Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solutions: With Answer Key
Uploaded by
Ria SriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solutions: With Answer Key
Uploaded by
Ria SriCopyright:
Available Formats
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) - 2017-18 (SET-A)
SOLUTIONS
WITH
ANSWER KEY
AITS-PT # 03 [SET-A]
DROPPER MEDICAL
(PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY)
TARGET : NEET - 2018
Exam. Date : 26-11-2017
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
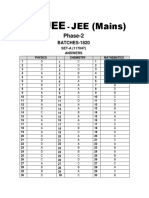
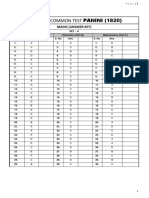
ANSWER KEYS FOR AITS-PT # 03 DROPPER MEDICAL [SET # A]
DATE : 26-11-2017
ANSWERS [PHYSICS]
1. B 2. Bonus 3. D 4. A 5. A 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. A 10. D
11. B 12. B 13. D 14. D 15. B 16. C 17. D 18. A 19. A 20. C
21. A 22. A 23. C 24. B 25. D 26. B 27. C 28. A 29. C 30. D
31. C 32. B 33. C 34. A 35. D 36. B 37. D 38. C 39. B 40. D
41. C 42. B 43. B 44. A 45. A
ANSWERS [CHEMISTRY]
46. C 47. A 48. A 49. B 50. C 51. D 52. D 53. B 54. A 55. C
56. D 57. B 58. C 59. B 60. C 61. D 62. C 63. C 64. A 65. D
66. C 67. C 68. A 69. B 70. C 71. A 72. C 73. C 74. A 75. A
76. C 77. A 78. D 79. C 80. C 81. B 82. C 83. B 84. D 85. D
86. B 87. D 88. A 89. B 90. A
ANSWERS [BOTANY]
91. B 92. B 93. D 94. C 95. B 96. A 97. B 98. B 99. B 100. B
101. D 102. A 103. C 104. B 105. A 106. B 107. B 108. B 109. D 110. B
111. D 112. A 113. D 114. A 115. C 116. A 117. C 118. A 119. A 120. D
121. B 122. D 123. A 124. Bonus125. C 126. D 127. B 128. A 129. C 130. A
131. C 132. A 133. C 134. C 135. D
ANSWERS [ZOOLOGY]
136. D 137. C 138. C 139. C 140. D 141. A 142. A 143. D 144. A 145. C
146. A 147. D 148. B 149. C 150. B 151. D 152. D 153. C 154. A 155. A
156. D 157. C 158. D 159. D 160. B 161. C 162. D 163. D 164. D 165. D
166. B 167. D 168. A 169. A 170. B 171. B 172. C 173. C 174. B 175. B
176. C 177. A 178. Bonus179. B 180. D
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 2
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
AITS-PT-03
Dropper Batch
PHYSICS Medical
1. In the ladder network shown, current through the resistor 3 is 0.25 A. The input voltage ‘V’ is equal to :
15
(A) 10 V (B) 20 V (C) 5 V (D) V
2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
2.
(A) 2R/3 (B) R/3 (C) 2R (D) 3 R
Hence the answer is (Bonus).
3. In the network shown in figure each resistance is 1 ohm. The effective resistance between P and Q is
R
R R
R R
P Q
R R
4 3 8
(A) (B) (C) 7 (D)
3 2 7
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 3
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
4. Arrange the order of power dissipated in the given circuits, if the same current is passing through the
system. The resistance of each resistor is ‘r’.
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(A) P2 > P3 > P4 > P1 (B) P1 > P4 > P3 > P2 (C) P1 > P2 > P3 > P4 (D) P4 > P3 > P2 > P1
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
5. A resistance of 2 is connected across one gap of a metre-bridge (the length of the wire is 100 cm) and
an unknown resistance, greater than 2 , is connected across the other gap. When these resistances are
interchanged, the balance point shifts by 20 cm. Neglecting any corrections, the unknown resistance is
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
6. Three rods A, B and C of same length and same cross-section area are joined as shown in the figure.
Their thermal conductivities are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 1.5. If the open ends of A and C are at 200°C and 18°C
respectively, the temperature at the junction of A and B in equilibrium is -
(A) 156oC (B) 116oC (C) 74oC (D) 148oC
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 4
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
7. Light of wavelength 3500 Å is incident on two metals A and B whose work functions are 4.2 eV and
1.9 eV respectively. Photoelectrons will be emitted by
(A) metal A only (B) metal B only (C) both A and B (D) none
The answer is (B).
8. The energy emitted per second by a black body at 1227ºC is E. If the temperature of the black body is
increased to 2727ºC, the energy emitted per second in terms of E is -
(A) 16 E (B) E (C) 4E (D) 2E
Solution :
The answer is (A).
9. If the radius of sun is Rs, radius of the orbit of earth about the sun is Re and is Stefan’s constant, then the
amount of radiations falling per second on a unit area of the earth’s surface is
2 2 2 2
Rs 4 Re 4 Rs Re T4
(A) T (B) T (C) 4 (D)
R
e R
s T Re Rs
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
10. A galvanometer has resistance 100 and it requires current 100µA for full scale deflection. A resistor
0.1 is connected in parallel to make it an ammeter. The smallest current required in the circuit to
produce the full scale deflection is:
(A) 1000.1 mA (B) 1.1 mA (C) 10.1 mA (D) 100.1 mA
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
11. In the figure shown the current through 2 resistor is
(A) 2A (B) 0A (C) 4A (D) 6A
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
12. In the given circuit, no current is passing through the galvanometer. If the cross-sectional diameter of the
wire AB is doubled, then for null point of galvanometer, the value of AC would be :
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 5
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
X
(A) 2 X (B) X (C) (D) None
2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
13. Two batteries of different emfs and different internal resistances are connected as shown. The voltage
across AB in volts is
(A) 1V (B) 2 V (C) 3V (D) 5V
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
14. In which of the following transitions will the wavelength be minimum in the case of hydrogen atom?
(A) n = 5 to n = 4 (B) n = 4 to n = 3 (C) n = 3 to n = 2 (D) n = 2 to n = 1
The answer is (D).
