Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Between
Uploaded by
eclipse1130Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Between
Uploaded by
eclipse1130Copyright:
Available Formats
ANEUPLOIDY Distinguish between KARYOTYPE
CLEAVAGE
FURROW and
CELL PLATE
Distinguish between
NONDISJUNCTION G1, S and G2 SISTER
(in Interphase) CHROMATIDS
CYTOKINESIS CENTROMERE FOUR STAGES OF
MITOSIS
(and main events of
each)
Distinguish between
CROSSING OVER BINARY FISSION MITOSIS
and
MEIOSIS
CHROMOSOME RECOMBINATION HOMOLOGOUS
FREQUENCY CHROMOSOMES
Karyotype – A procedure that is done Cleavage Furrow – Occurs in animal Aneuploidy – When a cell has either
to determine if an individual has the cells to finish cytokinesis. Involves the too few or too many chromosomes—
correct number of chromosomes. narrowing of the region between the an abnormal number. Polyploidy is a
new daughter cells followed by the type of aneuploidy.
cells pinching off from one another.
Cell Plate – Occurs in plant cells to
finish cytokinesis. Involves the
formation of a plate between daughter
cells.
Sister Chromatids - Two identical G1 – First phase of Interphase. During this Nondisjunction - Situation where
copies of a time the cell grows and the processes of chromosomes fail to separate properly
chromosome that cellular respiration and protein synthesis during Meiosis (I or II). This results in
take place.
are bound together an abnormal
S – Second phase of Interphase. During
at the centromere. this time the DNA is copied while other number of
These exist after cellular processes also continue. chromosomes
DNA replication. G2 – Last phase of Interphase. During in a daughter
this time the cell grows and the processes cell.
of cellular respiration and protein synthesis
take place.
Prophase - Chromosomes condense Centromere- Region of chromosome Cytokinesis – The division of the
and become visible. where sister chromatids attach to each cytoplasm and its contents. Occurs
Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in other. after the process of mitosis.
the middle of the cell.
Anaphase – sister chromatids are
pulled apart by microtubules (spindle
fibers).
Telophase - Cytokinesis (cell splitting)
begins.
Mitosis - Cell division resulting in two Binary Fission- Spitting of cell into Crossing Over – Occurs during
identical cells. two daughter cells after DNA Prophase I of Meiosis. Sister
replication. A form of asexual chromatids exchange genetic material.
Meiosis - Cell division resulting in four reproduction in bacteria.
gamete cells (each with half the
number of chromosomes as the
original cell). Crossing over occurs in
meiosis. A diploid cell divides into four
haploid cells.
Homologous Chromosomes- Pair of Recombination Frequency - The Chromosome – Segment of DNA,
chromosomes that share the same frequency at which two genes that are containing specific genes. Human
genetic information. One homologous on the same chromosome cross over beings have 46 chromosomes in each
chromosome comes from each. (thus separating alleles that were of their somatic cells.
originally on the same chromosome). DNA is condensed into visible
chromosomes just before mitosis
Linked genes = 2 genes on the same occurs.
