Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2002 Exam Answers
Uploaded by
Ranu GamesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2002 Exam Answers
Uploaded by
Ranu GamesCopyright:
Available Formats
Name GT#________
ECE 2030b, Intro. To Computer Eng., Final Exam
Dec. 13, 2002
Prof. John A. Copeland
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
RULES.
i This quiz is closed book.
ii. Calculators may not be used.
iii Answer all questions and show all work to receive full credit.
iv All questions have the same weight. (10 Points). All sub-questions within a
question are weighted equally.
v Please do not ask the proctors any questions during the exam about exam
questions. Part of the test is understanding the question as written, without supplemental
information. If you feel additional data is needed to solve the problem, make (and state) an
assumption and then work the problem.
Question 1 – Minterm and Maxterm Indices
For the truth tables below, show the minterm sum of products, and the maxterm product of sums. Below
that list the minterm indices and the maxterm indices
A B C F
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0
sum of products A'BC' + A'BC + AB'C' + ABC'
product of sums (A+B+C) (A+B+C') (A'+B+C') (A'+B'+C')
minterm indices 2,3,4,6
maxterm indices 0,1,5,7
ECE2030b Fall ’02 - Exam p. 1 of 5
Name __________________________
Question 2 – Karnaugh Map For the Karnaugh map below, circle the Prime Implicants and label
the Essential Prime Implicants with “EPI”.
AB \ CD 00 01 11 10
00 0 1 0 0
01 1 1 1 1
11 0 1 0 1
10 0 1 0 0
Write the reduced logic expression: A'B + C'D + BCD'_
minterm indices (decimal) 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 13, 14__
Question 3 – Mixed Logic. Design a logic circuit for the logic function with NOR gates.
X = ( (AB' + C) + D )’
using the mixed logic technique. Assume only signals A, B, C, and D are available. A’ = NOT A..
Step 1.
Step 2. Show gates in standard form (not DeMorgan alternate forms) and no bars.
ESC2030b Fall ’02 - Exam p. 2
Name __________________________
Question 4 – CMOS Logic Gates. Draw a CMOS circuit to implement the logic function
A + B' C.
Question 5. Write the missing integer numbers in binary, hex, and decimal representations. For hex and
binary show the number as an eight-bit 2's compliment number.
Decimal Hex Binary
112 70 0111 0000
180 B4 1011 0100
149 95 1001 0101
Question 6. Memory. Complete the table below. A “2M x 16” memory has 2M words of 16 bits.
Memory Total Bits # of addresses # of # of data lines
address
lines
4M x 8 32M 4M 22 8
1K x 32 32K 1K 10 32
128K x 16 2M 128K 17 16
1M x 4 4M 1M 20 4
ESC2030b Fall ’02 - Exam p. 3
Name __________________________
Question 7 – Binary Arithmetic in Two’s Complement Notation
Do the arithmetic below in two’s compliment binary arithmetic (8-bit integers, -128 to +127).
+28 _______ 0001 1100 ____________
- 48 add (-48) _______ 1101 0000 _______ 48 = 0011 0000, -48 = 1100 1111 + 1
= -20 _______ 1110 1100_________ absolute value = 0001 0011 +1 = 0001 0100 = 20
Question 8. Our MIPS architecture has only “Branch on Equal” (BEQ $X, $Y) and “Branch on Not
Equal” (BNE $X, $Y) commands. Show how to use the “Set on Less Than” (SLT $1, $X, $Y) and BEQ or
BNE to make as two-command equivalent of the following (note: $0 always = 0 ):
BLT $2, $3
SLT $1, $2, $3
BNE $0, $1, label branch if $1 == 1
BGT $2, $3
SLT $1, $3, $2 $1 = 1 if $3 < $2, $1 = 0 if $3 >= $2
BNE $0, $1, label branch if $1 == 1
Question 9. Branch and Jump Commands (for R4000). Please write answers in the box at
left.
[____ Conditional ______] Branch commands are always (conditional, unconditional)
[____ relative _______] and (absolute, relative).
[_____ Unconditional ___] Jump commands are always (conditional, unconditional)
[________ absolute _____] and (absolute, relative).
[_________ X + 4 _______] If a subroutine is called by an instruction at memory location X, what is the
location of the first instruction executed after the subroutine returns.
[______ on the stack _____] If there are nested subroutines, where are the return locations kept?.
[_____ recursive _________] A subroutine that can calls itself is called ____.