15. If potential energy of electron in the first excited state of hydrogen atom is taken to be zero then energy
of first excited state and that of the first line of Lyman series are respectively
(A) –3.4 eV, 10.2 eV (B) 3.4 eV, 10.2 eV (C) –3.4 eV, 3.4 eV (D) 3.4 eV, –3.4 eV
The answer is (B).
16. The de Broglie wavelength of an electron in the nth Bohr orbit is related to the radius R of the orbit as
3
(A) n = nR (B) n R (C) n = 2R (D) n = 4R
2
The answer is (C).
17. Three radioactive substances have their activity in the ratio 1 : 3 : 5. The substances are heated to double
its temperature. Then, the activity will be
(A) 5 : 3 : 1 (B) 3 : 1 : 5 (C) 3 : 5 : 1 (D) 1 : 3 : 5
The answer is (D).
18. Statement-1 : In a Meter Bridge experiment, null point for an unknown resistance is measured. Now, the
unknown resistance is put inside an enclosure maintained at a higher temperature. The null point can be
obtained at the same point as before by increasing the value of the standard resistance.
Statement-2 : Resistance of a metal increases with increase in temperature.
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 6
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Solution :
The answer is (A).
19. The effective resistance between points P and Q of the electrical circuit shown in the figure is :
2Rr 2R(R r) 5R
(A) (B) (C) 2r + 4R (D) 2r
Rr 3R r 2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
20. The resistance of a wire is 5 ohm at 50º C and 6 ohm at 100ºC. The resistance of the wire at 0ºC will be
(A) 2 ohm (B) 1 ohm (C) 4 ohm (D) 3 ohm
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
21. Shown in the figure below is a meter-bridge set up with null deflection in the galvanometer.
The value of the unknown resistor R is
(A) 220 (B) 110 (C) 55 (D) 13.75
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 7
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
22. If a wire is stretched to make it 0.2% longer, its resistance will :
(A) increase by 0.4% (B) increase by 0.2% (C) decrease by 0.2% (D) decrease by 0.05%
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
23. Two electric bulbs marked 25W – 220V and 100W – 220 V are connected in series to a 440V supply.
Which of the bulbs will fuse ?
(A) both (B) 100W (C) 25W (D) neither
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
24. In an electric circuit containing battery, the positive charge inside the battery : (If the battery acts as a
load)
(A) always goes from the positive terminal to the negative terminal
(B) may go from the positive terminal to the negative terminal
(C) always goes from the negative terminal to the positive terminal
(D) does not move.
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 8
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
25. A resistor of resistance R is connected to a cell of internal resistance 5 . The value of R is varied from
1 to 10 . The power consumed by R :
(A) increases continuously (B) decreases continuously
(C) first decreases then increases (D) first increases then decreases.
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
26. The efficiency of a cell when connected to a resistance R is 60%. What will be its efficiency if the
external resistance is increased to six times :
(A) 80 % (B) 90% (C) 55% (D) 95%
Solution :
The answer is (B).
27. The current i in the circuit of figure is -
1 1 1 1
(A) amp. (B) amp. (C) amp. (D) amp.
45 15 10 5
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
28. The ammeter shown in figure consists of a 480 coil connected in parallel to a 20 shunt. Find the
reading of the ammeter.
50 40 50 73
(A) A (B) A (C) A (D) A
73 53 93 50
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 9
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
29. Statement-1 : The current density J at any point in ohmic resistor is in direction of electric field E at
that point.
Statement-2 : A point charge when released from rest in a region having only electrostatic field always
moves along electric lines of force.
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
30. Statement-1 : Magnitude of potential difference across the terminals of a non-ideal battery in a circuit
cannot be greater than its emf.
Statement-2 : When a current of magnitude I is passing through a battery of emf E and internal resistance
r as shown, the magnitude of potential difference (V) across the battery is given by V = E– I r
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
31. Statement-1 : If potential difference between two points is non zero in an electric circuit, electric current
between those two points may be zero.
Statement-2 : Current always flows from high potential to low potential
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 10
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Statement-2 is wrong as in this case A is at high potential and B is at low potential and there is no current
from A to B. It also justifies Statement-1.
Hence the answer is (C).
32. In the figure shown :
(A) current will flow from A to B (B) current may flow from A to B
(C) current will flow from B to A (D) the direction of current will depend on r.
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
33. In a wire of cross section radius r, free electrons travel with drift velocity V when a current I flows
through the wire. What is the current in another wire of half the radius and of the same material when the
drift velocity is 2 V ?
(A) 2 I (B) I (C) I/2 (D) I/4
The answer is (C).
34. An electric bulb marked 40 W and 200 V, is used in a circuit of supply voltage 100 V. Now, its power is :
(A) 10 W (B) 20 W (C) 40 W (D) 100 W
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
35. A wire of length L is drawn such that its diameter is reduced to half of its original diameter. If the initial
resistance of the wire is 10 its new resistance would be :
(A) 40 (b) 80 (C) 120 (D) 160
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 11
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
36. In the figure shown the thermal power generated in ‘y’ is maximum when y = 4 . Then X is :
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 1 (D) 6
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
37. Power developed in a uniform wire when connected to a certain cell of negligible internal resistance is P.
If the wire is melted and recast in a wire of length double that of the original and the new wire is
connected to the same cell, then the power developed in the wire would be :
(A) 2 P (B) 4 P (C) P (D) P/4
The answer is (D).
