Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AEB Descripcion Motor QSK78
Uploaded by
hugoarica74Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AEB Descripcion Motor QSK78
Uploaded by
hugoarica74Copyright:
Available Formats
Customer
Engineering
Bulletin
Title: This CEB is for the following applications:
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information
Automotive Industrial Marine
G-Drive
Date: 14 January 2016 Refer to CEB00044 for Safety Practices, CEB Number: 00069
Guidelines and Procedures
Engine models included: QSK78 (D773001CX03, D773003CX03)
Owner: Kyle Fields Approver: per Procedure GCE-AS-1 Page 1 of 19
This CEB supersedes CEB00069 dated 29 September 2015.
Introduction
This CEB introduces the QSK78 diesel engine from Cummins Inc. It is an 18 cylinder engine with a total
displacement of 78 liters. It is available in both single and two stage turbocharged arrangements.
The QSK78 two stage turbocharged engine is designed for use in Industrial applications. The engine has been
certified at U.S. EPA Tier 2 Nonroad emission standards. The Tier 2 design is parented off of the Tier 1 engine
platform. The Tier 2 design incorporates improved camshafts, injectors, and pistons to deliver the emissions
required for Tier 2. The engine still utilizes a 2-pump 2-loop (2P2L) cooling system with Low Temperature
Aftercoolers (LTAs) and intercoolers.
The QSK78 single stage turbocharged engine is designed for use in Industrial and Locomotive applications. The
engine has been designed to meet U.S. EPA Locomotive Tier 2 Linehaul emissions standards. The design is
parented off of the 2.75 MW Power Generation engine platform. The design includes new injectors, pistons, and
turbochargers. The design also incorporates turbochargers that are water-cooled, as well as CENSE, and 2P2L
cooling system with LTAs.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 1 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Table of Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................ 1
Table of Contents ...................................................................................................................................................... 2
Fuel Rating ................................................................................................................................................................ 3
Calibration Requests .............................................................................................................................................. 3
Engine Details............................................................................................................................................................ 3
Base Engine Features ............................................................................................................................................... 3
Engine Envelope .................................................................................................................................................... 3
Gear Housing/Geartrain ......................................................................................................................................... 4
Fuel System ............................................................................................................................................................... 4
Fuel Pump and Connections.................................................................................................................................. 5
Cooling System.......................................................................................................................................................... 5
Surge Tank and Filling ........................................................................................................................................... 6
Coolant Treatment and Filtration ........................................................................................................................... 7
QSK78 2-Stage Cooling System Flow Diagram .................................................................................................... 8
QSK78 Single Stage Cooling System Flow Diagram ............................................................................................ 9
Plug .......................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Venting ................................................................................................................................................................. 10
Lubrication System .................................................................................................................................................. 10
CentinelTM Continuous Oil Replacement System ................................................................................................ 11
Oil Pan ................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Air Handling and Exhaust System ........................................................................................................................... 13
Table of 2-Stage Exhaust Flow: ........................................................................................................................... 13
Table of Single Stage Exhaust Flow: ................................................................................................................... 13
Engine Mounting ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
Breather ................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Electronic Control System ....................................................................................................................................... 14
Prelubrication ........................................................................................................................................................... 15
Starters .................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Flywheel Housing .................................................................................................................................................... 15
Accessory Drive ....................................................................................................................................................... 15
Alternator ................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Refrigerant Compressor .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Hydraulic Pump Drive .............................................................................................................................................. 16
Air Compressor ........................................................................................................................................................ 16
Fan Drive ................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Change Log ............................................................................................................................................................. 17
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 2 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Fuel Rating
Fuel ratings (FR options) for the QSK78 engine range from:
- 2461 kW (3300 hp): Single stage turbocharged
- 2207 kW - 2610 kW (2960 hp - 3500 hp): 2-stage turbocharged
The complete list of QSK78 Tier 2 ratings can be found on the GCE website under the Ratings and Datasheets
section (https://gce.cummins.com/ice/ice_present/ice_qsk78/index-qsk78.html).
Calibration Requests
Custom calibrations are requested via the PowerMatch engineering tool for supported HHP platforms. Supported
platforms will use generic calibrations as a baseline for the tool. A complete list of PowerMatch generic
calibrations can be found in the “Ratings and Datasheets” section of the engine's GCE page. Refer to
PowerMatch to identify supported HHP platforms.
HHP platforms not included in the PowerMatch engineering tool must use the VPCR / QNIR process.
Reference AEB 24.48, “Industrial Calibration Development Process” for more details on the PowerMatch process
and the QNIR process.
Engine Details
Table 1: Engine characteristics of the single and 2-stage configurations
D773001CX03 D773003CX03
(2-Stage) (Single Stage)
Non-certified US EPA Tier 2 US EPA Tier 2
Locomotive Linehaul
No. Cylinders 18 18 18
Bore x Stroke (mm) 170 x 190 170 x 190 170 x 190
Displacement (L) 77.6 77.6 77.6
Base Engine Features
Engine Envelope
Table 2: QSK78 2-stage and single stage engine dimensions
D773001CX03 D773003CX03
(2-Stage) (Single Stage)
45 deg side out Left and front out Top out exhaust
Height above Centerline of
1639 mm 1822 mm 1242 mm
Crankshaft
Overall Engine Height
2429 mm 2612 mm 1851 mm
Overall Length
3377 mm 3318 mm 2961 mm
Overall Width
1663 mm 1591 mm 1588 mm
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 3 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Gear Housing/Geartrain
The cast iron front gear housing encloses the heavy-duty front gear train, which has low gear loading and robust
fatigue strength.
