Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Scrum Methodology
Uploaded by
srimkbCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Scrum Methodology
Uploaded by
srimkbCopyright:
Available Formats
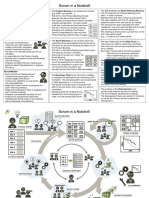
6 Main Principles of Scrum Methodology
Scrum principles are the foundation on which the Scrum framework is based. The principles of
Scrum can be applied to any type of project or organization, and they must be adhered to in order
to ensure appropriate application of Scrum.
The aspects and processes of Scrum can be modified to meet the requirements of the project, or
the organization using it, but Scrum principles are non-negotiable and must be applied as
described in the framework presented in A Guide to the Scrum Body of Knowledge the SBOK™
Guide. Keeping the principles intact and using them appropriately instills confidence in the
Scrum framework with regard to attaining the objectives of the project.
Empirical Process Control—This principle emphasizes the core philosophy of Scrum
based on the three main ideas of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Self-organization—This principle focuses on today’s workers, who deliver significantly
greater value when self-organized and this results in better team buy-in and shared
ownership; and an innovative and creative environment which is more conducive for
growth.
Collaboration—This principle focuses on the three core dimensions related to
collaborative work: awareness, articulation, and appropriation. It also advocates project
management as a shared value-creation process with teams working and interacting
together to deliver the greatest value.
Value-based Prioritization—This principle highlights the focus of Scrum to deliver
maximum business value, from early in the project and continuing throughout.
Time-boxing—This principle describes how time is considered a limiting constraint in
Scrum, and used to help effectively manage project planning and execution. Time-boxed
elements in Scrum include Sprints, Daily Standup Meetings, Sprint Planning Meetings,
and Sprint Review Meetings.
Iterative Development—This principle defines iterative development and emphasizes
how to better manage changes and build products that satisfy customer needs. It also
delineates the Product Owner’s and organization’s responsibilities related to iterative
development.
Scrum principles are the core guidelines for applying the Scrum framework and should
mandatorily be used in all Scrum projects. The Scrum aspects and processes, however, can be
modified to meet the requirements of the project or the organization.
You might also like
- ScrumDocument12 pagesScrumMuhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- Ylimannela RiskManagementAgileDocument8 pagesYlimannela RiskManagementAgileMarcus CaldevillaNo ratings yet
- Management of Project Knowledge and ExperienceDocument13 pagesManagement of Project Knowledge and ExperienceperhakooNo ratings yet
- BPMN Fundamentals: Stephen A. White, IBM Notation Working Group ChairDocument33 pagesBPMN Fundamentals: Stephen A. White, IBM Notation Working Group ChairlidewasoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management in Agile ProjectsDocument5 pagesKnowledge Management in Agile ProjectsCognizant100% (2)
- Evaluating Agile and Scrum With Other Software MethodologiesDocument41 pagesEvaluating Agile and Scrum With Other Software MethodologiesdlokNo ratings yet
- A Ion Between Agile and Traditional SW Development MethodologiesDocument84 pagesA Ion Between Agile and Traditional SW Development Methodologiesturki2011No ratings yet
- Asset Management (Word Document)Document54 pagesAsset Management (Word Document)GaiusNo ratings yet
- Project Management Plan - Moraleta's GroupDocument9 pagesProject Management Plan - Moraleta's GroupAxiahle Duarte PrüdenteNo ratings yet
- Organizational Agility ScaleDocument15 pagesOrganizational Agility ScaleSaba Munir100% (1)
- 2016 Changepoint Ppm-Agile White-PaperDocument14 pages2016 Changepoint Ppm-Agile White-PaperAnappara AchammaNo ratings yet