38. In the circuit shown the readings of ammeter and voltmeter are 4A and 20V respectively. The meters are
non-ideal, then R is
(A) 5 (B) less than 5 (C) greater than 5 (D) between 4 and 5
The answer is (C).
39. A battery consists of variable number (n) of identical cells having internal resistance r each, connected in
series. The terminals of the battery are short-circuited and the current I measured. Which of the following
graphs gives correct relationship between I and n?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
The answer is (B).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 12
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
40. Two conducting wires of radius of cross section r and 2r respectively, made up of different materials are
having same current. If the densities of charge carriers in the two wires are in the ratio 1 : 4, then the drift
velocity of electrons in the two wires will be in the ratio :
(A) 1 : 1 (B) 2 : 1 (C) 4 : 1 (D) 16 : 1
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
41. A uniform wire of resistance R is stretched uniformly n times & then cut to form five identical wires.
These wires are arranged as shown in the figure. The effective resistance between A & B will be :
nR R n 2R n 2R
(A) (B) (C) (D)
5 5n 2 5 2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
42. A copper wire and an iron wire, each having an area of cross.section A and lengths L1 and L2 are joined
end to end. The copper end is maintained at a potential V 1 and the iron end at a lower potential V2. If 1
and 2 are the conductivities of copper and iron respectively, then the potential of the junction will be :
1V1 2 V2
1V1 2 V2 L1 L2
(A) ( / L ) ( / L ) (B)
1 1 2 2 1 / L1 2 / L 2
(1 / L1 ) (2 / L 2 ) 1V1 – 2 V2
(C) 1V1 2 V2 (D) ( / L ) ( / L )
1 1 2 2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 13
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
43. In figure-1 VB – VA = 12 V and in
In figure-2 VA – VB = 15 then choose the correct option.
If same battery is used in both the circuits
(A) = 12.6 V (B) = 13.2 V (C) = 13.6 V (D) = 14.0 V
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
44. Three indentical bulbs each of resistance 2 are connected as shown. The maximum power that can be
consumed by individual bulb is 32W, then the maximum power consumed by the combination is :
(A) 48 W (B) 96 W (C) 128 W (D) 160 W
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
45. Two spheres of radii r1 and r2 have densities 1 and 2 and specific heats s1 and s2 respectively. If they
are heated to the same temperature, then the ratio of their rates of coolling intially in the same surrounding
will be : (assume that both surface has same emisivity)
r22s2 r22s1 r11s1 r21s1
(A) r s (B) r s (C) r s (D) r s
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 1
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 14
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
AITS-PT-03
Dropper Batch CHEMISTRY Medical
46. How many grams of HCl should be dissolved in sufficient water to get 500 ml of an aqueous
solution of pH, 2.0 ?
(A) 0.01 (B) 0.005 (C) 0.1825 (D) 0.365
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
47. What is the pH of solution made by mixing equal volumes of 0.1 N–H2SO4, 0.1 N–HNO3, 0.1
N–HCl ?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
48. An aqueous solution is prepared by dissolving 0.1 mole H2CO3 in sufficient water to get 100 ml
solution at 25OC. For H2CO3, Ka1 = 4.0 10–6 and Ka2 = 5.0 10–11. The only incorrect
equilibrium concentration is
(A) [H+] = 6.32 10–4 M (B) [HCO 3 ] = 2 10–3 M
(C) [CO32–] = 5 10–11 M (D) [OH–] = 5 10–12 M
Hence the answer is (A).
49. For the reaction : 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g), Ho = 18 kcal and So = 30 cal/K at 300
K. The equilibrium constant, KPO of the reaction at 300 K is
(A) e15 (B) e–15 (C) e–18 (D) e–12
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 15
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
50. The equilibrium constant for the reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) is 4.0 10–4 at 2000 K. In
the presence of a catalyst, the equilibrium is attained 10 times faster. Therefore, the equilibrium
constant in presence of the catalyst at 2000 K is
(A) 4 10–3 (B) 4 10–5 (C) 4 10–4 (D) Unpredictable
Solution :
There will not be any affect on equilibrium constant.
Hence the answer is (C).
51. What is the approximate value of log KP for the reaction :
N 2 (g) 3H 2 (g) 2NH3 (g) at 25o C.
The standard enthlpy of formation of NH3(g) is –40.0 kJ/mol and standard entropies of N2(g),
H2(g) and NH3(g) are 191, 130 and 192 JK–1 mol–1, respectively.
(A) 0.04 (B) 7.05 (C) 8.6 (D) 3.73
Hence the answer is (D).
52. The equilibrium constants for the reaction: A 2 2A at 500 K and 1000 K are 1 10–10 and
1 10–5, respectively. The reaction is
(A) Exothermic (B) Very slow (C) Very fast (D) Endothermic
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 16
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
53. The progress of the reaction A nB, with time is represented by the graph given below..
The value of n is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Hence the answer is (B).
54. KP for the reaction: N2O4(g) 2NO2 is 640 mm at 775 K. The percentage dissociation of N2O4
at equilibrium pressure of 160 mm is
100 50
(A) (B) 50 (C) (D) 10 2
2 2
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 17
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
55. At a certain temperature, KP for the reaction: 2CO(g) CO2(g)+C (graphite) is 0.1 atm–1. What
is the ratio of partial pressure of CO and CO2 at equilibrium, taking the total pressure to be 1.1
atm ?