chromosome
You might also like
- Cellular Signal Processing - An Introduction To The Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction (2017, Garland Science)Document656 pagesCellular Signal Processing - An Introduction To The Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction (2017, Garland Science)asfsdgsadghadfhNo ratings yet
- Meiosis BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesMeiosis BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionYihui WongNo ratings yet
- Worksheets Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesWorksheets Cell Divisionsalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Cell Biology quiz questionsDocument13 pagesCell Biology quiz questionskahfiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle N Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell Cycle N Cell DivisionDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Worksheet: Prophase Metaphase InterphaseDocument3 pagesMitosis Worksheet: Prophase Metaphase InterphaseChristopher John Sumilang100% (2)
- Cell Division LessonDocument9 pagesCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- Reviewer in General ZoologyDocument12 pagesReviewer in General ZoologyJasmine Fritz CabreraNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab ReviewDocument72 pagesAP Biology Lab ReviewPaweenwat ThongprasopNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Survival GuideDocument4 pagesSurvival Guideeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle&MitosisDocument43 pagesCell Cycle&MitosisPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- MITOSIS VS MEIOSIS COMPARISONDocument6 pagesMITOSIS VS MEIOSIS COMPARISONEvcha WangagNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS and MITOSISDocument4 pagesMEIOSIS and MITOSISHannaj May De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- VC1 - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesVC1 - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAnubhab DasNo ratings yet
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- MustakDocument3 pagesMustakMh Mari HereNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- 5.cell DivisionDocument54 pages5.cell DivisionRaymond LundaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionSsonko EdrineNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument87 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Document16 pagesBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Cell Cycle: AmoebaDocument4 pagesCell Division and Cell Cycle: AmoebaGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- BTN222 L4 CellCycle 2019Document51 pagesBTN222 L4 CellCycle 2019rafiya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Science ResearchDocument3 pagesScience ResearchShaira Jea ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StagesDocument8 pagesMeiosis StagesAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionArnavNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - Clay ModellingDocument4 pagesMeiosis - Clay ModellingAlexandra M.No ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis InfographDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis InfographPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesMeiosis: Cell DivisionAthena AretaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Chromosome ReplicationDocument5 pagesCell Division and Chromosome Replicationkami gourgaemNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlidesDocument19 pagesCell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlideslkjosNo ratings yet
- WMSTU Bio2 Course Genetics Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisDocument5 pagesWMSTU Bio2 Course Genetics Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisCobe Christian LascunaNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Cell Division WorkbookDocument8 pagesCell Division WorkbookKaitlyn DuarteNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument6 pagesMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument3 pagesGenbioMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Cell DivisionDocument5 pages2.5 - Cell DivisionAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- 99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Document33 pages99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Nicole Xie [Student]No ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocument11 pagesCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNo ratings yet
- Human Bio and Genetics Week 3 Cell Division Mitosis and MeiosisDocument31 pagesHuman Bio and Genetics Week 3 Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosisflowersalive11No ratings yet
- Ch-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument4 pagesCh-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionHans RajNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesShafa SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument5 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleSTEINER 97No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ReviewerNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionZaineNo ratings yet
- AP Cell Cycle-Mitosis and MeiosisDocument31 pagesAP Cell Cycle-Mitosis and MeiosisRexNo ratings yet
- PPT 2 Mitosis vs MeiosisDocument21 pagesPPT 2 Mitosis vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 3 2Document9 pagesExercise No. 3 2ramirezllei942No ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument6 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- What Happens When Food Reaches The StomachDocument9 pagesWhat Happens When Food Reaches The StomachAvegail MantesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument6 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamAishley BerdinNo ratings yet
- Meiosis. GametogenesisDocument21 pagesMeiosis. GametogenesisRiya PatelNo ratings yet
