Professional Documents
Culture Documents
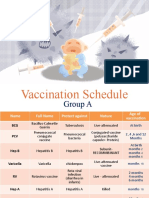
Age Interval Table
Uploaded by
wenyinrianto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesTabel interval imunisasi
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTabel interval imunisasi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesAge Interval Table
Uploaded by
wenyinriantoTabel interval imunisasi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
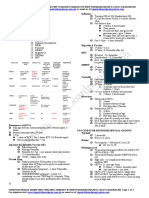
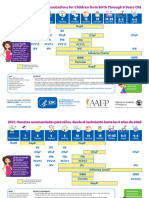
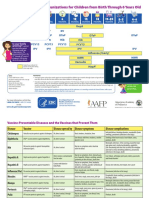
Recommended and Minimum Ages and Intervals
Between Doses of Routinely Recommended Vaccines1,2,3,4
Recommended Minimum
Recommended Minimum age
Vaccine and dose number interval to next interval to next
age for this dose for this dose
dose dose
Diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (DTaP)-15 2 months 6 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
DTaP-2 4 months 10 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
6
DTaP-3 6 months 14 weeks 6-12 months 6 months6
DTaP-4 15-18 months 15 months6 3 years 6 months
DTaP-57 4-6 years 4 years — —
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)-18 2 months 6 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
Hib-2 4 months 10 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
Hib-39 6 months 14 weeks 6-9 months 8 weeks
Hib-4 12-15 months 12 months — —
Hepatitis A (HepA)-15 12-23 months 12 months 6-18 months 6 months
HepA-2 >18 months 18 months — —
Hepatitis B (HepB)-1 Birth Birth 4 weeks-4 months 4 weeks
HepB-2 1-2 months 4 weeks 8 weeks-17 months 8 weeks
HepB-310 6-18 months 24 weeks — —
11
Herpes zoster (HZV) >60 years 60 years — —
Human papillomavirus (HPV)-112 11-12 years 9 years 8 weeks 4 weeks
HPV-2 11-12 years 9 years 4 months 12 weeks12
(+ 2 months) (+ 4 weeks)
HPV-312,13 11-12 years 9 years — —
(+ 6 months) (+5 months)
Influenza, inactivated (IIV)14 >6 months 6 months15 4 weeks 4 weeks
14
Influenza, live attenuated (LAIV) 2-49 years 2 years 4 weeks 4 weeks
Measles-mumps-rubella (MMR)-116 12-15 months 12 months 3-5 years 4 weeks
MMR-216 4-6 years 13 months — —
Meningococcal conjugate (MenACWY)-117 11-12 years 6 weeks18 4-5 years 8 weeks
MenACWY-2 16 years 11 years19 — —
(+ 8 weeks)
Meningococcal polysaccharide (MPSV4)-116 — 2 years 5 years 5 years
MPSV4-2 — 7 years — —
Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)-18 2 months 6 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
PCV-2 4 months 10 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
PCV-3 6 months 14 weeks 6 months 8 weeks
PCV-4 12-15 months 12 months — —
Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV)-1 — 2 years 5 years 3 years
PPSV-220 — 7 years — —
Poliovirus, Inactivated (IPV)-15 2 months 6 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
IPV-2 4 months 10 weeks 8 weeks-14 months 4 weeks
IPV-3 6-18 months 14 weeks 3-5 years 6 months
IPV-421 4-6 years 4 years — —
Rotavirus (RV)-122 2 months 6 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
RV-2 4 months 10 weeks 8 weeks 4 weeks
RV-322 6 months 14 weeks — —
Tetanus-diphtheria (Td) 11-12 years 7 years 10 years 5 years
23
Tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis (Tdap) >11 years 7 years — —
16
Varicella (Var)-1 12-15 months 12 months 3-5 years 12 weeks24
Var-216 4-6 years 15 months25 — —
1 Combination vaccines are available. Use of licensed combination vaccines is generally preferred to separate injections of their
equivalent component vaccines. When administering combination vaccines, the minimum age for administration is the oldest age
for any of the individual components. The minimum interval between doses is equal to the greatest interval of any of the individual
components.
2 Information on travel vaccines including typhoid, Japanese encephalitis, and yellow fever, is available at www.cdc.gov/travel.
Information on other vaccines that are licensed in the US but not distributed, including anthrax and smallpox, is available at
https://emergency.cdc.gov/bioterrorism/.
3 “Months” refers to calendar months.