- Software Project ManagementDocument82 pagesSoftware Project ManagementSri yazhini DeviNo ratings yet
- Agile M I 9.7.20 Class 1Document19 pagesAgile M I 9.7.20 Class 1priyanka kumar100% (1)
- The Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2From EverandThe Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Josh Wright Scrum The Complete Guide To The Agile Project ManagementDocument102 pagesJosh Wright Scrum The Complete Guide To The Agile Project ManagementJUANnn100100% (1)
- SCRUM: Mastering Agile Project Management for Exceptional Results (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandSCRUM: Mastering Agile Project Management for Exceptional Results (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- What Is Scrum in AgileDocument4 pagesWhat Is Scrum in AgileJasiekNo ratings yet
- Scrum: The Agile Framework for Efficient Software Development. Collaborative Teamwork with ScrumFrom EverandScrum: The Agile Framework for Efficient Software Development. Collaborative Teamwork with ScrumNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Agile ProcessDocument3 pagesOverview of The Agile ProcessianNo ratings yet
- Refresher For SM and PODocument19 pagesRefresher For SM and POSteven AbuelNo ratings yet
- Agile Project Management Implementation Approach: Abrachan PudusserryDocument11 pagesAgile Project Management Implementation Approach: Abrachan Pudusserryopenwebmini100% (1)
- Scrum Fundamentals Certified Exam AnswersDocument26 pagesScrum Fundamentals Certified Exam AnswersLUIS TORRES100% (3)
- Scrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersFrom EverandScrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Scrum Master HandbookDocument44 pagesScrum Master HandbookSolimooni100% (3)
- Atif Ahmed KhanDocument4 pagesAtif Ahmed Khanshazain.zeeshanNo ratings yet
- PM AssignmentDocument6 pagesPM AssignmentAdane AmbayeNo ratings yet
- Agile Vs ScrumDocument4 pagesAgile Vs ScrumMMBNo ratings yet
- From SAFe to Spotify: Comparing Enterprise Agile FrameworksFrom EverandFrom SAFe to Spotify: Comparing Enterprise Agile FrameworksNo ratings yet
- ScrumFramework 17x11Document19 pagesScrumFramework 17x11Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Agile Techniques ScrumDocument6 pagesAgile Techniques ScrumUmair BaBerNo ratings yet
- Scrum@Scale GuideDocument19 pagesScrum@Scale GuidegkgvenuNo ratings yet
- Scrum Master CertifiedDocument4 pagesScrum Master Certifiedtanu0% (1)
- Scrum@Scale GuideDocument20 pagesScrum@Scale GuideShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Name: Jawad Ali. Class: FA20-BSE-3C-098. Submitted To: Ma'am Hyfza Ali. Subject: Introduction To SoftwareDocument5 pagesName: Jawad Ali. Class: FA20-BSE-3C-098. Submitted To: Ma'am Hyfza Ali. Subject: Introduction To SoftwareSTAR JAWADNo ratings yet
- Agile ScrumDocument61 pagesAgile ScrumMAFIX BINODNo ratings yet
- Scrum GuideDocument80 pagesScrum Guidewaznedane1No ratings yet
- How To Apply Scrum Methodology in Your BusinessDocument2 pagesHow To Apply Scrum Methodology in Your BusinessvicsukNo ratings yet
- Introducing Agile Project Management With Scrum: Why You Need To Use Scrum And How To Make It Work In Your Individual SituationFrom EverandIntroducing Agile Project Management With Scrum: Why You Need To Use Scrum And How To Make It Work In Your Individual SituationNo ratings yet
- Scrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementFrom EverandScrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Agile Project ManagementDocument13 pagesAgile Project ManagementKaushik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Agile: What You Need to Know About Agile Project Management, the Kanban Process, Lean Thinking, and ScrumFrom EverandAgile: What You Need to Know About Agile Project Management, the Kanban Process, Lean Thinking, and ScrumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- COURSEDocument47 pagesCOURSEManu JesusNo ratings yet
- Scrum: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize the Performance of Your Business. Learn Effective Strategies, Overcome Challenges and Achieve Successful Results.From EverandScrum: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize the Performance of Your Business. Learn Effective Strategies, Overcome Challenges and Achieve Successful Results.No ratings yet
