Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PVDH GDH: Chapter Seventeen
Uploaded by
Easwaran NampoothiriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PVDH GDH: Chapter Seventeen
Uploaded by
Easwaran NampoothiriCopyright:
Available Formats
17.
68 CHAPTER SEVENTEEN
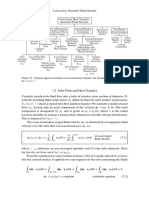
TABLE 17.13 Important Dimensionless Groups for Internal Flow Forced Convection Heat Transfer
and Flow Friction Useful in Heat Exchanger Design
Dimensionless Definitions and working
groups relationships Physical meaning and comments
Reynolds pVDh GDh A flow modulus proportional to the ratio of inertia force to
number Re - - -kt - g viscous force
T,w
Fanning friction '--~
f = ~t"PVZ/2gc The ratio of wall shear (skin frictional) stress to the flow kinetic
factor energy per unit volume; commonly used in heat transfer literature
f = A p * rh _ Ap rh
L (pVZ/2gc) L
rh
Apparent Fanning fapp = Ap* -- Includes the effects of skin friction and the change in the momen-
friction factor L tum rates in the entrance region (developing flows)
L
Incremental K(x)=(f~pp-~d) r--~ Represents the excess dimensionless pressure drop in the
pressure drop entrance region over that for fully developed flow
number K(oo) = constant for x --)
Darcy friction fo = 4f = Ap , Dh Four times the Fanning friction factor; commonly used in fluid
factor
L
mechanics literature
Ap
Euler number Eu -- ~ p * - - ~ The pressure drop normalized with respect to the dynamic veloc-
(pVZ/2gc)
ity head
X
Dimensionless X+ _ The ratio of the dimensionless axial distance (X/Dh) to the
axial distance Dh Re Reynolds number; useful in the hydrodynamic entrance region
for the fluid
flow problem
h q"Dh
Nusselt number Nu- The ratio of the convective conductance h to the pure molecular
k/Dh k(Tw- Tin)
thermal conductance k/Dh
h
Stanton number St- The ratio of convection heat transfer (per unit duct surface area)
Gcp
to amount virtually transferable (per unit of flow cross-sectional
Nu Nu area); no dependence upon any geometric characteristic dimen-
St sion
Pe Re Pr
Colburn factor j = St Pr 2/3= (Nu pr-1/3)/Re A modified Stanton number to take into account the moderate
variations in the Prandtl number for 0.5 ~< Pr ~< 10.0 in turbulent
flow
v gcp
Prandtl number Pr- - A fluid property modulus representing the ratio of momentum
o~ k
diffusivity to thermal diffusivity of the fluid
P6clet number Pe = pcpVDh= VDh.= Re Pr Proportional to the ratio of thermal energy convected to the fluid
k tx
to thermal energy conducted axially within the fluid; the inverse
of Pe indicates relative importance of fluid axial heat conduction
X X
Dimensionless X*- - ~ Useful in describing the thermal entrance region heat transfer
axial distance
Dh Pe Dh Re Pr results
for the heat
transfer problem
Gz-rhcp-PeP- P 1
Graetz number Conventionally used in the chemical engineering literature related
kL 4L 4Dh X* to x* as shown when the flow length in Gz is treated as a length
Gz = n/(4x*) for a circular tube variable
You might also like
- Dimensionless Nummbers in Heat TransferDocument2 pagesDimensionless Nummbers in Heat Transferjovan.filipovicNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: J.P. Abraham, E.M. Sparrow, W.J. MinkowyczDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: J.P. Abraham, E.M. Sparrow, W.J. MinkowyczZahra GhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Compressible Flows in Pipelines: Dr. Ahmed Elmekawy Fall 2018Document74 pagesFundamentals of Compressible Flows in Pipelines: Dr. Ahmed Elmekawy Fall 2018Tamunoiboumie ElijahNo ratings yet
- Fact at Your Finger TipsDocument2 pagesFact at Your Finger TipsboyzbrilliantNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200812-Fluid FlowDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200812-Fluid Flowonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Horizontal Performance Through The PipelineDocument7 pagesHorizontal Performance Through The Pipelinekhalid alrawiNo ratings yet
- Saturated Water Flow: SSC107 - Fall 2000 Chapter 3 Page 3-1Document14 pagesSaturated Water Flow: SSC107 - Fall 2000 Chapter 3 Page 3-1Shalimar11No ratings yet
- Lista de Simbolos - MattinglyDocument5 pagesLista de Simbolos - MattinglyAnne Beatriz MendesNo ratings yet
- Cve341lecturenotes1 220921133246 9aa9c294Document61 pagesCve341lecturenotes1 220921133246 9aa9c294Krishna P. YadavNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer ThoughDocument15 pagesNumerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer ThoughКирилл МаксимовNo ratings yet
- Ryddner Trujillo2015 Article ModelingUrea WaterSolutionDropDocument18 pagesRyddner Trujillo2015 Article ModelingUrea WaterSolutionDropSteve WanNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Lecture 11 Notes: Introduction To Compressible FlowsDocument4 pagesFluids - Lecture 11 Notes: Introduction To Compressible FlowsdanielNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200410-Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200410-Fluid Mechanicsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- (8.4) Drilling Hydraulics FormulaeDocument3 pages(8.4) Drilling Hydraulics FormulaeTsani SabilaNo ratings yet