Table 3: Geartrain information
Item
Number Gear Description Rotation
1 Crankshaft (rear) CW
8 7 2 Crankshaft (front) CW
6 3 Lube Pump Idler CCW
9 4 Lube Pump CW
1
5
5 Accessory Comp Idler CCW
12 6 Cam Comp CCW
2 7 Left Bank CW
8 Right Bank Cam Idler CW
10
13 9 Right Bank CCW
3
11 10 Water Pump Idler CCW
4
11 Water Pump CW
12 Fuel Pump Drive CW
13 LTA Pump Drive CW
Figure 1: Geartrain as viewed from the front of the engine.
Fuel System
The CELECT fuel system on the QSK78 engine features Cummins’ HPI fuel system. The HPI fuel system uses
open nozzle injectors. Open nozzle fuel injection gives a “soft” start of injection, and thus lowers combustion
noise. Injection timing is infinitely variable allowing for optimal emissions and fuel economy.
The QSK78 fuel rail flow is to feed each bank from each end. The fuel manifolds are located outside the air
intake manifolds. The fuel rails have five drillings running the length of the manifold. The top two are for timing,
the middle is for drain, and the bottom two are rail. The timing fuel is fed into the outer of the top two drillings.
The fuel then goes to each end of the outer drilling and crosses over to the inner drilling. The fuel then goes from
each end of the inner drilling feeding the ports through the intake manifolds and the heads to the injector. The rail
fuel takes the same path in the lower two drillings. The drain fuel is fed back to the manifold through the heads
and intake manifolds to the center drilling and then to the front of each manifold. The left bank fuel for the rail and
timing is fed to the fuel manifold by tubes routed from the left bank fuel block located behind the Electronic Control
Valve Assembly (ECVA). The right bank fuel for the rail and timing is fed across the block to the right bank fuel
block located behind the Eliminator™ and then to the fuel manifold by tubes.
On the single stage configuration, a fuel lift pump is available for applications that have difficulty meeting fuel inlet
restriction requirements that will use an auxiliary fuel tank (day tank). The lift pump is gear driven and mounted
on the rear left bank of the gear housing. Refer to AEB 29.06, “Locomotive and Track Maintenance Equipment
Application Guidelines” for more information on fuel transfer pumps (specifically for locomotive applications).
For fuel cooler sizing, please refer to data sheets on GCE. Reference AEB 24.07, “Installation Requirements -
Fuel Temperature” for fuel cooling information.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 4 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Fuel Pump and Connections
The QSK78 fuel pump and connections are located at the left bank near the front of the engine, with two separate
fuel filter heads used in parallel. There is a hose from the front filter head to the fuel pump and a hose from the
fuel pump to the ECVA. The fuel drain check valve is supplied with the engine and is located in the same location
as the QSK45/60 drain valve. The fuel drain valve is mounted on the top right-bank side of the gear housing.
The engine uses six spin-on fuel filters located on the left bank of the engine. Filtration media is capable up to 10
microns. There is one fuel inlet for the engine, located at the rear of the parallel fuel filter heads.
Figure 2: Fuel pump and filter canisters being used in parallel
Cooling System
The cooling system is a 2-pump, 2-loop system that requires both a High Temperature Circuit (HTC) radiator and
a Low Temperature Circuit (LTC) radiator. A Low Temperature Aftercooler (LTA) is a coolant-to-air heat
exchanger that is used to reduce the temperature of the compressed air entering the intake manifold. A 2-pump,
2-loop system provides the means to get higher power densities while meeting Tier 2 emission standards.
The HTC is used to cool the engine block and critical components. The LTC supplies coolant solely to the LTAs.
The two cooling circuits share a common top tank. Each coolant circuit must have its own radiator. For a complete
listing of installation requirements, please refer to AEB 24.26 “Two-Pump, Two-Loop (2P-2L) Cooling System
Installation Requirements and Recommendations.” Additional information can also be found in AEB 24.18,
“Industrial Installation Requirements- LDI/MR/HD/HHP Cooling System Design.”
Each cooling circuit has its own coolant pump impeller, independently driven from the front gear train, please refer
to Figure 1 and Table 3.
High Temperature Circuit (HTC)
The main engine coolant circuit cools the oil cooler, engine block, jacket water thermostats, and the water pump.
There are four thermostats for the HTC, two per bank, located at the front of the engine next to the gear housing.
The vent connections for the HTC are located on top of the thermostat housing, one per bank. Refer to the engine
installation drawing on GCE for more details. Figure 3 shows the coolant flow through the HTC.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 5 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Figure 3: HTC Coolant Flow Path
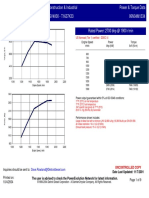
Refer to the fuel rating datasheets for specific heat rejection values. The maximum top tank temperature is 100 °C
(212 °F).
Low Temperature Circuit (LTC)
The QSK78 Tier 2 engine uses a low temperature coolant circuit, which consists of the LTC thermostats, water
pump, and the LTAs. There are two thermostats for the LTC located above the front gear housing. The vent
connection for the LTC is located on the water bypass tube near the LTC thermostat housing. This coolant loop
must have its own radiator. The LTC radiator must be designed to provide coolant cold enough to cool the intake
air to 60 °C [140 °F] on a 25 °C [77 °F] ambient day. The two cooling circuits share a common top tank. Refer to
the engine installation drawing on GCE for more details.
