Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ischemic Heart Disease
Uploaded by
Nurul Aqilah MazlanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ischemic Heart Disease
Uploaded by
Nurul Aqilah MazlanCopyright:
Available Formats
ISCHEMIC
HEART DISEASE/ CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
IHD/CAD is a condition in which there is inadequate supply and demand of blood and
oxygen to a portion of the myocardium
IHD/CAD can be presented as:
• Chronic coronary artery disease (CCAD): Stable angina
• Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS)
o Non ST-‐segment Elevation (NSTEACS)
§ Unstable angina
§ NSTEMI
o ST-‐segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
• Others: asymptomatic ( DM,HTN, elderly, females)
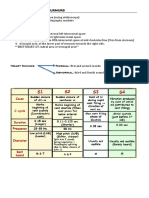
CCAD ACS
Stable Angina NSTEACS STEMI
Unstable Angina NSTEMI
Pathophysio Stable fixed Sudden plaque rupture> Sudden plaque rupture> Sudden plaque rupture>
atherosclerotic plaque partial occlusion partial platelet+partial partial platelet+complete
(platelet aggregation) thrombus occlucion acclusive thrombus
-Rest angina
-New onset
-Post infarct angina
-Post coronary
procedure angina
Characteristics Heavy, Tightness, Aching, Burning Heavy, crushing, burning
Sites Deep retrosternal Deep retrosternal
Radiation Lower jaw, neck, arm(left 20x common), epigastrium, interscapular and back
Relieving & A-With exertion Occur at rest
aggravating R- Rest & Not relieved by nitroglycerine
nitroglycerine
Duration Avg 3-5 mins > 15-20 mins
Associated Strangling in throat Pallor, nause, vomiting, sweating, dyspnea, syncope
symptoms
PE S3 during attack Cold, clammy, muffled heart sound, gallop rhythm,
systolic murmur (MVP), basal crackles
ECG Normal Low risk: Normal NSTEMI: ST depression, no Q waves,T wave
High risk: ST inversion
depression, T wave STEMI: +/- Deep Qwaves, T wave inversion, ST
inversion or tall upright elevation. Associated with LBBB/WPW/ Ven Tach
T waves
Cardiac Enzymes - -Troponin I/T: Non -Troponin I/T: Detectable
*Sequence of detectable in low risk, -CK: Elevated
elevated detectable in high risk
biomarkers- Trop- -CK: normal
T,CKMB,AST,LDH
*CKMB- useful for
reinfarction MI
*Troponin I most
specific
Special definitive ECG ECG
dx test Coronary angiography (strong +ve stress exercise Cardiac enzymes
ECG, resistant to medical treatement, angina after Technetium pyrophosphate scanning (posterolateral
MI, suspected angina, suspected left main AMI_
coronary artery disease) Echo (early stage MI/other test not diagnose)
Coronary angiography
Management -Medical First line (Outside hospital)
*acute attack - Perform ECG; clasify ACS
#Nitroglycerine/ -Oxygen 4-6L/min
nifedipine-CCB -Secure IV line (draw blood for cardiac enzyme)
#Aspirin -Nitroglycerine (every 5 min- take ½ intially, maximum 3 tab in 15 mins)
*Mild (predictable -Aspirin
with stressful -Morphine (IV statim bolus; 1mg/min until pain relief up to 15mg)
activities)
#Nitroglycerin * Re-establish flow *Re-establish flow
#Aspirin/ clopidogrel -PCI /Angioplasty with stent ( thrombolytic -Thrombolytic
#consider Beta theraphy not benefit) theraphy; door to
blocker/ long acting -CABG needly time <30 min
nitrate/ nicorandil *other same as STEMI -PCI /Angioplasty;
*Moderate #complications of angiopplasty door to balloon time
(predictable with -acute coronary occlusion <90min; >12 hours not
moderate exercise) -restenosis recommended
# add beta blocker -CABG
*Persistent (not #Stent patients require long term antiplatelet
prevented by beta (aspirin+clopidogrel) *Adjunct theraphy
blocker) -aspirin/ clopidogrel
#add dihydropyridine -heparin for 24-36 h
CCB #Indications for CABG:
• Over 50% left main coronary artery stenosis after rt-PA(not after
-Non-medical streptokinase)
*PCI/Angioplasty • Over 70% stenosis of the proximal left - +/- glycoprotein
with stent anterior descending (LAD) and proximal IIb/IIIa platelet
*CABG circumflex arteries inhibitor
• Three-vessel disease in asymptomatic patients
or those with mild or stable angina *Beta blocker + ACE
• Three-vessel disease with proximal LAD inhibitor
*Statin
stenosis in patients with poor left ventricular
(LV) function
• One- or two-Vessel disease and a large area of
viable myocardium in high-risk area in
patients with stable angina
• Over 70% proximal LAD stenosis with either
an ejection fraction (EF) below 50% or
demonstrable ischemia on noninvasive testing
Others Causes of angina: Types: Complications
Coronary artery -Nocturnal angina STEMI:
atheroma -Decubitus angina: occurs 0-24 hours
Valvular lesions when lying down, relieved by -Acute LV failure
Arrhythmia sitting up -Cardiogenic shock
Anemia -Variant/ Prinzmental angina- -Arrhythmia
Vasculitis due to coronary artery spasm
Trauma 1-3 days
Collagen disease -Pericarditis
3-14 days
-Venticuar septal
rupture & Mitral valve
papillary rupture
2 weeks-several month
-Post-AMI syndrome
(Dresler syndrome)
-LV aneurysm
Aqilah Mazlan