(A) 9 : 1 (B) 10 : 1 (C) 1 : 10 (D) 1 : 9
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 18
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
56. An aqueous solution of volume 500 ml, when the reaction: 2Ag+(aq) + Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) +
2Ag(s), reached equilibrium, the concentration of Cu2+ ions was x M. To this solution, 500 ml of
water is added. At the new equilibrium, the concentration of Cu2+ ions would be
(A) 2x M (B) x M (C) between x and 0.5x M (D) less than 0.5x M
Hence the answer is (D).
57. Attainment of the equilibrium A(g) 2C (g) + B(g) gave the following graph. Find the correct
option. (% dissociation = fraction dissociated 100)
(A) At t = 5 sec equilibrium has been reached and Kc = 40 (mol/litre)2
(B) At t = 5 sec equilibrium has been reached and % dissociation of A is 20%
(C) At t = 5 sec equilibrium has been reached and % dissociation of A is 30%
(D) None of these
Solution :
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 19
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Hence the answer is (B).
58. At 527oC, the reaction given below has Kc = 4
1 3
NH 3 (g) N 2 (g) H 2 (g)
2 2
What is the Kp for the reaction?
N 2 (g) 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g)
2 2
2 800R 1
(A) 16 (800 R) (B) (C) (D) None of these
4 4 800R
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
59. The equilibrium constant for the reaction N 2 (g) O2 (g) 2NO(g) at temperature (T) is
1 1
4 104 . The value of Kc for the reaction NO(g) N 2 (g) O 2 (g) at the same
2 2
temperature is :
(A) 4 104 (B) 50 (C) 2.5 102 (D) .02
Solution :
Hence the answer is (B).
60. For the equilibrium SO 2Cl2 (g) SO 2 (g) Cl2 (g), what is the temperature at which
K p (atm)
3?
K c (M)
(A) 0.027 K (B) 0.36 K (C) 36.54 K (D) 273 K
Hence the answer is (C).
61. Consider the following gaseous equilibria given below :
I) N2 + 3H2 2NH3; Eqm. Constant = K1
II) N2 + O2 2NO; Eqm. Constant = K2
1
III) H 2 O 2 H2O; Eqm. Constant = K3
2
5
The equilibrium constant for the reaction, 2NH 3 O 2 2NO 3H 2O in terms of K1, K2
2
and K3 will be :
K1K 2 K1K 32 K 2 K 33
(A) K1 K2 K3 (B) (C) (D)
K3 K2 K1
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 20
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Hence the answer is (D).
62. 9.2 grams of N2O4(g) is taken in a closed one litre vessel and heated till the following equilibrium
is reached N2O4(g) 2NO2(g)
At equilibrium, 50% N2O4(g) is dissociated. What is the equilibrium constant (in mol litre–1)
(molecular mass of N2O4=92)
(A) 0.1 (B) 0.4 (C) 0.2 (D) 2
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
63. In the presence of excess of anhydrous SrCl2, the amount of water taken up is governed by
Kp=1012 atm–4 for the following reaction at 273 K
SrCl2 . 2H2O(s) + 4H2O(g) SrCl2 . 6H2O(s)
What is equilibrium vapour pressure (in torr) of water in a closed vessel that contains SrCl2 .
2H2 O(s)?
(A) 0.001 torr (B) 103 torr (C) 0.76 torr (D) 1.31 torr
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
64. I2 (aq) I (aq) I3 (aq). We started with 1 mole of I2 and 0.5 mole I– in one litre flask.
After equilibrium is reached, excess of AgNO3 gave 0.25 mole of yellow precipitate. Equilibrium
constant is :
(A) 1.33 (B) 2.66 (C) 2.0 (D) 3.0
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 21
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
65. In a system A(s) 2B(g) 3C(g), if the concentration of C at equilibrium is increased by a
factor of 2, it will cause the equilibrium concentration of B to change to :
(A) two times the original value (B) one half of its original value
1
(C) 2 2 times to the original value (D) times the original value
2 2
Hence the answer is (D).
66. When heated, ammonium carbamate decomposes as follows :
NH 4COONH 2 (s) 2NH 3 (g) CO 2 (g)
At a certain temperature, the equilibrium pressure of the system is 0.318 atm. Kp for the reaction
is :
(A) 0.128 (B) 0.426 (C) 4.76 10 3 (D) None of these
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
67. COCl2 gas dissociates according to the equation, COCl2(g) CO(g)+Cl2(g). When heated to 700
K the density of the gas mixture at 1.16 atm and at equilibrium is 1.16 g/litre. The degree of
dissociation of COCl2 at 700 K is :
(A) 0.28 (B) 0.50 (C) 0.72 (D) 0.42
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
68. Determine the value of equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction
A 2 (g) B2 (g) 2AB(g)
if 10 moles of A2, 15 moles of B2 and 5 moles of AB are placed in a 2 litre vessel and allowed
to come to equilibrium. The final concentration of AB is 7.5 M :
(A) 4.5 (B) 1.5 (C) 0.6 (D) None of these
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 22
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
69. For the dissociation reaction N2O4(g) 2NO2(g), the degree of dissociation ( ) in terms of Kp
and total equilibrium pressure P is
4P K P KP KP
(A) (B) (C) (D) None of these
KP 4P K P 4P
Hence the answer is (B).
1
70. AB3(g) is dissociates as AB3(g) AB2(g)+ B2(g).
2
When the initial pressure of AB3 is 800 torr and total pressure developed at equilibrium is 900
torr, what fraction of AB3(g) is dissociated?