Figure 4: LTC Coolant Flow Path
Surge Tank and Filling
A common surge tank is used for both cooling circuits. Both the LTC and HTC are filled from this common surge
tank. As a common reservoir, the surge tank allows a small quantity of coolant from both circuits to be mixed
during engine operation. OEM’s need to provide make-up lines and venting.
The common surge tank should be designed to reduce the turbulence in the tank so that acceptable dearation
and draw-down are achieved. Baffles may need to be incorporated into the surge tank to reduce turbulence.
Petcocks on water-cooled bearing housing turbos and intercoolers need to be kept open at the time of initial filling
of the system to ensure deaeration of the system.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 6 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Coolant Treatment and Filtration
Mixture of 50/50 water and antifreeze is recommended with Fleetguard coolant additive DCA4 or Fleetguard Fully
Formulated Coolant. Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA) must always be used, and the Fleetguard SCA is
known specifically as “DCA4” in the marketplace. The two coolant filters contain 46 units of SCA (23 units each).
Additional SCA must be added to the system. The quantity of DCA4 coolant additive needs to be calculated
based upon total system capacity (HTC + LTC + radiators + plumbing). It is recommended that 3.0 units of DCA4
per gallon be used for initial coolant pre-charge. The DCA4 level should be maintained between 1.2 and 5.0 units
per gallon of coolant. Reference Service Bulletin #3666132.
The two spin-on coolant filters are necessary to filter the coolant. As coolant gets mixed in a common surge tank
there is no need for separate filters for the LTC.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 7 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
QSK78 2-Stage Cooling System Flow Diagram
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 8 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
QSK78 Single Stage Cooling System Flow Diagram
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 9 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Venting
The venting of the QSK78 2-stage engine is similar to the QSK45/60 engines, requiring venting of both front and
rear intercoolers to the surge tank. Venting must then be performed to the jacket water HTC at thermostat
housing and left bank (LB) rear low pressure (LP) turbo coolant drain. Open all turbo petcocks when filling the
cooling system, and close after a steady stream of coolant flows from each.
The venting of the QSK78 single stage engine is similar to the 2.75 MW engines, but with the required addition of
water-cooled turbo housings vents on the turbochargers.
Refer to installation drawings on GCE for vent locations.
Lubrication System
The Cummins Eliminator™ lube oil filter is standard equipment and is the only option available for the QSK78
engine. This allows for increased productivity and reduced cost over the life of the engine, with reduced
downtime. The Eliminator™ filter is a combination of an automatic, self-cleaning full flow filter and a centrifugal
bypass filter housed within a single unit, which is engine mounted. The full flow automatic, self-cleaning portion is
a stainless steel filter that screens particles as small as 20 microns from the oil flow. Ninety-five percent of the oil
that passes through the automatic first-stage filter goes directly into lubricating the engine. The remaining five
percent is used to backflush the filter, keeping it clean. The oil that is used to backflush the filter is then sent to a
centrifugal separator. The spinning action of the disk-stack centrifuge removes solid particles less than 2 microns
in size, depositing the heaviest particles on a replaceable liner inside the centrifuge bowl.
The unique features of the Eliminator™ filter include:
- Filter service at 1,000 hours or one year for the centrifuge (hours dependent upon load factor, oil quality, local
conditions – see Service Procedure 102-002 Maintenance Schedule)
- Bolts directly to the engine block
- Totally sealed system to reduce the possibility of contamination/dirt
- Full flow filter life equivalent to the life of the engine
Figure 5: Cummins Eliminator™ oil flow diagram
Refer to AEB 41.12, “Eliminator™ Filtration on QSK19, K38/50, QSK38/50, QSK45/60, and QSK78 Industrial
Products”, for additional information on Eliminator™.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 10 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Centinel™ Continuous Oil Replacement System
This system is standard equipment for the QSK78 engine, and is a means of disposing of used engine oil in a
productive manner as engine fuel. The CentinelTM system is a way to significantly reduce maintenance costs
while maximizing uptime and productivity. This is done through optimized oil management, and enhanced engine
protection with a system that ensures that oil quality remains stable and thus gives greater protection over the
long run.
This patented system utilizes the concept of burning used engine oil at a rate dependent upon load factor. The
burned oil is replaced by the circulation of oil from a remote auxiliary oil tank. The system pulls oil from the
engine rifle and meters it into the fuel inlet. An electronic control module will monitor the oil level in the sump as
well as the remote auxiliary oil tank. CentinelTM can operate as a burn and make-up system or a burn and
maintain system. Reference AEB 48.04, “Industrial HHP Products for Oil Service Interval Extension”, for further
information on Integrated Centinel™.
Figure 6: Centinel™ flow diagram
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 11 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Oil Pan
The QSK78 two stage engine utilizes an oil pan adapter and a bolt-on sump. Sumps can be added to four
locations on the pan adapter. The addition of the sump will provide increased capacity for meeting angularity
requirements. The QSK78 double-deep sump oil pan has a capacity of 76 US gallons of oil. The entire engine
lube system has a capacity of 90 US gallons of oil with the double-deep sump and Eliminator™ filter.
Figure 7: Double deep oil pan used on the QSK78 2-stage engine
The QSK78 single stage engine utilizes a sub-base (structural) oil pan. The QSK78 sub-base oil pan has a
capacity of 89.5 US gallons of oil. The entire engine lube system has a capacity of 121.5 US gallons of oil with
the sub-base oil pan and Eliminator™ filter.
