Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Social Science
Uploaded by
Vijay PatelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Social Science
Uploaded by
Vijay PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
The section on the fundamental rights has been referred to as the conscience of the Constitution.
Fundamental Rights protect us against arbitrary and absolute exercise of power by the state. The
constitution guarantees right of individuals against state as well as other individuals
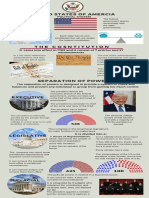
Right to Equality Indian Constitution Secularism
Right to Freedom Fundamental Set of Rules & Principles by which Separation of religion from state
Right against exploitation Rights All religion are equal - State does not
country to be governed
Right to freedom of religion promote any religion as state religion
Cultural & Educational rights Why? - Constitution provide safeguards against misuse of
Right to constitutional remedies Indian Secularism: The Constitution mandates that the Indian state be
authority by our political leaders. It prevent tyranny or
domination by the majority or powerful people over minority. secular and ensures following: 1 One religion community does not
dominate other. 2 Some members do not dominate the other member of
State government are autonomous in same community. 3 The state does not enforce any particular religion nor
exercising powers and taking decision take away the religious freedom of individual
for their area on certain issues, fulfilling
Constitution says all three organs
the laws of the central government.
Federalism Separation of Power exercise different powers so that
Constitution details out issues that
More than one level of govt each acts as a check on other to
each tier of govt can make laws on.
ensures balance of power bn all
Also specifies where each tier of govt
three
can get money for their working
State Central Legislatures & Executives Judiciary Independent
Judiciary Role-Upholding laws & Fundamental Rights
Legislative Assembly Parliamentary form of govt - Parliament -Dispute Resolution & Judicial Review
People directly elect their representatives -Universal adult suffrage/franchise: People directly elect Independent Judiciary to ensure Separation of Power
(MLA) to legislative assembly (Vidhan
their representatives to parliament (legislatures) Structure Supreme, High & District Courts
Sabha). Seven state has upper house
known as legislative council -Small Group from these form government (executives) Different legal System Criminal & Civil law
Does - Everyone has equal right to justice through courts
Parliament
Rajya Sabha-MP Lok Sabha-MP
House of People Does - All persons are equal before law. The
Council of states
President 2 - Lower House - 543 low cannot discriminate bn the persons on the
233-Upper House-12
basis of religion, caste or gender. Laws apply to
all equally and nobody is above the law
including government and president
Role of Parliament How do new laws come about?
To select National Government (Executives) Un popular & Controversial Laws
To Control Guide and Inform the Government
To make Laws
You might also like
- ConclusionDocument3 pagesConclusionAli SchehzadNo ratings yet
- Usa Political SystemDocument1 pageUsa Political SystemFrançois Xavier BalmedyNo ratings yet
- India's Constitution: Key FeaturesDocument26 pagesIndia's Constitution: Key FeaturesSWARA MEHTALIANo ratings yet
- The Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesThe Indian ConstitutionhridaykagalkarNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument82 pagesConstitution of IndiaPrasan NandaNo ratings yet
- Limited Government Social ContractDocument28 pagesLimited Government Social Contractcullw1984No ratings yet
- Law School Legal DoctrinesDocument5 pagesLaw School Legal DoctrinesjohnbriancabalunaofficialNo ratings yet
- ArticlesofConfed - Student - 2022-23 2Document20 pagesArticlesofConfed - Student - 2022-23 2blair ChingNo ratings yet
- Secular Federal RepubicDocument5 pagesSecular Federal RepubicHajirath AmreenNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument36 pagesNotesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Constitutionalism - Saiby KhanDocument9 pagesConstitutionalism - Saiby KhanSaiby KhanNo ratings yet
- Document 25Document4 pagesDocument 25Abrar Ahmed 815-SE/BSEF/F20No ratings yet
- Comparing Unitary vs Federal Gov Structures and Power DistributionDocument5 pagesComparing Unitary vs Federal Gov Structures and Power Distributionariah janeNo ratings yet
- Democracy and ParticipationDocument4 pagesDemocracy and ParticipationCatherine Keira IlaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 and 4 GovernmentDocument24 pagesChapter 3 and 4 GovernmentCovet AngelNo ratings yet
- Structure:-The Indian Constitution Originally Consisted of 395 Art, 22 Parts, 8 Schedules. ButDocument16 pagesStructure:-The Indian Constitution Originally Consisted of 395 Art, 22 Parts, 8 Schedules. ButSameer KaleNo ratings yet
