Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group A. Electrophoresis
Uploaded by
wiwid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageelektroforesis
Original Title
Group a. Electrophoresis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentelektroforesis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageGroup A. Electrophoresis
Uploaded by
wiwidelektroforesis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
ELECTROPHORESIS
Group A February 26th, 2018
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method
used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins
according to molecular size. In gel electrophoresis,
the molecules to be separated are pushed by an
electrical field through a gel that contains small pores.
The molecules travel through the pores in the gel at a
speed that is inversely related to their lengths. This
means that a small DNA molecule will travel a
greater distance through the gel than will a larger
DNA molecule.
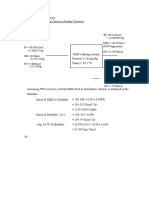
The rate of migration of charged molecules
Types of electrophoresis are:
depends upon following factors: 1. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
(a) The strength of electric field, size and shape. 2. Discontinuous Gel Electrophoresis
(b) Relative hydrophobicity of the sample. 3. Nucleic Acid Sequencing Gels
(c) Ionic strength and temperature of the buffer. 4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate- Polyacrylamide Gel
(d) Molecular size of the taken biomolecule. Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
(e) Net charge density of the taken bio mole-cule. 5. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
(f) Shape of the taken biomolecule. 6. Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE)
As previously mentioned, gel electrophoresis 7. Isoelectric Focusing of Protein
involves an electrical field; in particular, this field is 8. Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis of Proteins
applied such that one end of the gel has a positive 9. Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
charge and the other end has a negative charge. 10. Immunoelectrophoresis (IE)
Because DNA and RNA are negatively charged
molecules, they will be pulled toward the positively
charged end of the gel. Proteins, however, are not Discuss and answer the following questions with
negatively charged; thus, when researchers want to your group. Find the answers in these
separate proteins using gel electrophoresis, they must references, Boyer (2012) pages 165-186; Wilson
first mix the proteins with a detergent called sodium & Walker (2010) pages 399-419.
dodecyl sulfate. This treatment makes the proteins
unfold into a linear shape and coats them with a 1. What is the principle of electrophoresis?
2. What are the factors affecting molecular
negative charge, which allows them to migrate
mobility of electrophoresis?
toward the positive end of the gel and be separated.
3. Compare the types of electrophoresis, including
Finally, after the DNA, RNA, or protein molecules
the medium?
have been separated using gel electrophoresis, bands 4. Show how to calculate molecular size with
representing molecules of different sizes can be electrophoresis?
detected.
All modes of electrophoresis are based on the
principles just outlined. The major difference among
the various methods is the type of support medium.
Cellulose and cellulose acetate are used as a support
medium for low-molecular-weight biochemical like
amino acids and carbohydrates. Polyacrylamide and
agarose gels are widely used as support media for
larger molecules. In capillary electrophoresis, several
different types of support media, including the
natural, untreated surfaces inside a silica narrow bore
are used.