Figure 8: Sub-base oil pan used on the QSK78 single stage engine
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 12 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Air Handling and Exhaust System
The QSK78 exhaust manifolds have been designed to reduce pumping losses. The standard two stage option
offers a 45 degree side out exhaust connection on both the left and right-bank sides, similar to the QSK60 2-stage
design. Another 2-stage option allows a 45 degree side out exhaust connection on the right-bank side, and a 60
degree front out exhaust connection on the left-bank side. Inconel bellows connections have been incorporated
into the exhaust system for improved durability and allow for thermal expansion. These connections minimize the
possibility of a cracked exhaust manifold due to thermal expansion.
The QSK78 two stage engine uses six HX60 and six HX82 high efficiency Holset turbochargers. The water-
cooled bearing HX60 turbochargers are used for the high pressure (HP) stage. The engine uses a two stage
approach to turbocharging for efficient performance and maximum altitude capability. The intake air is first
compressed in the low pressure- (LP) turbocharger. Then air is cooled through an intercooler. The second
compression occurs in the HP turbocharger. After the second compression, the air flows through the aftercooler
and enters the combustion chamber.
The QSK78 single stage engine uses four HX83 high efficiency Holset turbochargers. The engine uses a single
stage approach to turbocharging for efficient performance and easier packaging. The intake air is compressed
and then flows through the aftercooler and enters the combustion chamber.
The exhaust flow for the QSK78 is different from the QSK60 engine. For the QSK60 engine, each bank (left or
right) exhaust flow will route through only one exhaust outlet. This allows the QSK60 to be viewed as being left-
bank or right-bank specific. However, the QSK78 engine is not bank specific. The left-bank exhaust flow can
route through both exhaust outlets. Likewise the right-bank flow can route through both outlets. This crossing of
exhaust flow is described in the table below. Note also that the QSK78 engine uses log exhaust manifolds, and
so certain cylinders can mix between different turbochargers.
Table of 2-Stage Exhaust Flow:
HP Turbo LP Turbo Exhaust Outlet
LBFHP LBFLP RB
LBMHP LBMLP RB
LBRHP LBRLP LB
RBFHP RBFLP RB
RBMHP RBMLP LB
RBRHP RBRLP LB
(i.e., LBFHP = left bank front high pressure turbo)
Table of Single Stage Exhaust Flow:
Turbo Exhaust Outlet
LBF FT
RBF FT
LBR RT
RBR RT
(i.e., LBF = left bank front turbo, FT = front top)
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 13 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Engine Mounting
The QSK78 single stage engine mounting system utilizes the sub-base oil pan with 6 mounting pads which are
used to mount to the OEM chassis. Refer to AEB 29.06, “Locomotive and Track Maintenance Equipment
Application Guidelines”, for more information on sub-base mounting.
The standard lifting arrangement for the QSK78 utilizes four lifting brackets located on rocker housings.
RB Lifting Bracket Locations LB Lifting Bracket Locations
On Cyl’s #2 & #8 On Cyl’s #2 & #8
Breather
A single open crankcase breather is incorporated into the left bank of the QSK78 engine. The angularity for the
single stage and two stage engine is dependent on the oil pan selected. The angularity limit is published in the
option notes on GCE.
The difference in the single stage engine compared to the two stage angularity is due to the oil pan and suction
tube design. The 2-stage engine uses a deeper pan and longer suction tube, allowing for greater angularity
ability.
The plumbing of crankcase gases into the air intake system [Closed Crankcase Ventilation (CCV)] is not allowed.
Crankcase gases contain oil and moisture, which if introduced into the air intake system, can result in engine
performance issues and/or damage to turbochargers.
Electronic Control System
The QSK78 engine uses an integrated electronic control system. Electronic control gives Cummins the ability to
tailor fuel system calibrations to unique off-highway application requirements. The electronic engine control
system consists of an Electronic Control Module (ECM), CENSETM module, speed sensors, temperature sensors,
pressure sensors, fueling control actuators, and various operator controlled inputs.
The CENSETM electronics engine monitoring system is standard equipment. The purpose of the Quantum
System Technology is to provide a “stand-alone” product that provides customers with a means of achieving the
design life of the engine due to a reduction of life-reducing incidents and progressive engine damage. With this
system, a network of strategically located sensors within the engine constantly monitors performance data,
sending a stream of data back to the electronic control module. The system monitors performance under specific
loads and conditions over a period of time. The system is equipped with the ability to communicate all this data
on a real-time basis via a communication system. The system provides the following features to maximize engine
availability and minimal cost of operation:
- Monitors Engine Parameters
- Warns the operator
- Engine shutdown protection
- Provides engine operating status
- Predicts engine durability
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 14 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
- Provides Diagnostics
- Leads service technicians to problem areas
- Provides snapshot failure data
- Provides data-logging
- Single cylinder diagnostics
- Key Benefits
- Extended rebuild intervals
- Avoid progressive damage
- Maximize vehicle availability (cost of operation)
Prelubrication
Engine prelubrication -- Prelub™ device -- is mandatory for the QSK78 Industrial engine. P4K-40 Prelub™ is
engine mounted and is controlled independently of the engine control system. Three options are currently
available on the single-stage engine: 1) Customer supplied, which will require Chief Engineer approval for use, 2)
Cummins supplied 24V, and 3) 64V prelube Cummins supplied option. On the two stage configuration, the PL
dependent option is automatically driven out by the selected ST (starter) option. All two stage prelube options are
24V. Reference AEB 44.02, “Prelub™ (Prelubrication Device) for QST30, K38/50, QSK38/50 and QSK45/60/78”,
for more information on P4K-40 Prelub™.
Starters
On the QSK78 single stage engine, two Cummins supplied starter options are available. One is 64V for
locomotive applications, and the other is 24V.