- Where Do Subducted Slabs Go?: Accumulates at The 670 KM DiscontinuityDocument13 pagesWhere Do Subducted Slabs Go?: Accumulates at The 670 KM DiscontinuityasdfghjNo ratings yet
- 공조냉동 Stoecker 2022Document123 pages공조냉동 Stoecker 2022안호준No ratings yet
- Fluid DerivationsDocument22 pagesFluid Derivations21M248 - SIBI SELVAN CNo ratings yet
- Rigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国Document6 pagesRigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国944062528qqNo ratings yet
- A Review of Forced Convective Heat Transfer in Stationary and AnnuliiDocument12 pagesA Review of Forced Convective Heat Transfer in Stationary and AnnuliiShibu ShibuNo ratings yet
- Dimension AnalysisDocument45 pagesDimension AnalysisJahir DipokNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document46 pagesLecture 3CHOWDHURY SAMINo ratings yet
- ConvectionDocument26 pagesConvectionDozdiNo ratings yet
- Transonic Laminar Boundary Layers With Surface CurvatureDocument17 pagesTransonic Laminar Boundary Layers With Surface CurvaturerelojucaNo ratings yet
- PHTAssignment#3 (Complete)Document63 pagesPHTAssignment#3 (Complete)Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- RANSE Calculations of Laminar-To-Turbulent Transition-Flow Around Sailing Yacht AppendagesDocument13 pagesRANSE Calculations of Laminar-To-Turbulent Transition-Flow Around Sailing Yacht AppendageskokahobyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop1Document15 pagesPressure Drop1song LiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Heat Transfer, Kaviany 1011Document1 pageEssentials of Heat Transfer, Kaviany 1011Samuel HollisNo ratings yet
- Study of Thermohydraulic Characteristics of Fluidflow Through MicrochannelsDocument32 pagesStudy of Thermohydraulic Characteristics of Fluidflow Through MicrochannelsmathiarmymechNo ratings yet
- Dosimetry: Dose Rate in AirDocument10 pagesDosimetry: Dose Rate in AirpawanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Level ControlDocument47 pagesLiquid Level ControlranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Internal Forced ConvectionDocument20 pagesInternal Forced ConvectionAbhiNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection LatestDocument35 pagesNatural Convection LatestPradyumna DhamangaonkarNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Prashant W. Deshmukh, Rajendra P. VedulaDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Prashant W. Deshmukh, Rajendra P. VedulaTejal BanmareNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering 325 Petroleum Production Systems: Wellbore Flow Performance I Single-Phase FlowDocument51 pagesPetroleum Engineering 325 Petroleum Production Systems: Wellbore Flow Performance I Single-Phase FlowBruno ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Notes in Compressible Uid Ow: April 2019Document15 pagesNotes in Compressible Uid Ow: April 2019Renata RamosNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Bernoulli's Equation - ME 319-ME32S3 - Fluid MachineriesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Bernoulli's Equation - ME 319-ME32S3 - Fluid MachineriesOkay Printing100% (1)
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument8 pagesBernoulli's EquationOkay Printing100% (1)
- Sistemas de Producción 11 - Curva de SalidaDocument59 pagesSistemas de Producción 11 - Curva de SalidaLuis Vallejo EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Section 12Document49 pagesSection 12Asad KhanNo ratings yet
- Report On Heat TransferDocument11 pagesReport On Heat TransferArbind BokadeNo ratings yet
- Piping Design and Operations Guidebook Volume 1 PDFDocument86 pagesPiping Design and Operations Guidebook Volume 1 PDFAn'nur Fauzi Syaputra100% (1)
- Convection Transfer EquationsDocument9 pagesConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutNo ratings yet
- Non Dimensional NumbersDocument29 pagesNon Dimensional NumbersNetaa sachinNo ratings yet
- Convective Heat Transfer in Rotating Radial Circular PipesDocument14 pagesConvective Heat Transfer in Rotating Radial Circular Pipesynb6yfhvgNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Lecture 10 Notes: Substantial DerivativeDocument3 pagesFluids - Lecture 10 Notes: Substantial DerivativeVedang KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Report-Slot FlowDocument20 pagesReport-Slot Flowbil LuNo ratings yet
- Twisted TapeDocument15 pagesTwisted Taperjshkmr745No ratings yet
- Spina 2002Document10 pagesSpina 2002hasantapNo ratings yet
- Asako2017 Numerico PDFDocument6 pagesAsako2017 Numerico PDFAbraham SilesNo ratings yet
- Problemas y Examen PDFDocument12 pagesProblemas y Examen PDFAlejandro CalamacoNo ratings yet
- Section 7Document51 pagesSection 7Asad Khan0% (1)
- NHT 2004Document20 pagesNHT 2004Tegar Unggul PratamaNo ratings yet