[_ push the current value__] What must a subroutine do before it can use a register.
[_ pop the old values back _] What must a subroutine do before it can return with regard to registers that
were used.
ESC2030b Fall ’02 - Exam p. 4
Name __________________________
Question 10 – CPU Control Lines
Show how the control lines are set to achieve the operations below. Assume msel = 1;
asl: 0=AU, 1=LU, 2=SU, 3 = invalid; ST: 0=arithmetic, 1=logical, 2=rotate, 3 = invalid;
LF: 0=AND, 1=OR, 2=XOR, 3 = invalid; a’/s: 0=add, 1= subtract rwe: 1=write, 0= do not write
Add $2 to the value in memory (address=$9) and put the result into $2. $5 = M[$9] + $2
(note: loading or storing data requires a separate CPU clock cycle)
Mem X Y Z rwe asl a’/s en ld en st en im en im va (Immediate
r’/w Value)
ESC2030b Fall ’02 - Exam p. 5
You might also like
- Vedic Maths: QuantDocument20 pagesVedic Maths: QuantIshan RatnakarNo ratings yet
- 7 Ops On FractionsDocument29 pages7 Ops On FractionsJonathan F. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Assertion and Reason - Class X - MathDocument36 pagesAssertion and Reason - Class X - MathE Sudipta Sekhar PatraNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesFrom EverandDigital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesNo ratings yet
- Friction of Pipe 2Document5 pagesFriction of Pipe 2Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Final Exam (2007)Document15 pagesComputer Science Final Exam (2007)Chantal RamezNo ratings yet
- CSEN102: Introduction To Computer Science Winter Semester 2019-2020Document17 pagesCSEN102: Introduction To Computer Science Winter Semester 2019-2020Khalid RadwanNo ratings yet
- CS302P - Sample PaperDocument10 pagesCS302P - Sample PaperMian GNo ratings yet
- Lab7: Part (A) : Design of 2-Out-Of-5 To BCD Code Converter With DisplayDocument7 pagesLab7: Part (A) : Design of 2-Out-Of-5 To BCD Code Converter With DisplaySanan yaqoobNo ratings yet
- T103 MTA Fall 2012 FormA SolutionsDocument7 pagesT103 MTA Fall 2012 FormA SolutionsIbrahimNo ratings yet
- CSC217 356 138-CSC217Document7 pagesCSC217 356 138-CSC217Aniket AmbekarNo ratings yet
- 2 Cs302 Mid Term Solved PaperDocument11 pages2 Cs302 Mid Term Solved Papermonis_rizviNo ratings yet
- CS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEDocument91 pagesCS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEattiqueNo ratings yet
- CS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEDocument91 pagesCS302 2005 2010 Midterm - Solved - MEGA FILEAli QureshiNo ratings yet
- Example Floating Point Problems: Problem 1Document4 pagesExample Floating Point Problems: Problem 1sivaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Final Exam (2012)Document14 pagesComputer Science Final Exam (2012)Chantal RamezNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 1Document34 pagesPractice Problems 1akbisoi1No ratings yet
- 19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Document56 pages19EC303 DPSD Learners Copy 11 03 24Marshmellow FFNo ratings yet
- Esd2 Problem Booklet 2020 s2Document37 pagesEsd2 Problem Booklet 2020 s2Yuhao CaoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document25 pagesChap 2salam salehNo ratings yet
- Dldlab6 justPreLabDocument10 pagesDldlab6 justPreLabArfaat SanitaryNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Minimization of Boolean FunctionsDocument9 pagesLab 5 Minimization of Boolean FunctionsMuhammad Hassan JavedNo ratings yet
- Exam1 f12Document15 pagesExam1 f12Ryan DavisNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Department of Computer and Communications Engineering Spring 2016 - 2017 CENG300 - Fundamentals of Digital Logic Design MidtermDocument12 pagesSchool of Engineering Department of Computer and Communications Engineering Spring 2016 - 2017 CENG300 - Fundamentals of Digital Logic Design MidtermAnjo VasquezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - SolutionsDocument5 pagesExercise 3 - SolutionsWirnkar Basil NsanyuyNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument23 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoHitesh BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Model Question PaperDocument2 pagesModel Question PaperAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Amankwah - 040119150 - L200 - B - Morning - Digital Computer Design - It 232Document11 pagesAmankwah - 040119150 - L200 - B - Morning - Digital Computer Design - It 232Qwerku GeorgeNo ratings yet
- CEG 2131 - Fall 2003 - FinalDocument14 pagesCEG 2131 - Fall 2003 - FinalAmin DhouibNo ratings yet