Flywheel Housing
The flywheel housing offered for the QSK78 is SAE “00” housings that have three magnetic pickup (speed
sensor) locations, at 10, 11, and 1 o-clock positions as viewed from the rear. Two magnetic pickup holes are
currently dedicated for use by OEM/customers. One location is currently used for the engine ECM and CENSE
monitoring/control in the ten o-clock position. All magnetic pickup holes available are M22 STOR threads.
Accessory Drive
No accessory drive option is currently available on the QSK78 single stage engine. The accessory drive option is
mandatory for the QSK78 two stage engine and can be used to drive the refrigerant compressor. The clockwise
rotation (as viewed facing the front of the engine) of the drives are the same as the QSKV engines. The ratios are
as follows:
DRIVE GEAR RATIO SPEED (at 1900 engine speed)
Refrigerant Compressor 1.21:1 2,294 RPM
Alternator Drive 1.73:1 3,290 RPM
Alternator
The alternator drive pulley is available on the right-bank of the engine. The alternator drives are common for both
the single and two stage engines. The QSK78 alternator drive is capable of providing power to a 260 Amp
alternator. A 5-groove poly-vee pulley and belt are utilized for alternator drives at or below 100 Amp. Above 100
Amp, a 10-groove poly-vee pulley and belt are used. The 260 Amp alternator drive option incorporates a
backside automatic idler arrangement. The alternator drive option is a dependent EH option that is driven out
when the customer selects the alternator (EE) and alternator mounting (EH) options.
The overall ratio for the alternator drive arrangement with 5 and 10 groove pulleys is 3.56:1.
No alternator option is currently available on the QSK78 single stage engine.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 15 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Refrigerant Compressor
The refrigerant compressor drive is located on the left bank of the two stage engine. The drive pulley is selected
via the mandatory AD option, and is offered as two single vee 3/8" groove belts (0.38 in) or as a poly-vee groove
pulley (8-groove PK-section). Two compressor mounting arrangements (CF option) are available. CF6008 is
compatible with a Sanyo refrigerant compressor model SD510, and CF6013 is compatible with the Alma 51-
86106A. A CF option is compatible with the Sanden 4545 models. CF 6008 is configured as a fixed center,
manual belt tension two pulley system while CF 6013 is a three pulley, auto tensioned system. See GCE for the
most up to date option availability.
No refrigerant compressor is currently available on the QSK78 single stage engine.
Hydraulic Pump Drive
The hydraulic drive option is a front gear train accessory drive and is located on the rear of the front gear train.
The LTA water pump must run on the front of the front gear train accessory drive.
Air Compressor
None available on the QSK78.
Fan Drive
The drive is capable of driving fans with requirement up to 150 hp with maximum fan inertia of 50 kg*m2. Fan
drives used on the QSK78 engines will have fixed fan centers. Tensioning will be accomplished by idler, which
needs to be adjusted manually. The fan drive and idler do not require external greasing during normal
maintenance schedules.
Fan drive uses a Rockford series 270 fan clutch. S270 clutch is a fully modulated, engine lubricating oil actuated
fan clutch with 270 mm diameter friction plate.
No fan drive is currently available on the QSK78 single stage engine.
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 16 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Change Log
Revision Date Author Change Page(s)
09 14Jan16 Kyle Fields Added text “(D773001CX03, D773003CX03)”. 1
Changed text from “The following QSK78 Industrial 3
ratings are available. Altitude capability of the QSK78
engine is enhanced with the availability of LTAs and
two stage turbocharging. Additional ratings can be
requested by submitting a Value Package Change
Request (VPCR). Also shown in the table is the
altitude capability for each rating. There is a 4% per
1000 ft power derate beyond the indicated altitude
threshold at rated conditions. For the latest ratings
information, refer to GCE (https://gce.cummins.com/
ice/ice_present/ice_qsk78/index_qsk78.htm).” to “Fuel
ratings (FR options) for the QSK78 engine range
from: 2461 kW (3300 hp): Single stage turbocharged.
2207 kW - 2610 kW (2960 hp - 3500 hp): 2-stage
turbocharged. The complete list of QSK78 Tier 2
ratings can be found on the GCE website under the
Ratings and Datasheets section (https://gce.cummins.
com/ice/ice_present/ice_qsk78/index-qsk78.html).”
Deleted old Table 1 “Ratings comparison between the 2 3
state and single configurations”.
Deleted rows “Specific Power (hp/L)”, “Mean Piston 3
Speed @ Rated (ft/sec)”, and “Engine Weight-Dry
(lb)” from Table 1.
Changed text from “lower” to “lowers”. 4
Added text “for”. 4
Changed text from “is” to “are”. 4, 15
Changed text from “Eliminator” to “Eliminator™”. 4, 12
Changed text from “Fuel Cooling Systems 4
Industrial Applications Installation Recommendations” to 4
“Installation Requirements - Fuel Temperature”.
Added text “up”. 5
Changed text from “Two separate cooling circuits are 5
used in the QSK78 engine. A 2P2L cooling circuit
makes use of an engine loop and a Low Temperature
Aftercooling (LTA) loop. The engine loop operates at
relatively higher temperatures and is therefore
referred to as the High Temperature Circuit (HTC).
