Professional Documents
Culture Documents
47 PDF
Uploaded by
Camelia Moise0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
47.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 page47 PDF
Uploaded by
Camelia MoiseCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
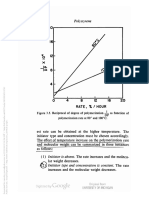
Basic Chemistry of Polystyrene
47
naphthalene is the initiator it is believed that the chains are
active on both ends since this initiator, a radical-ion, initiates
chains with a radical on one end and an anion on the other.
The radicals couple to form a chain with an anion on each end.
Ziegler catalysts, consisting of a trialkyl aluminum com-
pound and titanium tetrachloride, are insoluble; the active
end of the growing chain is believed to be an anion associated
with a metal ion bound to the surface of the catalyst particle.
Isotactic polystyrene is most easily made with Ziegler catalysts.
Cationic polymerization of styrene and alpha-methylstyrene
can be carried out at low temperatures if a Friedel-Crafts type
of initiator such as BF3, SnCl4 or A1C13 is used. These initia-
tors can accept a pair of electrons from the double bond,
forming a positive charge on one carbon atom which becomes
the active center. Because of its low molecular weight poly-
styrene prepared at room temperature with such initiators
is very brittle. Although low temperatures favor high molecu-
lar weights such a process is not used commercially.
Copolymerization
Mixtures of styrene and other vinyl monomers will form
copolymers in which both kinds of monomer units are present
in each polymer chain. This can be illustrated by the follow-
ing equation in which R, represents any growing polymer
chain:
Generated for camelia_moise@yahoo.com on 2013-04-10 16:38 GMT / http://hdl.handle.net/2027/mdp.39015016511761
R, + CH2=CH or CH2=CH
-» R—CH2—CH-
R'
R—CH2—CH, + CH2=CH
* R—CH2—CH—CH2-CH-
R'
R'
Public Domain, Google-digitized / http://www.hathitrust.org/access_use#pd-google
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- DATA Space ReplaimDocument3 pagesDATA Space ReplaimCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 44 PDFDocument1 page44 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 51 PDFDocument1 page51 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 54 PDFDocument1 page54 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 40 PDFDocument1 page40 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 48 PDFDocument1 page48 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 41 PDFDocument1 page41 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 43 PDFDocument1 page43 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 42 PDFDocument1 page42 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 46 PDFDocument1 page46 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 52 PDFDocument1 page52 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 55 PDFDocument1 page55 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 53 PDFDocument1 page53 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 49 PDFDocument1 page49 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 56 PDFDocument1 page56 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 45 PDFDocument1 page45 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 57 PDFDocument1 page57 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 50 PDFDocument1 page50 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 59 PDFDocument1 page59 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 60 PDFDocument1 page60 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Polystyrene Process DetailsDocument1 pageManufacture of Polystyrene Process DetailsCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 58 PDFDocument1 page58 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 62 PDFDocument1 page62 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- Polystyrene Production via Suspension PolymerizationDocument1 pagePolystyrene Production via Suspension PolymerizationCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 64 PDFDocument1 page64 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 104 PDFDocument1 page104 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 65 PDFDocument1 page65 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 102 PDFDocument1 page102 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 99 PDFDocument1 page99 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)