- Exam2 f06Document12 pagesExam2 f06Sumiah AlalwaniNo ratings yet
- SLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 4Document7 pagesSLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 4princeyahweNo ratings yet
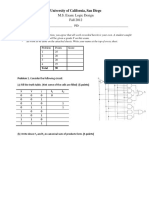
- University of California, San Diego: M.S. Exam: Logic Design Fall 2012Document7 pagesUniversity of California, San Diego: M.S. Exam: Logic Design Fall 2012Manuel VegaNo ratings yet
- Solution: Mid-Term ExamDocument3 pagesSolution: Mid-Term ExamMai Anh ThưNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 - Introduction To ComputingDocument43 pagesChapter 0 - Introduction To ComputingBuket CüvelenkNo ratings yet
- Assingnment# 1Document8 pagesAssingnment# 1Tayyab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Exam1 f01Document11 pagesExam1 f01serhatandic42No ratings yet
- Invitation To Computer Science 6Th Edition Schneider Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesInvitation To Computer Science 6Th Edition Schneider Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFvirginia.romo181100% (11)
- Invitation To Computer Science 6th Edition Schneider Solutions Manual 1Document9 pagesInvitation To Computer Science 6th Edition Schneider Solutions Manual 1stephan100% (48)
- Kami Export - Year7ICT2021 22term1Document6 pagesKami Export - Year7ICT2021 22term1TANG YI QINGNo ratings yet
- Computations in Mechanical Engineering: Numbers and VectorsDocument18 pagesComputations in Mechanical Engineering: Numbers and VectorsTanaka OkadaNo ratings yet
- 6390 Fall 2022 MidtermDocument20 pages6390 Fall 2022 MidtermDaphne LIUNo ratings yet
- B38DB ClassExs2sDocument33 pagesB38DB ClassExs2sNabil IshamNo ratings yet
- Solution PDFDocument5 pagesSolution PDFCedric SunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (NumberBaseConversion)Document43 pagesLecture 1 (NumberBaseConversion)sdNo ratings yet
- COE301 T232 Midterm Exam Key LatestDocument15 pagesCOE301 T232 Midterm Exam Key Latestb9lah10No ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument6 pagesSample QuestionsKrisleen AbrenicaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Forward Error Correction in Fiber-Optic SystemDocument42 pagesThe Role of Forward Error Correction in Fiber-Optic System17585No ratings yet
- Logic CircuitDocument1 pageLogic Circuitハムザアブドゥル マリクNo ratings yet
- Past Paper 10015 21 - QDocument20 pagesPast Paper 10015 21 - QYang ZhouNo ratings yet
- CPP MidTermDocument8 pagesCPP MidTermkalabNo ratings yet
- L04 - Combinational LogicDocument27 pagesL04 - Combinational LogicPirzada SwatiNo ratings yet
- DSD Model Paper 1Document7 pagesDSD Model Paper 1VigneshNo ratings yet
- CS61C Final: University of California, Berkeley College of EngineeringDocument10 pagesCS61C Final: University of California, Berkeley College of EngineeringOliver HeNo ratings yet
- Chapt 4Document72 pagesChapt 4jannngirNo ratings yet
- IE507 Lab02 UpdatedDocument5 pagesIE507 Lab02 UpdatedHari NarayanNo ratings yet
- DLD Mid II V2 Fall 2018Document4 pagesDLD Mid II V2 Fall 2018Emaan AliNo ratings yet
- Comb Circ PDFDocument63 pagesComb Circ PDFSrinivasan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Comb Circ PDFDocument63 pagesComb Circ PDFMengistu KetemaNo ratings yet
- Reg. No: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksDocument2 pagesReg. No: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksWINORLOSENo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic Ckts by JYOTHIDocument44 pagesCombinational Logic Ckts by JYOTHIMurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 2020A FE AM QuestionDocument29 pages2020A FE AM Questionaungyezaw.devNo ratings yet
- IOR Assignment 2Document3 pagesIOR Assignment 2jenny henlynNo ratings yet
- DISCRIPTIONDocument8 pagesDISCRIPTIONRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Extreme Events On Transmission and Distribution SystemsDocument10 pagesImpacts of Extreme Events On Transmission and Distribution SystemsRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- What Is Permeable Concrete?: Design of The SampleDocument1 pageWhat Is Permeable Concrete?: Design of The SampleRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Cover Page PDFDocument1 pageCover Page PDFRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Format of The BalancesheetDocument2 pagesFormat of The BalancesheetRanu Games100% (1)