Electrophoresis
You might also like
- Absensi HIMABIODocument1 pageAbsensi HIMABIOwiwidNo ratings yet
- LPJ Bee 2017Document16 pagesLPJ Bee 2017wiwidNo ratings yet
- Different Species Problems and Their Resolution: Kevin de QueirozDocument7 pagesDifferent Species Problems and Their Resolution: Kevin de QueirozNissa RNo ratings yet
- Group B. ChromatographyDocument1 pageGroup B. ChromatographywiwidNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Calcium Citrate: Sample - Not For Official UseDocument1 pageCalcium Citrate: Sample - Not For Official UseTanatorn TongsumrithNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Chapter 13Document46 pagesGeneral Chemistry Chapter 13SEMİH PALAZNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet PH and pOH AnswersDocument3 pagesWork Sheet PH and pOH Answersparamabc27No ratings yet
- Multicomponent Distillation FundamentalsDocument62 pagesMulticomponent Distillation FundamentalsNoaman Ahmed100% (2)
- Laboratory Apparatus and Equipment ReviewerDocument6 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Equipment ReviewerHera VictrixNo ratings yet
- Pka BasesDocument1 pagePka BasesCarlos ArzaluzNo ratings yet
- SPE and Its SPME AdvancesDocument49 pagesSPE and Its SPME AdvancesPaul MatamaneNo ratings yet
- Amendment - List 03 - To - IP - 2022Document6 pagesAmendment - List 03 - To - IP - 2022QC qcNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec Ii A Sa-751Document6 pagesAsme Sec Ii A Sa-751ronaldogeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Vinegar AnalysisDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 1 Vinegar AnalysisRobin TorresNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Structure of Solids and Characterization of Materials PDFDocument83 pagesUnit 2. Structure of Solids and Characterization of Materials PDFShail RajNo ratings yet
- Iodimetric Titration: Aim: PrincipleDocument2 pagesIodimetric Titration: Aim: PrincipleHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 - Gravimetric Analysis-Subjects Autosaved 1 0Document57 pagesUnit 14 - Gravimetric Analysis-Subjects Autosaved 1 0Them Mendoza Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Validation of A Quantitative Liquid Chromatog - 2014 - JournalDocument12 pagesOptimization and Validation of A Quantitative Liquid Chromatog - 2014 - JournalADINDA PUTRI SUCI RAHMADINANo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 Acid Base TitrationDocument3 pagesExperiment No 1 Acid Base TitrationJaya ShriNo ratings yet
- Royal Society of Chemistry Resources For A Level Chemistry PracticalsDocument3 pagesRoyal Society of Chemistry Resources For A Level Chemistry Practicalsmariana kakishNo ratings yet
- Ion ChromatographyDocument36 pagesIon ChromatographyTinh Huynh VanNo ratings yet
- Abhay Pandey Quality Manager / QC Head ResumeDocument4 pagesAbhay Pandey Quality Manager / QC Head ResumeAbhay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Dia FilterDocument20 pagesDia FiltermadhujayarajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 DistillationDocument13 pagesLecture 11 Distillationrajathhm65No ratings yet
- Texto 1. Cristalografía - Sistemas Cristalinos Nomenclatura e Convenções PDFDocument8 pagesTexto 1. Cristalografía - Sistemas Cristalinos Nomenclatura e Convenções PDFSaray NiñoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of NOx in Ambient AirDocument12 pagesAnalysis of NOx in Ambient AirECRDNo ratings yet
- Methanol Water Separation in A Packed Column: by Alvin Hong Dodji Cohovi Roberto MontenegroDocument15 pagesMethanol Water Separation in A Packed Column: by Alvin Hong Dodji Cohovi Roberto MontenegroDr.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument40 pagesChem NotesFelicia LeNo ratings yet
- Isolation Antitumor Alkaloids From: Cephalotaxus HarringtoniaDocument4 pagesIsolation Antitumor Alkaloids From: Cephalotaxus HarringtoniaEkin Dwi ArifNo ratings yet
- Transylvania Summer School in ChromatographyDocument1 pageTransylvania Summer School in Chromatographybogdan_dumitru_85No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)Document3 pagesChemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)tahjsalmon100% (2)
- Material Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)Document29 pagesMaterial Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)noelNo ratings yet
- MANIPAL UNIVERSITY JAIPUR Sieve Plate Distillation Column ExperimentDocument5 pagesMANIPAL UNIVERSITY JAIPUR Sieve Plate Distillation Column ExperimentAmoluck BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Isobaric Vapor-Liquid and Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For Chloroform + Methanol + 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Trifluoromethanesulfonate at 100 KpaDocument6 pagesIsobaric Vapor-Liquid and Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For Chloroform + Methanol + 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Trifluoromethanesulfonate at 100 Kpaluis fernando muro cordovaNo ratings yet