The LTA loop operates at lower temperatures and is
therefore often referred to as the Low Temperature
Circuit (LTC). The two circuits make use of two
separate water pumps. The HTC main engine loop is
used to circulate the engine jacket coolant and the
LTA loop provides coolant to intercoolers (intercoolers
on two stage only) and aftercoolers. The high output
LTA water pump is located at the front left bank side
of the engine. The engine water pump is located at
the front right-bank side of the engine. Two separate
radiators are required, one for the engine heat
rejection (engine) radiator and the other radiator for
aftercooler heat rejection (LTA radiator). Separate
thermostats control the LTA and HTC loops. There
are eight thermostats (four per side) used for the HTC
engine loop, with the thermostats located in the
thermostat housing at the front center of the engine.
There are four thermostats used for the LTC
aftercooler loop, with the thermostats located inside
the box at the front left bank. Refer to the schematic
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 17 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
for coolant flow and plumbing on the next page. Refer
to AEB 24.26, “Two Pump, Two Loop Cooling System
Installation Requirements and Recommendations”.” to
“The cooling system is a 2-pump, 2-loop system that
requires both a High Temperature Circuit (HTC)
radiator and a Low Temperature Circuit (LTC)
radiator. A Low Temperature Aftercooler (LTA) is a
coolant-to-air heat exchanger that is used to reduce
the temperature of the compressed air entering the
intake manifold. A 2-pump, 2-loop system provides
the means to get higher power densities while
meeting Tier 2 emission standards. The HTC is used
to cool the engine block and critical components. The
LTC supplies coolant solely to the LTAs. The two
cooling circuits share a common top tank. Each
coolant circuit must have its own radiator. For a
complete listing of installation requirements, please
refer to AEB 24.26 “Two-Pump, Two-Loop (2P-2L)
Cooling System Installation Requirements and
Recommendations.” Additional information can also
be found in AEB 24.18, “Industrial Installation
Requirements- LDI/MR/HD/HHP Cooling System
Design.” While each circuit has its own water pump
impeller, the pumps share the same housing and are
driven by a common shaft. The water pumps are
mounted off the back of the front gear housing on the
lower right bank.”
Added new section “High Temperature Circuit (HTC)”. 5-6
Added new section “Low Temperature Circuit (LTC)”. 6
Deleted text “circuits” after text “HTC” in Surge Tank and 6
Filling section.
Changed text from “HTC circuit + LTC circuit” to “HTC + 7
LTC”.
Deleted text “circuit” after text “LTC” in last sentence in 7
Coolant Treatment and Filtration section.
Changed text from “LB rear LP” to “left bank (LB) rear 10
low pressure (LP)”.
Changed text from “Angularity for the QSK78 two stage 14
engine is 15 degrees in all directions.” to “The
angularity for the single stage and two stage engine is
dependent on the oil pan selected. The angularity limit
is published in the option notes on GCE.”
Deleted text “Angularity for the QSK78 single stage 14
engine is nine degrees longitudinal (including any
braking affects in locomotive applications) and eight
degrees lateral.” from Breather section.
Changed text from “Engineering” to “Engineer”. 15
08 29Sep15 Arine Hillery Initial creation of CEB from AEB 10.81 All
07 15Apr14 Leigha Curtin Added “Calibration Requests” section 3
06 13Dec13 Leigha Curtin Updated owner. 1
Added text “The plumbing of crankcase gases into the air 13
intake system [Closed Crankcase Ventilation (CCV)]
is not allowed. Crankcase gases contain oil and
moisture, which if introduced into the air intake
system, can result in engine performance issues
and/or damage to turbochargers.”
05 14Jan13 Jeremiah Cole Updated technical data, layout and formatting, AEB All
references. 3
Changed Rated BSFCl was 0.344, is 0.346. 3
Changed Compression Ratio; was 15.3:1, is 15.5:1. 3
Changed Engine Weights; were 24,546 and 21,900, is
26,044 and 24,084. 4
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 18 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
QSK78 Mechanical Product Information CEB 00069
Updated Engine Envelope table. 9
Changed hours; was 2,000, is 1,000.
04 30Jul10 Blair Duguid Added QSK78 single stage information all
03 15May10 Blair Duguid Removed reference to air intake system since 14
information is on base engine datasheets
02 1July09 Blair Duguid Added Tier 2 information – Blair Duguid 1, 3,
Updated compressor information 15
01 30Jan08 Blair Duguid Edited by K. Blair Duguid. See updates in blue. all
00 January2001 Orvin Kendal Originally authored by Orvin Kendall
Internal Use Only - For business use only by employees and authorized non-Cummins entities with a need to know basis per
CORP-00-24-0-00.
Revision 09, 14 January 2016 Page 19 of 19 © Copyright 2016 Cummins Inc.
