Professional Documents
Culture Documents
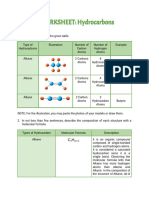
Alkanes & Alkenes
Uploaded by
Jesseca ValenciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkanes & Alkenes
Uploaded by
Jesseca ValenciaCopyright:
Available Formats
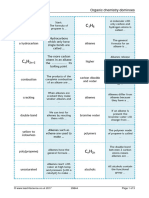
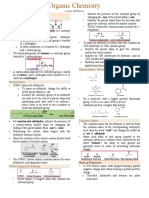
HOW ARE ALKANES AND ALKENES FACTS ABOUT
DIFFERENT? ALKANES! FACTS ABOUT
ALKENES ARE UNSATURATED ALKENES!
HYDROCARBONS. THEY CONTAIN A • any of a group of aliphatic
DOUBLE BOND, WHICH IS SHOWN AS hydrocarbons whose molecules • Alkenes contain contain at
TWO LINES BETWEEN TWO OF THE contain only single bonds which least one double bond
CARBON ATOMS. THE PRESENCE OF is the chemical bond.
between the carbon atoms.
THIS DOUBLE BOND ALLOWS • Alkenes are unsaturated, as
• said to have a continuous
ALKENES TO REACT IN WAYS THAT they have spare bonds that
chain if each carbon atom in its
they can use. This is especially
ALKANES CANNOT. molecule is joined to at most useful in making polymers.
ALKANES PHYSICAL PROPERTIES two other carbon atoms • Alkenes decolourise bromine
• it is said to have a branched water.
it is a saturated hydrocarbon and all of its • Alkenes form polymers. This is
chain if any of its carbon atoms
bond is a complete covalent bond. is joined to more than two other because their double bonds
ALKANES CHEMICAL PROPERTIES carbon atoms
open up to join other
monomers, but this will be
Alkanes is a covalent compound which • The first four continuous-chain
explained in more detail further
alkanes are methane, CH4;
has a relatively low boiling and melting down the article.
ethane, C2H6; propane, C3H8; • Alkenes burn with a smoky
point. The more the carbon atom or the
and butane, C4H10 flame. This means that is
longer the chain in an alkane compound, • alkanes with 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 incomplete combustion, where
the higher its boiling and melting carbon atoms in their molecules not enough oxygen is getting to
point.The more the branches in the are pentane, hexane, heptane, the burning object, which
means that it produces carbon
ALKANES &
octane, nonane, and decane,
carbon chain, the lower its boiling and dioxide, carbon monoxide,
respectively
melting point. • Chemically, the alkanes are
water and carbon (soot).
• The general formula for
ALKENES PHYSICAL PROPERTIES relatively unreactive
alkenes is CnH2n.
ALKENES
The physical properties of alkenes are • They are obtained by fractional
distillation from petroleum and
comparable with those of alkanes. The physical
are used extensively as fuels.
state depends on molecular mass (gases from • sometimes referred to as the
ethene to butene - liquids from pentene methane series (after the
HYDROCARBONS ARE COMPOUNDS MADE FROM
CARBON AND HYDROGEN ATOMS JOINED BY
onwards). The simplest alkenes, ethene, simplest alkane) or as paraffins. COVALENT BONDS.
propene and butene are gases. Linear alkenes • highly flammable compound at -ALKANES ARE SATURATED - THEY HAVE ONLY
high temperatures SINGLE BONDS. ALKENES HAVE A DOUBLE BOND
of approximately five to sixteen carbons are - THEY ARE UNSATURATED.
• it is a saturated hydrocarbon
liquids, and higher alkenes are waxy solids. and all of its bond is a complete
ALKENES REACT WITH BROWN BROMINE WATER
AND DECOLOURISE IT, BUT ALKANES DO NOT.
ALKENES CHEMICAL PROPERTIES covalent bond. -ALKENES CAN ACT AS MONOMERS. UNDER HIGH
Combustion of Alkenes • Alkanes have lower acidity PRESSURE AND IN THE PRESENCE OF A
CATALYST MANY MONOMER MOLECULES JOIN
The alkenes are highly flammable and burn level if you compare it with the
TOGETHER TO MAKE POLYMER MOLECULES.
acidity level of alkenes. THESE POLYMER MOLECULES ARE SATURATED.