(A) 10% (B) 20% (C) 25% (D) 30%
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
71. For the reaction : N 2 (g) 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g); H 93.6 kJ mol–1
The number of moles of H2 at equilibrium will increase if :
(A) volume is increased (B) volume is decreased
(C) argon gas is added at constant volume (D) NH3 is removed
Solution :
Volume increase leads the reaction to move towards more gaseous moles.
Hence the answer is (A).
72. Some inert gas is added at constant volume to the following reaction at equlibrium
NH4HS(s) NH3(g) + H2S(g)
Predict the effect of adding the inert gas :
(A) The equilibrium shifts in the forward direction
(B) The equilibrium shifts in the backward direction
(C) The equilibrium remains unaffected
(D) The value of Kp is increased
Solution :
Addition of inert gas at constant volume has no effect.
Hence the answer is (C).
73. For which of the following reaction is product formation favoured by low pressure and low
temperature?
(A) CO2(g)+C(s) 2CO(g); H o 172.5kJ (B) CO(g)+2H2(g) CH3OH; Ho – 21.7kJ
(C) 2O3(g) 3O2(g); H o –285 kJ (D) H2(g)+F2(g) 2HF(g); H o –541 kJ
Solution :
Forward reaction must be exothermic with more gaseous moles at product side.
Hence the answer is (C).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 23
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
74. Consider the following reactions at equilibrium and determine which of the indicated changes will
cause the reaction to proceed to the right.
(1) CO(g)+3H2(g) CH4(g)+H2O(g) (add CH4)
(2) N2(g)+3H2(g) 2NH3(g) (remove NH3)
(3) H2(g)+F2(g) 2HF(g) (add F2)
(4) BaO(s)+SO3(g) BaSO4(s) (add BaO)
(A) 2, 3 (B) 1, 4 (C) 2, 4 (D) 2, 3, 4
Hence the answer is (A).
75. A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
the reaction must be :
(A) Exothermic (B) Endothermic
(C) One with negligible enthalpy change (D) Highly spontaneous at ordinary temperature
Solution :
For endothermic; H < 0 Slope is negative
Hence the answer is (A).
76. Kp has the value of 10–6 atm3 and 10–4 atm3 at 298 K and 323 K respectively for the reaction
CusO 4 .3H 2O(s) CuSO4 (s) 3H 2O(g) r H o for the reaction is :
(A) 7.7 kJ/mol (B) –147.41 kJ/mol (C) 147.41 kJ/mol (D) None of these
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
77. The most stable oxides of nitrogen will be :
(A) 2NO2(g) N2(g) + 2O2(g); K = 6.7 1016 mol L–1
(B) 2N2O5(g) 2N2(g) + 5O2(g); K = 1.2 1024 mol5 L–5
(C) 2NO(g) N2(g) + O2(g); K = 2.2 1030
(D) 2N2O(g) 2N2(g) + O2(g); K = 3.5 1033 mol L–1
Solution :
The value of Keq is the measure of extent of reaction. For most stable oxide K eq should be
minimum.
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 24
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
78. Solid Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as
Ca(HCO3 )2 (s) CaCO3 (s)+CO2 (g)+H2 O(g)
If the total pressure is 0.2 bar at 420 K, what is the standard free energy change for the given
reaction ( r G o ) ?
(A) 840 kJ/mol (B) 3.86 kJ/mol (C) 6.98 kJ/mol (D) 16.083 kJ/mol
Solution :
Hence the answer is (D).
79. One mole of N2(g) is mixed with 2 moles of H2(g) in a 4 litre vessel. If 50% of N2(g) is
converted to NH3(g) by the following reaction:
N2(g)+3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
What will be the value of Kc for the following equilibrium?
1 3
N H 3 (g) N 2 (g ) H 2 (g)
2 2
1
(A) 256 (B) 16 (C) (D) None of these
16
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
80.
The gas A2 in the left flask allowed to react with gas B2 present in right flask as A2(g) +
B2(g) 2AB(g); Kc = 4 at 27oC. What is the concentration of AB when equilibrium is
established ?
(A) 1.33 M (B) 2.66 M (C) 0.66 M (D) 0.33 M
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 25
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
Solution :
Hence the answer is (C).
81. Two solid compounds X and Y dissociates at a certain temperature as follows
X(s) A(g) 2B(g); K P1 9 103 atm3
Y(s) 2B(g) C(g); KP2 4.5 103 atm3
The total pressure of gases over a mixture of X and Y is :
(A) 4.5 atm (B) 0.45 atm (C) 0.6 atm (D) None of these
Solution :
Let x is partial pressure of A and y is partial pressure of C when both equilibrium simultaneously
established in a vessel
Hence the answer is (B).
82. The thermal dissociation equilibrium of CaCO3(s) is studied under different conditions
CaCO3 (s) CaO(s) CO 2 (g). For this equilibrium, then incorrect statement(s) is (are)
(A) H is dependent on T
(B) K is independent of the initial amount of CaCO3
(C) K is dependent on the pressure of CO2 at a given T
(D) H is independent of catalyst, if any
Solution :
K is dependent on temperature. But not pressure.
Hence the answer is (C).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 26
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
83. The % yield of ammonia as a function of time in the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g),
H 0 at (P, T1) is given below
If this reaction is conducted at (P, T2), with T2>T1, the % yield of ammonia as a function of time
is represented by
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Solution :
Initially on incresing temperature rate of reaction will increase, so % yield will also increase with
time. But at equilibrium % yield at high temperature (T 2) would be less than at T 1 as reaction is
exothermic so the graph is
Hence the answer is (B).
84. At constant temperature, the equilibrium constant (Kp) for the decomposition reaction
N2O4 2NO2 is expressed by Kp = (4x2P)/ (1–x2), where P = pressure, x = extent of
decomposition. Which one of the following statements is true ?