4 A hyphen used to express a range (as in “12-15 months”) means “through.”
5 Combination vaccines containing a hepatitis B component (Pediarix and Twinrix) are available. These vaccines should not be
administered to infants younger than 6 weeks because of the other components (i.e., Hib, DTaP, HepA, and IPV).
6 The minimum recommended interval between DTaP-3 and DTaP-4 is 6 months. However, DTaP-4 need not be repeated if
administered at least 4 months after DTaP-3. This is a special grace period of 2 months, which can be used when evaluating
records retrospectively. An additional 4 days should not be added to this grace period prospectively, but can be added
retrospectively.
7 If a fourth dose of DTaP is given on or after the fourth birthday, a fifth dose is not needed.
8 Children receiving the first dose of Hib or PCV13 vaccine at age 7 months or older require fewer doses to complete the series.
9 If PedvaxHib is administered at ages 2 and 4 months, a dose at age 6 months is not required. The minimum age for the final
dose is 12 months.
10 HepB-3 should be administered at least 8 weeks after HepB-2 and at least 16 weeks after HepB-1, and should not be
administered before 24 weeks of age.
11 Herpes zoster vaccine is recommended as a single dose for persons 60 years of age and older.
12 Gardasil and Gardasil 9 are approved for males and females 9 through 26 years of age. The minimum age for HPV-3 is
based on the baseline minimum age for the first dose (i.e., 9 years) and the minimum interval of 5 months between the first
and third dose. Dose 3 need not be repeated if it is administered at least 5 months after the first dose, and if the intervals
between doses 1 and 2, and doses 2 and 3, are 4 weeks and 12 weeks, respectively.
13 A two-dose HPV vaccine schedule is recommended for most persons who begin the series before the 15th birthday. See
www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/65/wr/pdfs/mm6549a5.pdf for details.
14 One dose of influenza vaccine per season is recommended for most people. Some children younger than 9 years of age
should receive 2 doses in a single season. See current influenza recommendations for details.
15 The minimum age for inactivated influenza vaccine varies by vaccine manufacturer. See package inserts for vaccine-specific
minimum ages.
16 Combination MMRV vaccine can be used for children 12 months through 12 years of age. See www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5903.pdf
for details.
17 Revaccination with meningococcal vaccine is recommended for previously vaccinated persons who remain at high risk for
meningococcal disease. See www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr6202.pdf for details.
18 High-risk children can receive Menactra as young as 9 months and Menveo as young as 2 months. MenHibrix is given as a four-dose
series at 2, 4, 6, and 12-18 months. It can be given as young as 6 weeks for high-risk children.
19 For routine, non-high risk adolescent vaccination, the minimum age for the booster dose is 16 years.
20 A second dose of PPSV23 5 years after the first dose is recommended for persons <65 years of age at highest risk for serious
pneumococcal infection, and for those who are likely to have a rapid decline in pneumococcal antibody concentration. See
www.cdc.gov/mmwr/PDF/rr/rr4608.pdf for details.
21 A fourth dose is not needed if the third dose was administered on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 months after the
previous dose.
22 The first dose of rotavirus must be administered no earlier than 6 weeks and no later than 14 weeks 6 days. The vaccine series
should not be started for infants 15 weeks 0 days or older. Rotavirus vaccine should not be administered to children older than 8
months 0 days, regardless of the number of doses received before that age. If two doses of Rotarix are administered as age
appropriate, a third dose is not necessary.
23 Only one dose of Tdap is recommended. Subsequent doses should be given as Td. For management of a tetanus-prone wound
in a person who has received a primary series of a tetanus-toxoid containing vaccine, the minimum interval after a previous dose
of any tetanus-containing vaccine is 5 years.
24 A special grace period of 2 months, based on expert opinion, can be applied to the minimum interval of 3 months, when evaluating
records retrospectively, which results in an acceptable minimum interval of 4 weeks. An additional 4 days should not be added to
this grace period.
25 A special grace period of 2 months, based on expert opinion, can be applied to the minimum age of 15 months when evaluating
records retrospectively, which will result in an acceptable minimum age of 13 months. An additional 4 days should not be added to
this grace period.