- Double Entry System, The Ledger and The Trial BalanceDocument37 pagesDouble Entry System, The Ledger and The Trial BalanceRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Discussion: Spur Gear & Helical Gears: Cutaway ModelDocument6 pagesDiscussion: Spur Gear & Helical Gears: Cutaway ModelRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Power Cycles 2019Document29 pagesPower Cycles 2019Ranu Games100% (1)
- DLTC Announcement 2017-NewDocument4 pagesDLTC Announcement 2017-NewRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- CS1032 RulesForProgrammingAssignmentDocument1 pageCS1032 RulesForProgrammingAssignmentRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Python Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Decision StructuresDocument83 pagesPython Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Decision StructuresRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics - 2005Document27 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics - 2005Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- Python Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Algorithm Design and RecursionDocument133 pagesPython Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Algorithm Design and RecursionRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document3 pagesLab 03Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- Python Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Objects and GraphicsDocument56 pagesPython Programming: An Introduction To Computer Science: Objects and GraphicsRanu GamesNo ratings yet
- Solving For A Variable: Useful TipDocument14 pagesSolving For A Variable: Useful TipIvan Darryl LopezNo ratings yet
- Find The Number of Factors of 120. (A) 16 (B) 12 (C) 8 (D) 10Document17 pagesFind The Number of Factors of 120. (A) 16 (B) 12 (C) 8 (D) 10Rashi KumariNo ratings yet
- Deviation Compare 1Document2 pagesDeviation Compare 1PajudoNo ratings yet
- How To Do Cube Roots of 9 Digit Numbers in Your HeadDocument5 pagesHow To Do Cube Roots of 9 Digit Numbers in Your HeadAnonymous vcdqCTtS9No ratings yet
- Nolasco - Mechanism ActivityDocument2 pagesNolasco - Mechanism ActivityLeah Mae NolascoNo ratings yet
- Divisibilty Rule FactorsDocument6 pagesDivisibilty Rule FactorsNarendanath ChowkidarNo ratings yet
- Mips Ref PDFDocument1 pageMips Ref PDFGrant SellersNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio Golden RatioDocument9 pagesGolden Ratio Golden Ratiojoshua bravoNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in Grade 7 Mathematics: A A, B, CDocument5 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Grade 7 Mathematics: A A, B, CMaricel Balbuena100% (1)
- Adders and Subtractors PDFDocument8 pagesAdders and Subtractors PDFrakshithaNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument189 pagesGeneralIzwan ZNo ratings yet
- Cot EnglishDocument14 pagesCot EnglishWinzlet Kate DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevDocument5 pagesUnit 2 RevKresh MudhooNo ratings yet
- (K-Map) OksanaYarem - KarnaughMapsDocument11 pages(K-Map) OksanaYarem - KarnaughMapsmaprofNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Maths 5may Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Exercise 2 7Document13 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 7 Maths 5may Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Exercise 2 7arvinda1981No ratings yet
- 12 ProbDocument2 pages12 ProbachandraNo ratings yet
- ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF TIME 11.10.2021 MondayDocument13 pagesADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF TIME 11.10.2021 Mondaysathiah2802No ratings yet
- Y X C y X CDocument12 pagesY X C y X CK.Prasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Tablice: Elementi Strojeva IDocument24 pagesTablice: Elementi Strojeva IKarlo KlobučarićNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 2)Document4 pagesTechnical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 2)chaNo ratings yet
- Complex NumberDocument49 pagesComplex NumberBhukya SandeepNo ratings yet
- Complete The Following Timing Diagram For A Two-Input XOR GateDocument5 pagesComplete The Following Timing Diagram For A Two-Input XOR Gatesebastian lopezNo ratings yet
- Giancoli - Physics Principles Appendix-2Document1 pageGiancoli - Physics Principles Appendix-2Aman KeltaNo ratings yet
- Math ArticleDocument6 pagesMath ArticleLuna ApayaoNo ratings yet
- DCLD (3rd) May2018Document2 pagesDCLD (3rd) May2018Karan MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Argand DiagramsDocument28 pagesCh.2 Argand DiagramsTuyết NgânNo ratings yet