readily in air, forming carbon dioxide and water
You might also like
- All India Career Point Test NEETDocument5 pagesAll India Career Point Test NEETsameerambekar660No ratings yet
- Conceptual Density Functional Theory PDFDocument82 pagesConceptual Density Functional Theory PDFAurélio Moreira100% (1)
- A Thousand and One NightsDocument2 pagesA Thousand and One NightsJesseca Valencia100% (1)
- Drilling Waste Management Technology ReviewDocument102 pagesDrilling Waste Management Technology ReviewPham Duc100% (1)
- ASTM C128 Standard Test Method for Relative Density and AbsorptionDocument23 pagesASTM C128 Standard Test Method for Relative Density and AbsorptionLC LeeNo ratings yet
- VS-HS Storage Systems Product Manual Ws PDFDocument38 pagesVS-HS Storage Systems Product Manual Ws PDFmehmacarNo ratings yet
- Base Oil Groups Manufacture Properties and PerformanceDocument4 pagesBase Oil Groups Manufacture Properties and Performanceiosalcido100% (1)
- AQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U7 Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U7 Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserDEVANDRAN A/L MOHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsDocument54 pagesQ2 - Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsTosee istosee100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry (Alkane, Alkene and Alkyne)Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Alkane, Alkene and Alkyne)Dazell Varron100% (1)
- MIDTERMS CHEM - MazonDocument10 pagesMIDTERMS CHEM - MazonMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Chem Lec Week 5Document4 pagesChem Lec Week 5Alexandra Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSDocument16 pagesSTPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3Document7 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Notes 2.3 - Properties of AlkanesDocument16 pagesNotes 2.3 - Properties of AlkanesNaseeb AliiNo ratings yet
- Class Notes 24 Jan 2021Document23 pagesClass Notes 24 Jan 2021JJ PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Document4 pagesHydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Paul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 HydrocarbonsDocument80 pagesCh. 4 HydrocarbonsCollo KarisNo ratings yet
- C9 - Crude Oil and FuelsDocument3 pagesC9 - Crude Oil and FuelsAbdul-Muizz KhanNo ratings yet
- A3 CosepeDocument4 pagesA3 CosepeSean Jodi CosepeNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument16 pagesAlkenesVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- Organic DominosDocument3 pagesOrganic DominosshyamalaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Name: Mauren D. Norbe November 10, 2021 Year/Course: Bscpe 1-Ge Assignment in ChemlecDocument3 pagesAlkanes: Name: Mauren D. Norbe November 10, 2021 Year/Course: Bscpe 1-Ge Assignment in ChemlecMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab: Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkanesDocument27 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab: Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkaneszazoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURUDocument11 pagesHydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURURaagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE (Materi Pembelajaran) : Organic Hydrocarbon: Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkyneDocument9 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE (Materi Pembelajaran) : Organic Hydrocarbon: Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkyneAmmar AbiNo ratings yet
- Advance Chem Report 1Document31 pagesAdvance Chem Report 1Keziah TaycoNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit 19.1Document13 pagesMYP Unit 19.1Regine BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Structures PropertiesDocument18 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes Structures PropertiesМария МановаNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumDocument13 pagesHydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumAva Mae SolidumNo ratings yet
- 14.2 AlkenesDocument26 pages14.2 Alkenessafiya_91No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lesson on Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lesson on Aldehydes and KetonesMARY JANE ANGELICA SEVANo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, and AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, and AlkynesBacadon JerryNo ratings yet
- Tata Nama AlkanaDocument18 pagesTata Nama Alkanania veronikaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 HydrocarbonsDocument58 pagesCH 3 HydrocarbonsCollo KarisNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument31 pagesAlkenesjesslynNo ratings yet
- Orgchm Homework1Document3 pagesOrgchm Homework1Aida FarwizahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDahyun KimNo ratings yet
- ALKENEDocument27 pagesALKENEChane ReponteNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument32 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesNicolás SerranoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument1 pageCarbon and Its CompoundsSK CreationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 122Document4 pagesChemistry 122Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes: 1. Physical StateDocument2 pagesAlkenes: 1. Physical State1101900No ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and AlkenesDocument22 pagesCarbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and Alkenesdr lailaNo ratings yet