Adapted from Table 3-1, ACIP General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization. September 2017
You might also like
- Vaccination Guide - Steyn SummaryDocument1 pageVaccination Guide - Steyn SummaryMichelle BrowneNo ratings yet
- The Baby Bump: 100s of Secrets to Surviving Those 9 Long MonthsFrom EverandThe Baby Bump: 100s of Secrets to Surviving Those 9 Long MonthsNo ratings yet
- Rivaan Vaccine ExcelDocument8 pagesRivaan Vaccine ExcelAnuj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)Document13 pagesImmunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)rajNo ratings yet
- Alexander - Peters VaccinationSchedule 04Document1 pageAlexander - Peters VaccinationSchedule 04Alex PetersNo ratings yet
- Vaccination EPI and Non EPIDocument19 pagesVaccination EPI and Non EPIRakhshanda khanNo ratings yet
- B. Schedule of Vaccination: A. Different Important VaccinesDocument4 pagesB. Schedule of Vaccination: A. Different Important VaccinesJane LappaoNo ratings yet
- Health Form Academic Year: Admission No: Student Name: Class & Section: Health InformationDocument1 pageHealth Form Academic Year: Admission No: Student Name: Class & Section: Health InformationNagraja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Catch-up Recommendations by Age and Prior DosesDocument1 pageVaccination Catch-up Recommendations by Age and Prior DosesLaurensia Erlina NataliaNo ratings yet
- Sara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetDocument2 pagesSara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetJan FloydNo ratings yet
- Malaria Updates: Fe Esperanza Espino Department of Parasitology Research Institute For Tropical MedicineDocument25 pagesMalaria Updates: Fe Esperanza Espino Department of Parasitology Research Institute For Tropical MedicineSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics - Arjuna 1.0 NEW 2Document9 pagesPaediatrics - Arjuna 1.0 NEW 2Ajay singhNo ratings yet
- Immunization ScheduleDocument18 pagesImmunization Scheduledr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument4 pagesVaccinesEbtesamNo ratings yet
- National Immunization Schedule: One Dose at 14 Weeks, Along With OPV3. Injectable Dose GivenDocument1 pageNational Immunization Schedule: One Dose at 14 Weeks, Along With OPV3. Injectable Dose GivenSandip PatilNo ratings yet
- Calendarul Vaccinarilor in Republica MoldovaDocument11 pagesCalendarul Vaccinarilor in Republica MoldovaAnisoara S.No ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Case StudyDocument10 pagesTyphoid Fever Case StudyArchana Sahu100% (3)
- Cat Breeding SOPDocument3 pagesCat Breeding SOPUrchNo ratings yet
- Food Room Temperature Refrigerator Freezer at 0°F in Out in Out in Out in OutDocument1 pageFood Room Temperature Refrigerator Freezer at 0°F in Out in Out in Out in OutmjhachemNo ratings yet
- Vaccine - Ate FormDocument2 pagesVaccine - Ate FormGodino ChristianNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument2 pagesVaccinesLana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument1 pageImmunizationMicah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination FormDocument1 pageVaccination Formkunal khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Case Stutdty 2Document13 pagesCase Stutdty 2HansrajNo ratings yet
- Review of Preventive and Social MedicineDocument1 pageReview of Preventive and Social MedicinemohanNo ratings yet
- VACCINESDocument1 pageVACCINESNensu-chanNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization RecordDocument4 pagesChildhood Immunization RecordJoseph Edward DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Immunisation 2013 PDFDocument1 pageImmunisation 2013 PDFjuniorebindaNo ratings yet
- EPI Schedule Malawi COM 2017Document2 pagesEPI Schedule Malawi COM 2017INNOCENT KHULIWANo ratings yet
- Glucose Ketone Index and Clinical Outcomes of Cancer Patients on Ketogenic DietDocument1 pageGlucose Ketone Index and Clinical Outcomes of Cancer Patients on Ketogenic DietjoycechicagoNo ratings yet
- The Periods of Eruption Milk and Permanent TeethDocument1 pageThe Periods of Eruption Milk and Permanent TeethNada AliNo ratings yet
- Immunization Child2005 EnglDocument4 pagesImmunization Child2005 EnglGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Vax 0-6Document2 pagesVax 0-6alvinmhNo ratings yet
- National Immunization ScheduleDocument4 pagesNational Immunization ScheduleKenneth Ralph UrbanNo ratings yet
- 11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraDocument2 pages11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraMJ Arcilla100% (1)
- Precept2 - Cardio BlockDocument9 pagesPrecept2 - Cardio BlockMary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule BWDocument4 pagesCatchup Schedule BWlcmurilloNo ratings yet