- NovoCyte Flow Cytometer Operator's GuideDocument98 pagesNovoCyte Flow Cytometer Operator's Guideeclipse1130No ratings yet
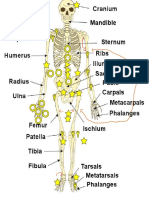
- Bones ModelDocument1 pageBones Modeleclipse1130No ratings yet
- Rental property details and contact infoDocument1 pageRental property details and contact infoeclipse1130No ratings yet
- 35 Pages A Day ATLSDocument1 page35 Pages A Day ATLSeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Not Applicable Case ReportDocument1 pageNot Applicable Case Reporteclipse1130No ratings yet
- Front MatterDocument1 pageFront Mattereclipse1130No ratings yet
- Practicetest4aamc PDFDocument28 pagesPracticetest4aamc PDFeclipse11300% (2)
- Rental property details and contact infoDocument1 pageRental property details and contact infoeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Basic Mecahnical Ventilation - Critical Concepts - PulmonaryDocument54 pagesBasic Mecahnical Ventilation - Critical Concepts - PulmonaryMarcela Catalina Fandiño VargasNo ratings yet
- Block 3Document51 pagesBlock 3eclipse1130No ratings yet
- 2 Page A Day Absite For Chapters Already Read 30+ Questions A Day UWORLD As Much Absite As You Can. Including Book/questionsDocument1 page2 Page A Day Absite For Chapters Already Read 30+ Questions A Day UWORLD As Much Absite As You Can. Including Book/questionseclipse1130No ratings yet
- The Stars of GalaxyDocument5 pagesThe Stars of Galaxyeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Block 1Document51 pagesBlock 1eclipse1130No ratings yet
- PauleeDocument1 pagePauleeeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Power ofDocument5 pagesPower ofeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Paula ShyDocument1 pagePaula Shyeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Power ofDocument5 pagesPower ofeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Tumors of The Dermis TableDocument8 pagesTumors of The Dermis Tableeclipse1130No ratings yet
- PeertoPeer NMD Burst Stimulation FINAL 5-5-14 CleanDocument34 pagesPeertoPeer NMD Burst Stimulation FINAL 5-5-14 Cleaneclipse1130No ratings yet
- Powerpoint of SecretDocument3 pagesPowerpoint of Secreteclipse1130No ratings yet
- Power ofDocument5 pagesPower ofeclipse1130No ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument1 pageNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationEarl Justin SaleNo ratings yet
- The SecretddDocument3 pagesThe Secretddeclipse1130No ratings yet
- Powerpoint of SecretDocument3 pagesPowerpoint of Secreteclipse1130No ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Karyokinesis and Cleavage PatternDocument22 pagesLecture 13 Karyokinesis and Cleavage PatternIQra KanwalNo ratings yet
- Biology Test CH 9 2014Document7 pagesBiology Test CH 9 2014Clara DestinityNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in CellDocument2 pagesSummative Test in CellRhazel CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10Th Edition Michael Cummings 1133106870 9781133106876 Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10Th Edition Michael Cummings 1133106870 9781133106876 Full Chapter PDFkelly.rhodes162100% (12)
- The stage where the kinetochore microtubules of the spindle fibers separate and move the sister chromatids toward opposite poles is called AnaphaseDocument59 pagesThe stage where the kinetochore microtubules of the spindle fibers separate and move the sister chromatids toward opposite poles is called AnaphaseJames PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Life Science Topic 10Document3 pagesLife Science Topic 10Auroloca LocaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Output in Genetics (Midterm) : Romblon State University Cajidiocan Campus Cajidiocan RomblonDocument21 pagesCompilation of Output in Genetics (Midterm) : Romblon State University Cajidiocan Campus Cajidiocan RomblonJudy RianoNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY MCQSDocument11 pagesBIOLOGY MCQSMuhammad Hamza100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Webquest-1Document5 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosis Webquest-1Arjun SheshadriNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Divisions: The Genetic Materials of CellsDocument11 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisions: The Genetic Materials of CellsJelly Anne BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis vs Meiosis: Key DifferencesDocument3 pagesMitosis vs Meiosis: Key Differencesshazia imamNo ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of ChromosomesDocument20 pagesCell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of ChromosomesSoumya SarkarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 5 CELL DIVISIONDocument30 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 5 CELL DIVISIONsmcmasaiNo ratings yet
- June 19 - QPDocument36 pagesJune 19 - QPDiva NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- Organelle TableDocument2 pagesOrganelle Tablejamkulit29No ratings yet
- STEM Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesSTEM Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionErolin PobleteNo ratings yet
- Bio Ass I QPDocument7 pagesBio Ass I QPSwayam GosaviNo ratings yet
- Biology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialDocument9 pagesBiology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialRachel FrankenfieldNo ratings yet
- Label The Cell AnimalDocument3 pagesLabel The Cell AnimalDaryhen GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Mitosis in Onion RootsDocument4 pagesExercise 4 Mitosis in Onion RootsCarlEspantoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Bio Experiment 5 (Mouse Dissection)Document14 pagesLab Report Bio Experiment 5 (Mouse Dissection)Hakim SunaeNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 9Document53 pagesBiology Ch. 9Juliet HipolitoNo ratings yet