Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2b - Fringe Benefits
Uploaded by
CPACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 2b - Fringe Benefits
Uploaded by
CPACopyright:
Available Formats
Taxation Review 1
Lecture on Fringe Benefits
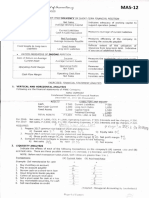
FRINGE BENEFITS- any good, service or other benefit furnished or granted by an employer, in cash or in kind, in
addition to basic salary to an individual employee.
Subject to FBT Not Subject to FBT
Those given to managerial or supervisory
Those given to rank-and-file employees
position*
Not subject to FBT, but Those benefits given
For purposes of determining what a managerial other than those which do not exceed the
position is, the decision-making test may apply. statutory threshold shall be subject to tax under
Normal Income Tax (5%- 32%)
Examples: Examples:
a. De Minimis, non-taxable if not exceeding the
a. Housing
limits, however, any excess of de minimis over
b. Expense Accounts
the statutory limits is added to the “Other
c. Vehicle of any kind
Bonuses” category subject to P 82,000 limit
d. Household personnel
taxable under Normal Tax
e. Interest
f. Membership fees b. those which are required and necessary to the
business of the employer
g. Expense for Foreign Travel
c. those which are for the convenience or
h. Holiday and vacation expenses
advantage of the employer
i. Educational assistance
j. Life or health insurance and other non- life
insurance premium in excess of what the law
allows
The employer is liable for FBT regardless of
whether he is taxable or not since he is
considered to be the withholding agent.
The grossed-up monetary value shall be an
expense deductible on the part of the employer,
computed as follows:
32%- FBT since January 1, 2000
GMV= MV/68% (for RC, NRC, RA, and NRAETB)
GMV= MV/75% (for NRANETB)
GMV= MV/85% (for employees in RAH, ROH, OBUs)
– special taxpayers
The fringe benefit tax shall be 32%, 25% and
15%
Monetary Values
If Cash, the face amount or value received.
If Property, wherein the ownership is transferred to the employee, the basis shall be the FMV,
Zonal Value, or Assessed Value, whichever is the HIGHEST.
If ONLY USUFRUCT (use):
a. Personal Property, FV to be depreciated by 5 years then divided by 2.
b. Real Property, ZV, AV, or FMV, whichever is the highest, to be depreciated by 20 years then
divided by 2.
If Interest, MV is equal to interest forgone.
Taxation Review 2
Lecture on Fringe Benefits
*Managerial Employee
Those who are vested with powers or prerogatives to lay down and execute management policies and/or
to hire, transfer, suspend, lay-off, recall, discharge, assign or discipline employees. (Labor Code of The
Philippines)
Supervisory Employee
Those who, in the interest of the employer, effectively recommend such managerial actions if the exercise
of such authority is not merely routinary or clerical in nature but require use of independent judgment.
(Labor Code of The Philippines)
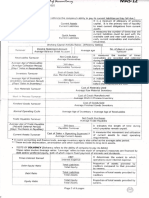
De Minimis Benefits
Whether rank-and-file or managerial/supervisory employee, the following de minimis benefits shall be
non-taxable:
1. Monetized unused vacation leave credits of private employees not exceeding 10 days during the
year;
2. Monetized value of vacation and sick leave credits paid to government officials and employees;
3. Medical cash allowance to dependents of employees not exceeding P750 per employee per semester
or P 125 per month;
4. Rice subsidy of P 1,500 or one (1) sack of 50-kg. rice per month amounting to not more than P 1,500;
5. Uniform and clothing allowance not exceeding P 5,000 per annum;
6. Actual yearly medical benefits not exceeding P 10,000 per annum;
7. Laundry allowance not exceeding P 300 per month;
8. Employees achievement awards which must be in the form of a tangible personal property other than
cash or gift certificate, with an annual monetary value not exceeding P 10,000 received by the employee
under an established written plan which does not discriminate in favor of highly paid employees;
9. Gifts given during Christmas and major anniversary celebrations not exceeding P 5,000 per
employee per annum;
10. Daily meal allowance for overtime work not exceeding twenty-five percent (25%) of the basic minimum
wage.