(A) Kp increases with increase of P (B) Kp increases with increase of x
(C) Kp increases with decrease of x (D) Kp remains constant with change in P and x
Solution :
At constant temperature Kp pressure constant. With change of pressure, x will change in such a
way that Kp remains a constant.
Hence the answer is (D).
85. The pH of a solution is 5. To this solution acid was added so that its pH value becomes 2.0. The
increase in H+ concentration is
(A) 100 times (B) 5 times (C) 2.5 times (D) 1000 times
Hence the answer is (D).
86. A solution has a pH = 9, it is 1000 times more basic than the original solution. What was the pH
of the original solution ?
(A) 12 (B) 6 (C) 9 (D) 10
Hence the answer is (B).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 27
AITS-PT # 03 (Solutions) (Medical Dropper) (SET-A) - 2017-18
87. Equal volumes of two HCl solutions of pH = 3 and pH = 5 were mixed. What is the pH of the
resulting solution ?
(A) 3.5 (B) 4.0 (C) 4.5 (D) 3.3
Solution :
When equal volumes are taken, the concentration becomes half.
Hence the answer is (D).
88. What is the percent ionization () of a 0.01 M HA solution ? (Ka = 10–4)
(A) 9.5% (B) 1% (C) 10.5% (D) 17%
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
89. Given the two concentration of HCN (Ka = 10–9) are 0.1 M and 0.001 M respectively. What will
be the ratio of degree of dissociation ?
(A) 1 (B) 0.1 (C) 0.003 (D) 0.01
Hence the answer is (B).
90. The [H+] of a resulting solution that is 0.01 M acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 × 10–5) and 0.01 M in
benzoic acid (Ka = 6.3 × 10–5)
(A) 9 × 10–4 (B) 81 × 10–4 (C) 9 × 10–5 (D) 2.8 × 10–3
Solution :
Hence the answer is (A).
Potential Coaching Institute PVT LTD Page. 28
You might also like
- WBJEE 2016 Solution Phy ChemDocument24 pagesWBJEE 2016 Solution Phy ChemAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Solutions: With Answer KeyDocument29 pagesSolutions: With Answer KeygorantlaatchyutakumarNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2019Document42 pagesFiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2019Kalai VananNo ratings yet
- 1 Jeem 2023 April 06 First Shift PaperDocument39 pages1 Jeem 2023 April 06 First Shift PaperSURAKSHA PATELNo ratings yet
- XI N.M. Major Test - 5 Key & Sol. PAPER - 1 (04-03-2024)Document29 pagesXI N.M. Major Test - 5 Key & Sol. PAPER - 1 (04-03-2024)Luv KaushikNo ratings yet
- 3 RdtermexamDocument8 pages3 RdtermexamAngelina LumbreNo ratings yet
- DPP-10-1 11 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesDPP-10-1 11 2019 PDFYasas MohantyNo ratings yet
- TEST - 2A (Paper-2) - Code-E All India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2019Document18 pagesTEST - 2A (Paper-2) - Code-E All India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2019RumiNo ratings yet
- AIATS JEE (A) 2022 Test-4A P-2 (Code-B) Sol FINALDocument12 pagesAIATS JEE (A) 2022 Test-4A P-2 (Code-B) Sol FINALAkshanda AludiyaNo ratings yet
- Wbjee 2018 Physics Chemistry SolutionDocument24 pagesWbjee 2018 Physics Chemistry SolutionPartha sarathi mannaNo ratings yet
- 2010 To 2023 - CompressedDocument826 pages2010 To 2023 - Compressedvasudevbajwa10bNo ratings yet
- Answers: FULL TEST 08 (Paper I) SolutionsDocument16 pagesAnswers: FULL TEST 08 (Paper I) Solutionstest1234No ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2009 Paper 1 Unsolved PDFDocument21 pagesIIT JEE 2009 Paper 1 Unsolved PDFDanish JunejaNo ratings yet
- 21-04-24 - ISR - IIT - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-B - Jee-Main - CTM-36 - KEY & SOLDocument16 pages21-04-24 - ISR - IIT - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-B - Jee-Main - CTM-36 - KEY & SOLjofofaf427No ratings yet
- P 7 X FDDda B3 GD8 TH RNF PiDocument17 pagesP 7 X FDDda B3 GD8 TH RNF PiGingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- Maths - Prelim PaperDocument36 pagesMaths - Prelim PaperKrishangi SinghNo ratings yet
- AIATS JEE (A) 2022 Test-1A P-2 (Code-F) 06-12-2020 SOLDocument9 pagesAIATS JEE (A) 2022 Test-1A P-2 (Code-F) 06-12-2020 SOLsonali.mukeNo ratings yet
- All India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2022: TEST - 1A (Paper-1) - Code-EDocument9 pagesAll India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2022: TEST - 1A (Paper-1) - Code-ENITIN NBNBNo ratings yet
- SSC-II Math Final PackageDocument9 pagesSSC-II Math Final Packageemaansadiq5No ratings yet
- Aops Community 1993 Amc 12/ahsmeDocument7 pagesAops Community 1993 Amc 12/ahsmeQFDqNo ratings yet
- Q.paper JEE Main 2019 Mock Test 5Document18 pagesQ.paper JEE Main 2019 Mock Test 5Utkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Aiats Jee Advancedaaasd Two Yrs 2017 Test 2 PDFDocument18 pagesAiats Jee Advancedaaasd Two Yrs 2017 Test 2 PDFJalaj LabanaNo ratings yet
- GATE Previous Year Solved Papers Mechanical PDFDocument229 pagesGATE Previous Year Solved Papers Mechanical PDFRandy LeeNo ratings yet
- RSPL 01 - Class 10 (STND)Document12 pagesRSPL 01 - Class 10 (STND)mondalkakoli83No ratings yet
- 6 JSG4 P Ss WT KN AWJh Eq 68Document22 pages6 JSG4 P Ss WT KN AWJh Eq 68Gingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- ODocument2 pagesOElaiza Araquel100% (1)
- Ldce - Ee - 08Document10 pagesLdce - Ee - 08Nilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 Jeem 2023 April 06 First Shift PaperDocument39 pages1 Jeem 2023 April 06 First Shift Paperaruna.kandikattu09No ratings yet
- Inter Class Math Quiz 2015Document5 pagesInter Class Math Quiz 2015jesudassajNo ratings yet
- 8 April Shift 1Document40 pages8 April Shift 1HimanshuNo ratings yet