You might also like
- QSK78 Owners Manual PDFDocument17 pagesQSK78 Owners Manual PDFjengandxb100% (2)
- Sulzer S20UDocument180 pagesSulzer S20Uhartley112100% (4)
- Gantt ChartDocument49 pagesGantt ChartJayaram ParlikadNo ratings yet
- Australian StandardDocument37 pagesAustralian StandardkrainajackaNo ratings yet
- Speed Signal ListDocument42 pagesSpeed Signal ListGoran Mann0% (1)
- 12V 4000 M73/M73L Diesel Engines: For Fast Vessels With High Load Factors (1B)Document3 pages12V 4000 M73/M73L Diesel Engines: For Fast Vessels With High Load Factors (1B)derfgthNo ratings yet
- Inventor ReportDocument7 pagesInventor Report2cekal50% (2)
- Catalogo Afa Cummins QSK45 Series PDFDocument76 pagesCatalogo Afa Cummins QSK45 Series PDFAlexis Sanchez100% (2)
- Power Generation Engine Performance DataDocument4 pagesPower Generation Engine Performance Dataacere18100% (1)
- QSK 45/60 cylinder head familiarization and troubleshootingDocument3 pagesQSK 45/60 cylinder head familiarization and troubleshootingnugraha kurniawanNo ratings yet
- QST30 G5Document2 pagesQST30 G5Hoang Minh Hung75% (4)
- DocumentDocument11 pagesDocumentthanhhai31No ratings yet
- 06R0862362+6067MK62 Piezas Comunes PDFDocument2 pages06R0862362+6067MK62 Piezas Comunes PDFAlexis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Mark11 Spare Parts Section - REV3Document72 pagesMark11 Spare Parts Section - REV3Orlando MelipillanNo ratings yet
- QSK60 Starting SystemDocument4 pagesQSK60 Starting SystemagvassNo ratings yet
- QSK78 G-Drive Mechanical ProductDocument24 pagesQSK78 G-Drive Mechanical Productquang_dtd09100% (2)
- Diesel Engines 8V 4000 M53/M63 SpecsDocument2 pagesDiesel Engines 8V 4000 M53/M63 Specsroberttv374No ratings yet
- DGB Dynamic Gas Blending CATDocument20 pagesDGB Dynamic Gas Blending CATEslamAldenAbdoNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel B20 Approval Information: Edward Lyford-Pike Michael O'DonnellDocument29 pagesBiodiesel B20 Approval Information: Edward Lyford-Pike Michael O'DonnelltstkupdhNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Afa Cummins QSK78 Series PDFDocument66 pagesCatalogo Afa Cummins QSK78 Series PDFAlexis Sanchez100% (2)
- MTU Solution Guide Marine Oct 2022Document59 pagesMTU Solution Guide Marine Oct 2022TwinNo ratings yet
- Capella Wiring Diagram ConverterDocument1 pageCapella Wiring Diagram ConverterRandalNo ratings yet
- MTU 20V4000 DS2800: Diesel Generator SetDocument4 pagesMTU 20V4000 DS2800: Diesel Generator SetMinaSaeedNo ratings yet
- Motor Detroit Serie 40eDocument212 pagesMotor Detroit Serie 40eJhoset Apaza Charca100% (1)
- Manual de Partes QSK45Document173 pagesManual de Partes QSK45ChristianM.Carrasco100% (1)
- 16V4000 - T1637K33 Rated Power 2700 BHP at 1900 R-MinDocument9 pages16V4000 - T1637K33 Rated Power 2700 BHP at 1900 R-MinJuan PujolNo ratings yet
- Mtu - Oil & Gas Sales ProgramDocument63 pagesMtu - Oil & Gas Sales Programalamen ZayidNo ratings yet
- M015710 04e PDFDocument211 pagesM015710 04e PDFTaz UddinNo ratings yet
- Genuine Cummins Celect PX Injectors: Better Reliability. Every TimeDocument2 pagesGenuine Cummins Celect PX Injectors: Better Reliability. Every TimeMassahiro Filho100% (1)
- Module 8 - MaintDocument19 pagesModule 8 - MaintWilliam RuizNo ratings yet
- Emissions Data For Cat EngineDocument4 pagesEmissions Data For Cat EngineRajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- QSX15 SpecDocument4 pagesQSX15 Specpdealers100% (1)
- Mids 3606-08Document12 pagesMids 3606-08Jorge EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Block InsertsDocument8 pagesBlock Insertsleaw81100% (1)
- Cat C175Document20 pagesCat C175Luis Torres Grugue100% (3)
- Series 4000: Engines For Industrial and Mining ApplicationsDocument2 pagesSeries 4000: Engines For Industrial and Mining Applicationswaleed yehia100% (1)
- QSK19G PerformanceDocument5 pagesQSK19G PerformancetroyNo ratings yet
- Lubricating Oil Consumption and Acceptable LimitsDocument18 pagesLubricating Oil Consumption and Acceptable LimitststkupdhNo ratings yet
- MTU CI Ag Mining SalesProgramDocument37 pagesMTU CI Ag Mining SalesProgramMarcial MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Schematic125 170Document4 pagesSchematic125 170agus haryono100% (1)
- Diesel Generator Set C Series: Specification SheetDocument4 pagesDiesel Generator Set C Series: Specification Sheetrobinknit2009No ratings yet
- 26455Document46 pages26455klo422No ratings yet
- KV 38-50Document101 pagesKV 38-50Hilaire Kamana100% (1)
- Sebp6454 00 00 AllDocument1,075 pagesSebp6454 00 00 AllAliHabesNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engines 8V/10V 2000 M72: For Vessels With High Load Factors (1B)Document2 pagesDiesel Engines 8V/10V 2000 M72: For Vessels With High Load Factors (1B)zaki100% (1)
- Data Sheet QSK60 PDFDocument3 pagesData Sheet QSK60 PDFjaimenovoah100% (1)
- qsk60 Engine ControlsDocument27 pagesqsk60 Engine Controlsзавир мансуровNo ratings yet
- 1100 Series PerkinsDocument2 pages1100 Series PerkinsGilberto Diaz CastilloNo ratings yet
- Kenr5396 04 01 AllDocument76 pagesKenr5396 04 01 AlllunikmirNo ratings yet