You might also like
- 7th Heart Sounds and MurmursDocument6 pages7th Heart Sounds and MurmursbabibubeboNo ratings yet
- Heart Murmurs Topic Review - From Description To AuscultationDocument15 pagesHeart Murmurs Topic Review - From Description To AuscultationRapmle PrasadNo ratings yet
- ECG ReviewDocument146 pagesECG ReviewThea DinoNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Complaint Emergency HandbookDocument306 pagesComplaint Emergency HandbookUsman Amjad100% (3)
- Cardiac MurmursDocument53 pagesCardiac MurmursdrgashokNo ratings yet
- Principles Auscultatory Areas: ND NDDocument5 pagesPrinciples Auscultatory Areas: ND NDPinay YaunNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular History: Chest PainDocument5 pagesCardiovascular History: Chest PainTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- Pathology of the Heart: Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac DeathDocument11 pagesPathology of the Heart: Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac DeathIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionDocument11 pagesDiagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionPauline Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument13 pagesCommon Medical Abbreviationsohio770No ratings yet
- Study Guide for Basic Clinical Cardiology ExamDocument59 pagesStudy Guide for Basic Clinical Cardiology ExamsugisweNo ratings yet
- Patho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Document12 pagesPatho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Grant GarcesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Document6 pagesCardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Jc MacujaNo ratings yet
- HEENT Cheat SheetDocument22 pagesHEENT Cheat SheetKatrina FeriNo ratings yet
- Radiology Chest X-Ray GuideDocument21 pagesRadiology Chest X-Ray GuideDawn MedranoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MurmursDocument28 pagesCardiac MurmursAlvin BlackwellNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideDocument32 pagesPneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideYan Sheng HoNo ratings yet
- Heart MurmursDocument16 pagesHeart MurmursPriyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1Document34 pagesArrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1preethi preethaNo ratings yet
- OSCEs SyllabusDocument133 pagesOSCEs SyllabusAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Lab: Pathology of The HeartDocument8 pagesPathology - Lab: Pathology of The HeartRazel PerezNo ratings yet
- Recognize Valvular Heart Diseases and Their Clinical FeaturesDocument8 pagesRecognize Valvular Heart Diseases and Their Clinical FeaturesRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- Sprint Interval TrainingDocument49 pagesSprint Interval TrainingAdam Weaver100% (1)
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Document8 pagesEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The man who wins is the man who thinks he canDocument51 pagesThe man who wins is the man who thinks he cankays30002403No ratings yet
- Definition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults (UPTODATE)Document17 pagesDefinition, Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Shock in Adults (UPTODATE)Annie K.No ratings yet
- Oncologic Emergencies Management GuideDocument5 pagesOncologic Emergencies Management GuideAra DiocosNo ratings yet
- 6 Head and Neck Trauma - Thoracic and Cardiovascular TraumaDocument7 pages6 Head and Neck Trauma - Thoracic and Cardiovascular TraumaMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Summary PDFDocument62 pagesCardiology Summary PDFSyamsuriWahyuNo ratings yet
- BURNS - Surgery Trans2Document9 pagesBURNS - Surgery Trans2JAMPTNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Angina Assessment and TreatmentDocument12 pagesAngina Assessment and TreatmentYasser AhmedNo ratings yet
- History Taking: Item DescriptionDocument22 pagesHistory Taking: Item DescriptionBikash Sah100% (1)
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesCongenital Heart Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Practice Questions: CHF, APGAR test, ultrasound safetyDocument37 pagesPractice Questions: CHF, APGAR test, ultrasound safetyGeo Navarro100% (1)
- Physiology and Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument29 pagesPhysiology and Cardiovascular System ReviewAssale Maen100% (1)
- Therapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDocument5 pagesTherapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDarnell DelgadoNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentDocument3 pagesConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Triads and Tetrads in MedicineDocument4 pagesTriads and Tetrads in MedicineCatherine SugandiNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyDocument3 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyLaiza JanelleNo ratings yet