- 81E-B Version - SEP - 2Document31 pages81E-B Version - SEP - 2Manasa HarshaNo ratings yet
- Target: Jee (Advanced) 2019: DPP No. # 1Document6 pagesTarget: Jee (Advanced) 2019: DPP No. # 1Alpha BetaNo ratings yet
- Eneral Ptitude Q. No. 1 - 5 Carry One Mark EachDocument18 pagesEneral Ptitude Q. No. 1 - 5 Carry One Mark EachGingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- 2011-GP Read Instructions On The Left Side of This Page Carefully 2011-GPDocument39 pages2011-GP Read Instructions On The Left Side of This Page Carefully 2011-GPacNo ratings yet
- GATE 2022 General Aptitude (GA)Document36 pagesGATE 2022 General Aptitude (GA)janakNo ratings yet
- 81-E PR PDFDocument44 pages81-E PR PDFkuldeep kumbharNo ratings yet
- 81-E PR PDFDocument44 pages81-E PR PDFRamesh fernandesNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For NTSE (Stage-I) 2019-20Document16 pagesQuestions & Answers: For NTSE (Stage-I) 2019-20Shona KhattarNo ratings yet
- All India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2022 TEST - 4A (Paper-2) - Code-FDocument8 pagesAll India Aakash Test Series For JEE (Advanced) - 2022 TEST - 4A (Paper-2) - Code-FNITIN NBNB100% (1)
- Answer Keys For Cpt-1 Dropper Medical (Code-A) : Answers (Physics)Document3 pagesAnswer Keys For Cpt-1 Dropper Medical (Code-A) : Answers (Physics)ashaNo ratings yet
- Circle The Correct Letter of The AnswerDocument6 pagesCircle The Correct Letter of The AnswerKarl FerrerNo ratings yet
- Kvpy-2014 QDocument10 pagesKvpy-2014 QikeaNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS JEE (Adv) - 2018 Test-1 Paper-2 (Code-C & D) (16!07!2017) XII StudyingDocument20 pagesSolutions AIATS JEE (Adv) - 2018 Test-1 Paper-2 (Code-C & D) (16!07!2017) XII StudyingdakshNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Jee Main PaperDocument29 pagesFiitjee Jee Main PaperKratosNo ratings yet
- 2012 H2 DC Circuits Tutorial (Tutor)Document15 pages2012 H2 DC Circuits Tutorial (Tutor)Wee Chee LimNo ratings yet
- TCS-NQT - Question-Paper - 3Document30 pagesTCS-NQT - Question-Paper - 3headtpoNo ratings yet
- Key Answer - 81e - ADocument32 pagesKey Answer - 81e - AAditya RamNo ratings yet
- Karnataka SSLC New Pattern MCQ Model Question Papers Set 2 - Maths (English Medium)Document5 pagesKarnataka SSLC New Pattern MCQ Model Question Papers Set 2 - Maths (English Medium)Supriya A SNo ratings yet
- 81E-C VersionDocument12 pages81E-C VersionBhashyavi BossNo ratings yet
- DPP (42-44) 12th Physics - E - WADocument6 pagesDPP (42-44) 12th Physics - E - WAMeena ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PDFDocument7 pagesMathematics PDFOkhare PaulNo ratings yet
- Phase Test-2 B Lot Answer KeysDocument3 pagesPhase Test-2 B Lot Answer KeysComputer GuyNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 10th Edition Sullivan Test Bank DownloadDocument212 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 10th Edition Sullivan Test Bank DownloadGeraldine Shipman100% (28)
- Panini-80 C-Lot Ph-2 Answer Keys All PaperDocument3 pagesPanini-80 C-Lot Ph-2 Answer Keys All PaperComputer GuyNo ratings yet
- 1719 BC Lot Class-11 Phase-3 Answer KeysDocument3 pages1719 BC Lot Class-11 Phase-3 Answer Keysamrit dasNo ratings yet
- Turn To Section 2 (Page 4) of Your Answer Sheet To Answer The Questions in This SectionDocument13 pagesTurn To Section 2 (Page 4) of Your Answer Sheet To Answer The Questions in This SectionMohamed MoselhyNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Question Paper Jan 29 Shift 2Document13 pagesJEE Main 2024 Question Paper Jan 29 Shift 2Nagasuraj BussaNo ratings yet
- Jee 5 - Class XiiDocument3 pagesJee 5 - Class XiiSoumya Ranjan NaikNo ratings yet
- Nmms2017 GujaratDocument16 pagesNmms2017 Gujaratvikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology MCQ PDF 1Document8 pagesBiology MCQ PDF 1Shubham MishraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PDFDocument19 pagesNutrition PDFRia SriNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PDFDocument19 pagesNutrition PDFRia SriNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PDFDocument19 pagesNutrition PDFRia SriNo ratings yet
- Aipmt Biology Sample PaperDocument20 pagesAipmt Biology Sample PaperRia SriNo ratings yet
- Xii PMT Adm Test QPDocument7 pagesXii PMT Adm Test QPRia SriNo ratings yet
- NeuralDocument4 pagesNeuralRia SriNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation-1Document48 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation-1Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Biology Mcqs 12Document5 pagesBiology Mcqs 12R.S.H100% (3)
- Living WorldDocument4 pagesLiving WorldRia SriNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Unit 1 Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesClass 12 Biology Unit 1 Assignment PDFRia SriNo ratings yet
- Xi Sem-I Biology Microbes in Human Welfare 2-11-2017Document5 pagesXi Sem-I Biology Microbes in Human Welfare 2-11-2017Ria SriNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Evolution Introduction AksDocument2 pagesDPP 1 Evolution Introduction AksRia SriNo ratings yet
- NCACDocument4 pagesNCACRia SriNo ratings yet
- Immunology 1Document3 pagesImmunology 1Ria SriNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologyRia SriNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Important Questions For Biology AssignmentDocument4 pagesClass 11 Important Questions For Biology AssignmentRia SriNo ratings yet
