubprepa-Extrait-4254 FDDocument3 pagesKlubprepa-Extrait-4254 FDCosSinNo ratings yet
- Modélisation Méca - Les Contacts PDFDocument4 pagesModélisation Méca - Les Contacts PDFAdrien LupinNo ratings yet
- HW8 0607Document4 pagesHW8 0607Wissem DhaouadiNo ratings yet
- Jonas Latt PHD ThesisDocument125 pagesJonas Latt PHD ThesislanwatchNo ratings yet
- Cours Initiation EHTP AutocadDocument28 pagesCours Initiation EHTP AutocadmarcosNo ratings yet
- Reading List 2Document1 pageReading List 2Ayoub bjnNo ratings yet
- Logique Propositionnelle & Logique Des Prédicats: Intelligence Artificielle - TD 5Document3 pagesLogique Propositionnelle & Logique Des Prédicats: Intelligence Artificielle - TD 5Ameni BoughanmiNo ratings yet