- Scrum Methodology - An Effective and Practical Guide To The Mastery of Scrum Project Management MethodologyDocument101 pagesScrum Methodology - An Effective and Practical Guide To The Mastery of Scrum Project Management MethodologysilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Scrum (Principles)Document10 pagesIntroduction To Scrum (Principles)gurungeNo ratings yet
- Tka Scrum HandbookDocument21 pagesTka Scrum HandbookAbdulNo ratings yet
- Scrum-Loc-Paper - No NamesDocument5 pagesScrum-Loc-Paper - No NamesJose EspañaNo ratings yet
- WWW Northeastern Edu Graduate Blog Project Management MethodologiesDocument9 pagesWWW Northeastern Edu Graduate Blog Project Management MethodologiesMohamed Mohideen SarhoonNo ratings yet
- M02 Homework Quezada GenessisDocument3 pagesM02 Homework Quezada GenessisgenesNo ratings yet
- Scrum Methodology: Cătuț Robert-CristianDocument7 pagesScrum Methodology: Cătuț Robert-CristianCatut RobertNo ratings yet
- 10 Keys To Successful Scrum Adoption: Best Practices White PaperDocument17 pages10 Keys To Successful Scrum Adoption: Best Practices White PaperJorge Antonio Villacorta BernalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Primary Role of A Scrum MasterDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Primary Role of A Scrum MasterSulagna ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - CombinedDocument137 pagesModule 1 - CombinedAnshita Arya100% (1)
- Intrguing Project Management Concepts and TopicsDocument5 pagesIntrguing Project Management Concepts and TopicsCindy Faye CrusanteNo ratings yet
- What Is Agile and ScrumDocument6 pagesWhat Is Agile and Scrumniyarenji1No ratings yet
- "Agile Project Management": Christoph Johann Stettina, Jeannette HörzDocument2 pages"Agile Project Management": Christoph Johann Stettina, Jeannette HörzHiethemAliraqiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology: Kendra Cherry A Board-Certified PhysicianDocument3 pagesCognitive Psychology: Kendra Cherry A Board-Certified PhysiciansrimkbNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Social Psychology: Kendra Cherry A Board-Certified PhysicianDocument3 pagesAn Overview of Social Psychology: Kendra Cherry A Board-Certified PhysiciansrimkbNo ratings yet
- Scrum Master Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageScrum Master Interview QuestionssrimkbNo ratings yet
- Estimate Story Points in AgileDocument3 pagesEstimate Story Points in AgilesrimkbNo ratings yet
- Scrum ArtifactsDocument1 pageScrum ArtifactssrimkbNo ratings yet
- Agile Development Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAgile Development Cheat SheetsrimkbNo ratings yet
- Situational ScrumDocument15 pagesSituational ScrumsrimkbNo ratings yet
- Contents of Service-Now Training-1Document9 pagesContents of Service-Now Training-1srimkbNo ratings yet
- Scrum in A Nutshell PDFDocument2 pagesScrum in A Nutshell PDFsrimkbNo ratings yet
- RPA Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesRPA Interview Questionssrimkb100% (1)
- PSISA Practice Test1 PDFDocument31 pagesPSISA Practice Test1 PDFsrimkbNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulaDocument3 pagesPMP FormulaCarmen SalazarNo ratings yet
- Essential ScrumMasterDocument3 pagesEssential ScrumMastersrimkbNo ratings yet
- Private Investigator Security Guard Training Manual January 2008Document573 pagesPrivate Investigator Security Guard Training Manual January 2008righttrack186% (7)
- QuestionsDocument95 pagesQuestionssrimkbNo ratings yet
- Employment by IndustryDocument21 pagesEmployment by IndustrysrimkbNo ratings yet
- Bow Valley College Lakeland College Medicine Hat College Norquest College Northern Alberta Institute of TechnologyDocument2 pagesBow Valley College Lakeland College Medicine Hat College Norquest College Northern Alberta Institute of TechnologysrimkbNo ratings yet
- JavaScript Built-In FunctionsDocument7 pagesJavaScript Built-In FunctionssrimkbNo ratings yet