11. All other benefits given by the employers which are not included in the above enumeration shall not be
considered as “de minimis” benefits, and hence, shall be subject to income tax as well as withholding tax
on compensation.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Learning Advancement Cpa Review Center: Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument4 pagesLearning Advancement Cpa Review Center: Revenue From Contracts With CustomersCPANo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- LeadDocument46 pagesLeadCPANo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Rurnover: '.::::"" ':'U ' O, .-Ffhsffihr"ODocument1 pageRurnover: '.::::"" ':'U ' O, .-Ffhsffihr"OCPANo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- MS 3412-8Document1 pageMS 3412-8CPANo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- J "0 A. N,", o ,: UnitDocument1 pageJ "0 A. N,", o ,: UnitCPANo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Afarq 2 Corporate LiquidationDocument4 pagesAfarq 2 Corporate LiquidationCPANo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Cpar AuditingDocument10 pagesCpar AuditingCPANo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- MS 3412-2Document1 pageMS 3412-2CPANo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Fif, T n'1t : Q, o D.".-,". R, , 5-Il, L"!,' 2qC! 2) I Ti 2) JTDocument1 pageFif, T n'1t : Q, o D.".-,". R, , 5-Il, L"!,' 2qC! 2) I Ti 2) JTCPANo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Toa 334-1 PDFDocument1 pageToa 334-1 PDFCPANo ratings yet
- MS 3412-3Document1 pageMS 3412-3CPANo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Financial: " " 1" 2. 3. 4. 5. RetiosDocument1 pageFinancial: " " 1" 2. 3. 4. 5. RetiosCPANo ratings yet
- Iht#I T:,Ffi, I:Trri ,:FFJLLLJ H:!:Iiiff: at ofDocument1 pageIht#I T:,Ffi, I:Trri ,:FFJLLLJ H:!:Iiiff: at ofCPANo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Toa 334-2Document1 pageToa 334-2CPANo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- RFBT 34new-3Document1 pageRFBT 34new-3CPANo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Toa 334-3Document1 pageToa 334-3CPANo ratings yet
- Toa 333-2 PDFDocument1 pageToa 333-2 PDFCPANo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Toa 333-1Document1 pageToa 333-1CPANo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting MsvegaDocument2 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting MsvegaCPANo ratings yet
- Toa 333-3 PDFDocument1 pageToa 333-3 PDFCPANo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Regulatory Framework For Business Transactions Madbolivar: Quiz 2-ContractsDocument2 pagesRegulatory Framework For Business Transactions Madbolivar: Quiz 2-ContractsCPANo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- RFBT 34new-2Document1 pageRFBT 34new-2CPANo ratings yet
- 1.3. Sales: Regulatory Framework For Business Transactions MadbolivarDocument9 pages1.3. Sales: Regulatory Framework For Business Transactions MadbolivarJims Leñar CezarNo ratings yet
- RFBT 34new-1Document1 pageRFBT 34new-1CPANo ratings yet
- C. D. A. B. C. It D.: Il', I:TjrDocument1 pageC. D. A. B. C. It D.: Il', I:TjrCPANo ratings yet
- Toa 34B-1Document1 pageToa 34B-1CPANo ratings yet
- RFBT Handout 4Document5 pagesRFBT Handout 4CPANo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- RFBT Handout 4Document5 pagesRFBT Handout 4CPANo ratings yet