- J A - T C L An Introduction:: OHN Ustin HE Ommand Theory OF AWDocument6 pagesJ A - T C L An Introduction:: OHN Ustin HE Ommand Theory OF AWSubhojit DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment Constitutionalism & Constitutional SpiritDocument31 pagesAssignment Constitutionalism & Constitutional SpiritSurabhi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Readings in Philippine HistoryDocument9 pagesReadings in Philippine HistoryAthen ShielNo ratings yet
- FC Sem 1 Basic Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument4 pagesFC Sem 1 Basic Features of Indian ConstitutionDineshNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument6 pagesSeparation of PowersPranav Khanna33% (3)
- Module 7 - Theory of Separation of PowersDocument24 pagesModule 7 - Theory of Separation of PowersChristian GeromianoNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Constitution of IndiaDocument26 pagesAspects of Constitution of Indiahemangi14780% (5)
- MOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextDocument13 pagesMOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextPulakNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument147 pagesUnit - I Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionNithin YMNo ratings yet
- constitution 5th sam notesDocument18 pagesconstitution 5th sam notesbcomllb2ketanNo ratings yet
- Separation of Powers Doctrine in Different ConstitutionsDocument7 pagesSeparation of Powers Doctrine in Different ConstitutionsRuin RExNo ratings yet
- 0 - Lspe NotesDocument154 pages0 - Lspe Notesyogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- The Principles of The ConstitutionDocument29 pagesThe Principles of The ConstitutionHabtamu AdimasuNo ratings yet
- Three branches of government and separation of powers doctrineDocument6 pagesThree branches of government and separation of powers doctrineTeesta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- U2 LP4 TextCodingDocument2 pagesU2 LP4 TextCodingcullw1984No ratings yet
- Applicability of Sepration of Power in India Administrative LawDocument9 pagesApplicability of Sepration of Power in India Administrative Lawsparsh lalNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument28 pagesSeparation of PowersAnam ShoaibNo ratings yet
- The Indian Constitution: NCERT Class 8 Civics Summary by ORACLE IASDocument46 pagesThe Indian Constitution: NCERT Class 8 Civics Summary by ORACLE IAShimal_panth996009No ratings yet
- Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument10 pagesDoctrine of Separation of PowerspriyaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law of IndiaDocument63 pagesConstitutional Law of IndiaShivani Vasudeva VermaNo ratings yet
- Rule of Law Rule of Law: Unit 2Document12 pagesRule of Law Rule of Law: Unit 2Yoseph LuelsegedNo ratings yet
- Branches of The Philippine Government: Separation of PowersDocument3 pagesBranches of The Philippine Government: Separation of PowersAl-zobair MacarayaNo ratings yet
- Consti - TSN Arellano 1Document18 pagesConsti - TSN Arellano 1Jeraldine Tatiana PiñarNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesUnit - I Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionVivekNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethics and Indian ConstitutionDocument147 pagesLegal Ethics and Indian ConstitutionAjithKumar0% (1)
- Industrial AND General Law: Topic Covered:-Coverage - 30 MarksDocument98 pagesIndustrial AND General Law: Topic Covered:-Coverage - 30 MarksRab RakhaNo ratings yet
- Seperation of PowersDocument23 pagesSeperation of PowersVidya ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowerDocument25 pagesSeparation of PowerKuber JaishiNo ratings yet
- ThebigpictureDocument3 pagesThebigpictureapi-266012824No ratings yet
- Administrative LawDocument44 pagesAdministrative Lawharshit anandNo ratings yet
- CLS CC Constitutional Law SummaryDocument22 pagesCLS CC Constitutional Law SummaryJabulani MakanyaNo ratings yet
- 7 Principles PowerPointDocument9 pages7 Principles PowerPointMarc BravoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 - Indian ConstitutionDocument27 pagesChapter-1 - Indian ConstitutionRC SectionNo ratings yet
- Constitutional and Judicial Legal Principles and DoctrinesDocument39 pagesConstitutional and Judicial Legal Principles and DoctrinesManu J PlamootilNo ratings yet
- Constitution & Constitutional LawDocument4 pagesConstitution & Constitutional LawBellaNo ratings yet
- SEVEN BASIC PRINCIPLESDocument6 pagesSEVEN BASIC PRINCIPLESMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument41 pagesDoctrine of Separation of Powersaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- LUIS RODRIGUEZ - Principles of Limited Gov - 2021Document2 pagesLUIS RODRIGUEZ - Principles of Limited Gov - 2021LUIS RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Law and Justice - The Column of CuraeDocument9 pagesRelation Between Law and Justice - The Column of CuraeSandesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Nigeria ND America LegislatureDocument2 pagesNigeria ND America LegislatureAmi EliudNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution at WorkDocument60 pagesIndian Constitution at WorkAnuragNo ratings yet