- Invoice TemplateDocument1 pageInvoice TemplatesrimkbNo ratings yet
- Retail DomainDocument108 pagesRetail DomainsrimkbNo ratings yet
- ServiceNow Sample Resume 2Document6 pagesServiceNow Sample Resume 2srimkb67% (3)
- Ibm Unica Campiagn Overview PDFDocument4 pagesIbm Unica Campiagn Overview PDFsrimkbNo ratings yet
- DataStage ArchitectureDocument10 pagesDataStage ArchitecturesrimkbNo ratings yet
- GFT Factsheet Regulatory Change Management Service enDocument2 pagesGFT Factsheet Regulatory Change Management Service ensrimkbNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu ServiceNowDocument30 pagesFujitsu ServiceNowsrimkbNo ratings yet
- SOW Implementation MethodologyDocument3 pagesSOW Implementation MethodologysrimkbNo ratings yet
- McCloskey Procrastination QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesMcCloskey Procrastination QuestionnaireAnika Kim TalingeNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm M2Document15 pagesOral Comm M2senbonzakura019No ratings yet
- 6AAN4043 Syllabus 2015 16Document3 pages6AAN4043 Syllabus 2015 16Marcus S. DoodleNo ratings yet
- Loseyjustin Elaresume 19-20Document2 pagesLoseyjustin Elaresume 19-20api-455356559No ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument14 pagesBudgetingAngelo PeÑa ArriolaNo ratings yet
- L2-Analyze Humor - Two Legs or OneDocument10 pagesL2-Analyze Humor - Two Legs or Oneashu karen100% (2)
- W.E.B. Du Bois (1868 - 1963) The Color LineDocument2 pagesW.E.B. Du Bois (1868 - 1963) The Color LineLola PolaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Curriculum Vitae Bahasa InggrisDocument1 pageContoh Curriculum Vitae Bahasa InggrisAlfien Pancen PuinterNo ratings yet
- Internal Sources of RecruitmentDocument8 pagesInternal Sources of RecruitmentDuke_007No ratings yet
- Artistic Interdisciplinarity and La Fura Dels Baus - 1979-1989 PDFDocument338 pagesArtistic Interdisciplinarity and La Fura Dels Baus - 1979-1989 PDFLuciano Flávio de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Group WorkDocument1 pageRubric For Group WorkJonalyn Tamayo100% (1)
- Lecture 04Document15 pagesLecture 04Kasiraman RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Rose CompanyDocument8 pagesRose Companyravina10008100% (1)
- Leadership & Management: IB Business and ManagementDocument33 pagesLeadership & Management: IB Business and Managementapi-529669983No ratings yet
- 2009 TarlingDocument57 pages2009 TarlingBalu KateNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis AssignmentDocument4 pagesData Analysis AssignmentManav khannaNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesPolytechnic University of The PhilippinesChristian Kokoy C. ChuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Managing TeamsDocument24 pagesChapter 14 Managing TeamsmevasNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Quality Circles in Indian CompaniesDocument20 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Quality Circles in Indian CompanieskodalipragathiNo ratings yet
- Dec 2-7 Week 4 DISS 11 DLLDocument3 pagesDec 2-7 Week 4 DISS 11 DLLRicardo Acosta Subad89% (9)
- OromummaaDocument183 pagesOromummaatajudinNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context LM For SHSPDFDocument191 pagesOral Communication in Context LM For SHSPDFornopia45_548639769No ratings yet
- Teaching PronunciationDocument11 pagesTeaching PronunciationAliya FaithNo ratings yet
- Aghayedo, Elmi-Homework 6Document3 pagesAghayedo, Elmi-Homework 6faizaNo ratings yet
- 6Zdr7Ve2Eemplgpfqc6zSA Tag Reading 1 PDFDocument3 pages6Zdr7Ve2Eemplgpfqc6zSA Tag Reading 1 PDFtarunNo ratings yet
- Lent 2011Document9 pagesLent 2011Marcelo SoaresNo ratings yet
- Research Project Consent FormDocument4 pagesResearch Project Consent FormRizlyana OthmanNo ratings yet
- Method of Job Evaluation: Ranking Method Classification MethodDocument6 pagesMethod of Job Evaluation: Ranking Method Classification MethodPooja AhlawatNo ratings yet
- The Very Cranky Bear3Document20 pagesThe Very Cranky Bear3Diego Antonio CancelaNo ratings yet
- Body ShamingDocument8 pagesBody ShamingAviralAlokNo ratings yet