- Toa 34B-2Document1 pageToa 34B-2CPANo ratings yet
- Handouts ConsolidationIntercompany Sale of Plant AssetsDocument3 pagesHandouts ConsolidationIntercompany Sale of Plant AssetsCPANo ratings yet
- IBRDDocument5 pagesIBRDMohsin G100% (1)
- Bài 12 - Bài tập thực hànhDocument2 pagesBài 12 - Bài tập thực hànhDuyên BùiNo ratings yet
- John Insurance Middle EastDocument52 pagesJohn Insurance Middle Eastjohn.brunoNo ratings yet
- New Venture Finance Startup Funding For Entrepreneurs PDFDocument26 pagesNew Venture Finance Startup Funding For Entrepreneurs PDFBhagavan BangaloreNo ratings yet
- Board Resolution FormatDocument3 pagesBoard Resolution Formatjayanthi_kondaNo ratings yet
- 2011 M1 ProspectusDocument130 pages2011 M1 ProspectusStanton OvertonNo ratings yet
- E-Way Bill - 7Document2 pagesE-Way Bill - 7AshishTrivediNo ratings yet
- Payment and Settlement Systems in IndiaDocument23 pagesPayment and Settlement Systems in IndiagopubooNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- TAX-CREBA VS Executive Secretary RomuloDocument2 pagesTAX-CREBA VS Executive Secretary RomuloJoesil Dianne100% (2)
- Insurance ThesisDocument2 pagesInsurance ThesisMinh LêNo ratings yet
- Q 029 We 4 UDocument11 pagesQ 029 We 4 UxjammerNo ratings yet
- Turkey Kriz: The Fall and Fall of LiraDocument26 pagesTurkey Kriz: The Fall and Fall of Lirasonam27No ratings yet
- AFAR 3 AnswersDocument5 pagesAFAR 3 AnswersTyrelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Wall Street Courier Services, Inc. PayslipDocument1 pageWall Street Courier Services, Inc. PayslipAimee TorresNo ratings yet
- RRL Matrix - ToPIC 1 Effect of The New IFRS 15 Adoption - Revenue Recognition To Earnings Quality of FirmsDocument12 pagesRRL Matrix - ToPIC 1 Effect of The New IFRS 15 Adoption - Revenue Recognition To Earnings Quality of FirmsEuniceChungNo ratings yet
- 2023 - Q1 Press Release BAM - FDocument9 pages2023 - Q1 Press Release BAM - FJ Pierre RicherNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam BDocument14 pagesComprehensive Exam Bjdiaz_646247No ratings yet
- Tally - Erp9 NotesDocument52 pagesTally - Erp9 NotessandeepNo ratings yet
- Financial LiteracyDocument22 pagesFinancial LiteracyRio Albarico100% (1)
- Income Tax Study PackDocument68 pagesIncome Tax Study PackKempton MurimiNo ratings yet
- What Do You Mean by OverheadsDocument6 pagesWhat Do You Mean by OverheadsNimish KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Report On NurseryDocument6 pagesProject Report On NurseryManju Mysore100% (1)
- Maybank List ReportDocument3 pagesMaybank List ReportpalmkodokNo ratings yet
- Quizzer #8 PPEDocument13 pagesQuizzer #8 PPEAseya CaloNo ratings yet
- GFGC - K. R. Pet - Preliminary Exam For Business Quiz - 2019Document2 pagesGFGC - K. R. Pet - Preliminary Exam For Business Quiz - 2019Kiran A SNo ratings yet
- CertificatesDocument21 pagesCertificatesJed AbadNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law Mamalateo PDFDocument99 pagesTaxation Law Mamalateo PDFErmawooNo ratings yet
- Super ProjectDocument2 pagesSuper ProjectQiang ChenNo ratings yet
- 2 Economics MAY 2019 AnswersDocument10 pages2 Economics MAY 2019 AnswersLala AlalNo ratings yet
- JAVA MicroprojectDocument31 pagesJAVA Microprojectᴠɪɢʜɴᴇꜱʜ ɴᴀʀᴀᴡᴀᴅᴇ.No ratings yet