Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generic Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction
Uploaded by
Kamille Anne Valdez DavidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Generic Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction
Uploaded by
Kamille Anne Valdez DavidCopyright:
Available Formats
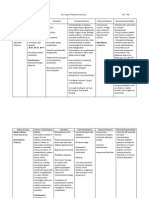
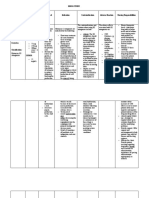
GENERIC CLASSIFICATION DOSAGE MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS ADVERSE REACTION
Metoclopramide HCl Antiemetics / Supportive Admin by slow IV or IM. Adult 10 mg 8 hrly. Metoclopramide enhances the motility of the upper GI tract and Nausea & vomiting due to GI disorders, Restlessness, drowsiness, headache,
Care Therapy increases gastric emptying without affecting gastric, biliary or after surgery & cancer chemotherapy. GI diarrhea. Extrapyramidal symptoms eg
Category B: Either animal-reproduction studies pancreatic secretions. It increases duodenal peristalsis which motility disorders. GERD & non ulcer acute dystonic reactions or Parkinsonian
have not demonstrated a foetal risk but there are decreases intestinal transit time, and increases lower oesophageal dyspepsia. Radiodiagnostic procedures in syndrome. Galactorrhoea due to increased
no controlled studies in pregnant women or sphincter tone. It is also a potent central dopamine-receptor the GIT. prolactin secretion.
animal-reproduction studies have shown an antagonist and may also have serotonin-receptor (5-HT3)
adverse effect (other than a decrease in fertility) antagonist properties.
that was not confirmed in controlled studies in Absorption: Rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI
women in the 1st trimester (and there is no tract (oral); peak plasma concentrations after 1-2 hr.
evidence of a risk in later trimesters). Distribution: Widely distributed; crosses the blood-brain barrier and
placenta; enters breast milk.
Metabolism: Extensively hepatic.
Excretion: Via urine (as unchanged drug, sulfate or glucuronide
conjugates and metabolites), faeces; 4-6 hr (terminal elimination
half-life).
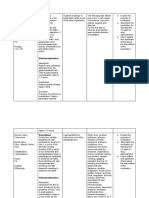
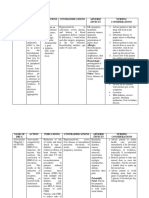
GENERIC CLASSIFICATION DOSAGE MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS ADVERSE REACTION
Losartan + hydrochlorothiazide Angiotensin II Tab 50/12.5 mg 1 tab. Max Dose: Tab Pharmacology. Losartan is a specific and selective Management of hypertension. Abdominal pain, edema, asthenia,
Antagonists / Diuretics 100/25 mg 1 tab, or Tab 50/12 mg 2 tab. angiotensin II receptor antagonist while HCTZ is a thiazide headache. Palpitation. Diarrhea,
Antihypertensive effect is achieved w/in 3 diuretic. The effects of both drugs on blood pressure are nausea. Back pain. Dizziness. Dry
wk. additive. Greater antihypertensive efficacy is generally cough, sinusitis, bronchitis,
achieved by adding a small dose of a thiazide diuretic eg, pharyngitis, upper resp infection.
HCTZ to the angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Losartan Rash.
lowers blood pressure by selectively blocking the AT1
receptor in vascular and other tissues to antagonize the
actions of angiotensin II. HCTZ, on the other hand, lowers
blood pressure by increasing the renal excretion of sodium.
Losartan tends to reverse hypokalemia caused by HCTZ.
You might also like
- Dementia Drug StudyDocument1 pageDementia Drug StudyHanna Raymundo IINo ratings yet
- Drugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingDocument10 pagesDrugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingTyrone IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArcoxiaDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArcoxiaSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFDocument18 pagesDrug Study 4C Case 2 Final PDFRegine Kate JuntoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanQueenie Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4. GI Tract PharmacologyDocument52 pagesLecture - 4. GI Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComEloisa BretañaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Davao Doctor College Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctor College Nursing Programember parkNo ratings yet
- Cilostazol (Pletal)Document4 pagesCilostazol (Pletal)Maria Leonie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Combizar Drug StudyDocument6 pagesCombizar Drug StudymrnmrsllNo ratings yet
- LopezBSN3C Medical InterventionDocument5 pagesLopezBSN3C Medical InterventionJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- NewcardiooooDocument32 pagesNewcardiooooCharlene RojasNo ratings yet
- Age Drug StudyDocument20 pagesAge Drug StudyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPAULA MAE F. ALMEIDANo ratings yet
- Los Art AnDocument2 pagesLos Art AnKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Enalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineDocument8 pagesEnalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineGabriel MatibagNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudynessaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RanitidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study RanitidineTipey SegismundoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LadyDocument8 pagesDrug Study LadyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument6 pagesDrug TabulationRosemarie Canete Delarita100% (1)
- CNS: Dizziness, Specific Senses: Skin: Rash, Pruritus. GI: DyspepsiaDocument1 pageCNS: Dizziness, Specific Senses: Skin: Rash, Pruritus. GI: DyspepsiaButts McgeeNo ratings yet
- Folic CHNDocument3 pagesFolic CHNErica EbradaNo ratings yet
- DRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarDocument9 pagesDRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibility BetahistineDocument16 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibility Betahistineclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Sedation, Headache, DepressionDocument2 pagesMedical Management: Sedation, Headache, DepressionGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- 1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONDocument4 pages1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONEdmon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideDocument8 pagesDrug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideFredie O HadjimudinNo ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering AgentsDocument2 pagesLipid Lowering Agentsapi-623203696No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- Age Drug StudyDocument13 pagesAge Drug StudyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYDocument23 pagesAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenNo ratings yet
- Micardis PlusDocument2 pagesMicardis PlusKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidinecen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Drug Study - DoxDocument3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study - Doxan naNo ratings yet
- Generic:: Drug Study #1Document1 pageGeneric:: Drug Study #1Patricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocument15 pagesDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- Threatened Abortion DrugsDocument1 pageThreatened Abortion DrugsDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- LosartanDocument2 pagesLosartanAngeliqueNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive AgentMuhammad Naufal FadhillahNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen: ClassificationDocument3 pagesAcetaminophen: ClassificationYosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Med Ward - Drug Study - LaoDocument3 pagesMed Ward - Drug Study - LaoLady Nadjma M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- My 6-Step Plan For Diagnosing & Managing The Pruritic DogDocument6 pagesMy 6-Step Plan For Diagnosing & Managing The Pruritic DogAnonymous TDI8qdYNo ratings yet
- C8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1Document7 pagesC8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1SANKET MATHURNo ratings yet
- Ken Russell Revealed:: Still Images 1954 - 1957Document4 pagesKen Russell Revealed:: Still Images 1954 - 1957Adriana ScarpinNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Gravity Loads PDFDocument4 pagesDerivation of Gravity Loads PDFHenry TuganoNo ratings yet
- Workbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaDocument125 pagesWorkbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaLourdes de Fatima Pacheco VasquezNo ratings yet
- CMC 2023 Senior Category Question BankDocument5 pagesCMC 2023 Senior Category Question BankNikita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- List Lagu EnglishDocument7 pagesList Lagu EnglishRyn ZulfanNo ratings yet
- Poems by Cawein, Madison Julius, 1865-1914Document126 pagesPoems by Cawein, Madison Julius, 1865-1914Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Msi MS 7529 Rev 1.1 PDFDocument33 pagesMsi MS 7529 Rev 1.1 PDFMisael Alves67% (3)
- Abortion Remedies From A Medieval Catholic Nun (!) - JSTOR DailyDocument12 pagesAbortion Remedies From A Medieval Catholic Nun (!) - JSTOR DailysiesmannNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan 3api-547884261No ratings yet
- Rossmann Repair Training Guide - Google SlidesDocument167 pagesRossmann Repair Training Guide - Google Slidesmirza baigNo ratings yet
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocument12 pagesJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitNguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- Op Amp AssignmentDocument10 pagesOp Amp AssignmentJuan-Wian CoetzerNo ratings yet
- Automatic Door Opener With PIC12C508 CircuitDocument3 pagesAutomatic Door Opener With PIC12C508 CircuitLingaraj BeharaNo ratings yet
- Essay Flooding and MitigationDocument3 pagesEssay Flooding and MitigationCindy HosianiNo ratings yet
- SLC Past and Future Hustrulid KvapilDocument26 pagesSLC Past and Future Hustrulid KvapilkinsaeyaNo ratings yet
- Exam of Refinery PDF 2Document20 pagesExam of Refinery PDF 2ئارام ناصح محمد حسێن0% (1)
- STAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesDocument152 pagesSTAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesLiban Ali MohamudNo ratings yet
- Homework 3rd SteelDocument4 pagesHomework 3rd SteelPiseth HengNo ratings yet
- A554-15 Standard Specification For Welded Stainless Steel Mechanical TubingDocument8 pagesA554-15 Standard Specification For Welded Stainless Steel Mechanical TubingChuthaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Fittings DimensionsDocument3 pagesCarbon Steel Fittings DimensionsgiorselNo ratings yet
- Elementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Document15 pagesElementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Jefferson WidodoNo ratings yet
- Sea Shanty PrintDocument3 pagesSea Shanty PrintDiego DracvsNo ratings yet
- LEED v4 For Interior Design and Construction ChecklistDocument3 pagesLEED v4 For Interior Design and Construction Checklisttarek.abbas8598No ratings yet
- The Book of JonahDocument2 pagesThe Book of JonahJames Hampton BeltonNo ratings yet
- CO Q1 TLE EPAS 7 8 Module 4 Preparing Technical DrawingsDocument47 pagesCO Q1 TLE EPAS 7 8 Module 4 Preparing Technical DrawingsNicky John Doroca Dela MercedNo ratings yet
- SN3308 Installation Manual Rev J PDFDocument132 pagesSN3308 Installation Manual Rev J PDFsav33No ratings yet
- MCQs Saudia Pharmacy Registration ExamDocument7 pagesMCQs Saudia Pharmacy Registration ExamAli ButtNo ratings yet