- C7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Document2 pagesC7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Functional GroupsDocument4 pages2.1 Functional GroupsBasti SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerDocument6 pagesUnsaturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Alkane GroupDocument26 pagesAlkane GroupKenneth AbatonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reviewerenriquezchloe167No ratings yet
- 14.1 AlkanesDocument48 pages14.1 Alkanessafiya_91No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Crude Oil Fractionation & Alkane PropertiesDocument77 pagesHydrocarbons: Crude Oil Fractionation & Alkane PropertiesMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes PowerpointDocument61 pagesChapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes PowerpointFreya An YbanezNo ratings yet
- Presentation 9Document8 pagesPresentation 9sun shineNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkenes and AlcoholsDocument4 pagesReactions of Alkenes and AlcoholsRaquel da Silva JustinoNo ratings yet
- Alkane, Alkene, Alkyne PDFDocument17 pagesAlkane, Alkene, Alkyne PDFEra MelaniaNo ratings yet
- Buhari, A. (2014, January 25) Science Revision. SlideshareDocument7 pagesBuhari, A. (2014, January 25) Science Revision. SlideshareHannah AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Unsaturated HC (Reactions) and Aromatics (Properties)Document8 pagesModule 4: Unsaturated HC (Reactions) and Aromatics (Properties)back upNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesOrganic ChemistryAlyssa EridioNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: 1 Semester - Petroleum Engineering Koya University 2021 - 2022 Hawar J. Sadiq HawezyDocument41 pagesGeneral Chemistry: 1 Semester - Petroleum Engineering Koya University 2021 - 2022 Hawar J. Sadiq HawezyZana NajatNo ratings yet
- Coek - Info AlkynesDocument12 pagesCoek - Info AlkynesDũng NgôNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Understanding Carbon CompoundDocument20 pagesLearning Objectives: Understanding Carbon Compoundheryana8100% (3)
- Course Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 9Document5 pagesCourse Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 9Nard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Alkane Chemistry AssignmentDocument6 pagesAlkane Chemistry AssignmentNafees ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Module HDocument21 pagesModule HDaniellhy 10No ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes 2Document2 pagesAlkanes Alkenes 2Jesseca ValenciaNo ratings yet
- AlkDocument2 pagesAlkJesseca ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes & AlkenesDocument2 pagesAlkanes & AlkenesJesseca ValenciaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentJesseca ValenciaNo ratings yet
- AlkDocument2 pagesAlkJesseca ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Methods For Diffusion Welding The Superalloy Udimet 700Document9 pagesMethods For Diffusion Welding The Superalloy Udimet 700Enary SalernoNo ratings yet
- Solid Hollow Plug PDFDocument3 pagesSolid Hollow Plug PDFSandra DevannyNo ratings yet
- Resin R3X1660 - Material Data Sheet - Part BDocument4 pagesResin R3X1660 - Material Data Sheet - Part BRavie OuditNo ratings yet
- Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, For General Industrial UseDocument10 pagesSteel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, For General Industrial UseRed RedNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Refrigeration and Air ConditioningGaryy EditsNo ratings yet
- 2D Transient Heat Transfer of Steel IngotDocument15 pages2D Transient Heat Transfer of Steel IngotAnonymous sUbNSWmQNo ratings yet
- Saranya IJPSRDocument8 pagesSaranya IJPSRBhavana GangurdeNo ratings yet
- Cell LineDocument12 pagesCell LineLuis PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Booster in Sunscreen INOLEX PDFDocument18 pagesBooster in Sunscreen INOLEX PDFrenatoporangaNo ratings yet
- 9 Nomenclature of Inorganic CompoundsDocument42 pages9 Nomenclature of Inorganic CompoundsGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- FCC Monograph PDFDocument4 pagesFCC Monograph PDFWilsonNo ratings yet
- Heating Element ArticleDocument10 pagesHeating Element ArticleFrea Kent-Dazze D'DrughiNo ratings yet
- 1200 TDSDocument2 pages1200 TDSRoxana LencinaNo ratings yet
- Agitated Nutsche Filter & Dryer (ANF/ANFD) : EquipmentsDocument8 pagesAgitated Nutsche Filter & Dryer (ANF/ANFD) : EquipmentsJiril JacobNo ratings yet
- Materials and Design: Sumrerng Rukzon, Prinya ChindaprasirtDocument6 pagesMaterials and Design: Sumrerng Rukzon, Prinya ChindaprasirthenryNo ratings yet
- This Document Certifies That: Precision Polymer Engineering Limited (PPE)Document2 pagesThis Document Certifies That: Precision Polymer Engineering Limited (PPE)JuanNo ratings yet
- Belonio, Roi Emman E.Document4 pagesBelonio, Roi Emman E.Adrian Nazrene BitoonNo ratings yet
- Ceilcote 2000 Flakeline+ds+engDocument4 pagesCeilcote 2000 Flakeline+ds+englivefreakNo ratings yet
- Special Fiber Optic PDFDocument18 pagesSpecial Fiber Optic PDFtarluzNo ratings yet
- Hot Fill Processing of BeveragesDocument3 pagesHot Fill Processing of BeveragesJavier Ignacio Leyton SotoNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler Experiment LabsheetDocument8 pagesMarcet Boiler Experiment LabsheetWan NurdyanaNo ratings yet
- API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)Document5 pagesAPI Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)Luis Ernesto Marin JaimesNo ratings yet
- Integración IV: Introducción A DWSIM 2018Document55 pagesIntegración IV: Introducción A DWSIM 2018willycoyote1990-1No ratings yet
- Evolution of Atomic Structure PDFDocument1 pageEvolution of Atomic Structure PDFAnonymous VI4gZ25FbaNo ratings yet