- What Is Constitutional LawDocument3 pagesWhat Is Constitutional LawPAOLO ABUYONo ratings yet
- LEGAL LANGUAGE: An Introduction to the Study of Law in IndiaFrom EverandLEGAL LANGUAGE: An Introduction to the Study of Law in IndiaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Separatn NoteDocument14 pagesSeparatn NoteVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Ten ReactionsDocument2 pagesTen ReactionsVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Rolling Without Slip-MechanicsDocument6 pagesRolling Without Slip-MechanicsSujay BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- AsamDocument1 pageAsamVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Letter DonatinDocument1 pageLetter DonatinVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Important Metal Ores and Their Chemical FormulasDocument1 pageImportant Metal Ores and Their Chemical FormulasVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Ten ReactionsDocument2 pagesTen ReactionsVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program1: Ms - Viray (Module 3 - IT1&HRS1)Document3 pagesNational Service Training Program1: Ms - Viray (Module 3 - IT1&HRS1)Guki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Figueroa vs. BarrancoDocument4 pagesFigueroa vs. BarrancoRommel P. AbasNo ratings yet
- Land Use ChargeDocument25 pagesLand Use ChargeOmoniyiOmoniyiNo ratings yet
- Castillo vs. NapolcomDocument7 pagesCastillo vs. NapolcomAsHervea AbanteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Philippine Constitution, Preamble and Bill of RightsDocument12 pagesLesson 2 - Philippine Constitution, Preamble and Bill of RightsMary Joy CuetoNo ratings yet
- Cancellation of Bail Sec 497Document6 pagesCancellation of Bail Sec 497Azad SamiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Online Training Materials - Usage AgreementDocument53 pagesOracle Online Training Materials - Usage Agreementحسين عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Legal Research and Writing Assignment Discussion of CasesDocument15 pagesLegal Research and Writing Assignment Discussion of CasesjsuarezdeangNo ratings yet
- PHELPS DUNBAR WELL CONTROL COVERAGESDocument3 pagesPHELPS DUNBAR WELL CONTROL COVERAGESgimgagNo ratings yet
- Challenging the Public/Private Divide: An OverviewDocument32 pagesChallenging the Public/Private Divide: An OverviewRafael Braga da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Setting Up a Legal Business Credit ProfileDocument7 pagesSetting Up a Legal Business Credit ProfileMaryUmbrello-Dressler83% (12)
- Vasquez v. Philippine National BankDocument11 pagesVasquez v. Philippine National BankKristine Faith CenizaNo ratings yet
- SAME SEX MARRIAGE TABOO IN INDIADocument10 pagesSAME SEX MARRIAGE TABOO IN INDIAanushka kashyap100% (1)
- Student Internship Program in The Philippines (Sipp)Document7 pagesStudent Internship Program in The Philippines (Sipp)ELMERNo ratings yet
- Case 10 (7) Nuova FucinatiDocument8 pagesCase 10 (7) Nuova FucinatiradislamyNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health Standards - DocumentationDocument6 pagesOccupational Safety and Health Standards - DocumentationJericho YangNo ratings yet
- 3 Estafa - Gallardo vs. PeopleDocument7 pages3 Estafa - Gallardo vs. PeopleAtty Richard TenorioNo ratings yet
- Classification of Law: International, Municipal, Public & PrivateDocument18 pagesClassification of Law: International, Municipal, Public & PrivateMrutyunjay SaramandalNo ratings yet
- Clark County Jail Pre-Book Sheet: DefendantDocument5 pagesClark County Jail Pre-Book Sheet: DefendantKGW NewsNo ratings yet
- Rescissible ContractDocument2 pagesRescissible ContractCATHY ROSALESNo ratings yet
- Rulings on Miranda Doctrine CasesDocument26 pagesRulings on Miranda Doctrine Casespit1xNo ratings yet
- MODULE I Intro To Labor LawDocument4 pagesMODULE I Intro To Labor LawAndrew BelgicaNo ratings yet
- India's Grand Advocates: A Legal Elite Flourishing in The Era of GlobalizationDocument31 pagesIndia's Grand Advocates: A Legal Elite Flourishing in The Era of GlobalizationBar & Bench100% (1)
- Estate Liability of Deceased Surety GuarantorDocument3 pagesEstate Liability of Deceased Surety GuarantorNic NalpenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DemocracyDocument22 pagesChapter 4 DemocracyDo KyungsoooooNo ratings yet
- Corpus Juris Secundum On Grand JuryDocument2 pagesCorpus Juris Secundum On Grand JurycelticfyrNo ratings yet
- 12 03 2019 Letter To European and US Institutions Regarding PlahotniucDocument80 pages12 03 2019 Letter To European and US Institutions Regarding Plahotniucmih50% (2)
- Active Assailant, Loss of Attraction and Threat (ALT) : FAQ'sDocument2 pagesActive Assailant, Loss of Attraction and Threat (ALT) : FAQ'sAnalia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Villavicencio V Lukban DigestDocument2 pagesVillavicencio V Lukban DigestAiken Alagban Ladines100% (5)
- FAO CharterDocument14 pagesFAO CharterFrancis Julius Romeo Del ValleNo ratings yet