- Public 1560308493 85265-Marineengine-Sm-2019Document90 pagesPublic 1560308493 85265-Marineengine-Sm-2019Dwiko RiyonoNo ratings yet
- 001a HM02316 - 00 Engine SpecificationsDocument92 pages001a HM02316 - 00 Engine SpecificationsBruno VenturaNo ratings yet
- CUMMINS New Intake and Exhaust Valves Cummins qsk60Document14 pagesCUMMINS New Intake and Exhaust Valves Cummins qsk60GazetoNo ratings yet
- Cummins Isx 15L Engine: Jacobs Engine Brake (Intebrake)Document2 pagesCummins Isx 15L Engine: Jacobs Engine Brake (Intebrake)mauricio olayaNo ratings yet
- SS815Document24 pagesSS815Adel Ahmed100% (1)
- System Overview TroubleshootingDocument18 pagesSystem Overview TroubleshootingPablo Cesar Poma ArrateaNo ratings yet
- MTU OE EX-MK-8-7 - Gen - Systems - Insp - Prev - Maint - ChecklistDocument1 pageMTU OE EX-MK-8-7 - Gen - Systems - Insp - Prev - Maint - ChecklistAfcade D'AgoueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Reusing Cylinder LinersDocument6 pagesGuidelines for Reusing Cylinder LinerssughieantoNo ratings yet
- QST30 MineriaDocument4 pagesQST30 MineriaElio Custodio Huachaca100% (1)
- Diesel Engine SupportDocument1 pageDiesel Engine SupportsxturboNo ratings yet
- Copia de QSK19 Engine Fuel System Familiarization (Sólo Lectura)Document73 pagesCopia de QSK19 Engine Fuel System Familiarization (Sólo Lectura)Gallego CarlosNo ratings yet
- Installation Conditions: Gas Engine-Generator Sets With Series 400, Series 500, and Series 4000 EnginesDocument62 pagesInstallation Conditions: Gas Engine-Generator Sets With Series 400, Series 500, and Series 4000 EnginesBen ZithaNo ratings yet
- Every Ton.: For Mining ApplicationsDocument4 pagesEvery Ton.: For Mining ApplicationsRichard Sequeiros AlvarezNo ratings yet
- SPB 46-Alternador Bearing MaintenanceDocument3 pagesSPB 46-Alternador Bearing MaintenanceedilbertoNo ratings yet
- Aeb 02463Document29 pagesAeb 02463Quang PhamNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diagramas Electricos de MotoresDocument3 pagesCummins Diagramas Electricos de Motoresyvette98% (57)
- Service.: The V8-5V EngineDocument52 pagesService.: The V8-5V EngineKushal ExpertNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For HOLES in BONDEK II SheetDocument4 pagesGuidelines For HOLES in BONDEK II SheetSK ChauNo ratings yet
- Vicat Apparatus Setting Time and Consistency of Cement: StandardsDocument1 pageVicat Apparatus Setting Time and Consistency of Cement: StandardsSciencetes PlusNo ratings yet
- M2LT Project Manual & SpecificationsDocument418 pagesM2LT Project Manual & SpecificationsfastreturnNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Conveyor Belt Operating ProcedureDocument3 pages4.7 Conveyor Belt Operating Procedurejohnson OlubiNo ratings yet
- The Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeDocument12 pagesThe Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeAndriNo ratings yet
- STD1 Crimping Chart March 2020 Final 2Document1 pageSTD1 Crimping Chart March 2020 Final 2Bernd RichterNo ratings yet
- Asad's Profile - Asda SAP-SD & MMDocument6 pagesAsad's Profile - Asda SAP-SD & MMTechneto TonicNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning With GisDocument9 pagesUrban Planning With GisMostaque AhmedNo ratings yet
- Flipkart's Big Billion Day Sale IT FailuresDocument21 pagesFlipkart's Big Billion Day Sale IT FailuresManisha KumariNo ratings yet
- Gyrolok CatalogDocument58 pagesGyrolok CatalogmartinvandoornNo ratings yet
- Chimney Sizing Chart For Fireplaces: 100 50 30 20 15 10 8 Flue Area, inDocument1 pageChimney Sizing Chart For Fireplaces: 100 50 30 20 15 10 8 Flue Area, inBen ZithaNo ratings yet
- Jerbi ResumeDocument6 pagesJerbi ResumeLeah Nadine QuimzonNo ratings yet
- Assam & Nagaland 1Document218 pagesAssam & Nagaland 1Ahmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Euskron Profile ENGDocument14 pagesEuskron Profile ENGEuskron Cutting ToolsNo ratings yet
- Technical ManualDocument36 pagesTechnical Manualneeshakothari31No ratings yet
- Philips: Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument74 pagesPhilips: Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisBunga MelurNo ratings yet
- An Architect Reviews Brigade Gateway Architecture IdeasDocument13 pagesAn Architect Reviews Brigade Gateway Architecture Ideasbala0% (1)
- Aluminium Composite Panel - ACP Fabrication - Cladding and Glazing - Partition SheetsDocument7 pagesAluminium Composite Panel - ACP Fabrication - Cladding and Glazing - Partition SheetsALEX PANELSNo ratings yet
- IRender NXT For SketchUp Rendering - RenderPlusDocument6 pagesIRender NXT For SketchUp Rendering - RenderPlusRender PlusNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engine Development Utilizing Design For Six Sigma (DFSS)Document8 pagesCombustion Engine Development Utilizing Design For Six Sigma (DFSS)dilip sahooNo ratings yet
- Pass RulesDocument40 pagesPass Ruleslvsaru50% (2)
- T100 Thrusters PropellerDocument15 pagesT100 Thrusters PropellerNikhilkrishna NairNo ratings yet
- Kitz Gate ValveDocument28 pagesKitz Gate ValvemohamedfirozNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Mobile Satellite (ROUTE) ServiceDocument47 pagesAeronautical Mobile Satellite (ROUTE) ServiceBrooke MayerNo ratings yet