- ABCD Matrix Vaccination Guideline 2017Document15 pagesABCD Matrix Vaccination Guideline 2017ana flavia PinheiroNo ratings yet
- VACCINES Eng Spa 0 To 6 Years ScheduleDocument4 pagesVACCINES Eng Spa 0 To 6 Years ScheduleMaría del Mar OrtizNo ratings yet
- Precept1 - Pulmo BlockDocument15 pagesPrecept1 - Pulmo BlockMary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- Sample CPCDocument50 pagesSample CPCCharles Gerard B. BeluanNo ratings yet
- We Wish You Best of LuckDocument2 pagesWe Wish You Best of LuckdnyaneshwarNo ratings yet
- TVCC Vaccination Presentation-1Document57 pagesTVCC Vaccination Presentation-1Gagandeep Singh DhamiNo ratings yet
- NR 446 Week 5 ATI Weekly Tips PediatricsDocument18 pagesNR 446 Week 5 ATI Weekly Tips PediatricsChristine LansdownNo ratings yet
- Dog & Cat Vaccination ScheduleDocument2 pagesDog & Cat Vaccination ScheduleEj PaulinoNo ratings yet
- PSM Golden PointsDocument43 pagesPSM Golden PointsRutujaNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Immunizations 2018Document4 pagesPEDIA Immunizations 2018Mary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- IMUNISASI2Document29 pagesIMUNISASI2RatnaSuryatiNo ratings yet
- 12 - Bakuna Atbp.Document4 pages12 - Bakuna Atbp.gilbert agudoNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument1 pageVaccinationKrishna SaiNo ratings yet
- EPI Schedule of NepalDocument4 pagesEPI Schedule of NepalUtsarg ChandNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsMatri SearchNo ratings yet
- Child Health Nursing - Nursing Process On Iron Deficiency Anemia - 16-03-2021Document28 pagesChild Health Nursing - Nursing Process On Iron Deficiency Anemia - 16-03-2021payel.das0607No ratings yet
- Immunisation Schedule Guide with Vaccine Ages and DatesDocument2 pagesImmunisation Schedule Guide with Vaccine Ages and Datesvu2brainsNo ratings yet
- Calendarul vaccinarilor in Republica MoldovaDocument1 pageCalendarul vaccinarilor in Republica MoldovaStahi OlgaNo ratings yet
- Vaccines!!!Document6 pagesVaccines!!!Stephanie OngNo ratings yet
- Hytirked PDFDocument2 pagesHytirked PDFAxel ZeroNo ratings yet
- Recommended storage temperatures for fresh produceDocument2 pagesRecommended storage temperatures for fresh produceHatim LechqerNo ratings yet
- High Risk Follow Up FileDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Follow Up Filedipen raiNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disinfection in HistopathologyDocument4 pagesCoronavirus Disinfection in Histopathologywenyinrianto100% (1)
- Part 13 Neonatal Resuscitation - AHA 2015Document19 pagesPart 13 Neonatal Resuscitation - AHA 2015Andi SuryajayaNo ratings yet
- Girl Growth ChartDocument2 pagesGirl Growth ChartwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- CD013277 AbstractDocument4 pagesCD013277 AbstractwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NeonatologyDocument45 pagesPediatric NeonatologywenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Transfusion Practice Guidelines For Medical Interns BangladeshDocument42 pagesClinical Transfusion Practice Guidelines For Medical Interns Bangladeshratriprimadiati100% (1)
- CPR PediatrikDocument31 pagesCPR PediatrikwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- NutriflexlipidperiDocument2 pagesNutriflexlipidperiwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- TBCDocument3 pagesTBCwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- Renal Tubular AcidosisDocument2 pagesRenal Tubular AcidosiswenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Nelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy 24th Edition 2018Document325 pagesNelson's Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy 24th Edition 2018Eduardo Rios Dubois100% (2)
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) StepsDocument1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) StepsLenox BlackNo ratings yet
- Cebm Prognosis Worksheet PDFDocument3 pagesCebm Prognosis Worksheet PDFthereberryNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) StepsDocument1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) StepsLenox BlackNo ratings yet
- Faktor Prognostik Pertumbuhan Bayi PrematurDocument7 pagesFaktor Prognostik Pertumbuhan Bayi PrematurwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- EpilepsiDocument21 pagesEpilepsiwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- CASP Cohort Study Checklist DownloadDocument7 pagesCASP Cohort Study Checklist DownloadRois HasyimNo ratings yet
- Post-Splenectomy Vaccine ProphylaxisDocument6 pagesPost-Splenectomy Vaccine ProphylaxisDavinPannaaustenNo ratings yet