- 440 - Med Surg HESI 2Document8 pages440 - Med Surg HESI 2Chalcey Polson87% (15)
- Congenital Heart Defects Test Five Nursing FourDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart Defects Test Five Nursing FourTiffany D'Alessandro GordonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Block 2Document53 pagesRespiratory Block 2Maya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- ECG Self Study BookDocument390 pagesECG Self Study BookChandramohan SettyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular MRI Pocket Guide 2013Document80 pagesCardiovascular MRI Pocket Guide 2013aegysabetterwayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 QuizDocument11 pagesChapter 1 QuizROHITNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesSudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- Pi Is 0168827817300156Document2 pagesPi Is 0168827817300156kookyin100% (1)
- Cardiac Murmurs and Maneuvers GuideDocument1 pageCardiac Murmurs and Maneuvers GuidePkernNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument132 pagesRheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDamie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Properties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting SystemsDocument38 pagesProperties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting Systemsnirilib100% (4)
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology 1:: Blood VesselsDocument48 pagesCardiovascular Pathology 1:: Blood VesselsRaiver CadenNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaNo ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditisDocument29 pagesInfective EndocarditistmtatroNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atLilly DayeNo ratings yet
- Pathoma Lecture Notes 2017Document42 pagesPathoma Lecture Notes 2017Priyesh PrinceNo ratings yet
- My Cardiac and Chest SymptomsDocument58 pagesMy Cardiac and Chest SymptomsDhamirah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure RevisionDocument4 pagesHeart Failure RevisionBlanaid MargaretNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanDocument27 pagesThyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanMarrah Avila Acuin100% (1)
- Mitral Valve ProlapseDocument5 pagesMitral Valve ProlapseDerofiez Hana RuhyadinNo ratings yet
- TransplantationDocument11 pagesTransplantationmardsz100% (1)
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Guideline JAMADocument11 pagesTransfusion Guideline JAMAandus007No ratings yet
- PROGRAMME ABSTRACT BOOK IACS ES 4 7 Oct 2023 Timisoara Romania - CORRDocument164 pagesPROGRAMME ABSTRACT BOOK IACS ES 4 7 Oct 2023 Timisoara Romania - CORRAlex MircescuNo ratings yet
- QRS ComplexDocument7 pagesQRS Complexchiusavi77No ratings yet
- Dutch Cardiac Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Guidelines PDFDocument52 pagesDutch Cardiac Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Guidelines PDFyohanNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Women 401 807Document407 pagesPsychology of Women 401 807Alessio TinerviaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document22 pagesCase Study 4Angel MayNo ratings yet
- Handbook July 2016 - Formatted v3Document172 pagesHandbook July 2016 - Formatted v3ElaineNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol in The Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease: A Critical ReappraisalDocument19 pagesMetoprolol in The Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease: A Critical ReappraisalLinto JohnNo ratings yet
- KAMIR TrialDocument7 pagesKAMIR TrialElias ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Medicin All Nov, Sep, OctDocument98 pagesMedicin All Nov, Sep, OctMohammad BanisalmanNo ratings yet
- Classification and Types of StrokeDocument11 pagesClassification and Types of StrokeJose Enrique OrtizNo ratings yet
- Index Index: SMN1 Mutation, 546Document9 pagesIndex Index: SMN1 Mutation, 546Luis Jose VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Stent ThrombosisDocument27 pagesStent ThrombosisAri NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Learner Cardiogenic Shock Secondary To Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesLearner Cardiogenic Shock Secondary To Acute Myocardial InfarctionHailee YakishNo ratings yet
- To PrankDocument7 pagesTo PrankGrace BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Formative Exam Paper 1 July 2020Document22 pagesFormative Exam Paper 1 July 2020Ruwanya AbeykoonNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviations - Taber's Medical DictionaryDocument15 pagesMedical Abbreviations - Taber's Medical DictionaryRose Antonette BenitoNo ratings yet
- NU 314 Course Syllabus Spring 2016Document4 pagesNU 314 Course Syllabus Spring 2016Agnes Buñag DoteNo ratings yet
- Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Across The SpectrumDocument34 pagesCoronary Microvascular Dysfunction Across The SpectrumChristian BuesaquilloNo ratings yet