- Mohit Paper 2Document23 pagesMohit Paper 2mohitNo ratings yet
- The Response of Thermal Newtonian and Non-Newtonian E H L To The Vertical Vibration of A RollerDocument9 pagesThe Response of Thermal Newtonian and Non-Newtonian E H L To The Vertical Vibration of A RollerJuan Pablo Cano MejiaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Transport PhenomenaDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Transport PhenomenaJoyce VicenteNo ratings yet
- Dimensionless Numbers in Heat TansferDocument2 pagesDimensionless Numbers in Heat TansferChirag DaveNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Thermodynamic Analysis of An Integrated Gas Turbine Power Plant Utilizing Cold Exergy of LNGDocument15 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of An Integrated Gas Turbine Power Plant Utilizing Cold Exergy of LNGEaswaran NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- Saintgits Newsletter 2015Document12 pagesSaintgits Newsletter 2015Easwaran NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- NPTEL - Gas SeparationDocument48 pagesNPTEL - Gas SeparationEaswaran NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- M&i Easwaran orDocument10 pagesM&i Easwaran orEaswaran NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- Tooth Paste-ExtrusionDocument6 pagesTooth Paste-ExtrusionEaswaran NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- Agitator Power Requirement and Mixing Intensity CalculationDocument26 pagesAgitator Power Requirement and Mixing Intensity CalculationWael Abdel-Mageed100% (1)
- Geotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Standard Penetration TestDocument14 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Standard Penetration TestPascasio PascasioNo ratings yet
- Bending DiesDocument31 pagesBending DiesTamirat Nemomsa100% (1)
- Direction: Analyze and Answer Carefully The Following Questions. Choose The BestDocument5 pagesDirection: Analyze and Answer Carefully The Following Questions. Choose The BestGener ToledoNo ratings yet
- Wagner EffectsDocument8 pagesWagner EffectsVictor FariaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Flow Through An Orifice Lab ReportDocument11 pagesExperiment 2 - Flow Through An Orifice Lab Reportlei heng yu100% (17)
- 1 .Reverse Osmosis System (RO) Bahan Baku 500ppmDocument2 pages1 .Reverse Osmosis System (RO) Bahan Baku 500ppmboynaduaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Compression MembersDocument25 pagesLecture 4 Compression MembersLhee Ann GarboNo ratings yet
- Plano Hidrulico de 272cDocument4 pagesPlano Hidrulico de 272cMaría Felisa López QuintoNo ratings yet
- Shear Force Experiment - 2Document6 pagesShear Force Experiment - 2Mohamad Afiq Afandi100% (1)
- 3Document8 pages3SHREYAS MSNo ratings yet
- Fan Sizing Calculations: Selecting A Fan Fan Selection DetailsDocument1 pageFan Sizing Calculations: Selecting A Fan Fan Selection DetailsmassomieNo ratings yet
- DownloadLecture 10 - Entropy, Clausius InequalityDocument4 pagesDownloadLecture 10 - Entropy, Clausius Inequalityeuglena6No ratings yet
- 84 Top Strength of Materials Question and AnswersDocument11 pages84 Top Strength of Materials Question and AnswersM Tatualla0% (1)
- Article Review: "Density Estimation For Ionic Liquids"Document26 pagesArticle Review: "Density Estimation For Ionic Liquids"Gie AndalNo ratings yet
- Complete GT Investigation Report Dt. 22.05.2013Document26 pagesComplete GT Investigation Report Dt. 22.05.2013parvez100% (1)
- Energy, Processes and CyclesDocument51 pagesEnergy, Processes and CyclesJodel SerranoNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Dynamic Earth Pressure Methods: Mononobe-Okabe MethodDocument2 pages5.3 Dynamic Earth Pressure Methods: Mononobe-Okabe MethodJesús Rodríguez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Drying of PaperDocument38 pagesDrying of PaperLingga MediatamaNo ratings yet
- UltracoolDocument4 pagesUltracoolYing Kei ChanNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses: Minor Principal Stress (Mpa)Document7 pagesPrincipal Stresses: Minor Principal Stress (Mpa)Dicxon DíazNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument39 pagesFracture MechanicsDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2020Document2 pagesAssignment 1 2020fgh fghfghfNo ratings yet
- Effects Temp On PropsDocument5 pagesEffects Temp On Propsdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- TMC To CumecsDocument2 pagesTMC To CumecsNaveen NagisettiNo ratings yet
- Ced 506 Hydraulics Assignment TwoDocument6 pagesCed 506 Hydraulics Assignment TwoCula Nauman TamaniiNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 Analysis - Computers and Structures, IncDocument6 pagesSAP2000 Analysis - Computers and Structures, IncshadabghazaliNo ratings yet
- Hostel SECOND TERM EXAMINATIONDocument6 pagesHostel SECOND TERM EXAMINATIONAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CEE220Document5 pagesSyllabus CEE220appstore500No ratings yet