- PertusisDocument28 pagesPertusiswenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnaemiaDocument132 pagesIron Deficiency AnaemiaHectorNo ratings yet
- CP Growth ChartDocument30 pagesCP Growth ChartJijie Azeera100% (1)
- GPU KARTU GRAFIS TERBARUDocument5 pagesGPU KARTU GRAFIS TERBARUEndi BurhanNo ratings yet
- Forrest PlotDocument29 pagesForrest Plotemergency2No ratings yet
- PertusisDocument28 pagesPertusiswenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- RituximabDocument14 pagesRituximabwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Post-Splenectomy Vaccine ProphylaxisDocument6 pagesPost-Splenectomy Vaccine ProphylaxisDavinPannaaustenNo ratings yet
- Sindrom AlagileDocument8 pagesSindrom AlagilewenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Congenital Pulmonary Valve StenosisDocument10 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Congenital Pulmonary Valve StenosiswenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- How I Treat Mixed-Phenotype Acute LeukemiaDocument10 pagesHow I Treat Mixed-Phenotype Acute LeukemiawenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- GiodeDocument43 pagesGiodebgtbingoNo ratings yet
- Meningococcal Meningitis - DR Ooi Phaik YeeDocument66 pagesMeningococcal Meningitis - DR Ooi Phaik YeeNg Chee KeongNo ratings yet
- FDA Approval GuideDocument38 pagesFDA Approval GuideYuwono WibowoNo ratings yet
- All About Vaccine Preventable DiseasesDocument57 pagesAll About Vaccine Preventable DiseasesCecilia FNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Meningococcal Pneumonia: A ReviewDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Meningococcal Pneumonia: A ReviewRizki Handayani SiregarNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedDocument11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedPatricia Bernadette PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Health History and Immunization Form: University of Valley Forge - Health CenterDocument4 pagesHealth History and Immunization Form: University of Valley Forge - Health CenterBernard AmetepeNo ratings yet
- Holding Company for Biological Products & VaccinesDocument65 pagesHolding Company for Biological Products & Vaccineskoky123456789No ratings yet
- Meningitis (Completed)Document26 pagesMeningitis (Completed)seema83% (6)
- Vaccine Plan: The Dr. Paul ApprovedDocument9 pagesVaccine Plan: The Dr. Paul Approvedpaul popescu100% (1)
- Dd/Mm/Yyyy Dd/Mm/Yyyy Dd/Mm/YyyyDocument6 pagesDd/Mm/Yyyy Dd/Mm/Yyyy Dd/Mm/YyyyJohn50% (2)
- Immunization - Dr. SarahDocument14 pagesImmunization - Dr. Sarahf6bk6xnppyNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument13 pagesAdult Combined ScheduleJustin Ng SincoNo ratings yet
- 2ndK Entry Require CompleteBookDocument13 pages2ndK Entry Require CompleteBookWXYZ-TV DetroitNo ratings yet
- Sanofi 2015Document109 pagesSanofi 2015Abdulwahab AfridiNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Administration Record For Children and TeensDocument2 pagesVaccine Administration Record For Children and TeensGian Franco ApesNo ratings yet
- Coding Preventive CareDocument42 pagesCoding Preventive CareNick flemmingNo ratings yet
- Pedsap 1 ImmunologyDocument96 pagesPedsap 1 ImmunologyNeha Oberoi100% (1)
- Vaccinations Spina Bifida and HydrocephalusDocument6 pagesVaccinations Spina Bifida and HydrocephalusShine CharityNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Schedule Recommended Adults 2022 v03Document2 pagesVaccine Schedule Recommended Adults 2022 v03mariumNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05Document2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05GAnnNo ratings yet
- Links To Clinical Info About The VaccineDocument9 pagesLinks To Clinical Info About The VaccinekarunaNo ratings yet
- Immunization FormsDocument6 pagesImmunization FormsNadya IrsalinaNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument6 pagesAdult Combined SchedulesharvaniNo ratings yet
- Pre-school Vaccination Schedule in KSADocument64 pagesPre-school Vaccination Schedule in KSAManal OtNo ratings yet
- Amy Pharma ClaimesDocument8 pagesAmy Pharma ClaimesVishwas BijjahalliNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Adverse Events Separating Myth From RealityDocument9 pagesVaccine Adverse Events Separating Myth From RealityPaul MuñozNo ratings yet
- Immunisation Schedule Victoria-November 2021Document6 pagesImmunisation Schedule Victoria-November 2021Julie PanditNo ratings yet
- 11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraDocument2 pages11 - ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR Pedia Handout by DR - Ian de VeraMJ Arcilla100% (1)
- What Is Meningitis?Document7 pagesWhat Is Meningitis?laujeroNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)