- Humoral Immunity 2Document1 pageHumoral Immunity 2Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Immunology 3Document1 pageImmunology 3Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Power Exercise 2A Immunology: AnswerDocument1 pagePower Exercise 2A Immunology: AnswerRia SriNo ratings yet
- One Marks Questions: by Dr. Atin Kumar SrivastavaDocument5 pagesOne Marks Questions: by Dr. Atin Kumar SrivastavaRia SriNo ratings yet
- Adolescence: Curiosity Motivates Him/her To Experiment. This Is Complicated Further by Effects That Might BeDocument2 pagesAdolescence: Curiosity Motivates Him/her To Experiment. This Is Complicated Further by Effects That Might BeRia SriNo ratings yet
- Human Health and Disease Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark Each)Document3 pagesHuman Health and Disease Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark Each)Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Humoral Immunity 1Document1 pageHumoral Immunity 1Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Humoral Immunity 1Document1 pageHumoral Immunity 1Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Conceptual QuestionsDocument3 pagesKinematics Conceptual QuestionsAbhi 7No ratings yet
- DPP - 1 - Buccal Cavity PART 4Document5 pagesDPP - 1 - Buccal Cavity PART 4Ria SriNo ratings yet
- Srinivasa Ramanujan - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesSrinivasa Ramanujan - Britannica Online EncyclopediaEvariste MigaboNo ratings yet
- College Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Document2 pagesCollege Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Sandeep DeyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesCell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisAmr NasserNo ratings yet
- English Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDocument3 pagesEnglish Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDaffa RaihanNo ratings yet
- Review Systems of Linear Equations All MethodsDocument4 pagesReview Systems of Linear Equations All Methodsapi-265647260No ratings yet
- Part 1. Question 1-7. Complete The Notes Below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER For Each AnswerDocument13 pagesPart 1. Question 1-7. Complete The Notes Below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER For Each Answerahmad amdaNo ratings yet
- Movie Review of THORDocument8 pagesMovie Review of THORSiva LetchumiNo ratings yet
- R35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersDocument13 pagesR35 Credit Analysis Models - AnswersSakshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimNo ratings yet
- MELASMA (Ardy, Kintan, Fransisca)Document20 pagesMELASMA (Ardy, Kintan, Fransisca)Andi Firman MubarakNo ratings yet
- Why You MeDocument18 pagesWhy You MeFira tubeNo ratings yet
- List of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDocument2 pagesList of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDiptangshu DeNo ratings yet
- Calculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementDocument52 pagesCalculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementNavice Kie100% (1)
- Sample Hum RepDocument21 pagesSample Hum RepPritam PiyushNo ratings yet
- Check List For Design Program of A Parish ChurchDocument11 pagesCheck List For Design Program of A Parish ChurchQuinn HarloweNo ratings yet
- THE Ketofeed Diet Book v2Document43 pagesTHE Ketofeed Diet Book v2jacosta12100% (1)
- Module 1Document64 pagesModule 1Jackyson RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIDocument18 pagesReviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIAngelica Faye95% (20)
- 7 ApportionmentDocument46 pages7 Apportionmentsass sofNo ratings yet
- Ijrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentDocument19 pagesIjrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentAbhay RanaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Document3 pagesENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Analiza Dequinto BalagosaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Core ConceptsDocument2 pagesNeuroscience Core Conceptseglantina alishollariNo ratings yet
- Musk Founded Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, or Spacex, in 2002 With TheDocument4 pagesMusk Founded Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, or Spacex, in 2002 With TheLauren Harris0% (1)
- Electric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. Kosow PDFDocument413 pagesElectric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. Kosow PDFzcjswordNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For ExcavationDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment For ExcavationAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Sample Engagement LetterDocument5 pagesSample Engagement Letterprincess_camarilloNo ratings yet
- Memo ALS Literacy MappingDocument4 pagesMemo ALS Literacy MappingJEPH BACULINANo ratings yet
- Rotc Reviewer FinalsDocument11 pagesRotc Reviewer FinalsAngel Atienza100% (1)
- Van Daley - Leadership ResumeDocument1 pageVan Daley - Leadership Resumeapi-352146181No ratings yet
- AMX Prodigy Install ManualDocument13 pagesAMX Prodigy Install Manualsundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pharmaceutical Blending and MixingFrom EverandPharmaceutical Blending and MixingP. J. CullenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Operational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueFrom EverandOperational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyFrom EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersFrom EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesFrom EverandThe HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet